【 OpenGauss源码学习 —— 列存储(Insert)】
列存储(Insert)
- 概述
- 相关函数
-
- ExecInsert
-
- RelationData 结构体
- FormData_pg_class 结构体
- HeapInsertCStore函数
-
- InsertArg 结构体
- CStoreInsert 类
- CStoreInsert::InitInsertArg函数
- heap_deform_tuple 函数
- bulkload_rows 结构体
- append_one_tuple 函数
- bulkload_vector 结构体
- CStoreInsert::BatchInsert 函数
- CStoreInsert::BatchInsertCommon 函数
- CStoreInsert::FlushIndexDataIfNeed 函数
- CStoreInsert::DeInitInsertArg 函数
声明:本文的部分内容参考了他人的文章。在编写过程中,我们尊重他人的知识产权和学术成果,力求遵循合理使用原则,并在适用的情况下注明引用来源。
本文主要参考了 OpenGauss1.1.0 的开源代码和《OpenGauss数据库源码解析》一书以及OpenGauss社区学习文档
概述
在先前的学习中分别介绍了列存储(创建表)和列存储(CopyTo),相比大家对列存储也有了初步的认识和了解。本文接下来将学习列存储(Insert)的相关知识。
这里再简单介绍一下列存储:
在 OpenGauss 中,列存储是一种高效的数据存储方式,它在处理分析查询和数据仓库工作负载时具有很高的性能优势。列存储将表中的数据按列存储在磁盘上,而不是按行存储,这样可以极大地提高数据读取和分析操作的效率。当涉及大量数据的扫描、聚合和过滤操作时,列存储可以比传统的行存储方式更加高效。
在列存储中执行 INSERT INTO 操作与传统的行存储方式有一些不同,因为列存储和行存储在数据组织和存储方面有显著的差异。以下是关于在列存储中执行 INSERT INTO 操作的一些要点:
- 批量插入优化: 列存储在插入数据时通常会倾向于使用批量插入优化。
- 数据排序: 列存储在插入数据时,通常会对数据进行排序以优化压缩和存储效率。
- 增量编码: 列存储可能会使用增量编码技术来减少存储空间。
- 数据压缩: 列存储通常会在插入数据时应用数据压缩技术。
- 并行处理: 类似于读取操作,在
INSERT INTO操作中也可以利用并行处理来提高插入性能。
相关函数
我们按照一个实际案例来学习,创建一个名为 sales 的列存储表,用于存储销售数据,表的结构如下:
--------创建表
CREATE TABLE sales (
sale_id INT,
product_id INT,
quantity INT,
sale_date DATE
) WITH (ORIENTATION = COLUMN);
--------插入数据
INSERT INTO sales (sale_id, product_id, quantity, sale_date)
VALUES
(1, 101, 5, '2023-08-22'),
(2, 102, 10, '2023-08-23'),
(3, 101, 8, '2023-08-24');
postgres=# select * from sales;
sale_id | product_id | quantity | sale_date
---------+------------+----------+---------------------
1 | 101 | 5 | 2023-08-22 00:00:00
2 | 102 | 10 | 2023-08-23 00:00:00
3 | 101 | 8 | 2023-08-24 00:00:00
(3 rows)
ExecInsert
ExecInsert 函数实现的函数名为 ExecInsertT,是 PostgreSQL 数据库中执行 INSERT 操作的核心函数之一。其作用是将数据插入到目标表中,并处理与插入相关的触发器、约束、外部存储等操作。以下是函数的主要步骤:
- 从输入的 slot 中提取出待插入的数据。
- 获取与目标表相关的信息,如关系描述符(result_relation_desc)等。
- 如果目标表具有 OIDs(对象标识符),则将要插入的数据的 OID 设置为无效(0),以便 heap_insert 在插入时分配新的 OID。
- 执行 BEFORE ROW INSERT 触发器(如果存在)。
- 根据情况,调用外部存储(FDW)的插入函数,或者使用内部的 heap_insert 函数插入数据到表中。
- 在插入数据后,执行相应的触发器(AFTER ROW INSERT)。
- 如果目标表有主键、唯一约束等,可能会执行相关约束检查。
- 最后,根据返回设置,可能执行 RETURNING 子句
ExecInsert 函数源码如下:(路径:src/gausskernel/runtime/executor/nodeModifyTable.cpp)
/* ----------------------------------------------------------------
* ExecInsert
*
* 对于 INSERT 操作,我们需要将元组插入目标关系中,
* 并在索引关系中插入适当的元组。
*
* 如果存在 RETURNING 结果,则返回 RETURNING 结果,否则返回 NULL。
* ----------------------------------------------------------------
*/
template <bool useHeapMultiInsert>
TupleTableSlot* ExecInsertT(ModifyTableState* state, TupleTableSlot* slot, TupleTableSlot* planSlot, EState* estate,
bool canSetTag, int options, List** partitionList)
{
HeapTuple tuple;
ResultRelInfo* result_rel_info = NULL;
Relation result_relation_desc;
Oid new_id = InvalidOid;
List* recheck_indexes = NIL;
Oid partition_id = InvalidOid;
Partition partition = NULL;
Relation heap_rel = NULL;
Relation target_rel = NULL;
CopyFromBulk bulk = NULL;
bool to_flush = false;
int2 bucket_id = InvalidBktId;
bool need_flush = enable_heap_bcm_data_replication();
#ifdef PGXC
RemoteQueryState* result_remote_rel = NULL;
#endif
/*
* 从 tuple table slot 中获取堆元组,并确保我们拥有一个可写的副本
*/
tuple = ExecMaterializeSlot(slot);
/*
* 获取关于(当前)结果关系的信息
*/
result_rel_info = estate->es_result_relation_info;
result_relation_desc = result_rel_info->ri_RelationDesc;
#ifdef PGXC
result_remote_rel = (RemoteQueryState*)estate->es_result_remoterel;
#endif
/*
* 如果结果关系具有 OIDs,则将要插入数据的 OID 设置为无效(0),
* 以便在插入时为其分配新的 OID。
*
* 注意:如果允许用户分配自己的 OID,可以在这里进行修改。
*/
if (result_relation_desc->rd_rel->relhasoids)
HeapTupleSetOid(tuple, InvalidOid);
/* BEFORE ROW INSERT 触发器
* 注意:我们对于每个尝试的插入都会触发 BEFORE ROW 触发器,
* 除非是 MERGE 或 INSERT ... ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE 语句。
*/
if (state->operation != CMD_MERGE &&
#ifdef ENABLE_MULTIPLE_NODES
state->mt_upsert->us_action == UPSERT_NONE &&
#endif
result_rel_info->ri_TrigDesc && result_rel_info->ri_TrigDesc->trig_insert_before_row) {
slot = ExecBRInsertTriggers(estate, result_rel_info, slot);
if (slot == NULL) /* "什么也不做" */
return NULL;
/* 触发器可能已更改元组 */
tuple = ExecMaterializeSlot(slot);
}
/* INSTEAD OF ROW INSERT 触发器
* 注意:对于每个尝试的插入都会触发 INSTEAD OF ROW 触发器,
* 除非是 MERGE 或 INSERT ... ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE 语句。
*/
if (state->operation != CMD_MERGE &&
#ifdef ENABLE_MULTIPLE_NODES
state->mt_upsert->us_action == UPSERT_NONE &&
#endif
result_rel_info->ri_TrigDesc && result_rel_info->ri_TrigDesc->trig_insert_instead_row) {
slot = ExecIRInsertTriggers(estate, result_rel_info, slot);
if (slot == NULL) /* "什么也不做" */
return NULL;
/* 触发器可能已更改元组 */
tuple = ExecMaterializeSlot(slot);
new_id = InvalidOid;
} else if (result_rel_info->ri_FdwRoutine) {
#ifdef ENABLE_MOT
if (result_rel_info->ri_FdwRoutine->GetFdwType && result_rel_info->ri_FdwRoutine->GetFdwType() == MOT_ORC) {
if (result_relation_desc->rd_att->constr) {
if (state->mt_insert_constr_slot == NULL) {
ExecConstraints(result_rel_info, slot, estate);
} else {
ExecConstraints(result_rel_info, state->mt_insert_constr_slot, estate);
}
}
}
#endif
/*
* 插入外部表:由 FDW 处理
*/
slot = result_rel_info->ri_FdwRoutine->ExecForeignInsert(estate, result_rel_info, slot, planSlot);
if (slot == NULL) {
/* "什么也不做" */
return NULL;
}
/* FDW 可能已更改元组 */
tuple = ExecMaterializeSlot(slot);
new_id = InvalidOid;
} else {
/*
* 检查元组的约束条件
*/
bool has_bucket = RELATION_OWN_BUCKET(result_relation_desc);
if (has_bucket) {
bucket_id = computeTupleBucketId(result_relation_desc, tuple);
}
if (result_relation_desc->rd_att->constr) {
if (state->mt_insert_constr_slot == NULL)
ExecConstraints(result_rel_info, slot, estate);
else
ExecConstraints(result_rel_info, state->mt_insert_constr_slot, estate);
}
#ifdef PGXC
if (IS_PGXC_COORDINATOR && result_remote_rel) {
slot = ExecProcNodeDMLInXC(estate, planSlot, slot);
/*
* 如果目标表使用 WITH OIDS,则应将其设置为插入的 OID,
* 但是在 Postgres-XC 中,Oid 在节点之间不一致,
* 所以目前将其设置为默认值 InvalidOid。
* 这至少能够修复所有其他 INSERT 命令的标签。
*/
new_id = InvalidOid;
} else
#endif
if (useHeapMultiInsert) {
TupleTableSlot* tmp_slot = MakeSingleTupleTableSlot(slot->tts_tupleDescriptor, false, result_relation_desc->rd_tam_type);
bool is_partition_rel = result_relation_desc->rd_rel->parttype == PARTTYPE_PARTITIONED_RELATION;
bulk = findBulk(((DistInsertSelectState*)state)->mgr,
(is_partition_rel ? heapTupleGetPartitionId(result_relation_desc, tuple)
: RelationGetRelid(result_relation_desc)),
bucket_id,
&to_flush);
if (to_flush) {
if (is_partition_rel && need_flush) {
/* partition oid for sync */
CopyFromMemCxt tmpCopyFromMemCxt = bulk->memCxt;
for (int16 i = 0; i < tmpCopyFromMemCxt->nextBulk; i++) {
*partitionList = list_append_unique_oid(*partitionList,
tmpCopyFromMemCxt->chunk[i]->partOid);
}
}
CopyFromChunkInsert<true>(NULL, estate, bulk, ((DistInsertSelectState*)state)->mgr,
((DistInsertSelectState*)state)->pcState, estate->es_output_cid,
options, result_rel_info, tmp_slot, ((DistInsertSelectState*)state)->bistate);
}
addToBulk<true>(bulk, tuple, true);
if (isBulkFull(bulk)) {
if (is_partition_rel && need_flush) {
/* partition oid for sync */
CopyFromMemCxt tmpCopyFromMemCxt = bulk->memCxt;
for (int16 i = 0; i < tmpCopyFromMemCxt->nextBulk; i++) {
*partitionList = list_append_unique_oid(*partitionList,
tmpCopyFromMemCxt->chunk[i]->partOid);
}
}
CopyFromChunkInsert<true>(NULL, estate, bulk, ((DistInsertSelectState*)state)->mgr,
((DistInsertSelectState*)state)->pcState, estate->es_output_cid, options,
result_rel_info, tmp_slot, ((DistInsertSelectState*)state)->bistate);
}
ExecDropSingleTupleTableSlot(tmp_slot);
} else if (state->mt_upsert->us_action != UPSERT_NONE && result_rel_info->ri_NumIndices > 0) {
TupleTableSlot* returning = NULL;
bool updated = false;
new_id = InvalidOid;
new_id = ExecUpsert(state, slot, planSlot, estate, canSetTag, tuple, &returning, &updated);
if (updated) {
return returning;
}
} else {
/*
* insert the tuple
*
* Note: heap_insert returns the tid (location) of the new tuple in
* the t_self field.
*/
new_id = InvalidOid;
switch (result_relation_desc->rd_rel->parttype) {
case PARTTYPE_NON_PARTITIONED_RELATION:
case PARTTYPE_VALUE_PARTITIONED_RELATION: {
if (RelationIsCUFormat(result_relation_desc)) {
HeapInsertCStore(result_relation_desc, estate->es_result_relation_info, tuple, 0);
} else if (RelationIsPAXFormat(result_relation_desc)) {
/* here the insert including both none-partitioned and value-partitioned relations */
DfsInsertInter* insert = CreateDfsInsert(result_relation_desc, false);
insert->BeginBatchInsert(TUPLE_SORT, estate->es_result_relation_info);
insert->TupleInsert(slot->tts_values, slot->tts_isnull, 0);
insert->SetEndFlag();
insert->TupleInsert(NULL, NULL, 0);
insert->Destroy();
delete insert;
} else {
target_rel = result_relation_desc;
if (bucket_id != InvalidBktId) {
searchHBucketFakeRelation(estate->esfRelations, estate->es_query_cxt,
result_relation_desc, bucket_id, target_rel);
}
new_id = tableam_tuple_insert(target_rel, tuple, estate->es_output_cid, 0, NULL);
}
} break;
case PARTTYPE_PARTITIONED_RELATION: {
/* get partititon oid for insert the record */
partition_id = heapTupleGetPartitionId(result_relation_desc, tuple);
searchFakeReationForPartitionOid(estate->esfRelations, estate->es_query_cxt,
result_relation_desc, partition_id, heap_rel, partition, RowExclusiveLock);
if (RelationIsColStore(result_relation_desc))
HeapInsertCStore(heap_rel, estate->es_result_relation_info, tuple, 0);
#ifdef ENABLE_MULTIPLE_NODES
else if (RelationIsTsStore(result_relation_desc)) {
HeapInsertTsStore(result_relation_desc, estate->es_result_relation_info, tuple, 0);
}
#endif /* ENABLE_MULTIPLE_NODES */
else {
target_rel = heap_rel;
if (bucket_id != InvalidBktId) {
searchHBucketFakeRelation(
estate->esfRelations, estate->es_query_cxt, heap_rel, bucket_id, target_rel);
}
new_id = tableam_tuple_insert(target_rel, tuple, estate->es_output_cid, 0, NULL);
}
} break;
default: {
/* never happen; just to be self-contained */
ereport(ERROR, (errmodule(MOD_EXECUTOR), (errcode(ERRCODE_UNRECOGNIZED_NODE_TYPE),
errmsg("Unrecognized parttype as \"%c\" for relation \"%s\"",
RelationGetPartType(result_relation_desc),
RelationGetRelationName(result_relation_desc)))));
} break;
}
/*
* insert index entries for tuple
*/
if (result_rel_info->ri_NumIndices > 0 && !RelationIsColStore(result_relation_desc))
recheck_indexes = ExecInsertIndexTuples(slot,
&(tuple->t_self),
estate,
RELATION_IS_PARTITIONED(result_relation_desc) ? heap_rel : NULL,
RELATION_IS_PARTITIONED(result_relation_desc) ? partition : NULL,
bucket_id, NULL);
}
}
if (canSetTag) {
#ifdef PGXC
if (IS_PGXC_COORDINATOR && result_remote_rel)
estate->es_processed += result_remote_rel->rqs_processed;
else
#endif
(estate->es_processed)++;
estate->es_lastoid = new_id;
setLastTid(&(tuple->t_self));
}
/* AFTER ROW INSERT Triggers
* Note: We fire AFTER ROW TRIGGERS for every attempted insertion except
* for a MERGE or INSERT ... ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE statement.
*/
if (state->operation != CMD_MERGE && state->mt_upsert->us_action == UPSERT_NONE &&
!useHeapMultiInsert)
ExecARInsertTriggers(estate, result_rel_info, partition_id, bucket_id, tuple, recheck_indexes);
/* try to insert tuple into mlog-table. */
if (target_rel != NULL && target_rel->rd_mlogoid != InvalidOid) {
/* judge whether need to insert into mlog-table */
insert_into_mlog_table(target_rel, target_rel->rd_mlogoid, tuple,
&tuple->t_self, GetCurrentTransactionId(), 'I');
}
list_free_ext(recheck_indexes);
/* Process RETURNING if present */
if (result_rel_info->ri_projectReturning)
#ifdef PGXC
{
if (TupIsNull(slot))
return NULL;
#endif
return ExecProcessReturning(result_rel_info->ri_projectReturning, slot, planSlot);
#ifdef PGXC
}
#endif
return NULL;
}
可以看到,ExecInsert 函数的源码非常的长,这里我们重点关注代码中与列存储相关的部分即可。首先,看以下代码段:
这段代码表示列存储表的插入: 当插入数据时,代码会根据目标表的属性来决定是插入到行组织表还是列组织表中。特别地,在以下的 switch 语句中处理了不同分区类型的情况。这部分可以涉及到列存储表的处理,但需要查看更多的上下文来确定具体涉及到哪些操作。
switch (result_relation_desc->rd_rel->parttype) {
case PARTTYPE_NON_PARTITIONED_RELATION:
case PARTTYPE_VALUE_PARTITIONED_RELATION: {
if (RelationIsCUFormat(result_relation_desc)) {
HeapInsertCStore(result_relation_desc, estate->es_result_relation_info, tuple, 0);
} else if (RelationIsPAXFormat(result_relation_desc)) {
/* 插入适用于行组织表和列组织表的操作 */
// ...
} else {
target_rel = result_relation_desc;
if (bucket_id != InvalidBktId) {
searchHBucketFakeRelation(estate->esfRelations, estate->es_query_cxt,
result_relation_desc, bucket_id, target_rel);
}
new_id = tableam_tuple_insert(target_rel, tuple, estate->es_output_cid, 0, NULL);
}
} break;
case PARTTYPE_PARTITIONED_RELATION: {
/* 获取分区 OID 用于插入记录 */
partition_id = heapTupleGetPartitionId(result_relation_desc, tuple);
// ...
} break;
default: {
/* 永远不会发生,仅供完整性自洽 */
ereport(ERROR, (errmodule(MOD_EXECUTOR), (errcode(ERRCODE_UNRECOGNIZED_NODE_TYPE),
errmsg("Unrecognized parttype as \"%c\" for relation \"%s\"",
RelationGetPartType(result_relation_desc),
RelationGetRelationName(result_relation_desc)))));
} break;
}
RelationData 结构体
其中,result_relation_desc 是数据库源代码中表示关系(表)的结构体指针。这个结构体指针通常用于表示正在被操作的目标关系(表)的元数据信息。在上述代码中,result_relation_desc 用于存储当前执行插入操作的目标表的元数据。结构体如下:(路径:src/include/utils/rel.h)
typedef struct RelationData* Relation;
/*
* 下面是关系缓存条目的内容。
*/
typedef struct RelationData {
RelFileNode rd_node; /* 关系的物理标识符 */
/* 使用 "struct" 避免需要包含 smgr.h 文件: */
struct SMgrRelationData* rd_smgr; /* 缓存的文件句柄,或 NULL */
int rd_refcnt; /* 引用计数 */
BackendId rd_backend; /* 持有该关系的后端进程 ID,如果是临时关系 */
bool rd_isscannable; /* 关系是否可被扫描 */
bool rd_isnailed; /* 关系是否在缓存中是固定的 */
bool rd_isvalid; /* 关系缓存条目是否有效 */
char rd_indexvalid; /* rd_indexlist 状态:0 = 无效,1 = 有效,2 = 临时强制 */
bool rd_islocaltemp; /* 关系是否是当前会话的临时关系 */
/*
* rd_createSubid 表示关系所属的最高子事务 ID,如果关系在当前事务内创建。
* 如果关系不是在当前事务内创建的,其值为零。这仅用于优化,因为在某些情况下,新建的状态可能会被"遗忘"(例如在 CLUSTER 之后)。
* 同理,rd_newRelfilenodeSubid 表示关系文件节点变更所属的最高子事务 ID,
* 如果在当前事务内对文件节点进行了变更,其值为零。这同样也可能会被"遗忘"。
*/
SubTransactionId rd_createSubid; /* 关系在当前事务内创建 */
SubTransactionId rd_newRelfilenodeSubid; /* 在当前事务内分配新的文件节点 */
Form_pg_class rd_rel; /* RELATION 元组 */
TupleDesc rd_att; /* 元组描述 */
Oid rd_id; /* 关系的对象 ID */
LockInfoData rd_lockInfo; /* 锁管理器锁定关系的信息 */
RuleLock* rd_rules; /* 重写规则 */
MemoryContext rd_rulescxt; /* rd_rules 的私有内存上下文,如果有的话 */
TriggerDesc* trigdesc; /* 触发器信息,如果关系有触发器,否则为 NULL */
/* 使用 "struct" 避免需要包含 rewriteRlsPolicy.h 文件 */
struct RlsPoliciesDesc* rd_rlsdesc; /* 行级安全策略,如果有的话 */
/* 由 RelationGetIndexList 管理的数据: */
List* rd_indexlist; /* 关系上索引的 OID 列表 */
Oid rd_oidindex; /* OID 唯一索引的 OID,如果有的话 */
Oid rd_refSynOid; /* 参考同义词 OID,如果有的话 */
/* 由 RelationGetIndexAttrBitmap 管理的数据: */
Bitmapset* rd_indexattr; /* 标识用于索引的列 */
Bitmapset* rd_idattr; /* 包含在副本标识索引中的列 */
/*
* 关系的复制标识索引,或者是 InvalidOid。仅在 RelationGetIndexList 被调用
* 或 rd_indexvalid > 0 时才设置正确。
*/
Oid rd_replidindex;
/*
* rd_options 在 rd_rel 被加载到关系缓存条目时设置。注意不能直接在 rd_rel
* 中查找这些数据。NULL 表示“使用默认值”。
*/
bytea* rd_options; /* 解析后的 pg_class.reloptions */
/* 以下字段仅对索引关系非 NULL: */
Oid rd_partHeapOid; /* 分区索引的分区对象 OID */
Form_pg_index rd_index; /* 描述该索引的 pg_index 元组 */
/* 使用 "struct" 避免需要包含 htup.h 文件 */
struct HeapTupleData* rd_indextuple; /* 所有 pg_index 元组 */
Form_pg_am rd_am; /* 索引的 pg_am 元组 */
int rd_indnkeyatts; /* 索引关系的索引键列数 */
TableAmType rd_tam_type; /* 表的访问方法类型 */
/*
* 索引访问支持信息(仅用于索引关系)
*
* 注意:仅缓存每个 opclass 的默认支持函数,即左右类型等于 opclass 的 opcintype。
* 数组通过支持函数编号进行索引,这已经足够标识支持函数。
*
* 注意:rd_amcache 可用于索引 AM 来缓存关于索引的私有数据。
* 这必须只是一个缓存,因为它可能在任何时候被重置
* (特别是,会为索引发送 relcache 失效消息)。如果使用,它必须指向在 rd_indexcxt
* 中分配的单个内存块。关系缓存的重置将包括释放该块,并将 rd_amcache 设为 NULL。
*/
MemoryContext rd_indexcxt; /* 这些信息的私有内存上下文 */
RelationAmInfo* rd_aminfo; /* 从 pg_am 中查找到的函数信息 */
Oid* rd_opfamily; /* 每个索引列的操作族 OID */
Oid* rd_opcintype; /* 声明的 opclass 输入数据类型的 OID */
RegProcedure* rd_support; /* 支持函数的 OID */
FmgrInfo* rd_supportinfo; /* 支持函数的查找信息 */
int16* rd_indoption; /* 每列 AM 特定标志 */
List* rd_indexprs; /* 索引表达式树,如果有的话 */
List* rd_indpred; /* 索引谓词树,如果有的话 */
Oid* rd_exclops; /* 排除运算符的 OID,如果有的话 */
Oid* rd_exclprocs; /* 排除运算符过程的 OID,如果有的话 */
uint16* rd_exclstrats; /* 排除运算符策略编号,如果有的话 */
void* rd_amcache; /* 索引 AM 可用的缓存 */
Oid* rd_indcollation; /* 索引排序的 OID */
/*
* 对外表支持
*
* rd_fdwroutine 必须指向在 t_thrd.mem_cxt.cache_mem_cxt 中分配的单个内存块。
* 在关系缓存重置时,它将被释放并重置为 NULL。
*/
struct FdwRoutine* rd_fdwroutine; /* 缓存的函数指针,或 NULL */
/*
* 对于 CLUSTER、ALTER TABLE 重写等操作的 HACK:
* 在写入表的新版本时,我们需要使插入其中的任何 TOAST 指针具有现有 TOAST 表的 OID,
* 而不是瞬时 TOAST 表的 OID。如果 rd_toastoid 不是 InvalidOid,
* 则它是要放置在插入到此关系中的 TOAST 指针的 OID。
* 这也会导致 toast_save_datum() 尝试保留 TOAST 值的 OID。
*/
Oid rd_toastoid; /* 真实 TOAST 表的 OID,或 InvalidOid */
Oid rd_bucketoid;/* pg_hashbucket 中的 bucket OID */
/* 桶键信息,指示用于计算哈希值的键 */
RelationBucketKey *rd_bucketkey;
/* 对于 1 级哈希表,它指向 HashBucketMap 实例;
* 对于 2 级哈希表,例如范围哈希,它指向 RangePartitionMap 实例。 */
PartitionMap* partMap;
Oid parentId; /* 如果是由 partitionGetRelation 构造的,这是分区 OID;
否则,这是 InvalidOid */
/* 使用 "struct" 避免需要包含 pgstat.h 文件 */
struct PgStat_TableStatus* pgstat_info; /* 统计信息收集区域 */
#ifdef PGXC
RelationLocInfo* rd_locator_info;
PartitionMap* sliceMap;
#endif
Relation parent;
/* 双链表节点,分区和桶关系将存储在资源所有者的 fakerels 列表中 */
dlist_node node;
Oid rd_mlogoid;
} RelationData;
FormData_pg_class 结构体
result_relation_desc->rd_rel->parttype 是访问关系对象的元数据中存储的分区类型的属性。在这段代码中,result_relation_desc 是一个指向当前正在操作的目标关系的指针,rd_rel 是一个指向该关系的元数据的指针,而 parttype 则是该元数据中表示分区类型的字段。分区类型 (parttype) 指示了关系是非分区关系、基于值的分区还是基于列表的分区。源码如下:(路径:src/include/catalog/pg_class.h)
CATALOG(pg_class,1259) BKI_BOOTSTRAP BKI_ROWTYPE_OID(83) BKI_SCHEMA_MACRO
{
/* 类名 */
NameData relname;
/* 包含此类的命名空间的 OID */
Oid relnamespace;
/* 隐式行类型在 pg_type 中的 OID */
Oid reltype;
/* 基础复合类型在 pg_type 中的 OID */
Oid reloftype;
/* 类的所有者 */
Oid relowner;
/* 索引访问方法的 OID;如果不是索引,则为 0 */
Oid relam;
/* 物理存储文件的标识符 */
Oid relfilenode;
/* relfilenode == 0 表示这是一个“映射”关系,请参阅 relmapper.c */
/* 关系所在表空间的标识符 */
Oid reltablespace;
/* 块数(不一定始终是最新的) */
float8 relpages;
/* 元组数(不一定始终是最新的) */
float8 reltuples;
/* 全部可见块数(不一定始终是最新的) */
int4 relallvisible;
/* TOAST 表的 OID;如果没有则为 0 */
Oid reltoastrelid;
/* 如果是 TOAST 表,则为 chunk_id 索引的 OID */
Oid reltoastidxid;
/* 如果是 ColStore 表,则不为 0 */
Oid reldeltarelid;
Oid reldeltaidx;
/* 如果是 ColStore 表,则不为 0;如果是 TsStore,则为分区 OID */
Oid relcudescrelid;
Oid relcudescidx;
/* 如果有(或曾经有)任何索引,则为真 */
bool relhasindex;
/* 如果在数据库间共享,则为真 */
bool relisshared;
/* 参见下面的 RELPERSISTENCE_xxx 常量 */
char relpersistence;
/* 参见下面的 RELKIND_xxx 常量 */
char relkind;
/* 用户属性的数量 */
/*
* pg_attribute 类必须恰好包含此类的 "relnatts" 个用户属性
* (其 attnums 范围从 1 到 relnatts)。还可以包含负 attnums
* 用于系统属性。
*/
int2 relnatts;
/* 类的 CHECK 约束数 */
int2 relchecks;
/* 如果为行生成 OID,则为真 */
bool relhasoids;
/* 如果有(或曾经有)主键索引,则为真 */
bool relhaspkey;
/* 如果有(或曾经有)任何规则,则为真 */
bool relhasrules;
/* 如果有(或曾经有)任何触发器,则为真 */
bool relhastriggers;
/* 如果有(或曾经有)派生类,则为真 */
bool relhassubclass;
/* 行压缩属性 */
int1 relcmprs;
/* 如果有(或曾经有)部分集群键,则为真 */
bool relhasclusterkey;
/* 启用或禁用行移动 */
bool relrowmovement;
/* 'p' 表示分区关系,'n' 表示非分区关系 */
char parttype;
/* 所有小于此值的 Xid 都已在此关系中冻结 */
ShortTransactionId relfrozenxid;
#ifdef CATALOG_VARLEN /* 可变长度字段从这里开始 */
/* 注意:这些字段不在 relcache 条目的 rd_rel 字段中。 */
/* 访问权限 */
aclitem relacl[1];
/* 访问方法特定选项 */
text reloptions[1];
#endif
/* 参见 REPLICA_IDENTITY_xxx 常量 */
char relreplident;
/* 所有小于此值的 Xid 都已在此关系中冻结(64 位) */
TransactionId relfrozenxid64;
/* 在 pg_hashbucket 中的桶信息 */
Oid relbucket;
/* 哈希分区的列编号 */
int2vector relbucketkey;
}
FormData_pg_class;
HeapInsertCStore函数
再来重点看以下代码段:
if (RelationIsColStore(result_relation_desc))
HeapInsertCStore(heap_rel, estate->es_result_relation_info, tuple, 0);
在这段代码中,首先进行了条件判断,判断了名为 result_relation_desc 的关系是否是一个列存储表(即判断是否满足某个条件)。如果是列存储表,那么就会执行相应的插入操作。
RelationIsColStore(result_relation_desc):这是一个用于判断关系是否是列存储表的函数。如果 result_relation_desc 关系是列存储表,那么这个条件会返回真(true),否则返回假(false)。HeapInsertCStore(heap_rel, estate->es_result_relation_info, tuple, 0):这是一个函数调用,用于将一个元组(tuple)插入到列存储表中。这个操作通常用于执行 INSERT 语句。
下面我们着重分析一下 HeapInsertCStore 函数,其函数源码如下所示:(路径:src/gausskernel/storage/access/heap/heapam.cpp)
/* HeapInsertCStore - 将元组插入到列存储表中 */
void HeapInsertCStore(Relation relation, ResultRelInfo *result_rel_info, HeapTuple tup, int option)
{
/* 初始化插入参数 */
InsertArg args;
CStoreInsert::InitInsertArg(relation, result_rel_info, false, args);
/* 创建了一个名为 cstoreInsert 的 CStoreInsert 类的实例对象 */
CStoreInsert cstoreInsert(relation, args, false, NULL, NULL);
/* 获取元组描述信息 */
TupleDesc tupDesc = relation->rd_att;
Datum *val = (Datum *)palloc(sizeof(Datum) * tupDesc->natts); /* 存储属性值的数组 */
bool *null = (bool *)palloc(sizeof(bool) * tupDesc->natts); /* 存储属性是否为NULL的数组 */
heap_deform_tuple(tup, tupDesc, val, null); /* 将元组解压为属性值和NULL标记 */
/* 创建批量加载行对象 */
bulkload_rows batchRow(tupDesc, RelationGetMaxBatchRows(relation), true);
/* 将单个元组添加到批量行对象中 */
/* 忽略返回值,因为只有一个元组被添加 */
(void)batchRow.append_one_tuple(val, null, tupDesc);
/* 设置结束标志并批量插入行数据 */
cstoreInsert.SetEndFlag();
cstoreInsert.BatchInsert(&batchRow, option);
/* 释放内存 */
pfree(val);
pfree(null);
CStoreInsert::DeInitInsertArg(args);
batchRow.Destroy();
cstoreInsert.Destroy();
}
InsertArg 结构体
InsertArg 结构体用于存储插入操作中的各种参数信息,以便在插入函数中使用。源码如下:(路径:src/include/access/cstore_insert.h)
/* InsertArg 结构体用于存储插入操作的参数信息 */
struct InsertArg {
/* 指向临时批量行对象的指针,用于列存储插入操作 */
bulkload_rows *tmpBatchRows;
/* 指向临时批量行对象的指针,用于索引的插入 */
bulkload_rows *idxBatchRow;
/* 指向结果关系信息结构体数组的指针,存储插入操作的结果关系信息 */
ResultRelInfo *es_result_relations;
/* 插入操作的排序类型,可以是元组排序或批量排序 */
int sortType;
/* 指定使用哪种方式进行插入操作,是矢量批量插入还是普通批量插入 */
bool using_vectorbatch;
/* 构造函数,初始化结构体中的字段 */
InsertArg()
{
tmpBatchRows = NULL;
idxBatchRow = NULL;
es_result_relations = NULL;
sortType = TUPLE_SORT; /* 默认使用元组排序方式 */
using_vectorbatch = true; /* 调用方应明确指定使用的插入方式 */
}
};
CStoreInsert 类
CStoreInsert 是一个 C++ 类的定义,这个类提供了一些用于列存储批量插入操作的 API。这个类包含了多个成员函数和成员变量,用于管理插入过程中的各种操作和状态。类中的成员函数提供了批量插入、CU 数据的写入、索引插入等功能,以支持列存储数据的高效插入操作。类中的注释提供了对每个成员函数和成员变量的解释说明,以帮助理解这个类的功能和作用。源码如下:(路径:src/include/access/cstore_insert.h)
/*
* CStoreInsert 类提供了一些用于列存储批量插入的 API。
* 在未来,可以添加更多的 API。
*/
class CStoreInsert : public BaseObject {
public:
/*
* 构造函数,初始化 CStoreInsert 对象。
* 参数包括插入的关系(relation)、插入参数(args)、是否为更新 CU、计划(plan)和内存信息(ArgmemInfo)。
*/
CStoreInsert(_in_ Relation relation, _in_ const InsertArg &args, _in_ bool is_update_cu, _in_ Plan *plan,
_in_ MemInfoArg *ArgmemInfo);
virtual ~CStoreInsert();
virtual void Destroy();
/* 开始批量插入操作,参数为插入参数 args */
void BeginBatchInsert(const InsertArg &args);
/* 结束批量插入操作 */
void EndBatchInsert();
/*
* 批量插入接口
*/
void BatchInsert(bulkload_rows *batchRowPtr, int options);
void BatchInsert(VectorBatch *pVec, int options);
void BatchInsertCommon(bulkload_rows *batchRowPtr, int options);
void FlashData(int options);
void CUInsert(_in_ BatchCUData *CUData, _in_ int options);
/* 设置插入结束标志 */
void SetEndFlag();
/* 判断插入是否结束 */
inline bool IsEnd()
{
return m_insert_end_flag;
}
/* 初始化插入参数 args,参数包括关系 rel、结果关系信息 resultRelInfo、是否使用矢量批量插入 using_vectorbatch 和插入参数 args */
static void InitInsertArg(Relation rel, ResultRelInfo *resultRelInfo, bool using_vectorbatch, InsertArg &args);
/* 释放插入参数 args */
static void DeInitInsertArg(InsertArg &args);
/* 初始化索引插入参数 args,参数包括堆关系 heap_rel、键映射 keys_map、键数量 nkeys 和插入参数 args */
static void InitIndexInsertArg(Relation heap_rel, const int *keys_map, int nkeys, InsertArg &args);
/* 初始化插入内存参数,参数为计划 plan 和内存信息 ArgmemInfo */
void InitInsertMemArg(Plan *plan, MemInfoArg *ArgmemInfo);
/* 关系信息对象 */
Relation m_relation;
/* AIO CU 指针 */
CU ***m_aio_cu_PPtr;
/* AIO 分发 CU 描述 */
AioDispatchCUDesc_t ***m_aio_dispath_cudesc;
/* AIO 分发索引 */
int *m_aio_dispath_idx;
/* 内存信息用于内存调整 */
MemInfoArg *m_cstorInsertMem;
private:
/* 释放 AIO 分配的内存 */
void FreeMemAllocateByAdio();
/* 是否需要分区排序 */
inline bool NeedPartialSort(void) const;
/* 将 CU 数据和 CUDesc 写入 */
void SaveAll(int options, const char *delBitmap = NULL);
/* 列表刷新所有 CU */
void CUListFlushAll(int attno);
/* 列表写完成 IO */
void CUListWriteCompeleteIO(int col, int count);
/* CU 写入 */
void CUWrite(int attno, int col);
/* 列表写入 */
void CUListWrite();
/* 压缩批量行数据为 CU,获取 CU 的最小/最大值 */
CU *FormCU(int col, bulkload_rows *batchRowPtr, CUDesc *cuDescPtr);
Size FormCUTInitMem(CU *cuPtr, bulkload_rows *batchRowPtr, int col, bool hasNull);
void FormCUTCopyMem(CU *cuPtr, bulkload_rows *batchRowPtr, CUDesc *cuDescPtr, Size dtSize, int col, bool hasNull);
template <bool hasNull>
void FormCUT(int col, bulkload_rows *batchRowPtr, CUDesc *cuDescPtr, CU *cuPtr);
template <bool hasNull>
void FormCUTNumeric(int col, bulkload_rows *batchRowPtr, CUDesc *cuDescPtr, CU *cuPtr);
template <bool hasNull>
void FormCUTNumString(int col, bulkload_rows *batchRowPtr, CUDesc *cuDescPtr, CU *cuPtr);
template <bool bpcharType, bool hasNull, bool has_MinMax_func>
bool FormNumberStringCU(int col, bulkload_rows *batchRowPtr, CUDesc *cuDescPtr, CU *cuPtr);
template <bool hasNull>
bool TryFormNumberStringCU(int col, bulkload_rows *batchRowPtr, CUDesc *cuDescPtr, CU *cuPtr, uint32 atttypid);
/* 初始化索引列 ID */
void InitIndexColId(int which_index);
/* 初始化索引信息 */
void InitIndexInfo();
/* 初始化 Delta 信息 */
void InitDeltaInfo();
/* 插入 Delta 表 */
void InsertDeltaTable(bulkload_rows *batchRowPtr, int options);
/* 插入索引表 */
void InsertIdxTableIfNeed(bulkload_rows *batchRowPtr, uint32 cuId);
/* 插入非部分排序索引 */
void InsertNotPsortIdx(int indice);
/* 刷新索引数据(如果需要) */
void FlushIndexDataIfNeed();
/* 初始化函数指针 */
void InitFuncPtr();
/* 初始化列空间分配 */
void InitColSpaceAlloc();
/* 尝试对数值进行编码 */
bool TryEncodeNumeric(int col, bulkload_rows *batchRowPtr, CUDesc *cuDescPtr, CU *cuPtr, bool hasNull);
/* 执行批量插入 */
void DoBatchInsert(int options);
/* 用于形成 CU 的函数指针 */
typedef void (CStoreInsert::*m_formCUFunc)(int, bulkload_rows *, CUDesc *, CU *);
/* FormCU 函数指针数组 */
struct FormCUFuncArray {
m_formCUFunc colFormCU[2];
};
/* 设置 FormCU 函数指针数组 */
inline void SetFormCUFuncArray(Form_pg_attribute attr, int col);
/* 是否为更新 CU */
bool m_isUpdate;
/* 函数指针数组区域 */
FuncSetMinMax *m_setMinMaxFuncs; /* 最小/最大值函数 */
FormCUFuncArray *m_formCUFuncArray; /* Form CU 函数指针数组 */
/* 如果关系有集群键,则用于部分排序 */
CStorePSort *m_sorter;
/* 所有列的 CUDesc 指针 */
CUDesc **m_cuDescPPtr;
/* 所有列的 CU 指针 */
CU **m_cuPPtr;
/* CU 存储 */
CUStorage **m_cuStorage;
/* 压缩选项 */
compression_options *m_cuCmprsOptions;
/* CU 临时压缩信息 */
cu_tmp_compress_info m_cuTempInfo;
/* 缓冲的批量行,用于许多 VectorBatch 值 */
bulkload_rows *m_bufferedBatchRows;
/* 临时批量行,用于从排序处理器中提取值 */
bulkload_rows *m_tmpBatchRows;
/* 用于避免批量插入期间的内存泄漏的内存上下文 */
MemoryContext m_tmpMemCnxt;
MemoryContext m_batchInsertCnxt;
/* Delta 插入相关 */
Relation m_delta_relation;
TupleDesc m_delta_desc;
bool m_append_only; /* 当为 true 时,不插入到 Delta 表 */
/* 索引插入相关 */
ResultRelInfo *m_resultRelInfo; /* 包含索引元信息 */
Relation *m_idxRelation; /* 索引关系 */
InsertArg *m_idxInsertArgs; /* 索引插入参数 */
CStoreInsert **m_idxInsert; /* 索引插入器 */
int **m_idxKeyAttr; /* 索引键 */
int *m_idxKeyNum; /* 索引键数量 */
bulkload_rows *m_idxBatchRow; /* 索引插入的浅复制 */
EState *m_estate; /* 执行状态信息 */
ExprContext *m_econtext; /* 当前表达式评估的上下文 */
Datum *m_fake_values; /* 用于形成虚假堆元组的值数组 */
bool *m_fake_isnull; /* 用于形成虚假堆元组的空值数组 */
/* ADIO 信息 */
MemoryContext m_aio_memcnxt;
int32 *m_aio_cache_write_threshold;
File **m_vfdList;
/* 一个 CU 内最大的值数量 */
int m_fullCUSize;
/* Delta 阈值 */
int m_delta_rows_threshold;
/* 压缩选项 */
int16 m_compress_modes;
/* 插入是否结束的标志 */
bool m_insert_end_flag;
};
CStoreInsert::InitInsertArg函数
CStoreInsert::InitInsertArg 函数的主要目的是在列存储的批量加载过程中初始化各种批量缓冲区。它接受关系(rel)、结果关系信息(resultRelInfo)、是否使用矢量批量插入标志(using_vectorbatch)和插入参数结构体(args)作为输入。根据关系的约束信息和是否具有索引,它可能会创建临时批量行缓冲区和索引批量缓冲区。这些缓冲区用于高效地批量插入数据。CStoreInsert::InitInsertArg 函数源代码如下:(路径:src/include/access/cstore_insert.h)
/*
* @Description: 初始化批量加载过程中的各种批量缓冲区。
* @OUT args: 各种批量缓冲区。
* @IN using_vectorbatch: 插入参数 InsertArg::using_vectorbatch 的标志。
* @IN rel: 要查询的关系。
* @IN resultRelInfo: 结果关系信息。
* @See also: 相关函数或资源引用
*/
void CStoreInsert::InitInsertArg(Relation rel, ResultRelInfo* resultRelInfo, bool using_vectorbatch, InsertArg& args)
{
TupleConstr* constr = rel->rd_att->constr; // 获取关系元组结构的约束信息
int maxValuesCount = RelationGetMaxBatchRows(rel); // 获取关系的最大批量行数
args.es_result_relations = resultRelInfo; // 设置插入参数中的结果关系信息
args.using_vectorbatch = using_vectorbatch; // 设置插入参数中的矢量批量插入标志
/* 如果关系具有主键约束,则创建临时批量行缓冲区 */
if (tupledesc_have_pck(constr)) {
args.tmpBatchRows = New(CurrentMemoryContext) bulkload_rows(rel->rd_att, maxValuesCount, true);
}
/* 如果关系具有索引,则为索引创建 BatchRows 缓冲区 */
if (relation_has_indexes(resultRelInfo)) {
/* 找到最大索引键数,我们将重用这些批量缓冲区 */
int max_key_num = get_max_num_of_index_keys(resultRelInfo); // 获取最大索引键数
args.idxBatchRow = bulkload_indexbatch_init(max_key_num, maxValuesCount); // 初始化索引批量缓冲区
}
}
四个入参含义如下:
heap_deform_tuple 函数
函数 heap_deform_tuple用于将一个存储在堆中的元组(tuple)解析为数据值和是否为 NULL 的标记,并存储到提供的值数组和是否为 NULL 的标记数组中。下面对应的源码注释和解释:(路径:src/gausskernel/storage/access/common/heaptuple.cpp)
/*
* heap_deform_tuple
* Given a tuple, extract data into values/isnull arrays; this is
* the inverse of heap_form_tuple.
*
* Storage for the values/isnull arrays is provided by the caller;
* it should be sized according to tupleDesc->natts not
* HeapTupleHeaderGetNatts(tuple->t_data, tupleDesc).
*
* Note that for pass-by-reference datatypes, the pointer placed
* in the Datum will point into the given tuple.
*
* When all or most of a tuple's fields need to be extracted,
* this routine will be significantly quicker than a loop around
* heap_getattr; the loop will become O(N^2) as soon as any
* noncacheable attribute offsets are involved.
*/
void heap_deform_tuple(HeapTuple tuple, TupleDesc tupleDesc, Datum *values, bool *isnull)
{
// 获取元组的数据头部
HeapTupleHeader tup = tuple->t_data;
bool hasnulls = HeapTupleHasNulls(tuple);
Form_pg_attribute *att = tupleDesc->attrs;
uint32 tdesc_natts = tupleDesc->natts;
uint32 natts; // 要提取的属性数量
uint32 attnum;
char *tp = NULL; // 指向元组数据的指针
long off; // 元组数据的偏移量
bits8 *bp = tup->t_bits; // 空值位图的指针
bool slow = false; // 是否可以使用/设置 attcacheoff?
// 确保元组没有被压缩
Assert(!HEAP_TUPLE_IS_COMPRESSED(tup));
// 获取实际存在的属性数量
natts = HeapTupleHeaderGetNatts(tup, tupleDesc);
/*
* 在继承情况下,实际的元组可能具有比调用者预期的更多的字段。
* 不要越界访问调用者的数组。
*/
natts = Min(natts, tdesc_natts);
if (natts > MaxTupleAttributeNumber) {
ereport(ERROR, (errcode(ERRCODE_TOO_MANY_COLUMNS),
errmsg("number of columns (%u) exceeds limit (%d)", natts, MaxTupleAttributeNumber)));
}
// 将 tp 指针指向了元组数据的实际开始位置
tp = (char *)tup + tup->t_hoff;
// 将偏移量 off 初始化为 0,表示初始时解析的位置位于元组数据的开始处
off = 0;
// 遍历所有属性
for (attnum = 0; attnum < natts; attnum++) {
// 获取第 attnum 个属性的属性描述信息
Form_pg_attribute thisatt = att[attnum];
// 如果该属性是 NULL
if (hasnulls && att_isnull(attnum, bp)) {
values[attnum] = (Datum)0; // 将值设置为 0 表示 NULL
isnull[attnum] = true; // 设置 NULL 标记为 true
slow = true; // 无法继续使用 attcacheoff
continue;
}
isnull[attnum] = false; // NULL 标记为 false
// 判断是否可以使用 attcacheoff
if (!slow && thisatt->attcacheoff >= 0) {
off = thisatt->attcacheoff;
} else if (thisatt->attlen == -1) {
// 对于可变长度数据类型,仅当偏移量已经适当对齐时才能缓存偏移量
if (!slow && (uintptr_t)(off) == att_align_nominal(off, thisatt->attalign)) {
thisatt->attcacheoff = off;
} else {
off = att_align_pointer(off, thisatt->attalign, -1, tp + off);
slow = true;
}
} else {
// 非可变长度数据类型,直接使用 att_align_nominal 对齐
off = att_align_nominal(off, thisatt->attalign);
if (!slow)
thisatt->attcacheoff = off;
}
// 提取属性值
values[attnum] = fetchatt(thisatt, tp + off);
// 计算下一个属性的偏移量
off = att_addlength_pointer(off, thisatt->attlen, tp + off);
if (thisatt->attlen <= 0) {
slow = true; // 无法继续使用 attcacheoff
}
}
}
注释:attcacheoff 是一种优化机制,用于加速从元组中提取属性值的过程。每个属性(列)都有一个关于其在元组数据中偏移位置的缓存信息。这个偏移位置可以帮助更快地访问和提取属性的值,因为它可以避免重复计算偏移量。
attcacheoff 是 Form_pg_attribute 结构体中的一个成员,用于存储属性在元组数据中的偏移位置。在 heap_deform_tuple 函数中,当解析元组数据并提取属性值时,首先会检查属性的 attcacheoff 值,以确定是否可以使用缓存的偏移位置。
调试信息如下:
- 获取实际存在的属性数量,这里输出为 4 表示案例中的以下四个属性:(
sale_id、product_id、quantity、sale_date)

- Form_pg_attribute 结构用于描述表中的每个属性(列)的元数据信息。att 是一个指向 TupleDesc 结构的属性描述信息数组,它包含了表中所有属性的描述信息。attnum 是属性的索引号,表示我们要获取的属性在属性描述信息数组中的位置。isnull 数组用于表示一个元组中每个属性是否为 NULL。

- 提取属性值并计算下一个属性的偏移量。


bulkload_rows 结构体
bulkload_rows 结构体负责批量加载的内存管理、存储属性值的向量等,并提供了一系列成员函数来初始化、添加数据、检查是否达到限制等。另外,还定义了 bulkload_rows_iter 结构用于遍历 bulkload_rows。整个代码主要是为了在批量加载过程中管理和处理批次的数据。源码如下:(路径:src/include/access/cstore_vector.h)
/* batch rows for bulk loading */
struct bulkload_rows : public BaseObject {
/* 内存上下文,用于管理内存分配和释放 */
MemoryContext m_context;
/* 记录已使用的内存大小,用于控制总内存使用量 */
Size m_using_blocks_total_rawsize;
Size m_using_blocks_init_rawsize;
/* 用于存储每个属性/字段的值向量 */
bulkload_vector *m_vectors;
int m_attr_num;
/* 当前以及最大值向量中可容纳的值的数量 */
int m_rows_maxnum;
int m_rows_curnum;
/* 是否已初始化 */
bool m_inited;
typedef bool (bulkload_rows::*FormAppendColumnFuncType)(TupleDesc tup_desc, VectorBatch *p_batch, int *start_idx);
FormAppendColumnFuncType m_form_append_column_func;
typedef Size (bulkload_rows::*FormSampleTupleSizeFuncType)(TupleDesc tup_desc, VectorBatch *p_batch,
int idx_sample);
FormSampleTupleSizeFuncType m_form_sample_tuple_size_func;
bool m_has_dropped_column;
/* 构造函数和析构函数 */
bulkload_rows(TupleDesc tuple_desc, int rows_maxnum, bool to_init = true);
~bulkload_rows()
{
}
void Destroy(void)
{
destroy();
}
void init(TupleDesc tup_desc, int rows_maxnum);
void reset(bool reuse_blocks);
bool append_one_vector(TupleDesc tup_desc, VectorBatch *p_batch, int *start_idx, MemInfoArg *m_memInfo = NULL);
bool append_one_tuple(Datum *values, const bool *isnull, TupleDesc tup_desc);
void append_one_column(Datum *values, const bool *isnull, int rows, TupleDesc tup_desc, int dest_idx);
Size total_memory_size(void) const;
/* 检查当前行数是否达到限制 */
inline bool full_rownum(void)
{
return (m_rows_curnum == m_rows_maxnum);
}
/* 检查总内存使用是否达到限制 */
inline bool full_rowsize(void)
{
return (m_using_blocks_total_rawsize >= BULKLOAD_MAX_MEMSIZE);
}
/* 计算元组大小 */
Size calculate_tuple_size(TupleDesc tup_desc, Datum *tup_values, const bool *tup_nulls) const;
private:
/* 以列为方向添加 */
template <bool hasDroppedColumn>
bool append_in_column_orientation(TupleDesc tup_desc, VectorBatch *p_batch, int *start_idx);
/* 以行为方向添加 */
bool append_in_row_orientation(TupleDesc tup_desc, VectorBatch *p_batch, int *start_idx);
/* 计算采样元组大小 */
template <bool hasDroppedColumn>
Size sample_tuple_size(TupleDesc tup_desc, VectorBatch *p_batch, int start_idx);
/* 销毁 */
void destroy(void);
};
/* 用于遍历 bulkload_rows 的迭代器 */
struct bulkload_rows_iter {
void begin(bulkload_rows *batch_rows);
void next(Datum *values, bool *nulls);
bool not_end(void) const;
void end(void);
private:
bulkload_rows *m_batch;
bulkload_vector_iter *m_vec_iters;
};
append_one_tuple 函数
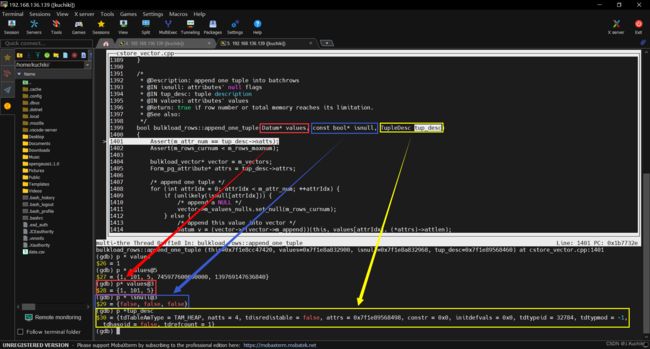
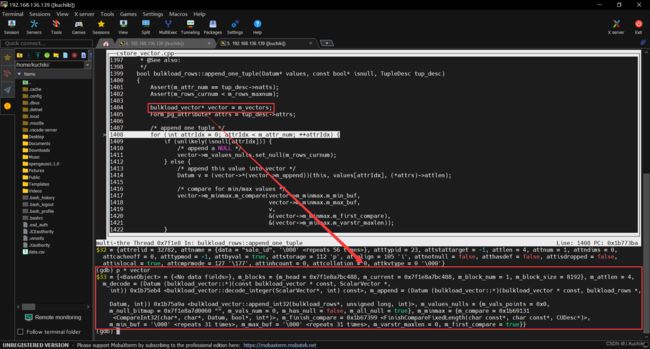
append_one_tuple 函数是关于在批量加载过程中将一个元组(tuple)添加到批处理行(batchrows)中的函数。这种批量加载通常用于高效地将多个元组插入数据库中。函数源码如下:(路径:src/gausskernel/storage/cstore/cstore_vector.cpp)
/*
* @Description: append one tuple into batchrows
* @IN isnull: attributes' null flags
* @IN tup_desc: tuple description
* @IN values: attributes' values
* @Return: true if row number or total memory reaches its limitation.
* @See also:
*/
bool bulkload_rows::append_one_tuple(Datum* values, const bool* isnull, TupleDesc tup_desc)
{
Assert(m_attr_num == tup_desc->natts);
Assert(m_rows_curnum < m_rows_maxnum);
bulkload_vector* vector = m_vectors;
Form_pg_attribute* attrs = tup_desc->attrs;
/* append one tuple */
for (int attrIdx = 0; attrIdx < m_attr_num; ++attrIdx) {
if (unlikely(isnull[attrIdx])) {
/* append a NULL */
vector->m_values_nulls.set_null(m_rows_curnum);
} else {
/* append this value into vector */
Datum v = (vector->*(vector->m_append))(this, values[attrIdx], (*attrs)->attlen);
/* compare for min/max values */
vector->m_minmax.m_compare(vector->m_minmax.m_min_buf,
vector->m_minmax.m_max_buf,
v,
&(vector->m_minmax.m_first_compare),
&(vector->m_minmax.m_varstr_maxlen));
}
/* advance to the next attribute */
++vector;
++attrs;
}
/* update rows' number */
++m_rows_curnum;
return full_rownum() || full_rowsize();
}
函数
bulkload_rows::append_one_tuple的入参如下:
详细解释一下这句代码:
Datum v = (vector->*(vector->m_append))(this, values[attrIdx], (*attrs)->attlen);
(vector->*(vector->m_append)):这部分代码使用了指针的成员函数调用语法。vector是一个指向bulkload_vector结构体的指针,m_append是一个函数指针,它指向了bulkload_vector结构体中的一个添加函数。通过(vector->*(vector->m_append)),我们实际上调用了m_append指向的函数。
(this, values[attrIdx], (*attrs)->attlen):这是调用函数时传递的参数。this指向当前的bulkload_vector对象,values[attrIdx]是属性值,(*attrs)->attlen是属性的长度。
bulkload_vector 结构体
bulkload_vector 结构体用于在列级别上进行批量加载。结构体包含了内存块、函数指针、值和空值信息、最小/最大值信息以及一系列用于初始化、配置、重置等操作的函数。其中,结构体中还包括了用于不同数据类型的添加和解码函数,以支持批量加载的各种数据类型。
/* bulkload_vector
* a batch of values for one column.
*/
// bulkload_vector 结构体表示一列的值的批处理。
struct bulkload_vector : public BaseObject {
/* memory block info && m_append api */
// 内存块信息和 m_append 函数的 API。
bulkload_block_list m_blocks; // 存储内存块的链表。
int m_attlen; // 属性的长度。
/* function pointer */
// 函数指针。
Datum (bulkload_vector::*m_decode)(ScalarVector *, int) const; // 解码函数指针,用于解码属性值。
Datum (bulkload_vector::*m_append)(bulkload_rows *, Datum, int); // 添加函数指针,用于将值添加到批处理行中。
/* Values/Nulls info */
// 值和空值的信息。
bulkload_datums m_values_nulls; // 存储值和空值的结构。
/* Min/Max info */
// 最小值和最大值的信息。
bulkload_minmax m_minmax; // 存储最小值和最大值的结构。
/* ====== bulkload_vector API ====== */
// bulkload_vector 的 API 函数。
void init(Form_pg_attribute attr, int max_values); // 初始化函数。
void configure(Form_pg_attribute attr); // 配置函数。
void reset(int max_values, bool reuse_blocks); // 重置函数。
void destroy(void); // 销毁函数。
Size data_size(void); // 计算数据大小。
void data_copy(char *outbuf); // 复制数据。
void new_fixedsize_block(int data_unit); // 创建新的固定大小的内存块。
void choose_fixedsize_block(bulkload_rows *batch_rows, int data_unit); // 选择固定大小的内存块。
void new_varsize_block(int data_len); // 创建新的变长大小的内存块。
void choose_varsize_block(bulkload_rows *batch_rows, int data_len); // 选择变长大小的内存块。
private:
/* append functions for all datatype */
// 所有数据类型的添加函数。
Datum append_int8(bulkload_rows *batch_rows, Datum v, int len); // 添加 int8 类型的值。
Datum append_int16(bulkload_rows *batch_rows, Datum v, int len); // 添加 int16 类型的值。
Datum append_int32(bulkload_rows *batch_rows, Datum v, int len); // 添加 int32 类型的值。
Datum append_int64(bulkload_rows *batch_rows, Datum v, int len); // 添加 int64 类型的值。
Datum append_fixed_length(bulkload_rows *batch_rows, Datum v, int len); // 添加固定长度的值。
template <int varlen>
Datum append_var_length(bulkload_rows *batch_rows, Datum v, int len); // 添加变长大小的值。
/* decode functions for all datatype */
// 所有数据类型的解码函数。
Datum decode_integer(ScalarVector *pvector, int rowIdx) const; // 解码整数类型的值。
Datum decode_fixed_length(ScalarVector *pvector, int rowIdx) const; // 解码固定长度的值。
Datum decode_var_length(ScalarVector *pvector, int rowIdx) const; // 解码变长大小的值。
};
CStoreInsert::BatchInsert 函数
这个函数用于将一批数据批量插入到列存储中。它处理了不同的情况来执行数据的批量插入操作。根据条件不同,它可能涉及到部分排序、增量插入、常规批量插入以及索引数据的处理。整体来说,这个函数在进行大规模数据插入时,根据情况调整执行路径以优化性能和内存使用。函数源码如下所示:(路径:src/gausskernel/storage/cstore/cstore_insert.cpp)
函数入参:
- batchRowPtr: 指向 bulkload_rows 对象的指针,表示包含要插入的数据的批次。
- options: 一个整数值,表示插入操作的选项和标志,可能用于控制插入的行为。
/*
* Batch insert interface for copy
*/
void CStoreInsert::BatchInsert(bulkload_rows* batchRowPtr, int options)
{
/* 切换内存上下文,以避免在批量插入期间发生内存泄漏 */
MemoryContext oldCnxt = MemoryContextSwitchTo(m_tmpMemCnxt);
if (NeedPartialSort()) {
/* 如果需要执行部分排序 */
/* 将批次数据放入排序器 */
if (batchRowPtr)
m_sorter->PutBatchValues(batchRowPtr);
/* 检查是否已满或插入结束 */
if (m_sorter->IsFull() || IsEnd()) {
/* 执行排序操作 */
m_sorter->RunSort();
/* 重置并获取下一个批次数据 */
DoBatchInsert(options);
/* 重置排序器并释放所有内存块 */
m_sorter->Reset(IsEnd());
m_tmpBatchRows->reset(false);
}
} else {
/* 如果不需要部分排序 */
if (ENABLE_DELTA(batchRowPtr)) {
/* 如果启用了增量插入 */
InsertDeltaTable(batchRowPtr, options);
} else {
/* 否则进行常规批量插入 */
BatchInsertCommon(batchRowPtr, options);
}
}
/* 处理索引数据 */
FlushIndexDataIfNeed();
/* 重置临时内存上下文并切换回之前的上下文 */
MemoryContextReset(m_tmpMemCnxt);
(void)MemoryContextSwitchTo(oldCnxt);
}
CStoreInsert::BatchInsertCommon 函数
CStoreInsert::BatchInsertCommon 函数函数负责实际的批量插入操作。
void CStoreInsert::BatchInsertCommon(bulkload_rows* batchRowPtr, int options)
{
// 如果传入的 batchRowPtr 为空或者其中没有数据,直接返回
if (unlikely(batchRowPtr == NULL || batchRowPtr->m_rows_curnum == 0))
return;
int attno = m_relation->rd_rel->relnatts; // 获取表的属性数量
int col = 0;
Assert(attno == batchRowPtr->m_attr_num); // 确保属性数量匹配
CHECK_FOR_INTERRUPTS(); // 检查是否有中断信号
// step 1: 根据数据形成 CU 和 CUDesc
for (col = 0; col < attno; ++col) {
// 跳过已删除的列
if (!m_relation->rd_att->attrs[col]->attisdropped) {
// 根据列数据形成 CU
m_cuPPtr[col] = FormCU(col, batchRowPtr, m_cuDescPPtr[col]);
// 标记该列的压缩选项已完成采样
m_cuCmprsOptions[col].m_sampling_fihished = true;
}
}
// 更新统计信息,根据是否是更新操作调用不同的函数
if (m_isUpdate)
pgstat_count_cu_update(m_relation, batchRowPtr->m_rows_curnum);
else
pgstat_count_cu_insert(m_relation, batchRowPtr->m_rows_curnum);
/*
* step 2: a) 分配 CUID 和 CUPointer
* b) 写入 CU 和 CUDesc
*/
SaveAll(options);
// step 3: 批量插入索引表
if (m_relation->rd_att->attrs[0]->attisdropped) {
// 如果第一个列被删除,找到第一个未删除的列的索引,插入对应的索引表
int fstColIdx = CStoreGetfstColIdx(m_relation);
InsertIdxTableIfNeed(batchRowPtr, m_cuDescPPtr[fstColIdx]->cu_id);
} else {
// 否则,插入第一个列的索引表
InsertIdxTableIfNeed(batchRowPtr, m_cuDescPPtr[0]->cu_id);
}
}
函数执行步骤如下:
- 首先,遍历表的每一列,跳过已删除的列。对于未删除的列,调用 FormCU 函数形成相应的压缩单元(CU)对象,并标记该列的压缩选项已完成采样。
- 根据操作类型(插入还是更新),更新统计信息。
- 分配压缩单元标识符(CUID)和压缩单元指针(CUPointer),然后将压缩单元数据和元数据写入存储。
- 如果第一个列被删除,找到第一个未删除的列的索引,将其压缩单元的标识符用于批量插入索引表操作。如果第一个列未被删除,直接使用第一个列的压缩单元标识符插入索引表。
m_cuCmprsOptions 的结构体变量的打印输出。该结构体包含了多个成员变量,每个成员变量都具有特定的标志位。下面是对这个结构体成员变量的逐个解释:
- m_sampling_fihished: 这个标志位为 true,表示采样过程已完成。
- m_adopt_numeric2int_ascale_rle: 这个标志位为 true,表示对于数值型数据转换为整数型数据,采用 AScale 进行压缩(Run Length Encoding)。
- m_adopt_numeric2int_int32_rle: 这个标志位为 true,表示对于将数值型数据转换为 32 位整数型数据,采用整数型的 Run Length Encoding 进行压缩。
- m_adopt_numeric2int_int64_rle: 这个标志位为 true,表示对于将数值型数据转换为 64 位整数型数据,采用整数型的 Run Length Encoding 进行压缩。
- m_adopt_dict: 这个标志位为 true,表示采用字典压缩。
- m_adopt_rle: 这个标志位为 true,表示采用 Run Length Encoding 进行压缩。
CStoreInsert::FlushIndexDataIfNeed 函数
CStoreInsert::FlushIndexDataIfNeed 函数的主要目的是在数据插入结束时,对索引进行刷新操作。它会遍历所有的索引插入器,对每个插入器进行以下操作:
- 设置索引插入器的插入结束标志,以便它知道数据插入已经结束。
- 调用索引插入器的 BatchInsert 函数,传入一个空的 bulkload_rows 对象和选项为 0,这实际上会触发将索引数据刷新到存储中
函数源码如下:(路径:src/gausskernel/storage/cstore/cstore_insert.cpp)
void CStoreInsert::FlushIndexDataIfNeed()
{
// 检查是否到达插入结束位置、是否有索引关联、是否有索引插入器
if (IsEnd() && m_resultRelInfo && m_idxInsert) {
// 遍历所有索引
for (int i = 0; i < m_resultRelInfo->ri_NumIndices; ++i) {
// 检查索引插入器是否存在
if (m_idxInsert[i] != NULL) {
// 设置索引插入结束标志
m_idxInsert[i]->SetEndFlag();
// 调用索引插入器的 BatchInsert 函数,传入 NULL 数据和选项 0
m_idxInsert[i]->BatchInsert((bulkload_rows*)NULL, 0);
}
}
}
}
CStoreInsert::DeInitInsertArg 函数
CStoreInsert::DeInitInsertArg 函数用于销毁插入参数。源码如下:(路径:src/gausskernel/storage/cstore/cstore_insert.cpp)
/*
* @Description: 销毁插入参数
* @IN args: 插入参数
* @See also:
*/
void CStoreInsert::DeInitInsertArg(InsertArg& args)
{
// 如果存在临时批处理行对象
if (args.tmpBatchRows) {
DELETE_EX(args.tmpBatchRows); // 删除对象并释放内存
}
// 如果存在索引批处理行对象
if (args.idxBatchRow) {
bulkload_indexbatch_deinit(args.idxBatchRow); // 对索引批处理行对象进行反初始化
}
}