C语言实现数据结构——链队列
定义
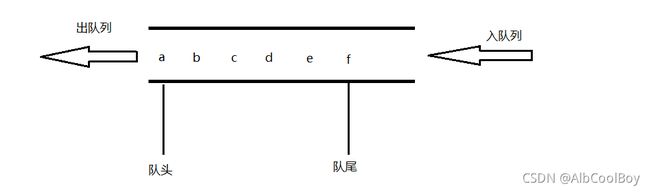
前面学习了栈这种数据结构,我们知道他的特点是数据先进后出。与栈相反,队列的特点时数据先进先出。即first in firsr out,简称FIFO。
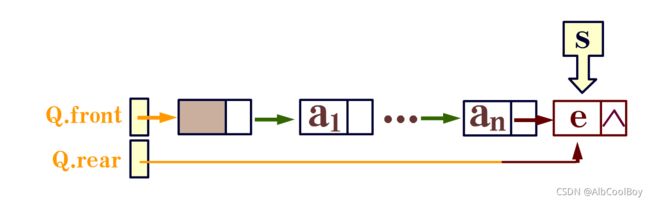
队列只允许在表的一端进行数据的插入,在另一端进行数据的删除。这和生活中的排队是一致的,最早进入队列的最先离开。在链表中,允许插入数据的一端叫队尾(rear),允许删除数据的一端叫队头(front)。假设将数据a,b,c,d,e,f输入到一个队列中,那么输入的顺序是a,b,c,d,e,f。输出的顺序也是a,b,c,d,e,f。
基本操作
- 初始化一个队列
Status InitQueue(LinkQueue *q)
- 销毁一个队列
Status DestoryQueue(LinkQueue *q)
- 清空一个队列
Status ClearQueue(LinkQueue *q)
- 判断队列是否为空
Status QueueEmpty(LinkQueue *q)
- 返回队列中可用元素的数量,即队列的长度
int QueueLength(LinkQueue *q)
- 返回队头
Status GetHead(LinkQueue Q, QElemType* e)
- 从队尾添加元素
tatus EnQueue(LinkQueue* Q, QElemType e)
- 将队头元素删除
Status DeQueue(LinkQueue* Q, QElemType* e)
- 队列的遍历
Status QueueTraverse(LinkQueue Q, void (Visit)(QElemType))
基本操作方法的代码实现
- 初始化一个队列
Status InitQueue(LinkQueue* Q) {
if(Q == NULL) {
return ERROR;
}
(*Q).front = (*Q).rear = (QueuePtr) malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if(!(*Q).front) {
exit(OVERFLOW);
}
(*Q).front->next = NULL;
return OK;
}
- 销毁一个队列
Status DestroyQueue(LinkQueue* Q) {
if(Q == NULL) {
return ERROR;
}
while((*Q).front) {
(*Q).rear = (*Q).front->next;
free((*Q).front);
(*Q).front = (*Q).rear;
}
return OK;
}
- 清空一个队列
Status ClearQueue(LinkQueue* Q) {
if(Q == NULL) {
return ERROR;
}
(*Q).rear = (*Q).front->next;
while((*Q).rear) {
(*Q).front->next = (*Q).rear->next;
free((*Q).rear);
(*Q).rear = (*Q).front->next;
}
(*Q).rear = (*Q).front;
return OK;
}
- 判断队列是否为空
Status QueueEmpty(LinkQueue Q) {
if(Q.front == Q.rear) {
return TRUE;
} else {
return FALSE;
}
}
- 返回队列中可用元素的数量,即队列的长度
int QueueLength(LinkQueue Q) {
int count = 0;
QueuePtr p = Q.front;
while(p != Q.rear) {
count++;
p = p->next;
}
return count;
}
- 返回队头
Status GetHead(LinkQueue Q, QElemType* e) {
QueuePtr p;
if(Q.front == NULL || Q.front == Q.rear) {
return ERROR;
}
p = Q.front->next;
*e = p->data;
return OK;
}
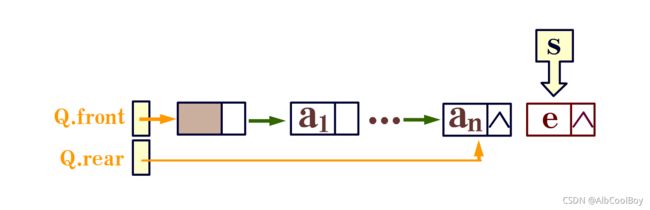
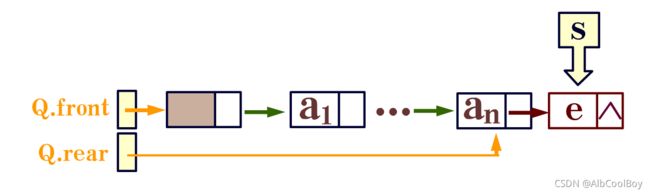
- 从队尾添加元素
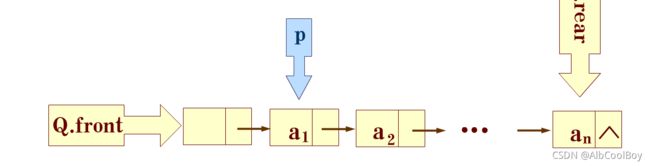
Status EnQueue(LinkQueue* Q, QElemType e) {
QueuePtr p;
if(Q == NULL || (*Q).front == NULL) {
return ERROR;
}
p = (QueuePtr) malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if(!p) {
exit(OVERFLOW);
}
p->data = e;
p->next = NULL;
(*Q).rear->next = p;
(*Q).rear = p;
return OK;
}
- 将队头元素删除
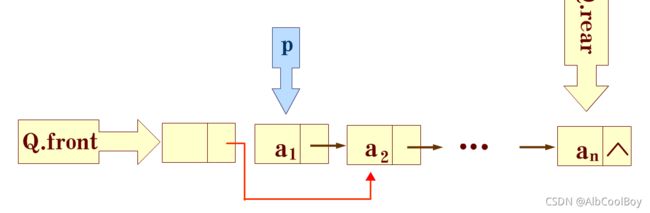
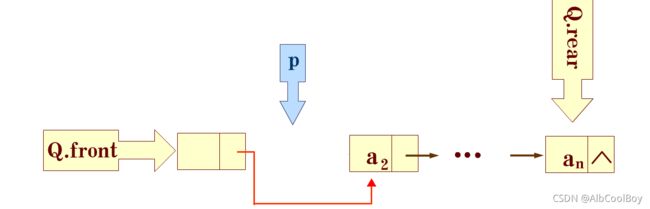
Status DeQueue(LinkQueue* Q, QElemType* e) {
QueuePtr p;
if(Q == NULL || (*Q).front == NULL || (*Q).front == (*Q).rear) {
return ERROR;
}
p = (*Q).front->next;
*e = p->data;
(*Q).front->next = p->next;
if((*Q).rear == p) {
(*Q).rear = (*Q).front;
}
free(p);
return OK;
}
- 队列的遍历
Status QueueTraverse(LinkQueue Q, void (Visit)(QElemType)) {
QueuePtr p;
if(Q.front == NULL) {
return ERROR;
}
p = Q.front->next;
while(p != NULL) {
Visit(p->data);
p = p->next;
}
printf("\n");
return OK;
}
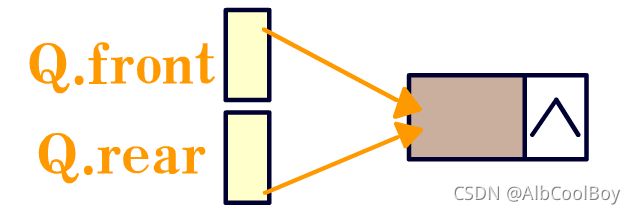
该源码实现的是链队列,所以设置了一个并不包含数据的头节点,实际上不设置此节点也能进行队列的操作,只不过添加头节点使得删除遍历灯过程更加的方便易懂
所有代码文件
- 状态码宏定义头文件
Status.h
#ifndef STATUS_H
#define STATUS_H
#include - 函数定义头文件
LinkQueue.h
#include - 函数实现头文件
LinkQueue.c
#include"LinkQuquq.h"
#include"Status.h"
Status InitQueue(LinkQueue* q)
{
if (q == NULL)
{
return ERROR;
}
(*q).front = (*q).rear = (QueuePtr)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if (!(*q).front)
{
exit(OVERFLOW);
}
(*q).front->next = NULL;
return OK;
}
//队列的销毁的函数并不是经常的用到
Status DestoryQueue(LinkQueue* q)
{
if (q == NULL)
{
return ERROR;
}
while ((*q).front)
{
(*q).rear = (*q).front->next;
free((*q).front);
(*q).front = (*q).rear;
}
return OK;
}
//内容置空,但是要将中间非头结点的空间释放
Status ClearQueue(LinkQueue* q)
{
if (q = NULL)
{
return ERROR;
}
(*q).rear = (*q).front->next;
while ((*q).rear) {
(*q).front->next = (*q).rear->next;
free((*q).rear);
(*q).rear = (*q).front->next;
}
(*q).rear = (*q).front;
return OK;
}
//判断队列是否为空
Status QueueEmpty(LinkQueue* q)
{
if (q->front == q->rear)
{
return TRUE;
}
else
{
return FALSE;
}
}
//返回队列中有效元素的个数
int QueueLength(LinkQueue* q)
{
int count = 0;
QueuePtr p = q->front;
while (p != q->rear)
{
count++;
p = p->next;
}
return count;
}
//取出队头元素
Status GetHead(LinkQueue* q,int* e)
{
QueuePtr p;
if (q->front == NULL || q->front == q->rear)
{
return ERROR;
}
p = q->front->next;
*e = p->data;
return OK;
}
Status Enter(LinkQueue* q, int e)
{
QueuePtr p;
if (q == NULL || (*q).front == NULL)
{
return ERROR;
}
p = (QueuePtr)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if (!p)
{
exit(OVERFLOW);
}
p->data = e;
p->next = NULL;
(*q).rear->next = p;
(*q).rear = p;
return OK;
}
//出队列,移除队头的元素
Status Out(LinkQueue* q, int e)
{
QueuePtr p;
if (q == NULL || q->front==NULL || q->front == q->rear)
{
return ERROR;
}
p = (*q).front->next;
e = p->data;
(*q).front->next = p->next;
if ((*q).rear == p)
{
(*q).front = (*q).rear;
}
free(p);
return OK;
}
void QueueTraverse(LinkQueue* q)
{
QueuePtr p;
if (q->front == NULL)
{
return ERROR;
}
p = q->front->next;
while (p != NULL)
{
printf("%d ", p->data);
p = p->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
- 测试主函数
LinkQueue-main.c
#include