Android学习之路(9) Bundle
Bundle的概念理解
Bundle经常出现在以下场合:
- Activity状态数据的保存与恢复涉及到的两个回调:
void onSaveInstanceState (Bundle outState)、void onCreate (Bundle savedInstanceState) - Fragment的setArguments方法:
void setArguments (Bundle args) - 消息机制中的Message的setData方法:
void setData (Bundle data) - 其他场景不再列举
Bundle从字面上解释为“一捆、一批、一包”,结合上述几个应用场合,可以知道Bundle是用来传递数据的,我们暂将Bundle理解为Android中用来传递数据的一个容器。官方文档对Bundle的说明如下:
Bundle实现了Parcelable接口,所以他可以方便的在不同进程间传输,这里要注意我们传输的数据必须能够被序列化。
bundle的作用主要时用于传递数据;它所保存的数据是以key-value(键值对)的形式存在的,也就是说bundle是保存数据的容器,内部使用了ArrayMap去存储数据,也提供了很多get,put方法。
bundle传递的数据包括:string、int、boolean、byte、float、long、double等基本类型或它们对应的数组,也可以是对象或对象数组。当bundle传递的是对象或对象数组时,必须实现Serialiable或Parcelable接口。
Bundle源码分析
Bundle操作的基本数据类型如下表所示,它们都继承自BaseBundle (From class android.os.BaseBundle )
| 返回类型 | 函数 | 函数说明 |
|---|---|---|
| void | clear() | Removes all elements from the mapping of this Bundle. |
| boolean | containsKey(String key) | Returns true if the given key is contained in the mapping of this Bundle. |
| object | get(String key) | Returns the entry with the given key as an object. |
| boolean | getBoolean(String key, boolean defaultValue) | Returns the value associated with the given key, or defaultValue if no mapping of the desired type exists for the given key. |
| boolean | getBoolean(String key) | Returns the value associated with the given key, or false if no mapping of the desired type exists for the given key. |
| boolean[] | getBooleanArray(String key) | Returns the value associated with the given key, or null if no mapping of the desired type exists for the given key or a null value is explicitly associated with the key. |
| double | getDouble(String key, double defaultValue) | Returns the value associated with the given key, or defaultValue if no mapping of the desired type exists for the given key. |
| double | getDouble(String key) | Returns the value associated with the given key, or 0.0 if no mapping of the desired type exists for the given key. |
| double[] | getDoubleArray(String key) | Returns the value associated with the given key, or null if no mapping of the desired type exists for the given key or a null value is explicitly associated with the key. |
| int | getInt(String key) | Returns the value associated with the given key, or 0 if no mapping of the desired type exists for the given key. |
| int | getInt(String key, int defaultValue) | Returns the value associated with the given key, or defaultValue if no mapping of the desired type exists for the given key. |
| int[] | getIntArray(String key) | Returns the value associated with the given key, or null if no mapping of the desired type exists for the given key or a null value is explicitly associated with the key. |
| long | getLong(String key) | Returns the value associated with the given key, or 0L if no mapping of the desired type exists for the given key. |
| long | getLong(String key, long defaultValue) | Returns the value associated with the given key, or defaultValue if no mapping of the desired type exists for the given key. |
| long[] | getLongArray(String key) | Returns the value associated with the given key, or null if no mapping of the desired type exists for the given key or a null value is explicitly associated with the key. |
| String | getString(String key) | Returns the value associated with the given key, or null if no mapping of the desired type exists for the given key or a null value is explicitly associated with the key. |
| String | getString(String key, String defaultValue) | Returns the value associated with the given key, or defaultValue if no mapping of the desired type exists for the given key or if a null value is explicitly associated with the given key. |
| String[] | getStringArray(String key) | Returns the value associated with the given key, or null if no mapping of the desired type exists for the given key or a null value is explicitly associated with the key. |
| boolean | isEmpty() | Returns true if the mapping of this Bundle is empty, false otherwise. |
| Set | keySet() | Returns a Set containing the Strings used as keys in this Bundle. |
| void | putAll(PersistableBundle bundle) | Inserts all mappings from the given PersistableBundle into this BaseBundle. |
| void | putBoolean(String key, boolean value) | Inserts a Boolean value into the mapping of this Bundle, replacing any existing value for the given key. |
| void | putBooleanArray(String key, boolean[] value) | Inserts a boolean array value into the mapping of this Bundle, replacing any existing value for the given key. |
| void | putDouble(String key, double value) | Inserts a double value into the mapping of this Bundle, replacing any existing value for the given key. |
| void | putDoubleArray(String key, double[] value) | Inserts a double array value into the mapping of this Bundle, replacing any existing value for the given key. |
| void | putInt(String key, int value) | Inserts an int value into the mapping of this Bundle, replacing any existing value for the given key. |
| void | putIntArray(String key, int[] value) | Inserts an int array value into the mapping of this Bundle, replacing any existing value for the given key. |
| void | putLong(String key, long value) | Inserts a long value into the mapping of this Bundle, replacing any existing value for the given key. |
| void | putLongArray(String key, long[] value) | Inserts a long array value into the mapping of this Bundle, replacing any existing value for the given key. |
| void | putString(String key, String value) | Inserts a String value into the mapping of this Bundle, replacing any existing value for the given key. |
| void | putStringArray(String key, String[] value) | Inserts a String array value into the mapping of this Bundle, replacing any existing value for the given key. |
| void | remove(String key) | Removes any entry with the given key from the mapping of this Bundle. |
| int | size() | Returns the number of mappings contained in this Bundle. |
首先看它的声明
public final class Bundle extends BaseBundle implements Cloneable, Parcelable
第一,它使用final修饰,所以不可以被继承
第二,它实现了两个接口,cloneable和Parcelable,这就意味着他必须实现以下方法:
public Object clone()
public int describeContents()
public void writeToParcel(Parcel parcel, int flags)
public void readFromParcel(Parcel parcel)
public static final Parcelable.Creator CREATOR = new Parcelable.Creator()
再看他的内存结构:
ArrayMap mMap = null;
使用的是ArrayMap,这个集合类存储的也是键值对,但是与Hashmap不同的是,hashmap采用的是“数组+链表”的方式存储,而ArrayMap中使用的是两个数组进行存储,一个数组存储key,一个数组存储value,内部的增删改查都将会使用二分查找来进行,这个和SparseArray差不多,只不过SparseArray的key值只能是int型的,而Arraymap可以是map型,所以在数据量不大的情况下可以使用这两个集合代替hashmap去优化性能。
我们知道Bundle其实就是一个容器,内部使用了ArrayMap去存储数据,那么就必然会提供get,put方法,由于Bundle支持的数据类型太多,这里我们就看一个布尔类型的,其他类型的方式都差不多。
public boolean getBoolean(String key, boolean defaultValue) {
unparcel();
Object o = mMap.get(key);
if (o == null) {
return defaultValue;
}
try {
return (Boolean) o;
} catch (ClassCastException e) {
typeWarning(key, o, "Boolean", defaultValue, e);
return defaultValue;
}
}
数据读取的逻辑很简单,就是通过key从ArrayMap里读出保存的数据,并转换成对应的类型返回,当没找到数据或发生类型转换异常时返回缺省值。
public void putBoolean(@Nullable String key, boolean value) {
unparcel();
mMap.put(key, value);
}
这里出现了一个unparcel()方法
/* package */
void unparcel() {
synchronized (this) {
final Parcel parcelledData = mParcelledData;
if (parcelledData == null) {
if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "unparcel "
+ Integer.toHexString(System.identityHashCode(this))
+ ": no parcelled data");
return;
}
if (LOG_DEFUSABLE && sShouldDefuse && (mFlags & FLAG_DEFUSABLE) == 0) {
Slog.wtf(TAG, "Attempting to unparcel a Bundle while in transit; this may "
+ "clobber all data inside!", new Throwable());
}
if (isEmptyParcel()) {
if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "unparcel "
+ Integer.toHexString(System.identityHashCode(this)) + ": empty");
if (mMap == null) {
mMap = new ArrayMap<>(1);
} else {
mMap.erase();
}
mParcelledData = null;
return;
}
int N = parcelledData.readInt();
if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "unparcel " + Integer.toHexString(System.identityHashCode(this))
+ ": reading " + N + " maps");
if (N < 0) {
return;
}
ArrayMap map = mMap;
if (map == null) {
map = new ArrayMap<>(N);
} else {
map.erase();
map.ensureCapacity(N);
}
try {
parcelledData.readArrayMapInternal(map, N, mClassLoader);
} catch (BadParcelableException e) {
if (sShouldDefuse) {
Log.w(TAG, "Failed to parse Bundle, but defusing quietly", e);
map.erase();
} else {
throw e;
}
} finally {
mMap = map;
parcelledData.recycle();
mParcelledData = null;
}
if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "unparcel " + Integer.toHexString(System.identityHashCode(this))
+ " final map: " + mMap);
}
}
先来看下BaseBundle中mParcelledData的定义:
Parcel mParcelledData = null;
在大部分情况下mParcelledData都是null,因此unparcel()直接返回。当使用构造函数public Bundle(Bundle b)创建Bundle时,会给mParcelledData赋值;
void copyInternal(BaseBundle from, boolean deep) {
synchronized (from) {
if (from.mParcelledData != null) {
if (from.isEmptyParcel()) {
mParcelledData = NoImagePreloadHolder.EMPTY_PARCEL;
} else {
mParcelledData = Parcel.obtain();
mParcelledData.appendFrom(from.mParcelledData, 0,
from.mParcelledData.dataSize());
mParcelledData.setDataPosition(0);
}
} else {
mParcelledData = null;
}
if (from.mMap != null) {
if (!deep) {
mMap = new ArrayMap<>(from.mMap);
} else {
final ArrayMap fromMap = from.mMap;
final int N = fromMap.size();
mMap = new ArrayMap<>(N);
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
mMap.append(fromMap.keyAt(i), deepCopyValue(fromMap.valueAt(i)));
}
}
} else {
mMap = null;
}
mClassLoader = from.mClassLoader;
}
}
从上述代码片段可以知道mParcelledData的取值有3种情况:
- mParcelledData = EMPTY_PARCEL
- mParcelledData = Parcel.obtain()
- mParcelledData = null
在unparcel()方法中就对上述几种情况做了不同的处理,当mParcelledData为null时,直接返回;当mParcelledData为EMPTY_PARCEL时,会创建一个容量为1的ArrayMap对象;当mParcelledData为Parcel.obtain()时,则会将里面的数据读出,并创建一个ArrayMap,并将数据存储到ArrayMap对象里面,同时将mParcelledData回收并置为null;
Parcelable接口分析
在Android中,Parcelable接口是用于实现对象序列化和反序列化的一种机制。它允许我们将自定义的Java对象转换成一个可传输的二进制数据流,以便在不同组件之间传递数据。通常在Activity之间传递复杂的自定义对象时,使用Parcelable接口比使用Java的Serializable接口更高效。
Parcelable接口的工作原理是通过将对象的数据拆分成原始数据类型,并在写入和读取时进行序列化和反序列化。这样可以避免使用Java的反射机制,提高了性能。
要实现Parcelable接口,首先需要让自定义的Java类实现Parcelable接口,并实现以下几个方法:
- writeToParcel(Parcel parcel, int flags): 将对象的数据写入Parcel对象,以进行序列化。在这个方法中,需要将对象的各个字段写入Parcel对象。
- createFromParcel(Parcel parcel): 从Parcel对象中读取数据,以进行反序列化。在这个方法中,需要读取Parcel中的数据,并将其设置为对象的各个字段。
- newArray(int size): 创建一个指定大小的对象数组,通常用于反序列化的过程。
接着,需要在类中添加一个静态的Parcelable.Creator对象,用于创建和反序列化对象。这个对象需要实现Parcelable.Creator接口,并实现以下方法:
- createFromParcel(Parcel parcel): 根据Parcel对象创建并返回对象实例。
- newArray(int size): 创建一个指定大小的对象数组。
最后,在类中添加一个public static final的Parcelable.Creator对象,以供系统使用。
下面是一个简单的示例,演示了如何在Android中实现Parcelable接口:
import android.os.Parcel;
import android.os.Parcelable;
public class Student implements Parcelable {
private String name;
private int age;
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
protected Student(Parcel in) {
name = in.readString();
age = in.readInt();
}
@Override
public void writeToParcel(Parcel dest, int flags) {
dest.writeString(name);
dest.writeInt(age);
}
@Override
public int describeContents() {
return 0;
}
public static final Creator CREATOR = new Creator() {
@Override
public Student createFromParcel(Parcel in) {
return new Student(in);
}
@Override
public Student[] newArray(int size) {
return new Student[size];
}
};
}
在这个例子中,我们创建了一个名为Student的类,实现了Parcelable接口。在writeToParcel方法中,我们将Student对象的name和age字段写入Parcel对象。在createFromParcel方法中,我们从Parcel对象中读取name和age字段,并创建一个新的Student对象。
通过实现Parcelable接口,我们可以在不同的Android组件之间传递Student对象,而不需要进行繁琐的序列化和反序列化操作。同时,Parcelable接口也比Serializable接口更高效,适用于在性能要求较高的场景下使用。
代码举例说明
当使用Parcelable接口时,我们可以将自定义的Java类对象传递给Android组件,例如Activity之间的传递。下面是一个简单的示例,展示如何实现Parcelable接口和在Activity之间传递自定义对象:
首先,创建一个名为Student的Java类,该类包含一些基本的字段和方法:
import android.os.Parcel;
import android.os.Parcelable;
public class Student implements Parcelable {
private String name;
private int age;
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
protected Student(Parcel in) {
name = in.readString();
age = in.readInt();
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
@Override
public void writeToParcel(Parcel dest, int flags) {
dest.writeString(name);
dest.writeInt(age);
}
@Override
public int describeContents() {
return 0;
}
public static final Creator CREATOR = new Creator() {
@Override
public Student createFromParcel(Parcel in) {
return new Student(in);
}
@Override
public Student[] newArray(int size) {
return new Student[size];
}
};
}
接下来,在发送方的Activity中,我们创建一个Student对象并使用Intent将其传递给接收方的Activity:
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
public class SenderActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_sender);
// 创建一个Student对象
Student student = new Student("Alice", 20);
// 使用Intent传递Student对象给ReceiverActivity
Intent intent = new Intent(this, ReceiverActivity.class);
intent.putExtra("student", student);
startActivity(intent);
}
}
最后,在接收方的Activity中,我们从Intent中获取传递过来的Student对象:
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
public class ReceiverActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_receiver);
// 从Intent中获取传递过来的Student对象
Student student = getIntent().getParcelableExtra("student");
if (student != null) {
// 使用Student对象的数据
String name = student.getName();
int age = student.getAge();
// 在这里进行相关操作,例如显示学生信息
}
}
}
通过实现Parcelable接口,我们可以轻松地在Activity之间传递自定义的Student对象,而不需要进行额外的序列化和反序列化操作。在接收方的Activity中,我们可以获取传递过来的Student对象,并使用其中的数据进行相应的处理。这样,我们就实现了自定义对象的传递和使用。
Bundle实战
在Activity to Activity传递数据时使用Bundle
① 当传递简单数据时
新建一个MainActivity,对应的布局文件比较简单,就是一个Button,点击这个按钮后,程序跳转到SecondActivity,并将传递的数据在SecondActivity的TextView中显示出来。这样,就使用Bundle实现了数据在Activity之间的传递。
package com.example.bundletest;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
//声明控件对象
private Button mButton;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
//获取控件的对象
mButton = findViewById(R.id.button);
//为Button绑定监听器
mButton.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
/**
* 存入数据
*/
//实例化一个Bundle
Bundle bundle = new Bundle();
Intent intent = new Intent(MainActivity.this, SecondActivity.class);
//设置数据
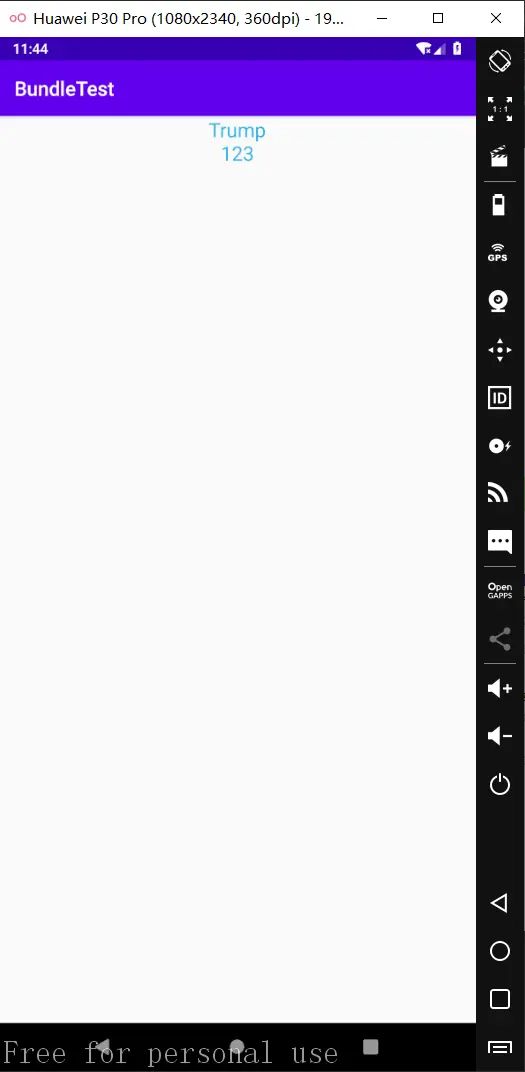
String name = "Trump";
int num = 123;
//把数据放入到Bundle容器中
bundle.putString("Name", name);
bundle.putInt("Num", num);
//把Bundle容器中的数据放到Intent中
intent.putExtra("Message", bundle);
//启动该Intent,实现Activity的跳转
startActivity(intent);
}
});
}
}
新建一个SecondActivity,用于显示传递的数据。对应的布局文件也很简单,就是一个TextView。
package com.example.bundletest;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.annotation.SuppressLint;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class SecondActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
//声明控件对象
private TextView textView;
@SuppressLint("SetTextI18n")
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_second);
//获取控件的对象
textView = findViewById(R.id.text_view);
/**
*读取数据
*/
Intent intent = getIntent();
//从Intent中取出Bundle
Bundle bundle = intent.getBundleExtra("Message");
//获取数据
assert bundle != null;
String name = bundle.getString("Name");
int num = bundle.getInt("Num");
//显示数据
textView.setText(name + "\n" + num);
}
}
运行程序后,结果如下图所示:
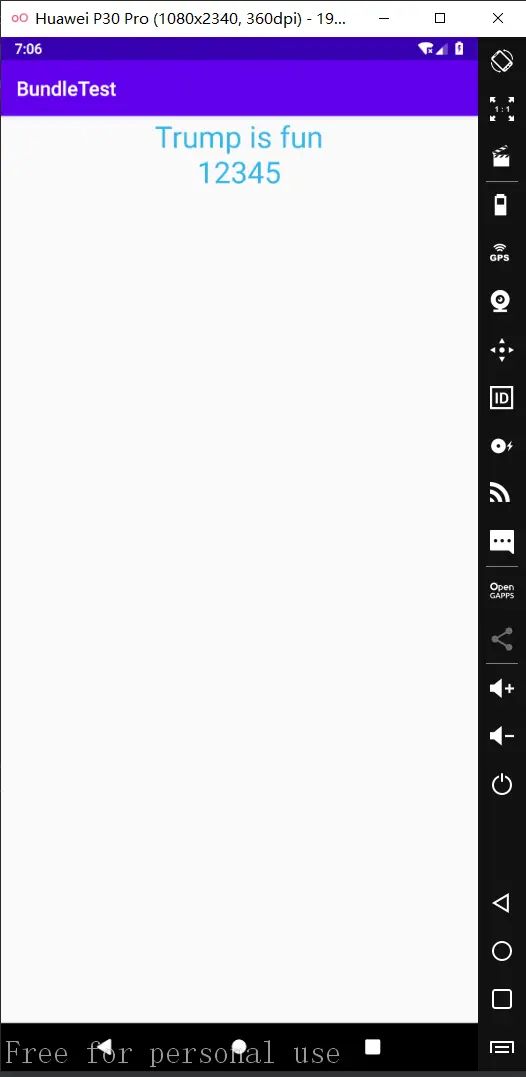
点击Button,结果如下图所示:
② 当传递的参数很多,或者传递一个类的对象时
新建一个JavaBean,将这个类命名为FunPerson,并实现Serializable接口。
package com.example.bundletest;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class FunPerson implements Serializable {
//创建实例变量
private String name;
private int num;
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setNum(int num) {
this.num = num;
}
public int getNum() {
return num;
}
}
修改MainActivity中的代码:
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
//声明控件对象
private Button mButton;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
//获取控件的对象
mButton = findViewById(R.id.button);
//为Button绑定监听器
mButton.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
/**
* 存入数据
*/
FunPerson person = new FunPerson();
//设置数据
String name = "Trump is fun";
int num = 12345;
person.setName("name");
person.setNum(num);
//实例化一个Bundle
Bundle bundle = new Bundle();
//把FunPerson数据放入到Bundle容器中
bundle.putSerializable("Person", person);
Intent intent = new Intent(MainActivity.this, SecondActivity.class);
//把Bundle容器中的数据放到Intent中
intent.putExtras(bundle);
//启动该Intent,实现Activity的跳转
startActivity(intent);
}
});
}
}
修改SecondActivity中的代码:
public class SecondActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
//声明控件对象
private TextView textView;
@SuppressLint("SetTextI18n")
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_second);
//获取控件的对象
textView = findViewById(R.id.text_view);
/**
*读取数据
*/
Intent intent = getIntent();
//从Intent中取出Bundle
Bundle bundle = intent.getExtras();
//获取FunPerson里的数据数据
assert bundle != null;
FunPerson person = (FunPerson)bundle.getSerializable("Person");
assert person != null;
String name = person.getName();
int num = person.getNum();
//显示数据
textView.setText(name + "\n" + num);
}
}
看下运行后的结果:
在Activity to Fragment传递数据时使用Bundle
Activity重新创建时,会重新构建它所管理的Fragment,原先的Fragment的字段值将会全部丢失,但是通过Fragment.setArguments(Bundle bundle)方法设置的bundle会保留下来。所以尽量使用Fragment.setArguments(Bundle bundle)方式来传递参数。
有两种实现方案。
① 方法一:使用Fragment的静态方法newInstance()来传递数据
新建MainActivity:
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private Button mButton;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
mButton = findViewById(R.id.button);
mButton.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
//发送数据
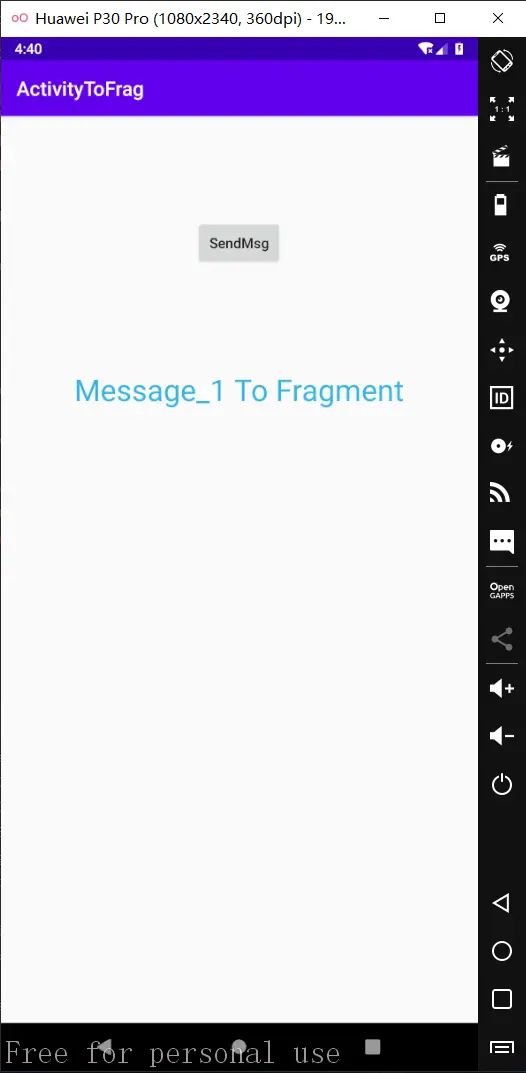
BlankFragment blankFragment = BlankFragment.newInstance("Message_1 To Fragment", "Message_2 To Fragment");
FragmentManager fragmentManager = getSupportFragmentManager();
FragmentTransaction fragmentTransaction = fragmentManager.beginTransaction();
//FrameLayout用于动态更新fragment
fragmentTransaction.replace(R.id.frame_layout, blankFragment);
fragmentTransaction.commit();
}
});
}
}
MainActivity的布局文件如下:
新建一个Fragment:
public class BlankFragment extends Fragment {
// TODO: Rename parameter arguments, choose names that match
// the fragment initialization parameters, e.g. ARG_ITEM_NUMBER
private static final String ARG_PARAM1 = "param1";
private static final String ARG_PARAM2 = "param2";
// TODO: Rename and change types of parameters
private String mParam1;
private String mParam2;
public static BlankFragment newInstance(String param1, String param2) {
BlankFragment fragment = new BlankFragment();
Bundle args = new Bundle();
args.putString(ARG_PARAM1, param1);
args.putString(ARG_PARAM2, param2);
fragment.setArguments(args);
return fragment;
}
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,
Bundle savedInstanceState) {
// Inflate the layout for this fragment
View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_blank, container, false);
TextView textView = view.findViewById(R.id.text_view);
//Fragment获取数据
Bundle bundle = getArguments();
String message = null;
if (bundle != null) {
message = bundle.getString(ARG_PARAM1);
}
textView.setText(message);
return view;
}
}
BlankFragment的布局文件比较简单,就是一个显示用的TextView。
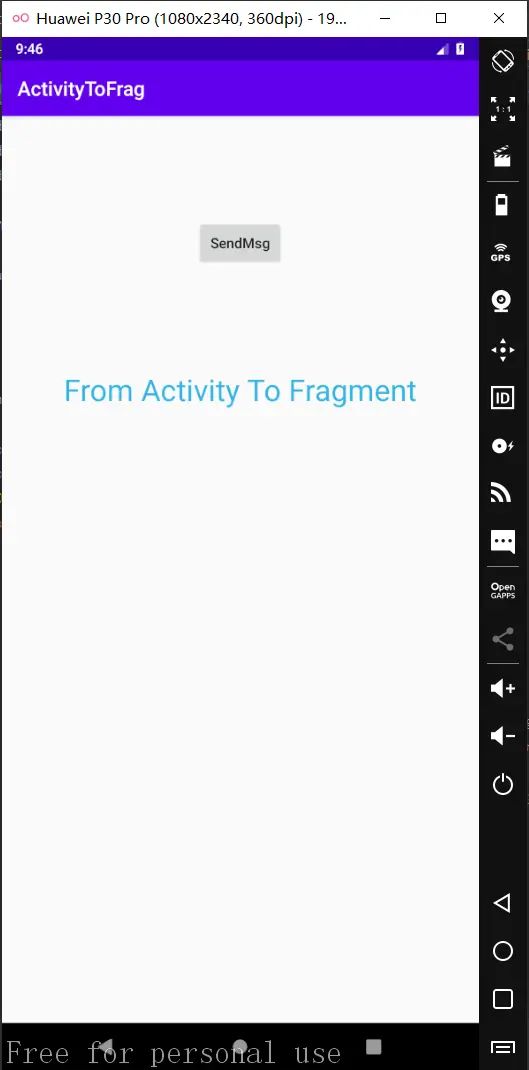
运行程序,点击Button,结果如下图bundle4所示:
② 方法二:
修改MainActivity的代码:
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
Button mButton = findViewById(R.id.button);
mButton.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
//发送数据
ToFragment fragment = new ToFragment();
//新建一个Bundle实例
Bundle bundle = new Bundle();
bundle.putString("data", "From Activity To Fragment");
//将数据传递到Fragment
fragment.setArguments(bundle);
FragmentManager fragmentManager = getSupportFragmentManager();
FragmentTransaction fragmentTransaction = fragmentManager.beginTransaction();
//FrameLayout用于动态更新fragment
fragmentTransaction.replace(R.id.frame_layout, fragment);
fragmentTransaction.commit();
}
});
}
}
新建一个碎片ToFragment,简单起见,就不给新建的碎片弄一个布局文件,直接使用BlankFragment的布局文件,节省时间:
public class ToFragment extends Fragment {
@Nullable
@Override
public View onCreateView(@NonNull LayoutInflater inflater, @Nullable ViewGroup container, @Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
//简单起见,此处直接使用BlankFragment的布局文件
View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_blank, container, false);
TextView textView = view.findViewById(R.id.text_view);
//得到从Activity传来的数据
Bundle bundle = this.getArguments();
String message = null;
if (bundle != null) {
message = bundle.getString("data");
}
textView.setText(message);
return view;
}
}
运行程序后结果如下所示:
3. 在消息机制的Message中使用setData()传递数据时用到Bundle
这个栗子的思路也很简单,点击屏幕,给Activity发送一个Message,传递两个参数,并通过Toast显示出来,最后finish()掉这个Activity。
新建一个Activity:
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
final static int FLAG = 1;
@SuppressLint("HandlerLeak")
public Handler mHandler = new Handler() {
@Override
public void handleMessage(@NonNull Message msg) {
super.handleMessage(msg);
switch (msg.what) {
case FLAG:
//获取Message传递过来的数据
String data1 = msg.getData().getString("text1");
String data2 = msg.getData().getString("text2");
init(data1, data2);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
};
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(new MyView(this, this));
}
public void init(String str1, String str2) {
//将获取的数据Toast出来
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, str1 + '\n' + str2, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
finish();
}
}
在建一个Java类:
@SuppressLint("ViewConstructor")
public class MyView extends View {
private MainActivity activity;
public MyView(Context context, MainActivity activity) {
super(context);
this.activity = activity;
}
@SuppressLint("ClickableViewAccessibility")
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
int x = (int)event.getX();
int y = (int)event.getY();
Rect rect = new Rect(0, 0, 320, 480);
if (rect.contains(x, y)) {
Message message = new Message();
message.what = MainActivity.FLAG;
//新建Bundle的实例
Bundle bundle = new Bundle();
//往Bundle中传入数据
bundle.putString("text1", "Trump want to ban TimTok");
bundle.putString("text2", "Make America great again");
//message利用bundle传递数据
message.setData(bundle);
//用activity中的handler发送消息
activity.mHandler.sendMessage(message);
}
return super.onTouchEvent(event);
}
}
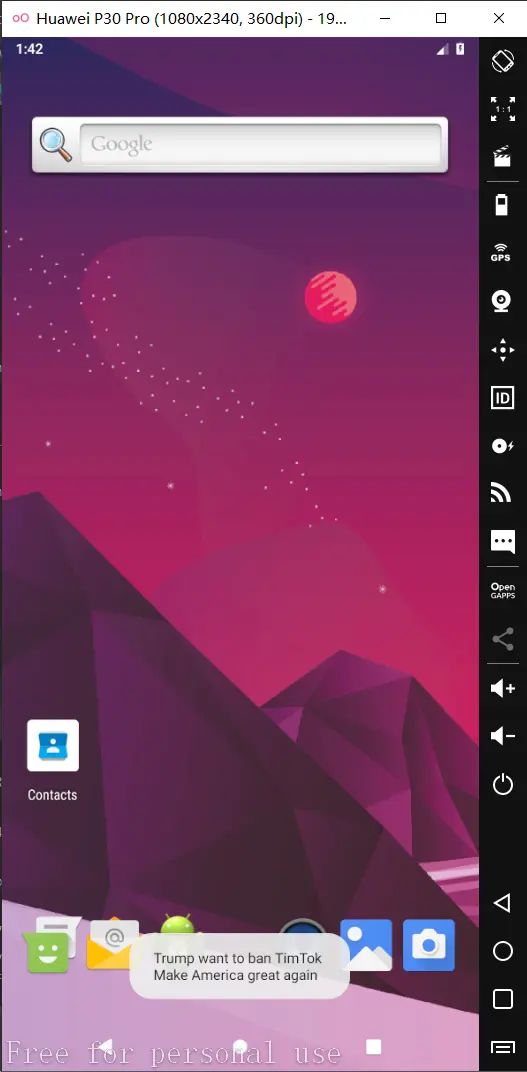
运行程序,得到如下结果:
点击屏幕指定区域,得到如下结果: