ThreadLocal详解
一、概念
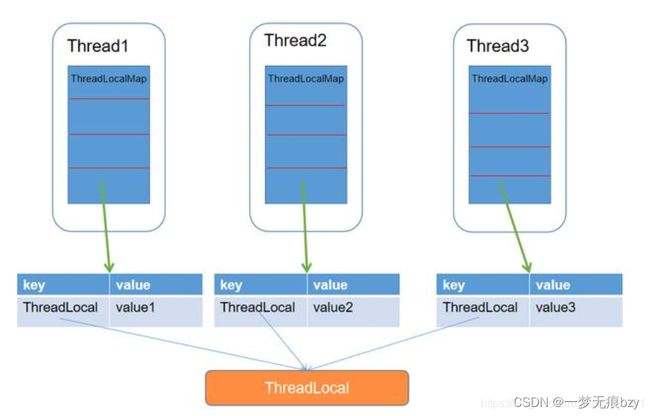
threadlocal是一个线程内部的存储类,可以在指定线程内存储数据,数据存储以后,只有指定线程可以得到存储数据。这也是spring声明式事务的原理
代码如下:
public class ThreadLocalDemo1 {
private static ThreadLocal<String> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<>();
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":"+threadLocal.get());
}).start();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
threadLocal.set("test");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":插入数据");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":"+threadLocal.get());
}).start();
}
}
运行结果:由此可见多个线程之间数据是不共享的
Thread-1:插入数据
Thread-1:test
Thread-0:null
Thread线程可以拥有多个ThreadLocal来维护自己ThreadLocalMap中的数据(ThreadLocalMap中每条数据的key值都是一个ThreadLocal对象)
package com.example.demo.thread;
public class ThreadLocalDemo1 {
private static ThreadLocal<String> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<>();
private static ThreadLocal<String> threadLocal1 = new ThreadLocal<>();
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
threadLocal.set("test");
threadLocal1.set("demo");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":"+threadLocal.get());
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":"+threadLocal1.get());
},"t1").start();
}
}
执行结果:
t1:test
t1:demo
二、具体应用
- 每个线程需要有自己单独的实例
- 实例需要在多个方法中共享,但不希望被多线程共享
第一种很简单,可以参考上面代码。现以第二种为例,展示代码
public class ThreadLocalDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
User user = new User("jack");
new Service1().service1(user);
}
}
class Service1 {
public void service1(User user){
//给ThreadLocal赋值,后续的服务直接通过ThreadLocal获取就行了。
UserContextHolder.holder.set(user);
new Service2().service2();
}
}
class Service2 {
public void service2(){
User user = UserContextHolder.holder.get();
System.out.println("service2拿到的用户:"+user.name);
new Service3().service3();
}
}
class Service3 {
public void service3(){
User user = UserContextHolder.holder.get();
System.out.println("service3拿到的用户:"+user.name);
//在整个流程执行完毕后,一定要执行remove
UserContextHolder.holder.remove();
}
}
class UserContextHolder {
//创建ThreadLocal保存User对象
public static ThreadLocal<User> holder = new ThreadLocal<>();
}
class User {
String name;
public User(String name){
this.name = name;
}
}
执行结果:
service2拿到的用户:jack
service3拿到的用户:jack
三、ThreadLocal原理
1、ThreadLocal的set()方法
public void set(T value) {
//1、获取当前线程
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
//2、获取线程中的属性 threadLocalMap ,如果threadLocalMap 不为空,
//则直接更新要保存的变量值,否则创建threadLocalMap,并赋值
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null)
map.set(this, value);
else
// 初始化thradLocalMap 并赋值
createMap(t, value);
}
每次在线程中threadLocal.set()时其实是往每个线程自己的map(ThreadLocalMap)中放入值,key是threadLocal、value是传入的对象。
2、map.set()
private void set(ThreadLocal<?> key, Object value) {
// We don't use a fast path as with get() because it is at
// least as common to use set() to create new entries as
// it is to replace existing ones, in which case, a fast
// path would fail more often than not.
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1);
for (Entry e = tab[i];
e != null;
e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) {
ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();
if (k == key) {
e.value = value;
return;
}
if (k == null) {
replaceStaleEntry(key, value, i);
return;
}
}
tab[i] = new Entry(key, value);
int sz = ++size;
if (!cleanSomeSlots(i, sz) && sz >= threshold)
rehash();
}
在map.set中其实是new出了一个Entry对象
3、Entry类
static class ThreadLocalMap {
/**
* The entries in this hash map extend WeakReference, using
* its main ref field as the key (which is always a
* ThreadLocal object). Note that null keys (i.e. entry.get()
* == null) mean that the key is no longer referenced, so the
* entry can be expunged from table. Such entries are referred to
* as "stale entries" in the code that follows.
*/
static class Entry extends WeakReference<ThreadLocal<?>> {
/** The value associated with this ThreadLocal. */
Object value;
Entry(ThreadLocal<?> k, Object v) {
super(k);
value = v;
}
}
}
Entry类实际上继承了WeakReference(弱引用),在构造方法中调用WeakReference的构造方法,也就是每次new Entry的时候调new WeakReference(key)把key(key和tl指向的是同一个ThreadLocal对象)变成了弱引用(被WeakReference对象指向)。而之所以是弱引用的目的是防止内存泄露,因为tl和key都指向同一个ThreadLocal对象,若key是其他引用类型即使tl=null ThreadLocal对象依然不会被回收,因为有key指向而我们又没法操作key=null(我们拿不到key),这就造成ThreadLocal对象占用的内存永远不会被回收也就是内存泄露,而用弱引用,只要gc启动它便被回收不会内存泄露。但是当ThreadLocal被回收了,key就等于null了,那么与之对应的value则永远不会被操作到(map能指向value,但是我们操作不到了),所以value还是会导致内存泄露,所以每次用完tl必须tl.remove(在这个方法内部其实是调用ThreadLocalMap的remove方法,彻底干掉key、value键值对)
4、createMap()
//这个是threadlocal 的内部方法
void createMap(Thread t, T firstValue) {
t.threadLocals = new ThreadLocalMap(this, firstValue);
}
//ThreadLocalMap 构造方法
ThreadLocalMap(ThreadLocal<?> firstKey, Object firstValue) {
table = new Entry[INITIAL_CAPACITY];
int i = firstKey.threadLocalHashCode & (INITIAL_CAPACITY - 1);
table[i] = new Entry(firstKey, firstValue);
size = 1;
setThreshold(INITIAL_CAPACITY);
}
5、get()
public T get() {
//1、获取当前线程
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
//2、获取当前线程的ThreadLocalMap
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
//3、如果map数据为空,
if (map != null) {
//3.1、获取threalLocalMap中存储的值
ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this);
if (e != null) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T result = (T)e.value;
return result;
}
}
//如果是数据为null,则初始化,初始化的结果,TheralLocalMap中存放key值为threadLocal,值为null
return setInitialValue();
}
private T setInitialValue() {
T value = initialValue();
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null)
map.set(this, value);
else
createMap(t, value);
return value;
}
protected T initialValue() {
return null;
}
6、remove()
public void remove() {
ThreadLocalMap m = getMap(Thread.currentThread());
if (m != null)
m.remove(this);
}
调用ThreadLocalMap的remove方法,彻底干掉key、value键值对,防止内存泄露