Java-day08(Object类的equals()方法与toString()方法,包装类,单元测试,基本数据类型/包装类与String之间的相互转化,static关键字)
Object类的equals()方法与toString()方法,包装类,单元测试,基本数据类型/包装类与String之间的相互转化,static关键字
Object类是所有Java类的根父类,若使用extends未指明父类,那父类默认Object类。
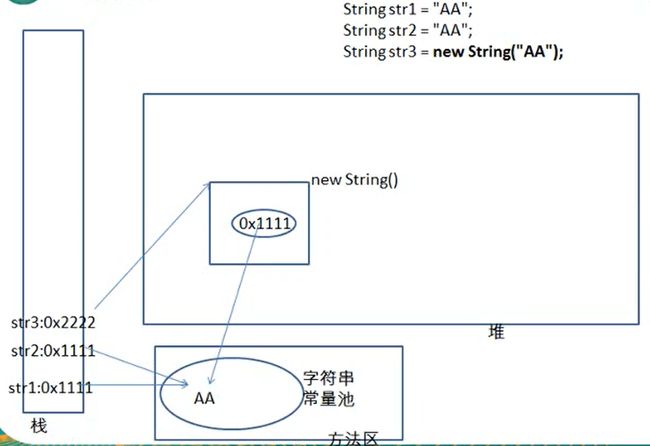
==
引用数据类型比较地址值,基本数据类型比较值(类型不同也可以)
equals()方法
- 只能处理引用数据变量
- 在Object类,equals()任是比较两个引用变量的地址值是否相等
- 像String,File,Date类这些重写Object类的equals()方法,比较的是两个对象的实体内容。
例:
public class Test{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Test3 t1 = new Test3();
Test3 t2 = new Test3();
System.out.println(t1.equals(t2));//false
System.out.println(t1 == t2);//false
String str1 = new String("AA");
String str2 = new String("AA");
String str3 = "AA";
System.out.println(str1.equals(str2));//true
System.out.println(str1 == str2);//false
System.out.println(str1.equals(str3));//true
System.out.println(str1 == str3);//false
}
}
class Test3{
}
题一
public class Test1{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Order o1 = new Order(1001, "Aa");
Order o2 = new Order(1001, "Aa");
System.out.println(o1 == o2);//false
System.out.println(o1.equals(o2));//未重写前为false,重写后为true
}
}
class Order{
private int orderld;
private String OrderName;
public Order(int orderld,String OrderName){
this.OrderName = OrderName;
this.orderld = orderld;
}
public int getOrderId(){
return orderld;
}
public String getOrderName(){
return OrderName;
}
public void setOrderId(int orderld){
this.orderld = orderld;
}
public void setOrderName(String OrderName){
this.OrderName = OrderName;
}
//比较两个Order对象的属性是否完全相同
public boolean equals(Object obj){
if(this == obj){
return true;
}else if(obj instanceof Order){
Order o1 = (Order)obj;
return this.orderld == o1.orderld && this.OrderName.equals(o1.OrderName);
}else{
return false;
}
}
}
题二
public class Test2{
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyDate m1 = new MyDate(14,3,1998);
MyDate m2 = new MyDate(14,3,1998);
if(m1 == m2){
System.out.println("m1 == m2");
}else{
System.out.println("m1 != m2");
}
if(m1.equals(m2)){
System.out.println("m1 is equal to m2");
}else{
System.out.println("m1 is not equal to m2");
}
}
}
class MyDate{
private int day;
private int month;
private int year;
public MyDate(int day,int month,int year){
super();
this.day = day;
this.month = month;
this.year = year;
}
public boolean equals(Object obj){
if(this == obj){
return true;
}else if(obj instanceof MyDate){
MyDate m1 = (MyDate)obj;
return this.day == m1.day && this.month == m1.month && this.year == m1.year;
}else{
return false;
}
}
}
toString()方法
- 在Object类中定义,返回String类型,返回类名和它的引用地址
- 打印对象引用时,实际上默认调用的是这个对象的toString()方法
- 打印的对象所在的类有重写toString()方法,那在打印时就使用重写的方法;反之,就默认使用Object类中的toString()方法。
- 重写toString()方法,我们常常是将对象的属性信息返回。
- 像String类,包装类,File类,Date类等,已实现了Object类中toString()方法的重写。
例
public class Test4{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p1 = new Person("晓华",22);
System.out.println(p1.toString());//此时显示的是对象的类与内存地址(toString()方法未重写时)
System.out.println(p1);//结果与上行一致(toString()方法未重写时)
}
}
class Person{
private int age;
private String name;
public Person(){
super();
}
public Person(String name,int age){
super();
this.age = age;
this.name =name;
}
public int getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
//重写toString()方法,注释掉此方法,那测试时调用的是Object中的toString()方法
public String toString(){
return "Person:name " + name + " age: " + age;
}
}
测试
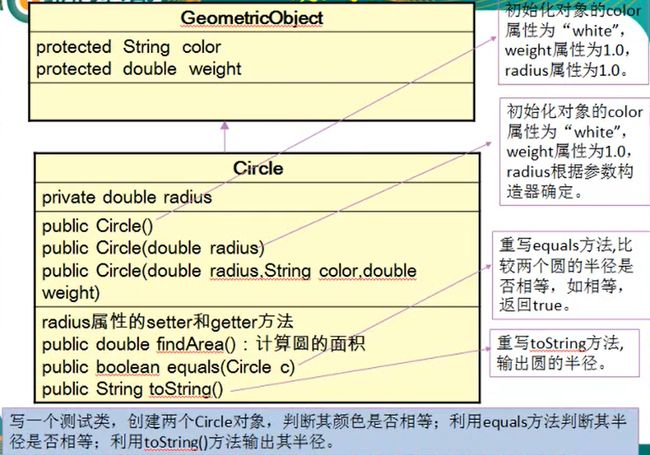
public class Test5{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Circle c1 = new Circle(2.3);
Circle c2 = new Circle(2.3);
System.out.println(c1.equals(c2));
System.out.println(c1.toString());
}
}
class GeometricObject{
protected String color;
protected double weight;
public GeometricObject(){
super();
this.color = "white";
this.weight = 1.0;
}
public GeometricObject(String color,double weight){
super();
this.color = color;
this.weight = weight;
}
public String getColor(){
return color;
}
public void setColor(String color){
this.color = color;
}
public double getWeight(){
return weight;
}
public void setWeight(double weight){
this.weight = weight;
}
}
class Circle extends GeometricObject{
private double radius;
//构造器
public Circle(){
this.radius = 1.0;
}
public Circle(double radius){
this.radius = radius;
}
public Circle(double radius,String color,double weight){
super(color,weight);
this.radius = radius;
}
//方法
public void setRadius(double radius){
this.radius = radius;
}
public double getRadius(){
return this.radius;
}
public double findArea(){
return Math.PI * radius * radius;
}
public boolean equals(Object obj){
if(obj == this)
return true;
else if(obj instanceof Circle){
Circle c1 = (Circle)obj;
return this.radius == c1.radius;
}else{
return false;
}
}
public String toString(){
return "Circle: color: " + color + " weight: " + weight + " radius: " + radius;
}
}
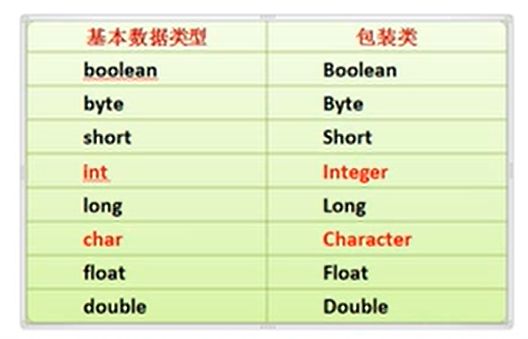
包装类(Wrapper)
Junit单元测试
eclipse版
1.当前工程下–右键build path-add libraries -Junit4
2.在主类中,创建一个空参无返回值的方法(public void test1())。用于代码测试,方法声明:@Test
3.导入import org.junit.Test;
4.在test1()方法中,进行代码的编写
5.测试:双击方法名,右键run as - junit Test即可
说明:如果执行结果没有异常是绿条,如果出现异常是红条
例
import org.junit.Test;
public class TestUnit{
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
@Test
public void test1(){
String str = "AA";
System.out.println(str);
}
@Test
public void test2(){
}
}
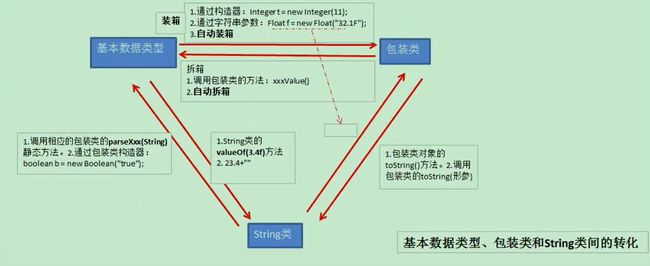
基本数据类型,包装类 及String之间的相互转化
import org.junit.Test;
public class TestUnit{
//基本数据类型,包装类与String之间的相互转化
@Test
public void test2(){
//基本数据类型或包装类 ---> String类:调用String类的静态的重载valueOf(xxx x)方法
int i1 = 100;
String str1 = i1 + ""; //"10"
String str2 = String.valueOf(i1);//"10"
Integer i2 = i1;
String str3 = String.valueOf(i2);//"10"
//基本数据类型或包装类 <--- String类:调用包装类的parseXxx(String str)方法
int i3 = Integer.parseInt(str3);
System.out.println(i3);
}
//基本数据类型与包装类之间的转化(JDK5.0后,有自动装箱和拆箱,可略过)
@Test
public void test1(){
int i = 10;
System.out.println(i);//10
Integer i1 = new Integer(i);
System.out.println(i1.toString());//10
//对于boolean来说,当形参为“true”返回true,除此之外都是false;
Boolean b1 = new Boolean("true");
System.out.println(b1);//true
//包装类--->基本数据类型:调用包装类的xxxValue()方法
int i2 = i1.intValue();
System.out.println(i2);//10
boolean b2 = b1.booleanValue();
System.out.println(b2);//true
//JDK5.0后,自动装箱和拆箱
int i4 = 12;
Integer i3 = i4;//自动装箱
int i5 = i3;//自动拆箱
}
}
//具体步骤:
//1.键盘输入学生成绩(Scanner对象)
//2.for(;;),从键盘依次获取学生的成绩,并填入由Vector v = new Vector()创建的对象v中
//3.求出正数中的最大数
//4.通过v.elementAt(i)依次获取v中的元素,同时判断各分数的等级并输出。
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Vector;
public class Test6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请依次输入学生的成绩:(负数代表结束)");
Vector v = new Vector();
int maxScore = 0;
for(;;){
int score = s.nextInt();
if(score < 0){
break;
}
//获取学生最高分
if(maxScore < score){
maxScore = score;
}
//学生成绩依次放入v中
v.addElement(score);//自动装箱
}
for(int i = 1;i < v.size();i++){
Integer score = (Integer)v.elementAt(i);
char level;
if(maxScore - score <= 10){
level = 'A';
}else if(maxScore - score <= 20){
level = 'B';
}else if(maxScore - score <= 30){
level = 'C';
}else{
level = 'D';
}
System.out.println("学生成绩为:" + score + ",等级:" + level);
}
}
}
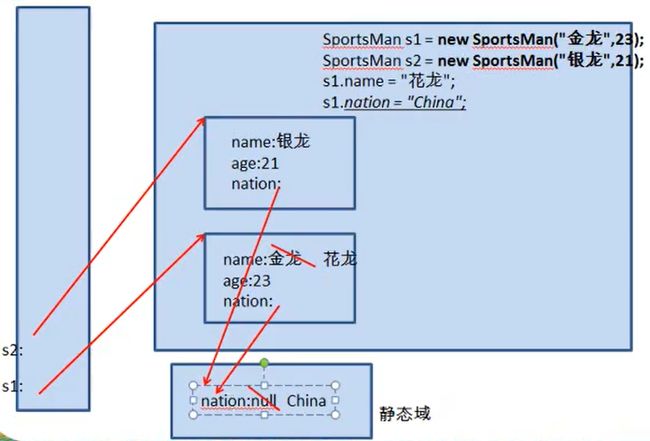
static关键字
static(静态),可以修饰属性,方法,代码块(或初始化块),内部类
static关键字修饰属性(类变量)
相当于常量,非static修饰的属性统称为实例变量
-
由类创建的所有的对象,都用这个属性
-
当其中一个对象对此属性进行修改,会导致其他对象对此属性的调用。(共用这个属性,一个对象改变,那它就会变)
-
类变量随着类的加载而加载,独一份;类变量的加载要早于对象,当有对象之后,可以通过"对象.类变量"使用,但"类.实例变量"是不行的
-
静态变量可以直接通过"类.类变量"的形式来调用
-
类变量存在静态域中
static String nation;
static关键字修饰方法(类方法)
与类变量基本一致
-
类方法随着类的加载而加载,独一份;类方法的加载要早于对象,当有对象之后,可以通过"对象.类方法"使用,但"类.实例方法"是不行的
-
静态方法可以直接通过"类.类方法"的形式来调用
-
内部可以调用静态的属性或静态的方法,而不能调用非静态的属性或方法;反之,非静态的方法是可以调用静态的属性与方法。
-
静态方法不可以有this或super关键字
public static void show(){
}
注:静态的结构(static的属性,方法,代码块(或初始化块),内部类)的生命周期都早于非静态的结构,同时回收也晚于非静态的结构
public class Test7{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Account a1 = new Account("ack123", 100);
Account a2 = new Account("ack123", 100);
System.out.println(a1);
System.out.println(a2);
}
}
class Account{
private int id;//账户
private String password;//密码
private double balance;//余额
private static double rate = 0.034;//利率
private static double minBalance = 100;//最小余额
private static int init = 1000;//账户的起始编号
public Account(String password,double balance){
init++;
this.id = init;
this.balance = balance;
this.password = password;
}
//续写get,set方法(init属性不需要),重写toString()
}
感谢大家的支持,关注,评论,点赞!
参考资料:
尚硅谷宋红康20天搞定Java基础中部