Python入门之最基础
Python入门之最基础
IDLE有两种模式,一种是交互模式,通俗讲就是写一个代码,会得到相应的反馈,另一种为编辑模式.
注意事项:
标点符号一定要用英文符号
要注意缩进
dir(builtins)可以看到python所有的内置函数;
基本语法
变量相当于一个名字
这个数值呼唤惊到我了,太牛了。
x = 3
y = 5
x,y = y,x
print(x,y)
5 3
字符串(string)
‘’ “” 涉及到单引号双引号的时候,会用到转义字符 \
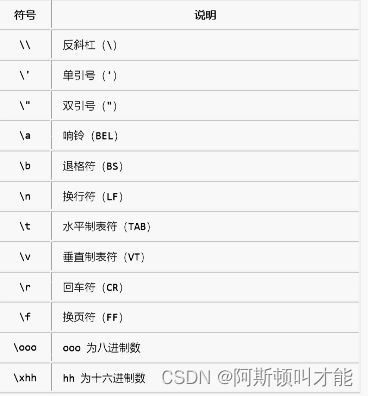
原始字符 row string
前面加 r 代表输出原始字符串
print(r"D:\three\two\one\now")
D:\three\two\one\now
若想字符换行,可在后加 \ ,可跨行
print(" * \n\
*** \n\
*****")
*
***
*****
长字符串 Triple quoted,也叫三引号字符串,‘’‘前后呼应’‘’,“”“成双成对”“”。
字符串加法与数字加法截然不同
'520'+'1314'
'5201314'
520+1314
1834
我每天爱你3000遍
print("我每天爱你3000遍\n" * 30)
我每天爱你3000遍
我每天爱你3000遍
我每天爱你3000遍
我每天爱你3000遍
我每天爱你3000遍
我每天爱你3000遍
我每天爱你3000遍
我每天爱你3000遍
我每天爱你3000遍
我每天爱你3000遍
我每天爱你3000遍
我每天爱你3000遍
我每天爱你3000遍
我每天爱你3000遍
我每天爱你3000遍
我每天爱你3000遍
我每天爱你3000遍
我每天爱你3000遍
我每天爱你3000遍
我每天爱你3000遍
我每天爱你3000遍
我每天爱你3000遍
我每天爱你3000遍
我每天爱你3000遍
我每天爱你3000遍
我每天爱你3000遍
我每天爱你3000遍
我每天爱你3000遍
我每天爱你3000遍
我每天爱你3000遍
if else语句与while语句
random随机数使用,生成1-10里的随机数
import random
random.randint(1,10)
random生成的随机数可以重现
x = random.getstate()
random.randint(1,10)
1
random.randint(1,10)
4
random.randint(1,10)
6
random.randint(1,10)
7
random.setstate(x)
random.randint(1,10)
1
random.randint(1,10)
4
random.randint(1,10)
6
random.randint(1,10)
7
数字类型
python数字类型分三种:整数、浮点数、复数
python的整数长度是不受限制的,可以随时随地进行大数运算
python的浮点数 ,是不是很惊讶,我也表示有点惊讶,原来我的口算能力还可以hhhhhh。
0.1+0.2
0.30000000000000004
i = 0
while i < 1:
i = i + 0.1
print(i)
0.1
0.2
0.30000000000000004
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.7999999999999999
0.8999999999999999
0.9999999999999999
1.0999999999999999
python的浮点数是采用IEEE754的标准来存储浮点数的,会产生一定精度的误差。
复数 包含实部和虚部
1+2j
(1+2j)
x = 1 + 2j
x.real
1.0
x.imag
2.0
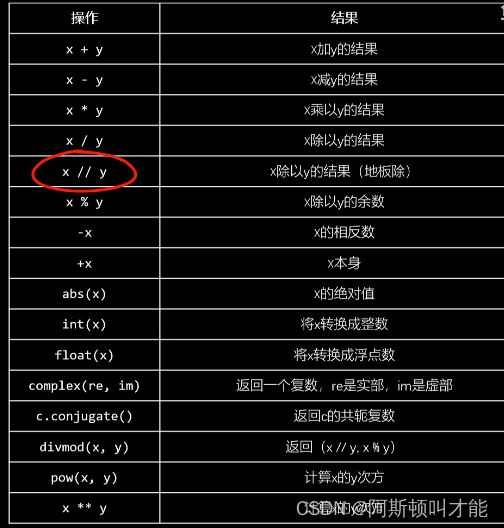
地板除 //,向下取整
3/2
1.5
3//2
1
1//2
0
-3 // 2
-2
x == (x // y) * y + (x % y)
divmod(-3,2)
(-2, 1)
-2 * 2 + 1
-3
x = -520
abs(x)
520
y = -3.14
abs(y)
3.14
z = 1 + 2j
abs(z)
2.23606797749979
int('520')
520
int(3.14)
3
int(520)
520
int(9.99)
9
float(3.14)
3.14
float('3.14')
3.14
float(520)
520.0
complex("1+2j")
(1+2j)
complex("1 + 2j")
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "" , line 1, in <module>
complex("1 + 2j")
ValueError: complex() arg is a malformed string
pow(2,3)
8
pow(2,3,5)
3
2 ** 3 % 5
3
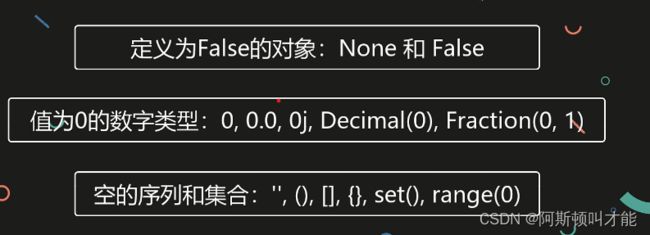
bool(None)
False
bool(False)
False
bool(0)
False
bool(0.0)
False
bool(0j)
False
bool(decimal.Decimal(0))
False
import fractions
bool(fractions.Fraction(0,1))
False
bool运算
1 == True
True
0 == False
True
True + False
1
True - False
1
True * False
0
True / False
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "" , line 1, in <module>
True / False
ZeroDivisionError: division by zero
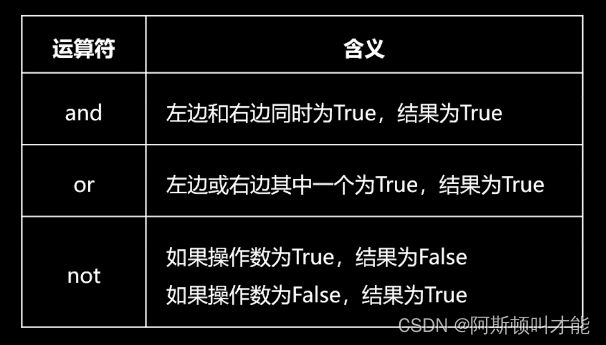
逻辑运算符
3 < 4 and 4 < 5
True
3 > 4 and 4 < 5
False
3 < 4 and 4 > 5
False
3 > 4 and 4 > 5
False
3 < 4 or 4 < 5
True
3 > 4 or 4 < 5
True
3 < 4 or 4 > 5
True
3 > 4 or 4 > 5
False
not True
False
not False
True
not 250
False
not 0
True
250
250
短路逻辑的核心思想
从左往右,只有当第一个操作数的值无法确定逻辑运算的结果时,才对第二个操作数进行求值。
(not 1) or (0 and 1) or (3 and 4) or (5 and 6) or (7 and 8 and 9)
4
False or 0 or 4 or 6 or 9
4
3 and 4
4
3 or 4
3
0 and 3
0
0 or 4
4
运算符优先级
1 + 2 > 3 - 4
True
not 1 < 2
False
not 1
False
0 or 1 and not 2
False
not 1 or 0 and 1 or 3 and 4 or 5 and 6 or 7 and 8 and 9
4
False or 0 or 4 or 6 or 9
4
好棒好棒,了解了这么多知识点,初入python,加鸡腿加脑子,继续努力。