Socket通信与WebSocket协议
文章目录
目录
文章目录
前言
一、Socket通信
1.1 BIO
1.2 NIO
1.3 AIO
二、WebSocket协议
总结
前言
一、Socket通信
Socket是一种用于网络通信的编程接口(API),它提供了一种机制,使不同主机之间可以通过网络进行数据传输和通信。Socket是支持TCP/IP协议栈的应用层与传输层之间的接口。
在Socket编程中,有两种常见的角色:客户端和服务器端。客户端负责发起连接请求,服务器端负责接收并处理连接请求。
Socket通信的基本流程如下:
- 服务器端创建一个ServerSocket对象,并指定一个端口号。该对象会监听该端口上的连接请求。
- 客户端创建一个Socket对象,并指定要连接的服务器的IP地址和端口号。
- 客户端使用Socket对象发起连接请求,向服务器发送连接请求。
- 服务器监听到连接请求后,通过accept()方法接受客户端的连接,创建一个Socket对象与客户端建立连接。
- 客户端和服务器端通过各自的Socket对象进行数据的读取和写入,实现双向的数据交换。
- 数据交换完成后,可以关闭连接。客户端和服务器端都可以使用close()方法关闭自己的Socket对象。
通过Socket编程,可以实现不同设备之间的网络通信。例如,可以使用Socket编程来开发基于TCP/IP的客户端-服务器应用、聊天程序、文件传输程序等。
需要注意的是,Socket编程只提供了底层的网络通信接口,对于数据的格式、协议、解析等需要自行定义和处理。在Java中,可以使用Java标准库中的java.net.Socket和java.net.ServerSocket来实现Socket编程。
socket编程步骤:
- 服务器监听:服务器启动后,它会有一个线程一直启动,等待着客户端端连接。它会定义好自己的端口号。
- 客户端请求:客户端端套接字提出连接请求,要连接的目标是服务端的套接字。客户端必须要指明服务端套接字的地址和端口号。
- 连接确认:当服务端收到客户端的连接请求就会响应客户端套接字的请求,建立一个新的线程处理客户端的请求。
1.1 BIO
BIO(Blocking I/O)是Java中的一种阻塞式I/O模型,也称为传统的I/O模型。在BIO中,每个I/O操作都会阻塞当前线程,直到数据准备好或者操作完成。
BIO的工作原理如下:
- 服务器端创建一个ServerSocket对象并监听指定的端口。
- 服务器通过accept()方法等待客户端发起连接请求。
- 当有客户端连接请求到达时,服务器通过accept()方法接受客户端的连接,并返回一个新的Socket对象。
- 服务器使用新的Socket对象与客户端进行数据的读取和写入。
- 客户端使用Socket对象与服务器进行通信,发送请求并接收响应。
- 服务器端和客户端通过读写操作进行数据的交互,但是这些操作都是阻塞的,直到数据完全发送或接收完毕。
BIO的特点:
- 阻塞:BIO的I/O操作是阻塞的,当没有数据可读或写时,线程会一直阻塞在相应的读写操作上,无法去处理其他任务。
- 线程池限制:由于每个连接都需要独占一个线程进行处理,当并发连接数很大时,线程资源会被耗尽,导致性能下降。
- 可靠性:由于阻塞的特性,BIO在网络不稳定或出现异常时可能会导致程序挂起或阻塞。
虽然BIO具有易于理解和使用的优点,但其在高并发应用场景下的性能较差。随着网络应用的发展,为了提高性能和扩展性,非阻塞I/O模型如NIO(New I/O)和异步I/O模型如AIO(Asynchronous I/O)逐渐成为主流。
需要注意的是,BIO仍然适用于某些特定的应用场景,特别是在连接数较少且对实时性要求不高的情况下。
服务器端
package com.rcg.testtwo;
import java.io.*;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
/**
* @author :[email protected] rcg
* @date :Created in 2023/8/24 14:47
* @description:服务端
* @modified By:
* @version:
*/
public class BioServer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//定义端口号
int port = 9999;
//定义服务器套接字
ServerSocket serverSocket = null;
try {
//创建服务器套接字
serverSocket = new ServerSocket(port);
//一直监听,是否有客户端请求过来
while (true) {
//每次都会新建一个线程,来处理接收到到请求
Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();
//每次都会新建一个线程,来处理接收到到请求
new Thread(new SocketHandler(socket)).start();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//如果服务器套接字不为空,则关闭
if (serverSocket!= null) {
try {
serverSocket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
serverSocket = null;
}
}
}
static class SocketHandler implements Runnable {
//定义socket
Socket socket = null;
public SocketHandler(Socket socket) {
this.socket = socket;
}
//处理读取的数据
@Override
public void run() {
BufferedReader reader = null;
PrintWriter writer = null;
try {
//读取数据,BIO 是面向流到,所以定义流 BufferedReader 来读取数据
reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream(), "UTF-8"));
//将收到的数据返回给客户端
writer = new PrintWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(socket.getOutputStream(), "UTF-8"));
String readMessage = null;
//循环读取数据
while (true) {
if ((readMessage = reader.readLine()) == null) {
break;
}
System.out.println("server reading........" + readMessage);
//将数据返回给客户端
writer.println("server recive : " + readMessage);
writer.flush();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (socket!= null) {
try {
socket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
socket = null;
}
if (reader!= null) {
try {
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
reader = null;
}
if (writer!= null) {
writer.close();
writer = null;
}
}
}
}
}
客户端
package com.rcg;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* @author :[email protected] rcg
* @date :Created in 2023/8/24 14:54
* @description:客户端
* @modified By:
* @version:
*/
public class BioClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//服务端到 ip 地址
String host = "127.0.0.1";
//和服务端到端口号一致
int port = 9999;
Socket socket = null;
BufferedReader reader = null;
PrintWriter writer = null;
//接收键盘输入数据
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
try {
//创建 socket 对象
socket = new Socket(host, port);
//创建 BufferedReader 对象
String message = null;
reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream(), "UTF-8"));
writer = new PrintWriter(socket.getOutputStream(), true);
//循环接收数据
while (true) {
message = scanner.nextLine();
//如果接收到 exit 则退出
if (message.equals("exit")) {
break;
}
//数据发送服务端
writer.println("客户端输入:" + message);
writer.flush();
//接收服务端的响应
System.out.println(reader.readLine());
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//关闭 socket 对象
if (socket!= null) {
try {
socket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
socket = null;
}
//关闭 BufferedReader 对象
if (reader!= null) {
try {
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
reader = null;
}
//关闭 PrintWriter 对象
if (writer!= null) {
writer.close();
writer = null;
}
}
}
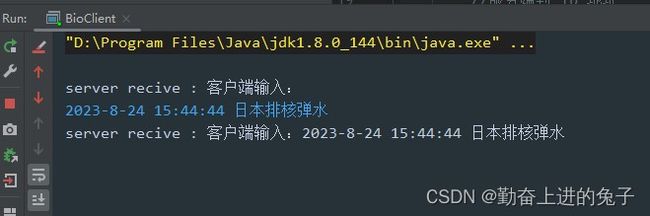
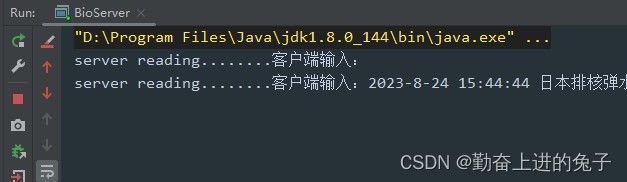
}效果
1.2 NIO
NIO(New I/O)是Java中提供的一种非阻塞式I/O模型,与传统的阻塞式I/O(BIO)相比,NIO能更高效地处理I/O操作和并发连接。
NIO的关键组件包括通道(Channel),缓冲区(Buffer)、选择器(Selector)和非阻塞模式。下面对每个组件进行简要介绍:
-
通道(Channel):通道是数据源和目标之间的连接,可以用于读取和写入数据。在NIO中,所有I/O操作都是通过通道进行的。不同类型的通道,如文件通道、套接字通道等,适用于不同的I/O场景。
-
缓冲区(Buffer):缓冲区是一个连续的内存块,用于存储数据。它使得读取和写入数据更加高效。在NIO中,所有数据的读取和写入都是通过缓冲区进行的。
-
选择器(Selector):选择器是用于检测通道上的事件的对象。通过选择器,可以实现单个线程管理多个通道,从而高效地处理并发连接。选择器可以监控通道上的事件类型,如接受连接、读取数据、写入数据等,并根据事件的发生情况来执行相应的操作。
-
非阻塞模式:NIO使用非阻塞模式进行通信。在非阻塞模式下,当一个通道没有数据可读取时,线程不会被阻塞,而是可以继续处理其他任务。这样可以避免每个连接都需要独占一个线程的资源浪费问题,实现更高效的并发连接处理。
NIO的工作原理如下:
- 服务器创建一个选择器,并将其注册到一个或多个通道上。
- 当有事件发生(如连接、读取、写入等),选择器会通过轮询的方式检测到事件的发生。
- 当事件发生时,选择器会返回一个包含已就绪事件的键集合,程序可以通过这些键来获取感兴趣的事件和相应的通道。
- 程序根据事件类型执行相应的操作,如接受连接、读取数据、写入数据等。
NIO相比于BIO具有以下优点:
- 高并发性:NIO使用选择器和非阻塞模式,能够高效地处理并发连接,减少线程的使用,提高系统的并发性能。
- 可扩展性:NIO支持单线程管理多个通道,适用于需要管理大量连接的场景,提供了更好的可扩展性。
- 非阻塞式:NIO采用非阻塞模式,不会因为一个通道的读写操作导致阻塞,可以同时处理多个通道的操作,提高了系统的响应速度。
需要注意的是,NIO的实现相对复杂,需要合理地使用和管理缓冲区、处理事件等。在Java中,可以使用java.nio包下的类来进行NIO编程,如SelectableChannel、ByteBuffer、Selector等。
总的来说,NIO是一种更高效和灵活的I/O模型,适用于需要处理大量并发连接的场景,如网络服务器、聊天程序、游戏服务器等。
服务器端
package com.rcg.testtwo;
/**
* @author :[email protected] rcg
* @date :Created in 2023/8/24 15:49
* @description:
* @modified By:
* @version:
*/
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class NioServer {
private static ByteBuffer readBuf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
private static ByteBuffer writeBuf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
public static void main(String[] args) {
int port = 9999;
Selector selector;
try {
//打开多路复用器
selector = Selector.open();
//定义一个 Channel
ServerSocketChannel channel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
//非阻塞模型
channel.configureBlocking(false);
//绑定端口号
channel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(port));
//channel 注册到 Selector 上面
channel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
System.out.println("服务已经启动了......");
while (true) {
//复用器开始监听
selector.select();
Iterator seletionKeys = selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while (seletionKeys.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = seletionKeys.next();
if (key.isValid()) {
//监听客户端第一次端连接信息
if (key.isAcceptable()) {
ServerSocketChannel ssc = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel();
SocketChannel sc = ssc.accept();
sc.configureBlocking(false);
sc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
System.out.println("accept a client : " + sc.socket().getInetAddress().getHostName());
} else {
read(key);
}
}
seletionKeys.remove();
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static void read(SelectionKey key) {
try {
//清空缓冲区
readBuf.clear();
//获取注册在通道里面的 key 对象
SocketChannel sc = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
//读取数据
int count = sc.read(readBuf);
//如果没有数据,则关闭连接
if (count == -1) {
key.channel().close();
key.cancel();
return;
}
//有数据则进行读取 读取之前需要进行复位方法(把position 和limit进行复位)
readBuf.flip();
//6 根据缓冲区的数据长度创建相应大小的byte数组,接收缓冲区的数据
byte[] bytes = new byte[readBuf.remaining()];
//7 接收缓冲区数据
readBuf.get(bytes);
String body = new String(bytes).trim();
System.out.println("服务端接受到客户端请求的数据: " + body);
//9 告诉客户端已收到数据
writeBuf.put(("你好,客户端,我已收到数据:" + body).getBytes());
//对缓冲区进行复位
writeBuf.flip();
//写出数据到服务端
sc.write(writeBuf);
//清空缓冲区数据
writeBuf.clear();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
} 客户端
package com.rcg;
/**
* @author :[email protected] rcg
* @date :Created in 2023/8/24 15:53
* @description:
* @modified By:
* @version:
*/
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class NioClient {
private static final String host = "127.0.0.1";
private static final Integer port = 9999;
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
//创建一个SocketChannel对象
SocketChannel channel = SocketChannel.open();
//连接服务端
channel.connect(new InetSocketAddress(host, port));
//设置为非阻塞模式
channel.configureBlocking(false);
//创建一个Selector对象
Selector selector = Selector.open();
//注册channel,可读,可写
channel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ, SelectionKey.OP_WRITE);
//开启新的线程监听,否则的话,客户端在控制台输入信息不好操作。
new Thread(() -> {
while (true) {
try {
//多路复用器开始监听
selector.select();
Iterator selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while (selectionKeys.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey selectionKey = selectionKeys.next();
if (selectionKey.isValid() && selectionKey.isReadable()) {
//建立写缓冲区
ByteBuffer readBuf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
//2 获取之前注册的socket通道对象
SocketChannel sc = (SocketChannel) selectionKey.channel();
//3 读取数据
int count = sc.read(readBuf);
if (count == -1) {
selectionKey.channel().close();
selectionKey.cancel();
return;
}
//5 有数据则进行读取 读取之前需要进行复位方法(把position 和limit进行复位)
readBuf.flip();
//6 根据缓冲区的数据长度创建相应大小的byte数组,接收缓冲区的数据
byte[] bytes = new byte[readBuf.remaining()];
//7 接收缓冲区数据
readBuf.get(bytes);
String body = new String(bytes).trim();
System.out.println("收到服务端的数据:" + body);
}
//移除未处理的key
selectionKeys.remove();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
//设置缓冲区大小
ByteBuffer writebuf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
while (true) {
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
System.in.read(bytes);
//把数据放到缓冲区中
writebuf.put(bytes);
//对缓冲区进行复位
writebuf.flip();
//写出数据到服务端
channel.write(writebuf);
//清空缓冲区数据
writebuf.clear();
}
} catch (
IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
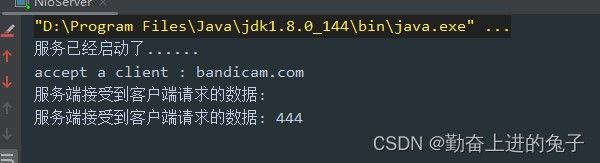
} 测试
1.3 AIO
AIO(Asynchronous I/O)是Java中提供的一种异步I/O模型,与传统的阻塞式I/O(BIO)和非阻塞式I/O(NIO)相比,AIO能更高效地处理I/O操作和并发连接。
AIO的关键组件包括通道(Channel)、缓冲区(Buffer)和完成通知机制。下面对每个组件进行简要介绍:
-
通道(Channel):通道是数据源和目标之间的连接,可以用于读取和写入数据。在AIO中,所有I/O操作都是通过通道进行的。不同类型的通道,如文件通道、套接字通道等,适用于不同的I/O场景。
-
缓冲区(Buffer):缓冲区是一个连续的内存块,用于存储数据。它使得读取和写入数据更加高效。在AIO中,所有数据的读取和写入都是通过缓冲区进行的。
-
完成通知机制:AIO使用回调和事件驱动的方式来处理I/O操作。当一个I/O操作完成时,操作系统会通知应用程序,并触发预先注册的回调函数,从而进行相应的处理。这种机制可以避免线程阻塞,提高系统的并发性能。
AIO的工作原理如下:
- 服务器创建一个通道,并注册一个或多个感兴趣的I/O事件和回调函数。
- 当有I/O事件发生时,操作系统会通知应用程序,并调用相应的回调函数。
- 在回调函数中,应用程序可以获取已完成的I/O操作的结果,并进行相应的处理,如读取数据、写入数据等。
AIO相比于BIO和NIO具有以下优点:
-
异步性:AIO通过使用回调和事件驱动的方式,实现真正的异步I/O操作。这意味着应用程序无需等待操作完成,而是可以继续执行其他任务,提高了系统的并发性能。
-
简化编程模型:AIO的异步特性可以简化编程模型,避免了繁琐的线程管理和同步操作。开发者只需要关注回调函数的处理即可,让操作系统来处理底层的I/O操作。
-
高性能:由于AIO的异步特性,可以充分利用系统资源,提供更高的并发性能和吞吐量。
需要注意的是,AIO在Java中是通过AsynchronousChannel和CompletionHandler来实现的。可以使用java.nio.channels.AsynchronousChannelGroup和java.nio.channels.AsynchronousServerSocketChannel等类来创建和管理异步通道,使用java.nio.channels.CompletionHandler来定义回调函数。
总的来说,AIO适用于需要处理大量并发连接且对性能要求较高的场景。然而,AIO在某些平台上的性能可能不如NIO,具体取决于操作系统和硬件的支持程度。在选择使用AIO还是NIO时,需要考虑特定的应用需求和目标平台的特性。
服务端
package com.rcg.testtwo;
/**
* @author :[email protected] rcg
* @date :Created in 2023/8/24 16:02
* @description:
* @modified By:
* @version:
*/
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.AsynchronousChannelGroup;
import java.nio.channels.AsynchronousServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.AsynchronousSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.CompletionHandler;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
public class AioServer {
private final int port;
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建一个端口号为9999的AioServer对象
int port = 9999;
// 创建一个AioServer对象,并传入端口号
new AioServer(port);
}
public AioServer(int port) {
// 将端口号传入AioServer对象
this.port = port;
// 监听
listen();
// 循环
while (true) {
try {
// 线程休眠1000000毫秒
Thread.sleep(1000000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
}
}
private void listen() {
try {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
AsynchronousChannelGroup threadGroup = AsynchronousChannelGroup.withCachedThreadPool(executorService, 1);
//创建一个异步的服务端套接字
final AsynchronousServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = AsynchronousServerSocketChannel.open(threadGroup);
//绑定端口
serverSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(port));
System.out.println("服务已经启动,监听端口:" + port);
//监听
serverSocketChannel.accept(null, new CompletionHandler() {
final ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
@Override
public void completed(AsynchronousSocketChannel result, Object attachment) {
System.out.println("I/O 操作成功,开始获取数据");
try {
//清空缓冲区
byteBuffer.clear();
//从异步缓冲区中读取数据
result.read(byteBuffer).get();
//将缓冲区的数据转换为字符串
byteBuffer.flip();
System.out.println("服务端接收到数据:" + new String(byteBuffer.array()).trim());
//将数据写入异步缓冲区
result.write(byteBuffer);
//将缓冲区的数据转换为字符串
byteBuffer.flip();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
//关闭异步套接字
result.close();
//接收下一个操作
serverSocketChannel.accept(null, this);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("操作完成");
}
@Override
public void failed(Throwable exc, Object attachment) {
System.out.println("I/O 操作失败:" + exc);
}
});
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
} 客户端
package com.rcg;
/**
* @author :[email protected] rcg
* @date :Created in 2023/8/24 16:02
* @description:
* @modified By:
* @version:
*/
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.AsynchronousSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.CompletionHandler;
public class AioClient {
private AsynchronousSocketChannel clientChannel;
// 定义一个AsynchronousSocketChannel类型的变量clientChannel
private static final String host = "127.0.0.1";
// 定义一个字符串类型的变量host
private static final Integer port = 9999;
// 定义一个整型类型的变量port
public AioClient() throws Exception {
// 创建一个AsynchronousSocketChannel实例
clientChannel = AsynchronousSocketChannel.open();
}
// 定义一个AioClient类的构造函数
public void connect(String host, int port) {
try {
// 调用AsynchronousSocketChannel的open()方法,创建一个AsynchronousSocketChannel实例
clientChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress(host, port), null, new CompletionHandler() {
// 定义一个CompletionHandler类型的变量attachment,用于存放连接结果
@Override
public void completed(Void result, Void attachment) {
try {
// 调用AsynchronousSocketChannel的write()方法,发送数据
clientChannel.write(ByteBuffer.wrap("你好师姐,客户端链接成功了".getBytes())).get();
System.out.println("数据已经发送成功!");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// 定义一个CompletionHandler类型的变量attachment,用于存放连接失败的异常
@Override
public void failed(Throwable exc, Void attachment) {
}
});
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
// 等待1秒
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 定义一个ByteBuffer准备读取数据
final ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
// 调用AsynchronousSocketChannel的read()方法,读取数据
clientChannel.read(byteBuffer, null, new CompletionHandler() {
// 定义一个CompletionHandler类型的变量attachment,用于存放读取结果
@Override
public void completed(Integer result, Object attachment) {
System.out.println("I/O操作完成" + result);
System.out.println("获取返回结果:" + new String(byteBuffer.array()).trim());
}
// 定义一个CompletionHandler类型的变量attachment,用于存放读取失败的异常
@Override
public void failed(Throwable exc, Object attachment) {
exc.printStackTrace();
}
});
}
// 定义一个main()方法,用于连接服务器
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 创建一个AioClient实例
AioClient aioClient = new AioClient();
// 调用AioClient的connect()方法,连接服务器
aioClient.connect(host, port);
}
}
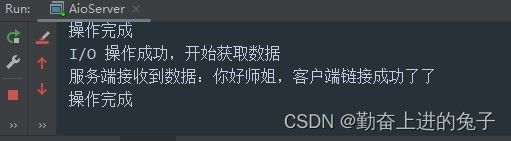
测试
二、WebSocket协议
WebSocket是一种在Web浏览器和服务器之间进行全双工通信的协议。它提供了一种持久连接的机制,允许客户端和服务器之间实时地交换数据,而不需要频繁地发起HTTP请求。
与传统的HTTP请求相比,WebSocket连接通过一个初始的HTTP握手阶段建立,并使用一种特殊的数据帧格式来传输数据。一旦建立了WebSocket连接,客户端和服务器之间可以随时互相发送消息,这样就实现了实时的双向数据交流。
WebSocket具有以下特点:
- 实时性:WebSocket连接保持持久性,客户端和服务器之间可以实时地发送和接收数据,避免了短轮询或长轮询的延迟。
- 双向通信:WebSocket连接支持全双工通信,即客户端和服务器可以同时发送和接收数据。
- 轻量级:WebSocket协议采用了更轻量级的数据帧格式,相对于HTTP请求来说,数据传输的开销更小。
- 更少的资源消耗:由于WebSocket连接的持久性,服务器端不需要为每个客户端连接创建一个新的线程或进程,从而减少了服务器资源的消耗。
- 跨域支持:WebSocket连接支持跨域通信,可以在不同域名下的客户端和服务器之间进行通信。
WebSocket广泛用于实时聊天应用、多人游戏、实时数据传输等需要高实时性和双向通信的Web应用场景。在前端开发中,可以使用JavaScript提供的WebSocket API来创建和管理WebSocket连接。在后端开发中,可以使用各种语言和框架提供的WebSocket库来处理WebSocket连接和消息的收发。
要在Web应用程序中使用WebSocket,你需要在客户端和服务器端分别进行相应的代码编写。下面是一个示例,展示了如何在JavaScript和Java中使用WebSocket。
客户端
// 创建WebSocket对象并指定服务器的URL
var socket = new WebSocket('ws://localhost:8080/mywebsocket');
// 连接建立时触发事件
socket.onopen = function(event) {
console.log('WebSocket连接已建立');
// 向服务器发送消息
socket.send('Hello Server!');
};
// 收到服务器消息时触发事件
socket.onmessage = function(event) {
var message = event.data;
console.log('收到服务器消息:' + message);
// 在此处对收到的消息进行处理
};
// 连接关闭时触发事件
socket.onclose = function(event) {
console.log('WebSocket连接已关闭');
};
// 发生错误时触发事件
socket.onerror = function(event) {
console.error('WebSocket出现错误');
};
服务器端(使用Java):
import javax.websocket.*;
import javax.websocket.server.ServerEndpoint;
import java.io.IOException;
@ServerEndpoint("/mywebsocket")
public class MyWebSocket {
@OnOpen
public void onOpen(Session session) {
System.out.println("WebSocket连接已建立");
// 向客户端发送消息
try {
session.getBasicRemote().sendText("Hello Client!");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@OnMessage
public void onMessage(String message, Session session) {
System.out.println("收到客户端消息:" + message);
// 在此处对收到的消息进行处理
// 向客户端发送消息
try {
session.getBasicRemote().sendText("Got your message: " + message);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@OnClose
public void onClose() {
System.out.println("WebSocket连接已关闭");
}
@OnError
public void onError(Throwable error) {
System.err.println("WebSocket发生错误");
error.printStackTrace();
}
}
在示例中,客户端使用JavaScript的WebSocket对象创建WebSocket连接,并通过相应的事件处理函数来处理连接建立、消息收发、连接关闭和错误等事件。服务器端使用Java的javax.websocket库,使用@ServerEndpoint注解指定WebSocket的URL,并编写相应的方法来处理连接建立、消息收发和连接关闭等事件。