代码随想录算法训练营第四天 | 24. 两两交换链表中的节点 | 19.删除链表的倒数第N个节点 | 面试题 02.07. 链表相交 | 142.环形链表II
24. 两两交换链表中的节点
题目点此跳转
卡哥的文章讲解点此跳转
卡哥的视频讲解点此跳转
题目描述: 给你一个链表,两两交换其中相邻的节点,并返回交换后链表的头节点。你必须在不修改节点内部的值的情况下完成本题(即,只能进行节点交换)
示例 1:
输入:head = [1,2,3,4]
输出:[2,1,4,3]
示例 2:
输入:head = []
输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:head = [1]
输出:[1]
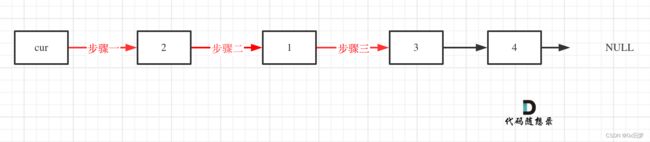
可以借助卡哥的图来理解交换过程
C语言写法
struct ListNode* swapPairs(struct ListNode* head){
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
ListNode* dummyhead = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
dummyhead->next = head;
ListNode* cur = dummyhead;
while(cur->next&&cur->next->next){
ListNode* tmp = cur->next;
ListNode* tmp1 = cur->next->next;
cur->next = cur->next->next;
cur->next = tmp;
cur->next->next->next = tmp1;
cur = cur->next->next;
}
return dummyhead->next;
}
由于笔者逐渐体会到了C++的精妙之处(实则是C语言太菜了),故这里同时给出C++的写法,当作对C++的一种学习。以后的题目会同时给出C/C++两种写法。
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* swapPairs(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* dummyhead = new ListNode(0);
dummyhead->next = head;
ListNode* cur = dummyhead;
while(cur->next&&cur->next->next){
ListNode* tmp = cur->next;
ListNode* tmp1 = cur->next->next->next;
cur->next = cur->next->next;
cur->next->next = tmp;
cur->next->next->next = tmp1;
cur=cur->next->next;
}
return dummyhead->next;
}
};
19.删除链表的倒数第N个节点
题目点此跳转
卡哥的文章讲解点此跳转
卡哥的视频讲解点此跳转
题目描述:
给你一个链表,删除链表的倒数第 n个结点,并且返回链表的头结点。
示例 1:
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], n = 2
输出:[1,2,3,5]
示例 2:
输入:head = [1], n = 1
输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:head = [1,2], n = 1
输出:[1]
这个题可以用双指针的思路来进行解答,定义fast和slow指针,fast指针先走n+1步(这样slow指针才可以指向我们要操作节点的上一个节点),然后两个指针同时移动。
同样借助卡哥的图进行理解:
C语言写法:
struct ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(struct ListNode* head, int n){
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
ListNode* dummyhead = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
dummyhead->next = head;
ListNode* fast = dummyhead;
ListNode* slow = dummyhead;
while(n--&&fast->next){
fast = fast->next;
}
fast = fast->next;
while(fast){
fast = fast->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
slow->next = slow->next->next;
return dummyhead->next;
}
C++写法:
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int n) {
ListNode* dummyhead = new ListNode(0);
dummyhead->next = head;
ListNode* fast = dummyhead;
ListNode* slow = dummyhead;
while(n--&&fast->next){
fast = fast->next;
}
fast = fast->next;
while(fast){
fast = fast->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
slow->next = slow->next->next;
return dummyhead->next;
}
};
面试题 02.07. 链表相交
题目点此跳转
卡哥的文章讲解
题目描述: 给你两个单链表的头节点 headA 和 headB ,请你找出并返回两个单链表相交的起始节点。如果两个链表没有交点,返回 null
图示两个链表在节点 c1 开始相交**:**
题目数据 保证 整个链式结构中不存在环。
注意,函数返回结果后,链表必须 保持其原始结构 。
示例 1:
输入:intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,0,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3
输出:Intersected at '8'
解释:相交节点的值为 8 (注意,如果两个链表相交则不能为 0)。
从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [4,1,8,4,5],链表 B 为 [5,0,1,8,4,5]。
在 A 中,相交节点前有 2 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点。
示例 2:
输入:intersectVal = 2, listA = [0,9,1,2,4], listB = [3,2,4], skipA = 3, skipB = 1
输出:Intersected at '2'
解释:相交节点的值为 2 (注意,如果两个链表相交则不能为 0)。
从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [0,9,1,2,4],链表 B 为 [3,2,4]。
在 A 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 1 个节点。
示例 3:
输入:intersectVal = 0, listA = [2,6,4], listB = [1,5], skipA = 3, skipB = 2
输出:null
解释:从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [2,6,4],链表 B 为 [1,5]。
由于这两个链表不相交,所以 intersectVal 必须为 0,而 skipA 和 skipB 可以是任意值。
这两个链表不相交,因此返回 null 。
注意一个点:交点不是数值相等,而是指针相等
C++写法
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) {
ListNode* curA = headA;
ListNode* curB = headB;
int lenA=0,lenB=0;
while(curA){
lenA++;
curA = curA->next;
}
while(curB){
lenB++;
curB = curB->next;
}
curA = headA;
curB = headB;
if(lenB>lenA){
swap(curA,curB);
swap(lenA,lenB);
}
int gap = lenA-lenB;
while(gap--){
curA = curA->next;
}
while(curA){
if(curA==curB)
return curA;
curA = curA->next;
curB = curB->next;
}
return NULL;
}
};
142.环形链表II
题目点此跳转
卡哥的文章讲解
卡哥的视频讲解
**题目描述:**给定一个链表的头节点 head ,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 null。
如果链表中有某个节点,可以通过连续跟踪 next 指针再次到达,则链表中存在环。 为了表示给定链表中的环,评测系统内部使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。如果 pos 是 -1,则在该链表中没有环。注意:pos 不作为参数进行传递,仅仅是为了标识链表的实际情况。不允许修改 链表。
示例 1:
输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
输出:返回索引为 1 的链表节点
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。
示例2:
输入:head = [1,2], pos = 0
输出:返回索引为 0 的链表节点
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第一个节点。
示例3:
输入:head = [1], pos = -1
输出:返回 null
解释:链表中没有环。
第一个问题,如何确定链表有环
我们可以使用快慢指针法来判断链表是否有环,一个指针每次移动两个节点,另外一个指针每次移动一个节点,如果两个指针在途中相遇 ,说明这个链表有环
借助卡哥的动图来理解一下
第二个问题,如何找到这个环的入口
假设从头结点到环形入口节点 的节点数为x。环形入口节点到 fast指针与slow指针相遇节点 节点数为y。从相遇节点 再到环形入口节点节点数为 z。 如图所示:
具体针对这一块的分析可以参考详细卡哥文章:点此跳转
动图如下:
C语言写法:
struct ListNode *detectCycle(struct ListNode *head) {
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
ListNode* fast = head;
ListNode* slow = head;
while(fast&&fast->next){
fast = fast->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
if(fast==slow){
ListNode* index1 = fast;
ListNode* index2 = head;
while(index1!=index2){
index1 = index1->next;
index2 = index2->next;
}
return index1;
}
}
return NULL;
}
C++写法:
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) {
ListNode* fast = head;
ListNode* slow = head;
while(fast&&fast->next){
fast = fast->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
if(fast==slow){
ListNode* index1 = fast;
ListNode* index2 = head;
while(index1!=index2){
index1 = index1->next;
index2 = index2->next;
}
return index1;
}
}
return NULL;
}
};
总结:
今天尝试了用C++完成了几个算法,以后的打卡都会有C&&C++两种写法。