SpringBoot part4 day15
1 实现用户数据校验
1.1实现单点登陆系统
1.1.1新建项目
创建maven项目,取名为jt-sso
1.1.2添加jar包/依赖
<!--添加依赖-->
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.jt</groupId>
<artifactId>jt-common</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
1.1.3创建项目结构
实现包结构

application.yml
server:
port: 8093
servlet:
context-path: /
spring:
datasource:
#引入druid数据源
#type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3307/jtdb?serverTimezone=GMT%2B8&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&autoReconnect=true&allowMultiQueries=true
#url: jdbc:mysql://192.168.126.129:8066/jtdb?serverTimezone=GMT%2B8&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&autoReconnect=true&allowMultiQueries=true
username: root
password: root
mvc:
view:
prefix: /WEB-INF/views/
suffix: .jsp
#mybatis-plush配置
mybatis-plus:
type-aliases-package: com.jt.pojo
mapper-locations: classpath:/mybatis/mappers/*.xml
configuration:
map-underscore-to-camel-case: true
logging:
level:
com.jt.mapper: debug
启动项:
package com.jt;
import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
@MapperScan("com.jt.mapper")
public class SpringBootRun {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringBootRun.class, args);
}
}
UserController
package com.jt.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class UserController {
@RequestMapping("/getMsg")
public String doGetMsg(){
return "实现单点登陆系统";
}
}
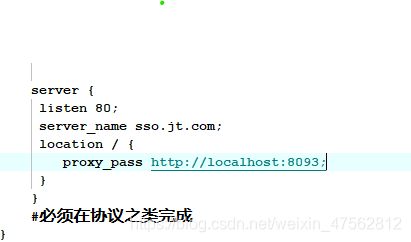
host文件

nginx配置文件
重启nginx
编辑启动项
启动测试

1.2用户数据校验
1.2.1业务说明
说明:当用户输入内容之后,当鼠标离焦时,应该发起Ajax请求去后端服务器JT-SSO校验数据是否存在. 如果数据存在应该提示用户,如果数据不存在则告知用户该数据可以使用.
1.2.2页面请求分析

1.2.3 业务接口文档
包含的类容:
1)业务的场景,业务功能属性等…
2)业务端调用的细节 web-sso
3)明确请求的路径 url地址
4)明确请求的参数信息 几个 类型 作用
5)明确返回值结果 void xxxx属性 对象
检查数据是否可用:

用户注册:

用户登陆:

通过ticket查询用户信息

1.2.4页面JS分析
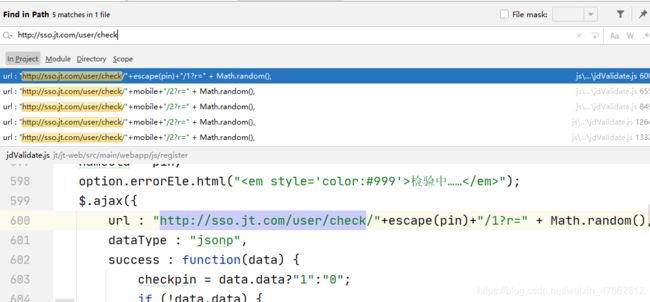
怎样快速定位发ajax请求的位置?????
搜索的方式检查代码的位置 先要分析请求路径的写死部分 利用检索所有代码,查找需要代码
ctrl+H
package com.jt.controller;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.util.JSONPObject;
import com.jt.service.UserService;
import com.jt.vo.SysResult;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@RequestMapping("/getMsg")
public String getMsg(){
return "单点登录系统测试完成";
}
/**
* JSONP
* 实现用户数据校验
* url:http://sso.jt.com/user/check/{param}/{type}
* 参数: /{param} 用户需要校验的数据
* /{type} 校验的字段.
* 返回值: SysResult对象(true/false)
*/
@RequestMapping("/check/{param}/{type}")
public JSONPObject checkUser(@PathVariable String param,
@PathVariable Integer type,
String callback){
//查询数据库获取响应信息.
boolean flag = userService.checkUser(param,type);
SysResult sysResult = SysResult.success(flag);
return new JSONPObject(callback, sysResult);
//callback(JSON结构)
}
}
1.2.6 编辑JT-SSO UserService
package com.jt.service;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.conditions.query.QueryWrapper;
import com.jt.mapper.UserMapper;
import com.jt.pojo.User;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
@Service
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService{
private static Map<Integer,String> paramMap = new HashMap<>();
static {
paramMap.put(1,"username");
paramMap.put(2,"phone");
paramMap.put(3,"email");
}
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
/**
* 根据用户传递的参数,获取数据库记录
* @param param
* @param type
* @return
*/
@Override
public boolean checkUser(String param, Integer type) {
String column = paramMap.get(type);
QueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.eq(column,param);
int count = userMapper.selectCount(queryWrapper);
//return count>0?true:false;
return count>0;
}
}
2 HTTPClient
2.1远程访问的调用流程
跨域(无法对结果进行二次操作):

跨域请求信息和返回值结果均显示在前端,有安全性问题:


跨域仅用于获取简单信息
HTTPClient
是微服务架构的底层实现
由service对参数和返回值进行封装,再由程序内部发起HTTP请求(此时浏览器不能监控)

2.2HTTPClient介绍
2.3入门案例
2.3.1添加jar包
<!--添加httpClient jar包 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.httpcomponents</groupId>
<artifactId>httpclient</artifactId>
</dependency>
package com.jt;
import com.sun.deploy.net.HttpUtils;
import org.apache.http.HttpEntity;
import org.apache.http.HttpResponse;
import org.apache.http.client.HttpClient;
import org.apache.http.client.methods.HttpGet;
import org.apache.http.impl.client.HttpClients;
import org.apache.http.util.EntityUtils;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import java.io.IOException;
public class TestHTTPClient {
/**
* 1.实例化httpCliet客户端对象
* 2.定义url地址
* 3.定义请求类型
* 4.发起httpCliet请求
* 5.获取响应结果 分析状态码信息 200 404 504 502
* 6 获取结果,进行后续操作
* */
@Test
public void testGet() throws IOException {
HttpClient httpClient= HttpClients.createDefault();
String url="http://www.baidu.com";
HttpGet httpGet=new HttpGet(url);
httpClient.execute(httpGet);
//获取响应
HttpResponse httpResponse=httpClient.execute(httpGet);
if(httpResponse.getStatusLine().getStatusCode()==200){
//表示请求一切正常
HttpEntity httpEntity= httpResponse.getEntity();//获取响应结果的实体对象
String result= EntityUtils.toString(httpEntity,"UTF-8");
System.out.println(result);
}else{
//表示请求有误
System.out.println("运行有误");
}
}
}
2.4 HttpClient案例说明
要求:
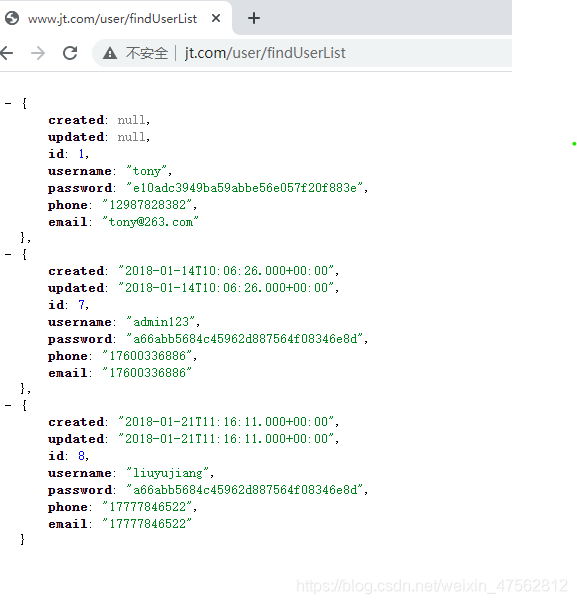
1通过http://www.jt.com/user/findUserList ,并且要求JSON结构返回用户数据
2JT-WEB服务器网址应该向JT-SSO获取用户信息
URL:http://sso.jt.com/userfindUserList 获取全部的用户信息
2.4.1编辑JT-SSO UserController
/**
* URL:http://sso.jt.com/userfindUserList
* 返回UserJSON
*
* */
@RequestMapping("/findUserList")
public List<User> findUserList(){
return userService.findUserList();
}
**2.4.2 UserServiceImpl**
@Override
public List<User> findUserList() {
return userMapper.selectList(null);
}
2.4.3 编辑jt-web前端页面
UserController
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private HttpClientService httpClientService;
/**
* 通过http://www.jt.com/user/findUserList
* 请求参数:无
* 返回值结果:List集合
* * */
@RequestMapping("/findUserList")
public List<User> doFindUserList(){
return httpClientService.findUserList();
}
HttpClientServiceImpl
package com.jt.service;
import com.jt.pojo.User;
import com.jt.util.ObjectMapperUtil;
import org.apache.http.HttpResponse;
import org.apache.http.client.HttpClient;
import org.apache.http.client.methods.HttpGet;
import org.apache.http.impl.client.HttpClients;
import org.apache.http.util.EntityUtils;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
@Service
public class HttpClientServiceImpl implements HttpClientService{
//jt-web 需要访问jt-sso获取数据 HttpClient
//http://sso.jt.com/userfindUserList
@Override
public List<User> findUserList() {
List<User> userList = new ArrayList<>();
String url = "http://sso.jt.com/user/findUserList";
HttpClient httpClient = HttpClients.createDefault();
HttpGet httpGet = new HttpGet(url);
try {
HttpResponse httpResponse = httpClient.execute(httpGet);
if(httpResponse.getStatusLine().getStatusCode() == 200){
String json =
EntityUtils.toString(httpResponse.getEntity(),"UTF-8");
userList = ObjectMapperUtil.toObject(json, userList.getClass());
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
return userList;
}
}
3 微服务的思想
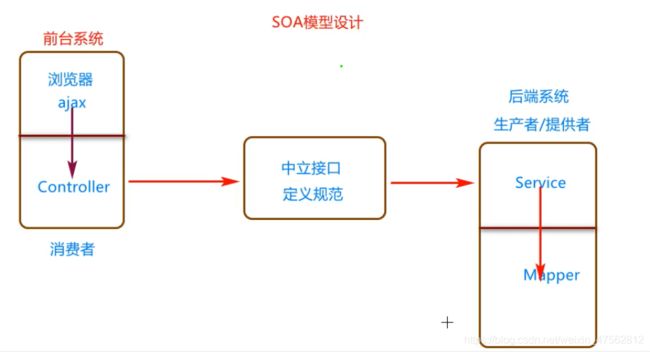
3.1SOA思想
面向服务的架构(SOA)是一个组件模型,它将应用程序的不同功能单元(称为服务)进行拆分,并通过这些服务之间定义良好的接口和协议联系起来。**接口是采用中立的方式进行定义的,它应该独立于实现服务的硬件平台、操作系统和编程语言。**这使得构件在各种各样的系统中的服务可以以一种统一和通用的方式进行交互。
3.2RPC
RPC是远程过程调用(Remote Procedure Call)的缩写形式。SAP系统RPC调用的原理其实很简单,有一些类似于三层构架的C/S系统,第三方的客户程序通过接口调用SAP内部的标准或自定义函数,获得函数返回的数据进行处理后显示或打印。
总结: 需要调用第三方完成本地的服务. 服务A想要完成某项任务,但是自己手中没有该资源,则通知服务B 帮我去完成该操作. 这样的操作方式称之为RPC
理解:由不同的服务之间进行的通讯就称为RPC。RPC通讯无需了解协议的细节,像调用本地服务一样简单,RPC调用本质就是代理思想的应用
本地过程调用:如果需要完成业务瑞吉,直接调用本地业务逻辑
远程过程调用:
具体用法: RPC不关注具体的实现guiz,用户不需要了解具体的协议,谁调用谁实现
3.4Http协议的规范
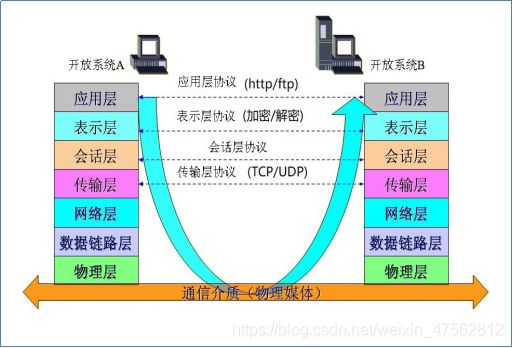
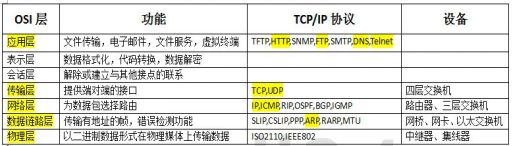
区别:
1.RPC是传输层协议(4层).而HTTP协议是应用层协议(7层).
2.RPC协议可以直接调用中立接口,HTTP协议不可以.
3.RPC通信协议是长链接,HTTP协议一般采用短连接需要3次握手(可以配置长链接添加请求头Keep-Alive: timeout=20).
(长连接,指在一个连接上可以连续发送多个数据包,在连接保持期间,如果没有数据包发送,需要双方发链路检测包。)
4.RPC协议传递数据是加密压缩传输.HTTP协议需要传递大量的请求头信息.
5.RPC协议一般都有注册中心.有丰富的监控机制.