调试wifi驱动,有时会将报文内容以16进制形式打印出来,如下是一个beacon报文的内容:
0000 80 00 00 00 ff ff ff ff ff ff 40 e3 d6 cb fe d0 0010 40 e3 d6 cb fe d0 70 29 7b 00 55 41 00 00 00 00 0020 64 00 11 01 00 06 50 61 72 72 6f 74 01 06 98 a4 0030 30 48 60 6c 03 01 95 05 04 00 01 00 00 20 01 00 0040 23 02 1b 00 30 14 01 00 00 0f ac 04 01 00 00 0f 0050 ac 04 01 00 00 0f ac 02 28 00 2d 1a ef 09 17 ff 0060 ff ff 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 0070 00 00 00 00 00 00 3d 16 95 0d 11 00 00 00 00 00 0080 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 7f 08 0090 04 00 08 00 00 40 00 40 bf 0c 91 59 82 0f ea ff 00a0 00 00 ea ff 00 00 c0 05 00 00 00 00 00 c3 03 01 00b0 3c 3c dd 07 00 0b 86 01 04 08 1b dd 18 00 50 f2 00c0 02 01 01 80 00 03 a4 00 00 27 a4 00 00 42 43 5e 00d0 00 62 32 2f 00
如果用这个16进制的内容自己去解析报文,分析各个IE,是不是很头疼?wireshark可以帮助你解决这个问题,下面介绍两种方法:
1、使用命令行将hexdump文件转换为pcap文件,再用wireshark打开pcap文件
将上述beacon内容保存到beacon.txt文件中,然后用text2pcap命令进行转换:
text2pcap -l 105 beacon.txt beacon.pcap
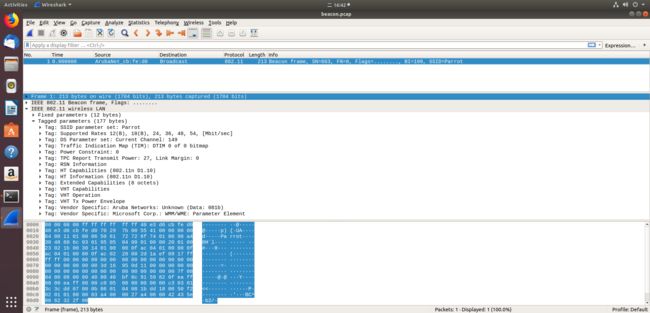
参数“-l 105”是在指定报文类型,105代表的是LINKTYPE_IEEE802_11即要把beacon.txt的内容转换为802.11格式的报文。然后用wireshark打开beacon.pcap即可,效果如下图所示:
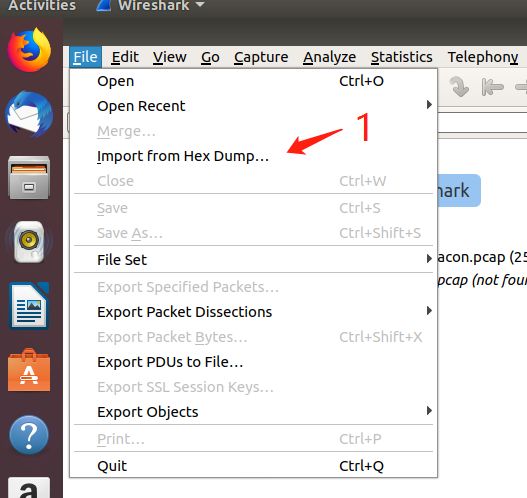
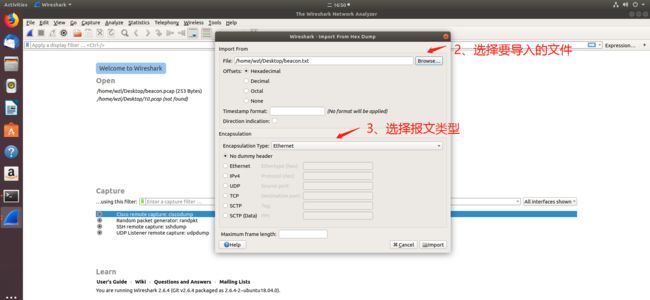
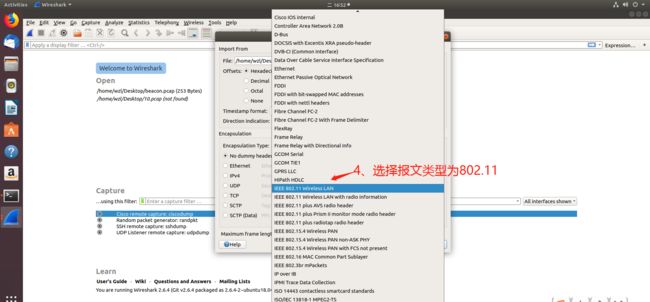
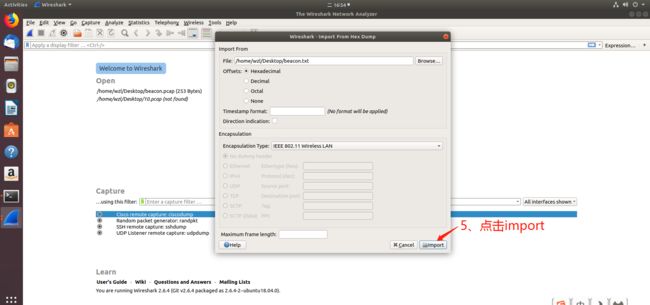
2.使用wireshark图形界面导入hexdump文件进行解析
具体步骤如下:
最终结果如下图所示:
在进行转换的时候需要注意一下几点:
1、text2pcap工具只能接受一定格式的hexdump,更详尽的用法:https://www.wireshark.org/docs/man-pages/text2pcap.html
2、出了802.11格式的报文外,text2pcap还可以处理很多种报文类型,详见:http://www.tcpdump.org/linktypes.html
3、hexdump的内容开始要是802.11头,结尾没有4字节FCS校验,如果有请去掉,不然报文解析会有问题。
4、有时候我们打印报文可能并不是从802.11头开始打印的,找到802.11头,去掉前面的内容后会变成如下这种样子:
0000 80 00 00 00 ff ff ff ff ff ff 40 e3 d6 cb 0020 fe d0 40 e3 d6 cb fe d0 70 29 7b 00 55 41 00 00 0030 00 00 64 00 11 01 00 06 50 61 72 72 6f 74 01 06 0040 98 a4 30 48 60 6c 03 01 95 05 04 00 01 00 00 20 0050 01 00 23 02 1b 00 30 14 01 00 00 0f ac 04 01 00 0060 00 0f ac 04 01 00 00 0f ac 02 28 00 2d 1a ef 09 0070 17 ff ff ff 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 0080 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 3d 16 95 0d 11 00 00 00 0090 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00a0 7f 08 04 00 08 00 00 40 00 40 bf 0c 91 59 82 0f 00b0 ea ff 00 00 ea ff 00 00 c0 05 00 00 00 00 00 c3 00c0 03 01 3c 3c dd 07 00 0b 86 01 04 08 1b dd 18 00 00d0 50 f2 02 01 01 80 00 03 a4 00 00 27 a4 00 00 42 00e0 43 5e 00 62 32 2f 00 da e2 e8 16
除最后一行外,有可能会出现每行不是16个字节,如果手动去把每行搞成16个字节并且把第一列每行的开始字节索引搞对会非常费劲,并且还容易出现手误,把某个字节给删掉的情况,影响工作效率。
下面我写了一个程序transform来解决这个问题,有3种用法,如下:
a) ./transform src.txt dst.txt
b) cat src.txt | ./transform dst.txt
c) cat src.txt | ./transform (会将结果打印出来)
transform源码如下:
1 #include2 #include <string.h> 3 #define BYTES_PER_LINE (16) 4 #define SPACE_PER_LINE (BYTES_PER_LINE) 5 #define PREFIX_NUM (6) 6 7 int process(char *src, char *dst) 8 { 9 static int line = 0; 10 char *pchar = NULL; 11 int offset = 0; 12 13 if (NULL == src || NULL == dst) 14 { 15 printf("Err: src:%p dst:%p\n",src, dst); 16 return -1; 17 } 18 19 offset = strlen(dst); 20 if (0 == offset) 21 { 22 sprintf(dst,"%06x ",line*BYTES_PER_LINE); 23 offset = strlen(dst); 24 } 25 26 pchar = strtok(src, " "); 27 while (pchar = strtok(NULL, " ")) 28 { 29 /* solve problems caused by Windows and linux line breaks \n \r\n*/ 30 if ((2 != strlen(pchar))) 31 { 32 if (!((3 == strlen(pchar) && pchar[2] != '\n') || 33 (4 == strlen(pchar) && 0 == strncmp(&pchar[2], "\r\n", 2)))) 34 { 35 continue; 36 } 37 } 38 else if ((strncmp(pchar, "\r\n", 2) == 0)) 39 { 40 continue; 41 } 42 43 dst[offset++] = pchar[0]; 44 dst[offset++] = pchar[1]; 45 if (((offset - 1 - line*2) % (BYTES_PER_LINE*2 + PREFIX_NUM + SPACE_PER_LINE -1)) == 0) 46 { 47 dst[offset++] = '\n'; 48 line++; 49 sprintf(&dst[offset],"%06x ", line*BYTES_PER_LINE); 50 offset += PREFIX_NUM + 1; 51 } 52 else 53 { 54 dst[offset++] = ' '; 55 } 56 } 57 } 58 59 int main(int argc, char *argv[]) 60 { 61 FILE *fpsrc = NULL; 62 FILE *fpdest = NULL; 63 char buf[1024]; 64 char *pchar = NULL; 65 int ret = 0; 66 char context[65535] = {0}; 67 int offset = 0; 68 69 switch (argc) 70 { 71 case 1: 72 /* Read from stdin and write to stdout */ 73 case 2: 74 { 75 /* Read from stdin and write to dest file */ 76 memset(buf, 0, sizeof(buf)); 77 while (fgets(buf, sizeof(buf), stdin) != NULL) 78 { 79 ret = process(buf, context); 80 if (0 != ret) 81 { 82 return ret; 83 } 84 memset(buf, 0, sizeof(buf)); 85 } 86 if (argc == 2) 87 { 88 fpdest = fopen(argv[1], "w"); 89 } 90 else 91 { 92 fpdest = stdout; 93 } 94 if (NULL == fpdest) 95 { 96 printf("Err can't open dst:%s\n", argv[2]); 97 return -1; 98 } 99 break; 100 } 101 case 3: 102 { 103 /* Read from src file and write to dest file*/ 104 fpsrc = fopen(argv[1], "r"); 105 if (fpsrc == NULL) 106 { 107 printf("Err: can't open src:%s\n",argv[1]); 108 return -1; 109 } 110 while(!feof(fpsrc)) 111 { 112 memset(buf, 0, sizeof(buf)); 113 fgets(buf, sizeof(buf), fpsrc); 114 ret = process(buf, context); 115 if (0 != ret) 116 { 117 return ret; 118 } 119 } 120 fpdest = fopen(argv[2], "w"); 121 if (NULL == fpdest) 122 { 123 printf("Err can't open dst:%s\n", argv[2]); 124 return -1; 125 } 126 127 break; 128 } 129 default: 130 printf("Err: argc:%d Wrong number of parameters!\n",argc); 131 return argc; 132 133 break; 134 } 135 136 fputs(context, fpdest); 137 138 printf("\ntransform success!\n"); 139 }