驱动开发——字符设备
字符设备
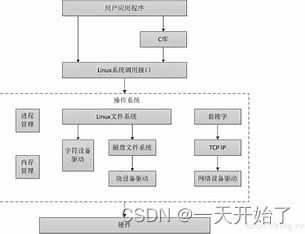
Linux 将系统设备分为:字符设备、块设备、网络设备。
工作原理
字符设备是 Linux 驱动中最基本的一类设备驱动,字符设备就是一个一个字节,
按照字节流进行读写操作的设备,读写数据是分先后顺序的。
在Linux的世界里面一切皆文件,所有的硬件设备操作到应用层都会被抽象成文件
的操作。我们知道如果应用层要访问硬件设备,它必定要调用到硬件对应的驱动程序。
1.在Linux文件系统中,每个文件都用一个struct inode结构体来描述,
这个结构体里面记录了 这个文件的所有信息,例如:文件类型,访问权限等。
struct inode信息
2.在Linux操作系统中,每个驱动程序在应用层的/dev目录下都会有一个
设备文件和它对应,并且该文件会有对应的主设备号和次设备号。
3.在Linux操作系统中,每个驱动程序都要分配一个主设备号,字符设备的设备号
保存在struct cdev结构体中。
struct cdev {
struct kobject kobj;
struct module *owner;
const struct file_operations *ops;//接口函数集合
struct list_head list;//内核链表
dev_t dev; //设备号
unsigned int count;//次设备号个数
};
4.在Linux操作系统中,每打开一次文件,Linux操作系统在VFS层都会分配一个struct file
结构体来描述打开的这个文件。该结构体用于维护文件打开权限、文件指针偏移值、私有
内存地址等信息。(strcut file有两个非常重要的字段:文件描述符和缓冲区)
字符驱动相关函数
注册
内核共提供了三个函数来注册一组字符设备编号,这三个函数分别是
register_chrdev_region()、alloc_chrdev_region()和 register_chrdev()。
注意事项
1.使用register_chrdev注册字符设备,其内部申请struct cdev 结构,
并调用cdev_add函数添加设备。
2.使用register_chrdev_region/alloc_chrdev_region注册字符设备,需要在外部事先
定义struct cdev 结构,然后使用函数cdev_init初始化它,最后还需在外部调用cdev_add
函数添加设备。
//比较老的内核注册的形式 早期的驱动
static inline int register_chrdev(unsigned int major, const char *name,
const struct file_operations *fops)
功能:
注册或者分配设备号,并注册fops到cdev结构体,
如果major>0,功能为注册该主设备号,
如果major=0,功能为动态分配主设备号。
参数:
@major : 主设备号
@name : 设备名称,执行 cat /proc/devices显示的名称
@fops : 文件系统的接口指针
返回值
如果major>0 成功返回0,失败返回负的错误码
如果major=0 成功返回主设备号,失败返回负的错误码
int register_chrdev_region(dev_t from, unsigned count, const char *name)
功能:
注册一个范围()的设备号
参数:
@from 设备号
@count 注册的设备个数
@name 设备的名字
返回值:
成功返回0,失败返回错误码(负数)
int alloc_chrdev_region(dev_t *dev, unsigned baseminor, unsigned count,
const char *name)
功能:
注册一个主设备号由内核动态分配,次设备号为baseminor~baseminor+count的设备驱动
参数:
@dev: 用来获取设备号
@baseminor:次设备号起始值
@count: 次设备号个数
@name: 设备名称
返回值:
成功返回0,失败返回错误码(负数)
//注销
static inline void unregister_chrdev(unsigned int major, const char *name)
void cdev_init(struct cdev *cdev, const struct file_operations *fops)
功能:
初始化cdev结构体
参数:
@cdev cdev结构体地址
@fops 操作字符设备的函数接口地址
返回值:
无
int cdev_add(struct cdev *p, dev_t dev, unsigned count)
功能:
添加一个字符设备到操作系统
参数:
@p cdev结构体地址
@dev 设备号
@count 次设备号个数
返回值:
成功返回0,失败返回错误码(负数)
void cdev_del(struct cdev *p)
功能:
从系统中删除一个字符设备
参数:
@p cdev结构体地址
返回值:
无
struct file_operations {
struct module *owner;//拥有该结构的模块的指针,一般为THIS_MODULES
loff_t (*llseek) (struct file *, loff_t, int);//用来修改文件当前的读写位置
ssize_t (*read) (struct file *, char __user *, size_t, loff_t *);//从设备中同步读取数据
ssize_t (*write) (struct file *, const char __user *, size_t, loff_t *);//向设备发送数据
ssize_t (*aio_read) (struct kiocb *, const struct iovec *, unsigned long, loff_t);//初始化一个异步的读取操作
ssize_t (*aio_write) (struct kiocb *, const struct iovec *, unsigned long, loff_t);//初始化一个异步的写入操作
int (*readdir) (struct file *, void *, filldir_t);//仅用于读取目录,对于设备文件,该字段为NULL
unsigned int (*poll) (struct file *, struct poll_table_struct *); //轮询函数,判断目前是否可以进行非阻塞的读写或写入
int (*ioctl) (struct inode *, struct file *, unsigned int, unsigned long); //执行设备I/O控制命令
long (*unlocked_ioctl) (struct file *, unsigned int, unsigned long); //不使用BLK文件系统,将使用此种函数指针代替ioctl
long (*compat_ioctl) (struct file *, unsigned int, unsigned long); //在64位系统上,32位的ioctl调用将使用此函数指针代替
int (*mmap) (struct file *, struct vm_area_struct *); //用于请求将设备内存映射到进程地址空间
int (*open) (struct inode *, struct file *); //打开
int (*flush) (struct file *, fl_owner_t id);
int (*release) (struct inode *, struct file *); //关闭
int (*fsync) (struct file *, struct dentry *, int datasync); //刷新待处理的数据
int (*aio_fsync) (struct kiocb *, int datasync); //异步刷新待处理的数据
int (*fasync) (int, struct file *, int); //通知设备FASYNC标志发生变化
int (*lock) (struct file *, int, struct file_lock *);
ssize_t (*sendpage) (struct file *, struct page *, int, size_t, loff_t *, int);
unsigned long (*get_unmapped_area)(struct file *, unsigned long, unsigned long, unsigned long, unsigned long);
int (*check_flags)(int);
int (*flock) (struct file *, int, struct file_lock *);
ssize_t (*splice_write)(struct pipe_inode_info *, struct file *, loff_t *, size_t, unsigned int);
ssize_t (*splice_read)(struct file *, loff_t *, struct pipe_inode_info *, size_t, unsigned int);
int (*setlease)(struct file *, long, struct file_lock **);
};
实例
#include