Java线程的创建方式以及线程池的使用
Java线程的创建方式以及线程池的使用
一、线程的创建方式一
/**
* 1.继承thread类,重写run方法
*/
@Test
void test1(){
new threadDemo().start();
}
class threadDemo extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
二、线程的创建方式二
/**
* 2.实现runnable接口,重写run方法
*/
@Test
void test2(){
new Thread(new runnableDemo()).start();
}
class runnableDemo implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
三、线程的创建方式三
/**
* 3.实现Callable接口,重写call方法
*/
@Test
void test3(){
FutureTask<Integer> futureTask = new FutureTask<>(new callAbleDemo());
new Thread(futureTask, "threadName").start();
Integer result = null;
try {
// 获取子线程执行的结果,此时主线程会被阻塞,会等到计算结果完成后,容易程序阻塞
// 可以通过使用CompletableFuture,解决FutureTask的缺陷问题
result = futureTask.get();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(result); // 输出result为45
}
class callAbleDemo implements Callable<Integer>{
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
sum += i;
}
return sum;
}
}
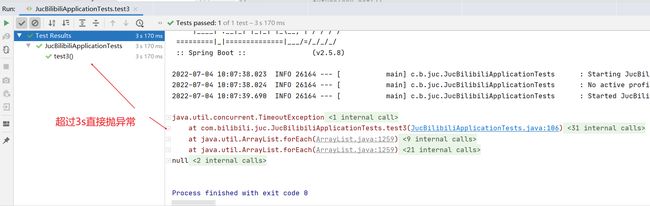
由于futureTask.get()时会阻塞主线程,我们可以指定超时时间,表示在规定时间内仍未完成则直接抛异常,改造后的代码如下:
/**
* 3.实现Callable接口,重写call方法
*/
@Test
void test3(){
FutureTask<Integer> futureTask = new FutureTask<>(new callAbleDemo());
new Thread(futureTask, "threadName").start();
Integer result = null;
try {
// 获取子线程执行的结果,此时主线程会被阻塞,会等到计算结果完成后,容易程序阻塞
// 可以通过使用CompletableFuture,解决FutureTask的缺陷问题
// result = futureTask.get();
result = futureTask.get(3, TimeUnit.SECONDS); // 指定超时时间,如果未执行完直接抛异常
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (TimeoutException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(result);
}
class callAbleDemo implements Callable<Integer>{
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
sum += i;
}
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5); // 沉睡5s,模拟耗时操作
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return sum;
}
}
同时我们也可以使用FutureTask的isDone方法,这个方法的作用是不断地轮询判断是否操作已经完成,但是这容易耗费cpu资源,改造后的代码如下:
/**
* 3.实现Callable接口,重写call方法
*/
@Test
void test3() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
FutureTask<Integer> futureTask = new FutureTask<>(new callAbleDemo());
new Thread(futureTask, "threadName").start();
Integer result = null;
// isDone轮询,是否已经计算完成,容易耗费cpu资源
while (true){
if (futureTask.isDone()){
// 可以通过使用CompletableFuture,解决FutureTask的缺陷问题
result = futureTask.get();
break;
}else {
System.out.println("还没完成呢");
}
}
System.out.println(result);
}
class callAbleDemo implements Callable<Integer>{
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
sum += i;
}
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); // 沉睡1s,模拟耗时操作
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return sum;
}
}
我们可以通过使用CompletableFuture,解决FutureTask的缺陷问题,FutureTask类图关系如下:
CompletableFuture
哔哩哔哩链接:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1ar4y1x727?p=22&vd_source=7c5f1f4c039688f19024d50ef51aaed1
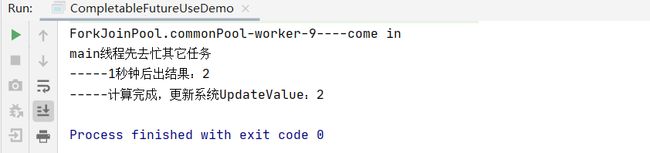
从java8开始引入CompletableFuture,是Future的功能增强版,减少阻塞和轮询,可以传入回调对象,当异步任务完成或者发生异常时,自动调用回调对象的回调方法。
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "----come in");
int result = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(10);
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("-----1秒钟后出结果:" + result);
return result;
}).whenComplete((v, e) -> {
if (e == null) {
System.out.println("-----计算完成,更新系统UpdateValue:" + v);
}
}).exceptionally(e -> {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("异常情况:" + e.getCause() + "\t" + e.getMessage());
return null;
});
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "线程先去忙其它任务");
//主线程不要立刻结束,否则CompletableFuture默认使用的线程池会立刻关闭:暂停3秒钟线程
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
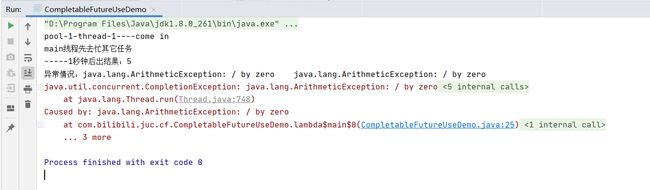
不使用CompletableFuture默认使用的线程池:
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException
{
ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
try
{
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "----come in");
int result = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(10);
try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
System.out.println("-----1秒钟后出结果:" + result);
if(result > 2)
{
int i=10/0;
}
return result;
},threadPool).whenComplete((v,e) -> {
if (e == null) {
System.out.println("-----计算完成,更新系统UpdateValue:"+v);
}
}).exceptionally(e -> {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("异常情况:"+e.getCause()+"\t"+e.getMessage());
return null;
});
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"线程先去忙其它任务");
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
threadPool.shutdown();
}
// 主线程不要立刻结束,否则CompletableFuture默认使用的线程池会立刻关闭:暂停3秒钟线程
// try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
}
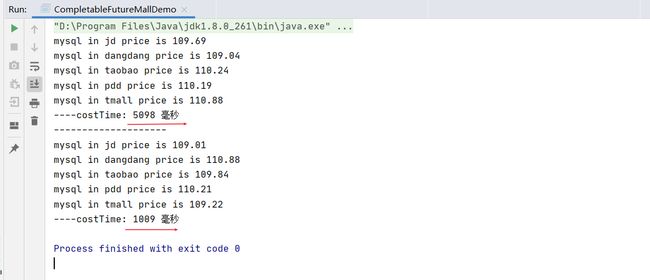
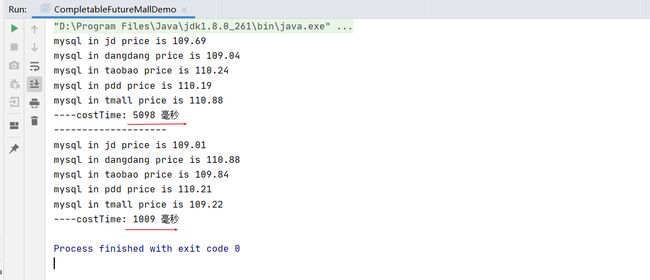
案例:电商比价需求
package com.bilibili.juc.cf;
import lombok.*;
import lombok.experimental.Accessors;
import java.awt.print.Book;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadLocalRandom;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
/**
*
* 案例说明:电商比价需求,模拟如下情况:
*
* 1需求:
* 1.1 同一款产品,同时搜索出同款产品在各大电商平台的售价;
* 1.2 同一款产品,同时搜索出本产品在同一个电商平台下,各个入驻卖家售价是多少
*
* 2输出:出来结果希望是同款产品的在不同地方的价格清单列表,返回一个List
* 《mysql》 in jd price is 88.05
* 《mysql》 in dangdang price is 86.11
* 《mysql》 in taobao price is 90.43
*
* 3 技术要求
* 3.1 函数式编程
* 3.2 链式编程
* 3.3 Stream流式计算
*/
public class CompletableFutureMallDemo
{
static List<NetMall> list = Arrays.asList(
new NetMall("jd"),
new NetMall("dangdang"),
new NetMall("taobao"),
new NetMall("pdd"),
new NetMall("tmall")
);
/**
* step by step 一家家搜查
* List ----->map------> List
* @param list
* @param productName
* @return
*/
public static List<String> getPrice(List<NetMall> list,String productName)
{
// 格式:《mysql》 in taobao price is 90.43
return list
.stream()
.map(netMall ->
String.format(productName + " in %s price is %.2f",
netMall.getNetMallName(),
netMall.calcPrice(productName)))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
/**
* List ----->List>------> List
* @param list
* @param productName
* @return
*/
public static List<String> getPriceByCompletableFuture(List<NetMall> list,String productName)
{
return list.stream().map(netMall ->
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> String.format(productName + " in %s price is %.2f",
netMall.getNetMallName(),
netMall.calcPrice(productName))))
.collect(Collectors.toList())
.stream()
.map(s -> s.join())
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
List<String> list1 = getPrice(list, "mysql");
for (String element : list1) {
System.out.println(element);
}
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("----costTime: "+(endTime - startTime) +" 毫秒");
System.out.println("--------------------");
long startTime2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
List<String> list2 = getPriceByCompletableFuture(list, "mysql");
for (String element : list2) {
System.out.println(element);
}
long endTime2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("----costTime: "+(endTime2 - startTime2) +" 毫秒");
}
}
class NetMall
{
@Getter
private String netMallName;
public NetMall(String netMallName)
{
this.netMallName = netMallName;
}
// 查询价格
public double calcPrice(String productName)
{
try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
// ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextDouble():0-1之间的随机小数
// "my".charAt(0)为m,这里与 + 连接,可以连接成一个数字,此处模拟一本书的价格
return ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextDouble() * 2 + productName.charAt(0);
}
}
CompletableFuture常用方法
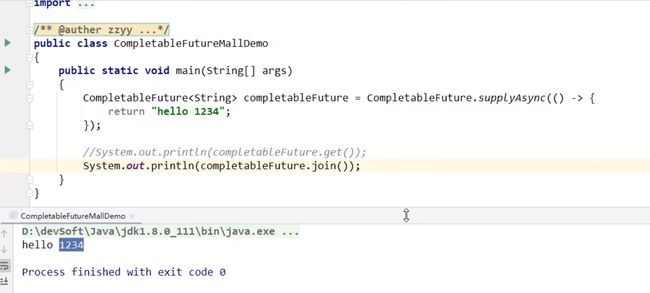
1.获取计算结果和触发计算
join和get方法
都可以获取结果,但是jion在编译期间不会去检查是否有异常
get、join、getNow、complete演示:
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException, TimeoutException {
group1();
}
/**
* 获得结果和触发计算
* @throws InterruptedException
* @throws ExecutionException
*/
private static void group1() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException {
CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
//暂停几秒钟线程
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "abc";
});
// System.out.println(completableFuture.get()); // 获取结果
// System.out.println(completableFuture.get(2L,TimeUnit.SECONDS));// 指定超时时间
// System.out.println(completableFuture.join()); // 都可以获取结果,但是jion在编译期间不会去检查是否有异常
// 暂停几秒钟线程
// try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
// getNow:立即获取结果不阻塞,如果此时未计算完成,直接返回xxx,计算完成则返回结果
// System.out.println(completableFuture.getNow("xxx"));
// complete:是否打断get方法立即返回括号值
System.out.println(completableFuture.complete("completeValue")+"\t"+completableFuture.get());
}
2.对计算结果进行处理
thenApply:计算结果存在依赖关系,这两个线程串行化,如果当前步错(存在异常),不走下一步
handle:计算结果存在依赖关系,这两个线程串行化,如果当前步错(存在异常),也可以走下一步,根据带的异常参数可以进一步处理
public static void main(String[] args){
ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() ->{
//暂停几秒钟线程
try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
System.out.println("111");
return 1;
},threadPool).thenApply(f -> {
// int i = 10/0;
System.out.println("222");
return f + 2;
}).thenApply(f -> {
System.out.println("333");
return f + 3;
}).whenComplete((v,e) -> {
if (e == null) {
System.out.println("----计算结果: " + v);
}
}).exceptionally(e -> {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
return null;
});
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"----主线程先去忙其它任务");
threadPool.shutdown();
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() ->{
//暂停几秒钟线程
try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
System.out.println("111");
return 1;
},threadPool).handle((f,e) -> {
int i = 10/0;
System.out.println("222");
return f + 2;
}).handle((f,e) -> {
System.out.println("333");
return f + 3;
}).whenComplete((v,e) -> {
if (e == null) {
System.out.println("----计算结果: " + v);
}
}).exceptionally(e -> {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
return null;
});
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"----主线程先去忙其它任务");
threadPool.shutdown();
}
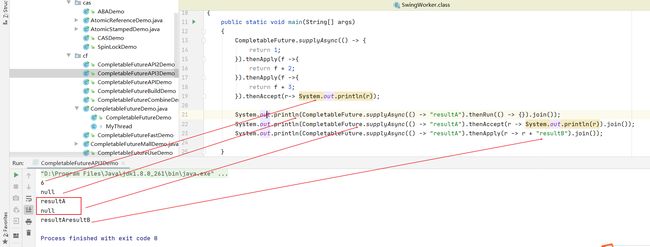
3.对计算结果进行消费
thenRun:任务A执行完执行B,并且B不需要A的结果
thenAccept:接受任务的处理结果,并消费处理,无返回结果,任务A执行完执行B,B需要A的结果,但是任务B无返回值
thenApply:任务A执行完执行B,B需要A的结果,同时任务B有返回值
public static void main(String[] args)
{
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
return 1;
}).thenApply(f ->{
return f + 2;
}).thenApply(f ->{
return f + 3;
}).thenAccept(System.out::println); // 6
// }).thenAccept(r-> System.out.println(r));
System.out.println(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "resultA").thenRun(() -> {}).join());
System.out.println(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "resultA").thenAccept(r -> System.out.println(r)).join());
System.out.println(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "resultA").thenApply(r -> r + "resultB").join());
}
4.对计算速度进行选用
applyToEither:谁快用谁
public static void main(String[] args)
{
CompletableFuture<String> playA = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("A come in");
try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
return "playA";
});
CompletableFuture<String> playB = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("B come in");
try { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
return "playB";
});
CompletableFuture<String> result = playA.applyToEither(playB, f -> {
return f + " is winer";
});
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t"+"-----: "+result.join());
}
5.对计算结果进行合并
thenCombine:两个CompletionStage任务都完成后,最终能把两个任务的结果一起交给thenCombine来处理,先完成的先等着,等待其他分支任务
public static void main(String[] args)
{
CompletableFuture<Integer> completableFuture1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t ---启动");
//暂停几秒钟线程
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return 10;
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> completableFuture2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t ---启动");
//暂停几秒钟线程
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return 20;
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> result = completableFuture1.thenCombine(completableFuture2, (x, y) -> {
System.out.println("-----开始两个结果合并");
return x + y;
});
System.out.println(result.join());
}
链式调用:
CompletableFuture线程池运行选择
代码演示:
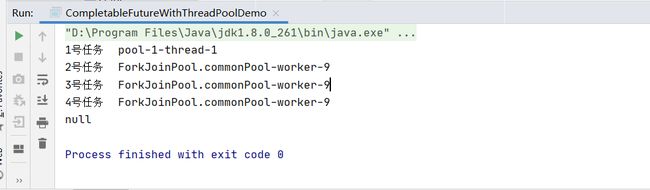
public static void main(String[] args)
{
ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
try
{
CompletableFuture<Void> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try { TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(20); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
System.out.println("1号任务" + "\t" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
return "abcd";
},threadPool).thenRunAsync(() -> {
try { TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(20); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
System.out.println("2号任务" + "\t" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}).thenRun(() -> {
try { TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(10); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
System.out.println("3号任务" + "\t" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}).thenRun(() -> {
try { TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(10); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
System.out.println("4号任务" + "\t" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
});
System.out.println(completableFuture.get(2L, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
threadPool.shutdown();
}
}
四、线程的创建方式四
/**
* 4.通过java提供的工具类Executors创建线程池,不推荐,会存在问题,推荐使用自定义线程池的方式
*/
@Test
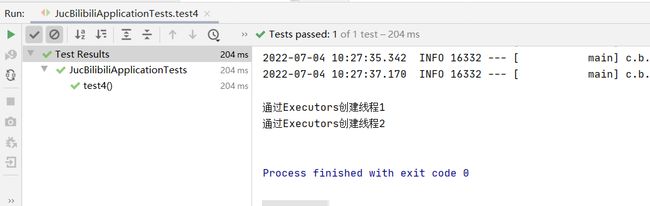
void test4(){
// 创建单个线程的线程池
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
executorService.submit(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("通过Executors创建线程1");
}
});
executorService.submit(()->{
System.out.println("通过Executors创建线程2");
});
// 销毁线程池
executorService.shutdown();
// executorService.shutdownNow();
}
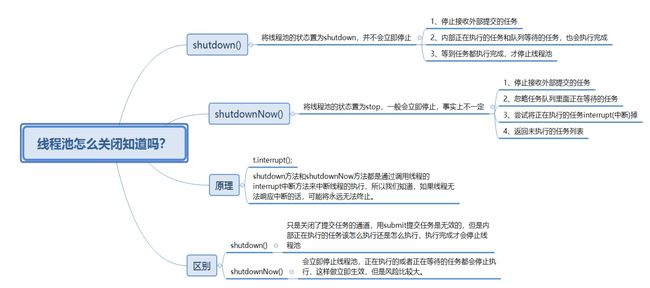
销毁线程池shutdown和shutdownNow的区别
自定义线程池
哔哩哔哩链接:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV15b4y117RJ?p=67&vd_source=7c5f1f4c039688f19024d50ef51aaed1
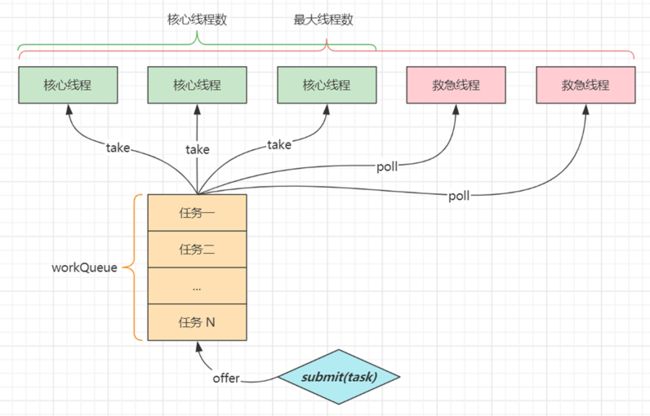
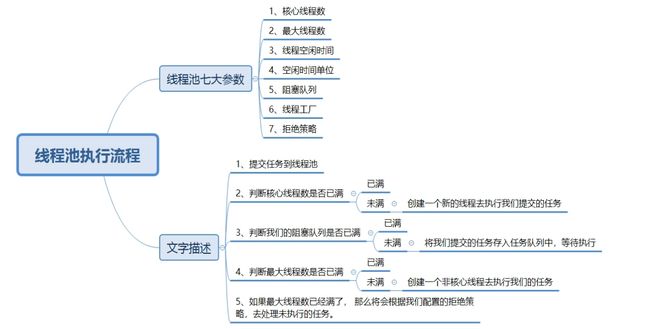
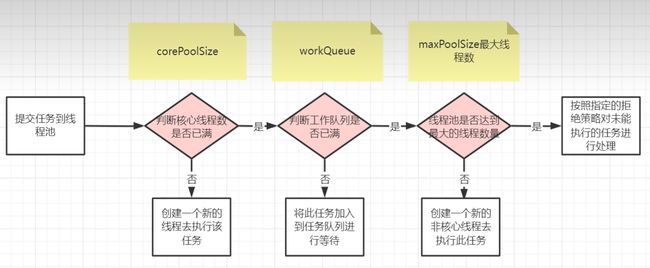
corePoolSize核心线程数目 - 池中会保留的最多线程数maximumPoolSize最大线程数目 - 核心线程+救急线程的最大数目keepAliveTime生存时间 - 救急线程的生存时间,生存时间内没有新任务,此线程资源会释放unit时间单位 - 救急线程的生存时间单位,如秒、毫秒等workQueue阻塞队列- 当没有空闲核心线程时,新来任务会加入到此队列排队,队列满会创建救急线程执行任务threadFactory线程工厂 - 可以定制线程对象的创建,例如设置线程名字、是否是守护线程等handler拒绝策略 - 当所有线程都在繁忙,workQueue 也放满时,会触发拒绝策略- 抛异常 java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy
- 由调用者(一般为main主线程)执行任务 java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy
- 丢弃任务 java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardPolicy
- 丢弃最早排队任务 java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardOldestPolicy
@Test
public void task(){
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
2, // 核心线程数
3, // 最大线程数,核心线程数 + 救急线程数
0, // 空闲存活时间
TimeUnit.SECONDS, // 时间单位
new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(2), // 工作队列中最多2个任务
r -> new Thread(r, "myThread" + new AtomicInteger(1).getAndIncrement()), // 线程工厂
new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy() // 拒绝策略
);
threadPoolExecutor.submit(()->{
System.out.println("自定义线程池");
});
}
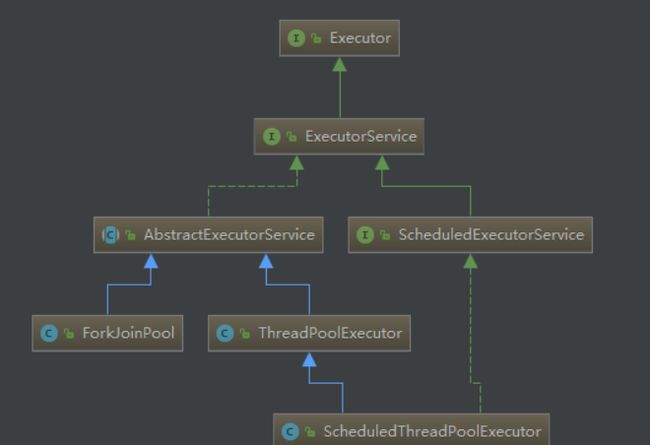
ThreadPoolExecutor是JDK中的线程池类,继承自Executor, Executor 顾名思义是专门用来处理多线程相关的一个接口,所有线程相关的类都实现了这个接口,里面有一个execute()方法,用来执行线程,线程池主要提供一个线程队列,队列中保存着所有等待状态的线程。避免了创建与销毁的额外开销,提高了响应的速度。相关的继承实现类图如下。
一、线程池接口:ExecutorService为线程池接口,提供了线程池生命周期方法,继承自Executor接口,ThreadPoolExecutor为线程池实现类,提供了线程池的维护操作等相关方法,继承自AbstractExecutorService,AbstractExecutorService实现了ExecutorService接口。
二、线程池的体系结构:
java.util.concurrent.Executor 负责线程的使用和调度的根接口
|–ExecutorService 子接口: 线程池的主要接口
|–ThreadPoolExecutor 线程池的实现类
|–ScheduledExceutorService 子接口: 负责线程的调度
|–ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor : 继承ThreadPoolExecutor,实现了ScheduledExecutorService
工具类 : Executors
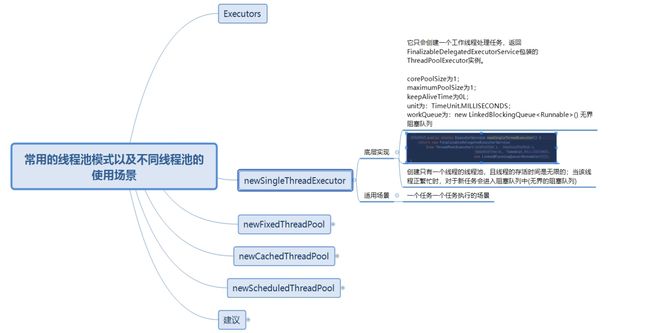
Executors为线程池工具类,相当于一个工厂类,用来创建合适的线程池,返回ExecutorService类型的线程池。有如下方法。
ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool() : 创建固定大小的线程池
ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool() : 缓存线程池,线程池的数量不固定,可以根据需求自动的更改数量。
ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor() : 创建单个线程池。 线程池中只有一个线程
ScheduledExecutorService newScheduledThreadPool() : 创建固定大小的线程,可以延迟或定时的执行任务
其中AbstractExecutorService是他的抽象父类,继承自ExecutorService,ExecutorService 接口扩展Executor接口,增加了生命周期方法。
创建一个制定大小的线程池,Exectuors工厂实际上就是调用的ExectuorPoolService的构造方法,传入默认参数。
哔哩哔哩链接:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43168010/article/details/97613895
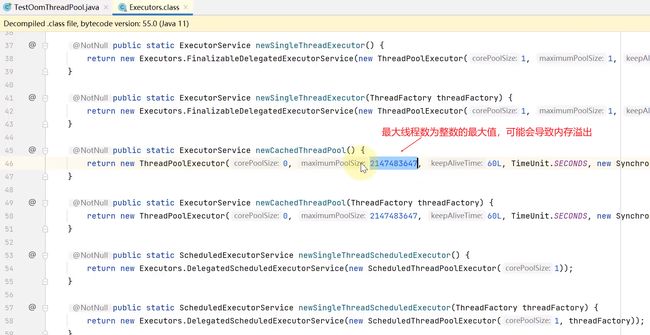
注意:使用工具类Executors创建线程池会存在问题,如newCachedThreadPool方法,核心线程数为0,而最大线程数为整数最大值,即如果任务过多会创建大量的救急线程,导致内存溢出。
再比如newFixedThreadPool方法,它创建了一个存放整数最大值的任务队列,也可能导致内存溢出。
哔哩哔哩链接:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1T44y1H7pu?spm_id_from=333.999.0.0&vd_source=7c5f1f4c039688f19024d50ef51aaed1
newSingleThreadExecutor
newFixedThreadPool
newCachedThreadPool
newScheduledThreadPool
建议
Spring下的自定义线程池
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor是spring包下的,是spring为我们提供的线程池类
public ThreadPoolTaskExecutor taskExecutorDing() {
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor taskExecutorDing = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
// 固定线程数
taskExecutorDing.setCorePoolSize(10);
// 最大线程数
taskExecutorDing.setMaxPoolSize(50);
// 指定任务队列数量
taskExecutorDing.setQueueCapacity(300);
// 线程空闲时间
taskExecutorDing.setKeepAliveSeconds(60);
// 是否允许超时
taskExecutorDing.setAllowCoreThreadTimeOut(true);
// 线程名称前缀
taskExecutorDing.setThreadNamePrefix("taskExecutorDing--");
/** 设置拒绝策略
* AbortPolicy
* -- 默认,当任务添加到线程池中被拒绝时(固定线程池、最大线程数以及任务队列都放满),它将抛出 RejectedExecutionException 异常。
* CallerRunsPolicy
* -- 当任务添加到线程池中被拒绝时(固定线程池、最大线程数以及任务队列都放满),由调用者(一般为main主线程)处理被拒绝的任务。
* DiscardOldestPolicy
* -- 当任务添加到线程池中被拒绝时(固定线程池、最大线程数以及任务队列都放满),线程池会放弃等待队列中最旧的未处理任务,然后将被拒绝的任务添加到等待队列中(最后面)。
* DiscardPolicy
* -- 当任务添加到线程池中被拒绝时(固定线程池、最大线程数以及任务队列都放满),线程池将丢弃被拒绝的任务。
*/
taskExecutorDing.setRejectedExecutionHandler(new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy());
// 线程池关闭时需等待所有的子任务执行完成才销毁对应的bean
taskExecutorDing.setWaitForTasksToCompleteOnShutdown(true);
// 等待的时间
taskExecutorDing.setAwaitTerminationSeconds(60);
// 初始化线程池
taskExecutorDing.initialize();
return taskExecutorDing;
}
五、守护线程
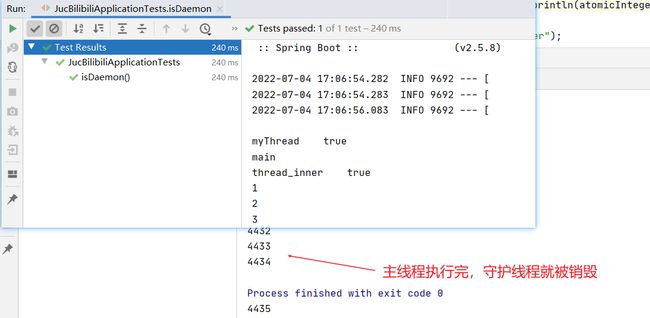
@Test
public void isDaemon(){
Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {
// 守护线程内创建的线程也为守护线程
Thread thread_inner = new Thread(() -> {
AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger(1);
while (true){
System.out.println(atomicInteger.getAndIncrement());
}
},"thread_inner");
thread_inner.start();
System.out.println(thread_inner.getName() + "\t" +thread_inner.isDaemon());
}, "myThread");
thread.setDaemon(true); // 设置为守护线程
thread.start();
System.out.println(thread.getName() + "\t" +thread.isDaemon());
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
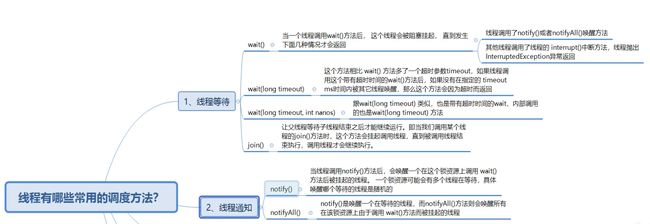
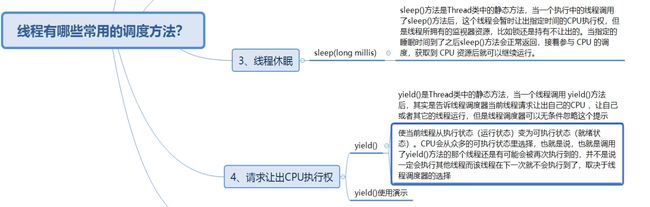
六、线程常用调度方法
哔哩哔哩链接:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Za411C7zN?spm_id_from=333.999.0.0&vd_source=7c5f1f4c039688f19024d50ef51aaed1
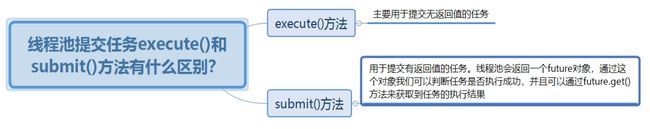
七、线程池execute和submit的区别
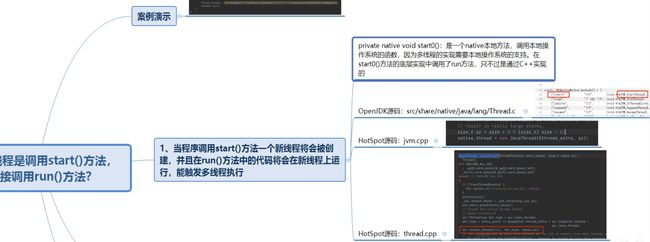
八、为什么启动线程是调用start方法,而不是run方法
哔哩哔哩链接:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1h44y1p7xe?spm_id_from=333.999.0.0&vd_source=7c5f1f4c039688f19024d50ef51aaed1
九、为什么使用线程池
十、线程池执行流程
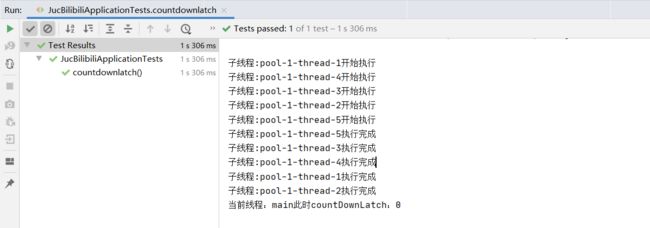
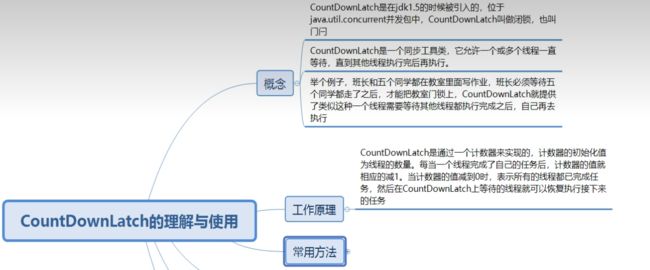
十一、 CountDownLatch的使用
哔哩哔哩链接:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1nr4y1a72f?spm_id_from=333.999.0.0&vd_source=7c5f1f4c039688f19024d50ef51aaed1

@Test
public void countdownlatch(){
final int THREAD_NUM = 5;
// 创建固定线程数的线程池
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(THREAD_NUM);
// 如果有n个子线程,我们就指定CountDownLatch的计数器为n
final CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(THREAD_NUM);
// 提交任务到线程池
for (int i = 0; i< THREAD_NUM; i++) {
executorService.execute(() -> {
try {
//模拟每个线程处理业务,耗时一秒钟
System.out.println("子线程:" +Thread.currentThread() . getName() + "开始执行");
//模拟每个线程处理业务,耗时一秒钟
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep( 1);
System. out.println("子线程:" +Thread.currentThread().getName() +"执行完成");
//当前线程调用此方法,则计数减一
countDownLatch.countDown();
}catch (InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
}
// 阻塞当前线程(此处为main线程),直到计数器的值为0,main线程才开始处理
try {
countDownLatch.await();
System.out.println("当前线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName()
+ "此时countDownLatch:" + countDownLatch.getCount());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 销毁线程池
executorService.shutdown();
}
十二、喜欢请关注我
至此,我们的Java线程的创建方式以及线程池的使用就讲解完成了。喜欢我的话可以关注我的微信公众号我爱学习呀嘻嘻 ,不定期分享各类资源哦。
![]()