C++ Day5
目录
一、静态成员
1.1 概念
1.2 格式
1.3 银行账户实例
二、类的继承
2.1 目的
2.2 概念
2.3 格式
2.4 继承方式
2.5 继承中的特殊成员函数
2.5.1 构造函数
2.5.2析构函数
2.5.3 拷贝构造函数
2.5.4拷贝赋值函数
总结:
三、多继承
3.1 概念
3.2 格式
3.3总结
一、静态成员
1.1 概念
静态数据成员和静态成员函数是属于类的,不属于类的实例,它们在所有类的实例中是共享。
在数据成员前加static ----->静态数据成员
在成员函数前加static ------>静态成员函数
静态变量的初始化必须在类外初始化,如果没有初始化(不建议),默认为0
静态成员函数只能访问静态数据成员。
1.2 格式
class 类名
{
static 数据类型 变量名; //静态数据成员
static 函数返回值类型 函数名(形参列表) //静态成员函数
{}
};
数据类型 类名::变量 = 初始化; 1.3 银行账户实例
#include
using namespace std;
//封装银行账户 类
class BankAccount
{
private:
double balance; //余额
static double interest_rate; //利率 静态数据成员 属于类的
public:
//无参构造
BankAccount() {}
//有参构造函数
BankAccount(double b):balance(b)
{}
//静态成员函数 获取当前的利率
static double getInterestRate()
{
return interest_rate;
}
//静态成员函数,设置当前利率
static void setInterestRate(double rate)
{
interest_rate = rate;
}
//静态成员函数 获取连本带利的余额
static double getLastMoney(BankAccount &account)
{
return account.balance*(1+interest_rate);
}
};
double BankAccount::interest_rate = 0.05; //在类外初始化 静态数据成员
int main()
{
cout << "当前利率:" << BankAccount::getInterestRate() << endl;
BankAccount::setInterestRate(0.03);
cout << "当前利率:" << BankAccount::getInterestRate() << endl;
BankAccount account1(1000.0);
BankAccount account2(2000.0);
cout << "第一个人连本带利的余额:" << BankAccount::getLastMoney(account1) << endl;
return 0;
} 二、类的继承
类的三大属性:封装、继承、多态
2.1 目的
1> 实现代码的重用性
2> 建立父类和子类之间的联系
3> 在实现多态的时候,通过继承,实现子类对父类函数的重写
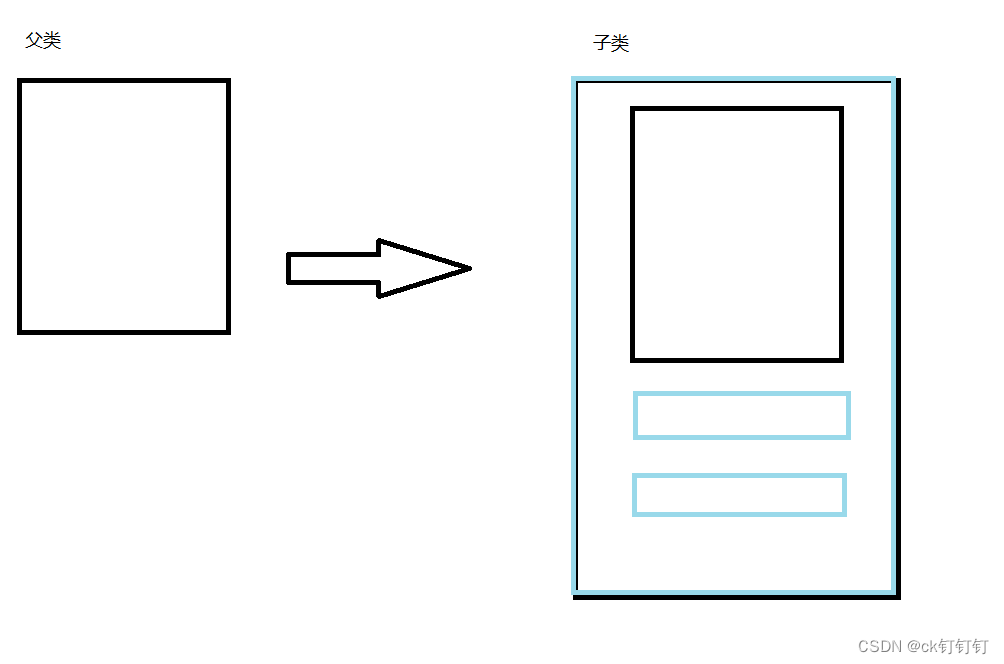
2.2 概念
保持已有类的特性,在原来基础上,增加新的特性,构造出新类的过程, 成为 继承 / 派生
被继承者 称为 父类 / 基类
继承者 称为 子类 / 派生类
2.3 格式
class 类名:继承方式 类名
{
子类的拓展;
};
//继承方式: public 共有继承 protected保护继承 private私有继承
//一般用public方式继承#include
using namespace std;
//封装 人 类 父类/基类
class Person
{
private:
string name;
int age;
public:
//无参构造函数
Person()
{
cout << "父类的无参构造函数" << endl;
}
//有参构造
Person(string name, int age):name(name),age(age)
{
cout << "父类的有参构造函数" << endl;
}
};
//封装 学生 类 共有继承人 类
class Stu:public Person //子类 、派生类
{
private:
int id;
int math;
public:
//无参构造函数
Stu()
{
cout << "子类的无参构造函数" << endl;
}
//有参构造函数
Stu(string name, int age, int id, int math):Person(name,age),id(id),math(math)
{
cout << "子类的有参构造函数" << endl;
}
};
int main()
{
Stu s("zhangsan",12,1001,78);
return 0;
} 2.4 继承方式
父类中成员权限 public | protected | private public | protected | private public | protected | private
继承方式 public protected private
继承到子类中该成员的权限 public | protected | 不可访问 protected | protected | 不可访问 private | private | 不可访问
类外是否可以访问子类 可以 | 不可以 | 不可以 不可以 | 不可以 | 不可以 不可以 | 不可以 | 不可以
从父类中继承下来的成员
2.5 继承中的特殊成员函数
2.5.1 构造函数
父类的初始化必须赶在子类之前,换句话说,先调用父类的构造函数,再调用子类的构造函数
2.5.2析构函数
析构函数调用的顺序:先调用子类的析构函数,再调用父类的析构函数。
先构造的 后析构。 后构造的 先析构
2.5.3 拷贝构造函数
父类的拷贝构造函数会继承到子类中,在子类的拷贝构造函数中使用父类的拷贝构造函数,来完成子类从父类继承下来的成员的拷贝工作。
如果涉及深拷贝,则需要在子类和父类各自完成深拷贝工作。
2.5.4拷贝赋值函数
父类的拷贝赋值函数会继承到子类中,在子类的拷贝赋值函数中使用父类的拷贝赋值函数,来完成子类从父类继承下来的成员的赋值工作。
如果涉及深拷贝,则需要在子类和父类各自完成深拷贝工作
#include
using namespace std;
//封装 人 类 父类/基类
class Person
{
private:
string name;
protected:
int age;
public:
int h;
public:
//无参构造函数
Person()
{
cout << "父类的无参构造函数" << endl;
}
//有参构造
Person(string name, int age, int h):name(name),age(age),h(h)
{
cout << "父类的有参构造函数" << endl;
}
//拷贝构造函数
Person(const Person & other):name(other.name),age(other.age),h(other.h)
{
cout << "父类的拷贝构造函数" << endl;
}
//拷贝赋值函数
Person & operator=(const Person &p)
{
name = p.name;
age = p.age;
h = p.h;
cout << "父类的拷贝赋值函数" << endl;
return *this;
}
void show()
{
cout << "父类的show" << endl;
}
};
//封装 学生 类 共有继承人 类
class Stu:public Person //子类 、派生类
{
private:
int id;
int math;
public:
//无参构造函数
Stu()
{
cout << "子类的无参构造函数" << endl;
}
//有参构造函数
Stu(string name, int age, int h, int id, int math):Person(name,age,h),id(id),math(math)
{
cout << "子类的有参构造函数" << endl;
}
//拷贝构造函数
Stu(const Stu & s):id(s.id),math(s.math),Person(s)
{
cout << "子类的拷贝构造函数" << endl;
}
//拷贝赋值函数
Stu & operator=(const Stu & s)
{
Person::operator=(s);
id = s.id;
math = s.math;
cout << "子类的拷贝赋值函数" << endl;
return *this;
}
void show()
{
cout << "子类的show" << endl;
cout << h << endl; //通过共有继承,类外、子类可以访问父类共有成员
cout << age << endl; //通过共有继承,子类可以访问父类保护成员,类外不可以访问
//cout << name << endl;//通过共有继承,子类不可访问父类私有成员,类外不可以访问
}
};
int main()
{
Stu s("zhangsan",12,190,1001,78);
Stu s2=s;
Stu s3;
s3 = s2;
// s.show();
// s.Person::show();
return 0;
}
总结:
1> 父类的初始化必须赶在子类之前,换句话说,先调用父类的构造函数,再调用子类的构造函数
2> 当父类的函数和子类的函数是同名同类型时,不会报错,原因是作用域不同,如果子类实例化出一个对象,这个对象调用该函数,调用的是子类的函数,如果想调用父类中函数。则需要加上类名和作用域限定符。
三、多继承
3.1 概念
一个类由多个类公共派生。
3.2 格式
class 类名:继承方式1 类名1,继承方式2 类名2,.....,继承方式n 类名n
{
子类的拓展
};#include
using namespace std;
//封装 沙发的类
class Sofa
{
private:
string sitting;
public:
//无参构造
Sofa() {cout << "沙发的无参构造" << endl;}
//有参构造函数
Sofa(string s):sitting(s)
{
cout << "沙发的有参构造" << endl;
}
void display()
{
cout << sitting << endl;
}
};
//封装 床 类
class Bed
{
private:
string sleep;
public:
//无参
Bed() {cout << "床的无参构造" << endl;}
//有参
Bed(string s):sleep(s)
{
cout << "床的有参构造" << endl;
}
void display()
{
cout << sleep << endl;
}
};
//封装 沙发床类 继承于沙发 和 床
class Sofa_Bed:public Bed,public Sofa
{
private:
int w;
public:
//
Sofa_Bed(){cout << "沙发床的无参构造" << endl;}
//有参构造
Sofa_Bed(string sit, string s, int w):Bed(s),Sofa(sit),w(w)
{
cout << "沙发床的有参构造" << endl;
}
};
int main()
{
Sofa_Bed s;
Sofa_Bed s1("可坐","可躺",123);
s1.Sofa::display();
s1.Bed::display();
return 0;
}
3.3总结
1> 子类由多个父类共同派生,子类调用调用构造函数顺序,肯是最后调用自己,对于多个父类的构造函数顺序的调用,和初始化列表的书写顺序无关,和继承的时候顺序有关。
2> 当多个父类中有同名同类型的函数,子类对象调用该函数时,需要表明哪个类的,加上类名和作用域限定符。