GDB用法(一)
预备
测试代码
main.cpp
#include
#include
#include "student.h"
using namespace std;
int add(int a, int b)
{
return a + b;
}
int main()
{
vector v = {1, 3};
Student* s1 = new Student("zz", 20);
Student* s2 = new Student("aa", 23);
Student* s3 = new Student("bb", 26);
int sum = add(s1->GetAge(), s2->GetAge());
// 显示Student信息
cout << s1->ToString() << endl;
cout << s2->ToString() << endl;
cout << s3->ToString() << endl;
delete s1;
delete s2;
delete s3;
return 0;
}
Functions/student.h
#ifndef _STUDENT_H_
#define _STUDENT_H_
#include
#include
class Student
{
private:
std::string m_name;
int m_age;
public:
Student(std::string name, int age);
int GetAge() const;
std::string GetName() const;
std::string ToString() const;
};
#endif
Functions/student.cpp
#include "student.h"
Student::Student(std::string name, int age): m_name(name), m_age(age)
{
}
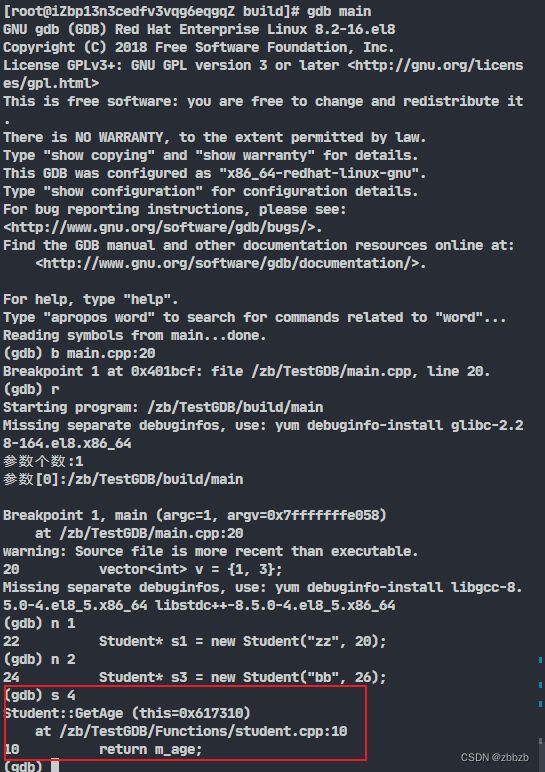
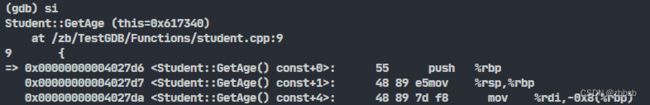
int Student::GetAge() const
{
return m_age;
}
std::string Student::GetName() const
{
return m_name;
}
std::string Student::ToString() const
{
return "学生姓名: " + m_name + "学生年纪: " + std::to_string(m_age);
}
CMakeLists.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.10)
project(main)
SET(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "${CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS} -g -Wall")
INCLUDE_DIRECTORIES(./)
INCLUDE_DIRECTORIES(./Functions)
AUX_SOURCE_DIRECTORY(./ MAIN)
AUX_SOURCE_DIRECTORY(./Functions FUNCTION)
add_executable(main ${MAIN} ${FUNCTION})
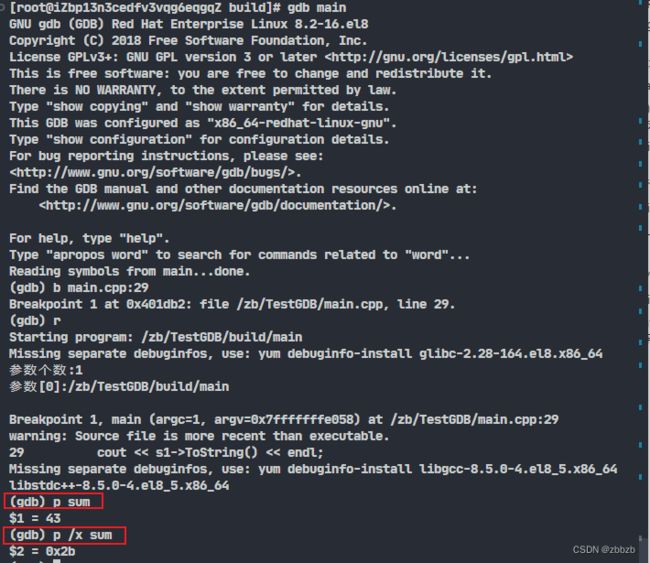
(gdb) 启动
gdb 可执行文件
后面带可执行文件, gdb会把可执行文件的符号表加载到gdb中
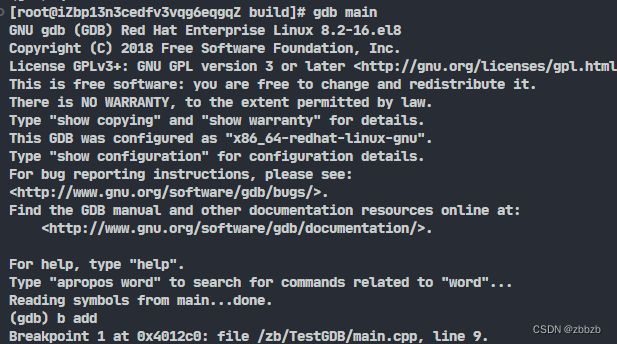
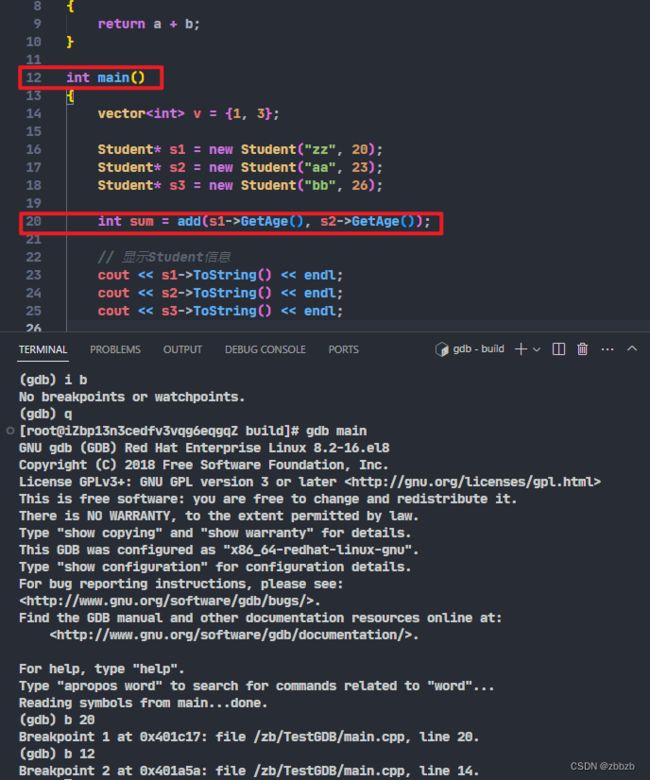
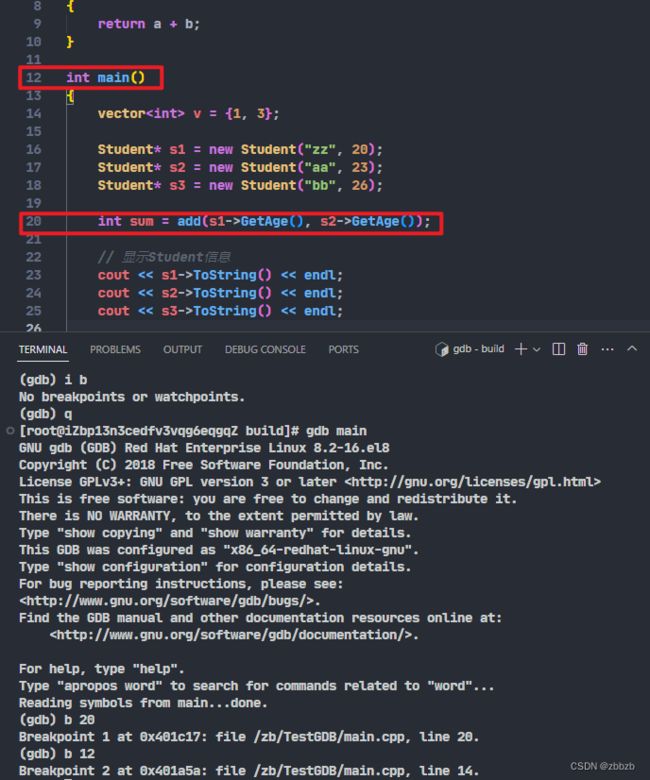
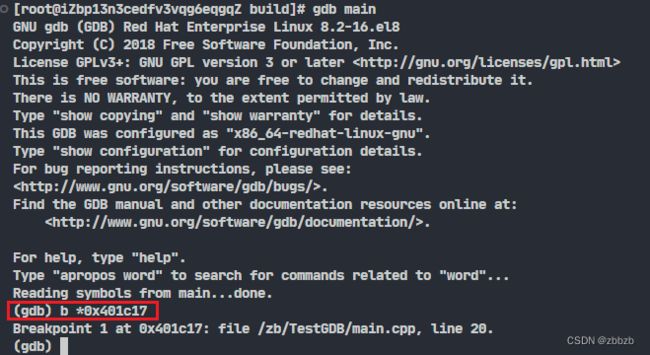
(break/b) 设置断点
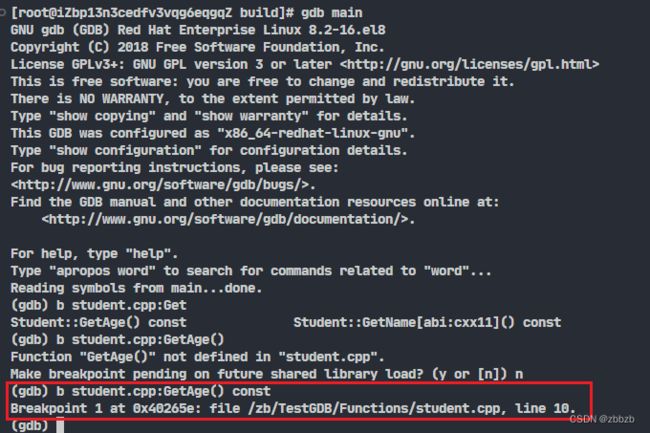
break 函数名
break 行号
断点是源程序中行号, 注意编译选项不要优化代码, 不然行号和优化后的代码对应不上
break 文件名: 行号
break 文件名:函数名
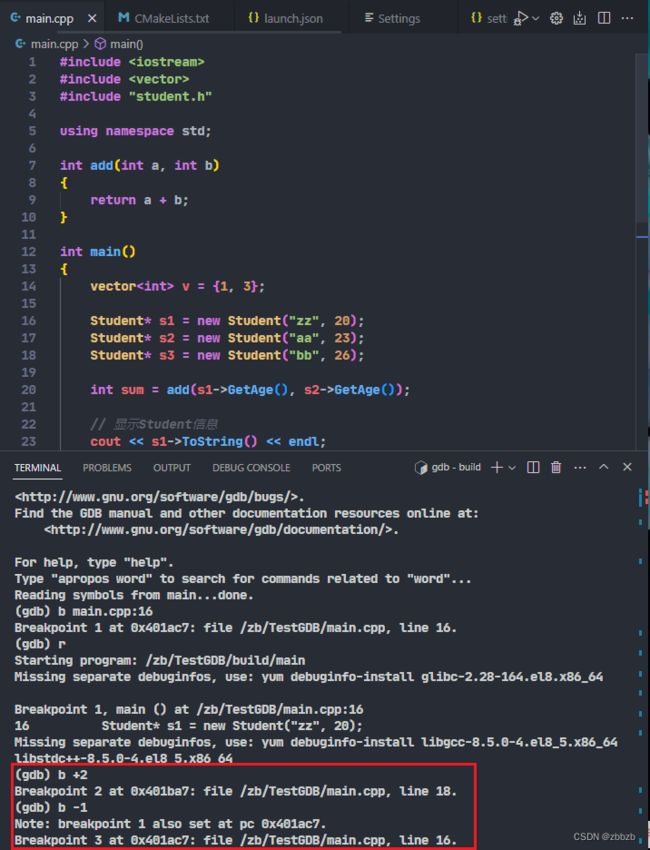
break + 偏移量
break - 偏移量
在运行时, 进入断点后, 使用偏移量, 对断点行号加/减多少行
break *地址
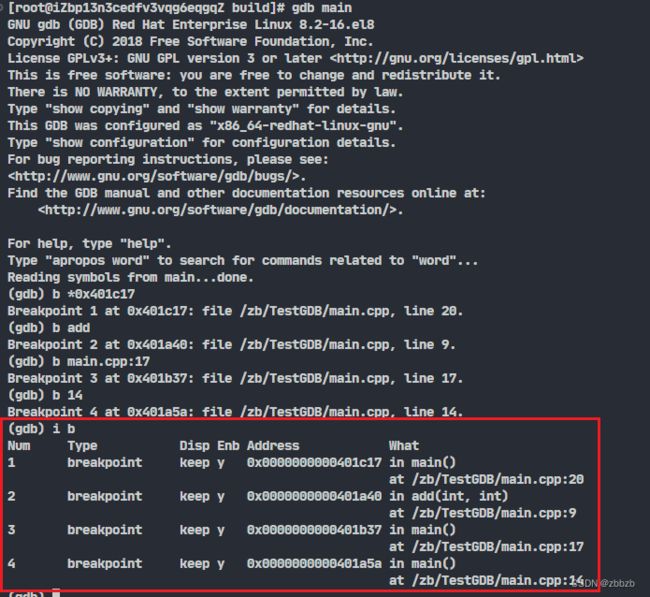
(info break/i b) 展示所有设置的断点
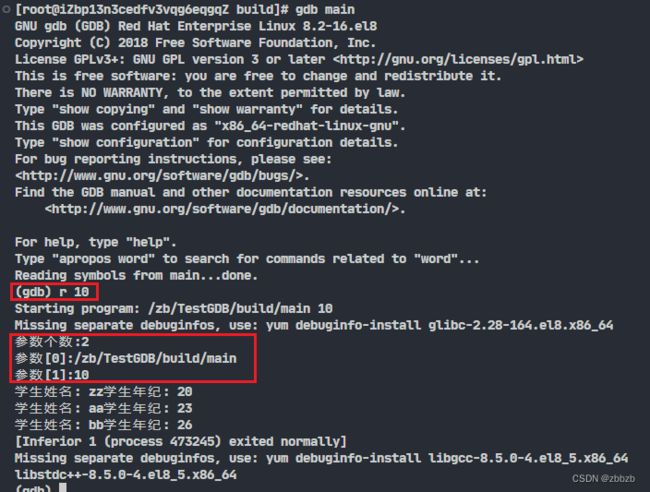
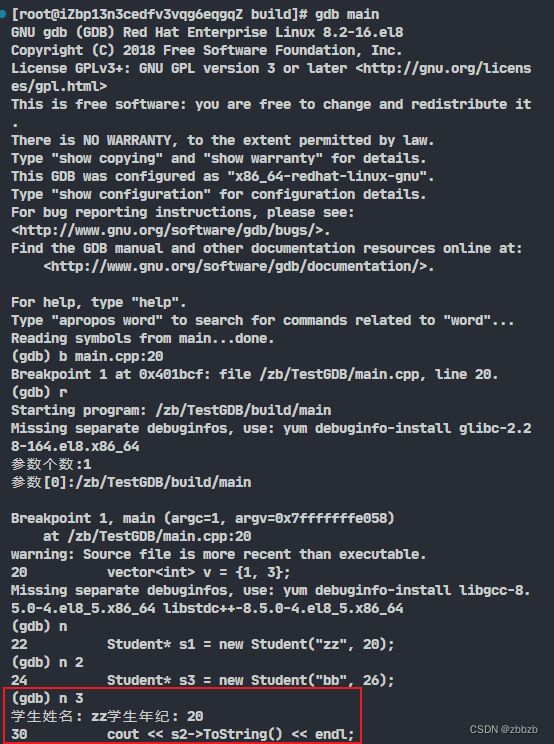
(run/r) 运行
run 参数
run后面可以带参数, 也就是给运行程序加参
修改main.cpp
#include
#include
#include "student.h"
using namespace std;
int add(int a, int b)
{
return a + b;
}
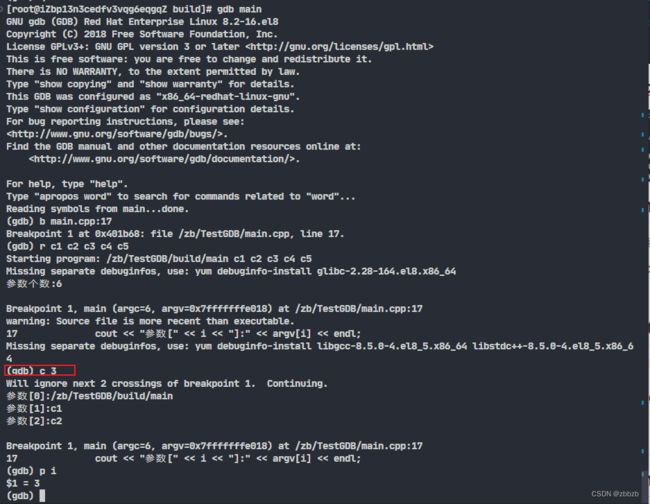
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
cout << "参数个数:" << argc << endl;
for(int i = 0; i < argc; i++)
{
cout << "参数[" << i << "]:" << argv[i] << endl;
}
vector v = {1, 3};
Student* s1 = new Student("zz", 20);
Student* s2 = new Student("aa", 23);
Student* s3 = new Student("bb", 26);
int sum = add(s1->GetAge(), s2->GetAge());
// 显示Student信息
cout << s1->ToString() << endl;
cout << s2->ToString() << endl;
cout << s3->ToString() << endl;
delete s1;
delete s2;
delete s3;
return 0;
}
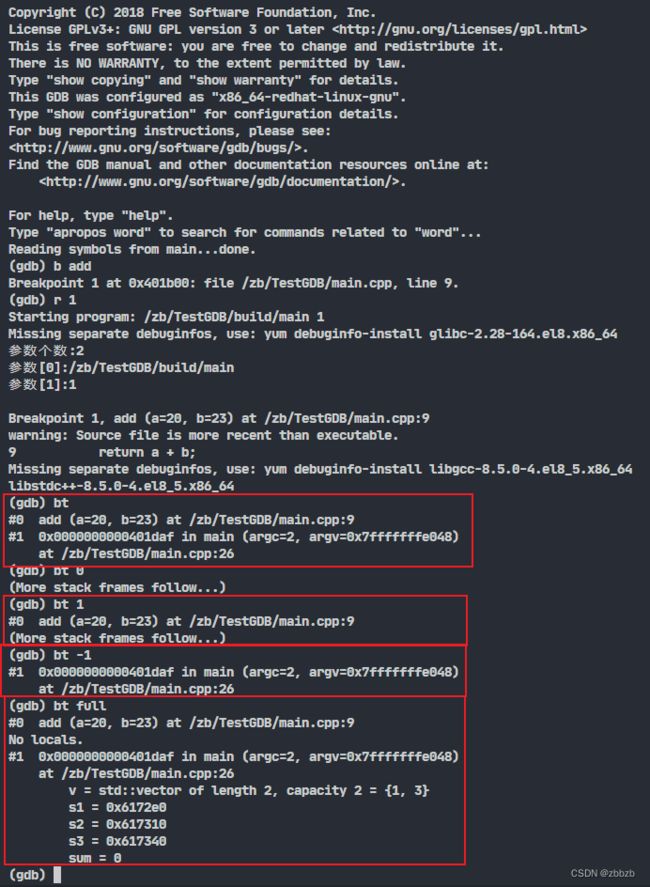
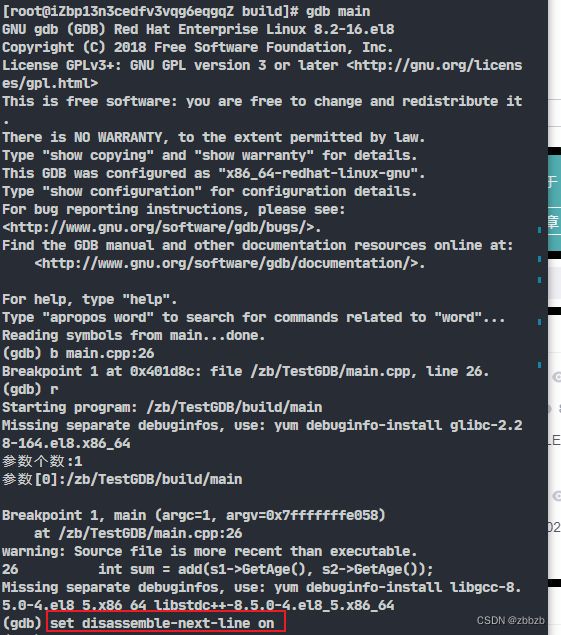
(backtrace/bt) 显示栈帧
bt // 显示所有栈帧
bt N //显示开头N个栈帧
bt -N // 显示最后N个栈帧
bt full // 不仅显示栈帧, 还显示局部变量
bt full N
bt full -N
(print/p) 显示变量
p /格式 变量
| 格式 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| x | 显示为十六进制数 |
| d | 显示为十进制数 |
| u | 显示为无符号十进制数 |
| o | 显示为八进制数 |
| t | 显示为二进制数, t的由来是two |
| a | 地址 |
| c | 显示为字符(ASCII) |
| f | 浮点小数 |
| s | 显示为字符串 |
| i | 显示为机器语言(仅在显示内存的x命令中可用) |
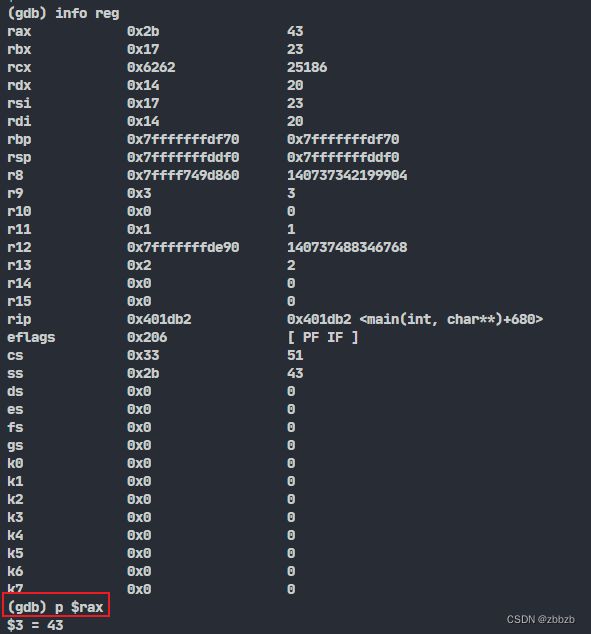
(info registers/info reg) 显示寄存器
寄存器名前面加$, 可现实各个寄存器的内容
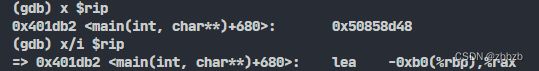
(x) 显示内存的内容
x/NFU ADDR
// ADDR为希望显示的地址
// N为重复次数
// F为前面显示变量中的格式(x, d, u, o, t, a, c, f, s, i)
// U为单位
| U代表单位 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| b | 字节 |
| h | 半字(2字节) |
| w | 字(4字节/默认值) |
| g | 双字(8字节) |
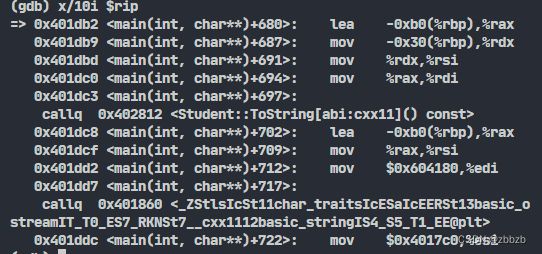
x/i 为显示汇编指令
从rip所指地址开始的10条指令(i)
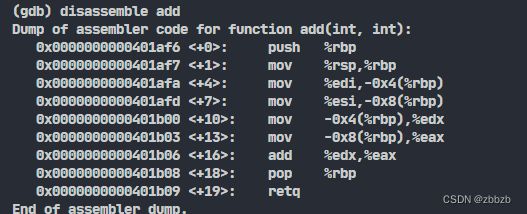
(dissassemble/disas) 反汇编
dissassemble [FUNCTION] // 反汇编当前函数
dissassemble 开始地址 结束地址 // 反汇编从开始地址到结束地址之前的部分
(next/n) 单步执行, 不会进入函数内部执行
n 行数
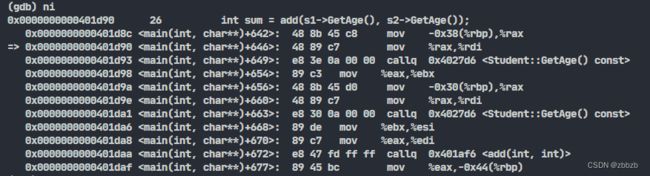
(nexti/ni) 汇编指令的单步执行
需要设置set disassemble-next-line on, 让gdb打印出下一条要执行的汇编代码
(step/s) 单步执行, 会进入函数内部执行
s 行数
(stepi/si) 汇编指令的单步执行
(continue/c) 继续执行
c 次数
后面加次数是指定次数忽略断点, c 5则5次遇到断点不停止, 第6次遇到断点时才暂停执行
跳过了参数0, 参数1,参数2, 3次断点, 第4次断点时暂停执行
(watch) 监视点
// 软件观察点
watch [options] <表达式> // 表达式发生变化时暂停运行
// 这里的表达式是指常量或变量
| 选项(options) | 表达式 |
|---|---|
| -l/-location | 指定只在被监视表达式的特定位置暂停程序的执行,能够避免多线程环境下的停顿问题 |
| -r/-read | 可以指定只在被监视表达式被读取时停止程序的执行 |
| -w/-write | 只在被监视表达式被修改时停止程序的执行 |
| -c | 在被监视变量被修改的时候,停止后继续执行的次数。如果指定了count,则每次监视到变量修改时计数器减1,当计数器为0时,程序会停止执行 |
| -s | 可以指定watch只在指定变量或表达式的值满足某个条件时停止程序的执行 |
// 硬件观察点
awatch <表达式> // 表达式被访问, 改变时暂停运行
rwatch <表达式> // 表达式被访问时暂停运行
设置监视点会降低速度
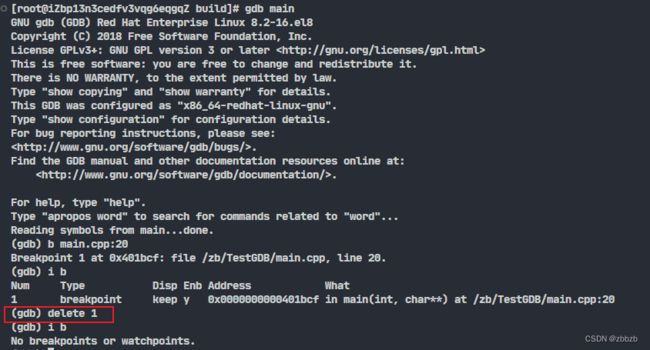
(delete/d) 删除断点和监视点
delete 编号
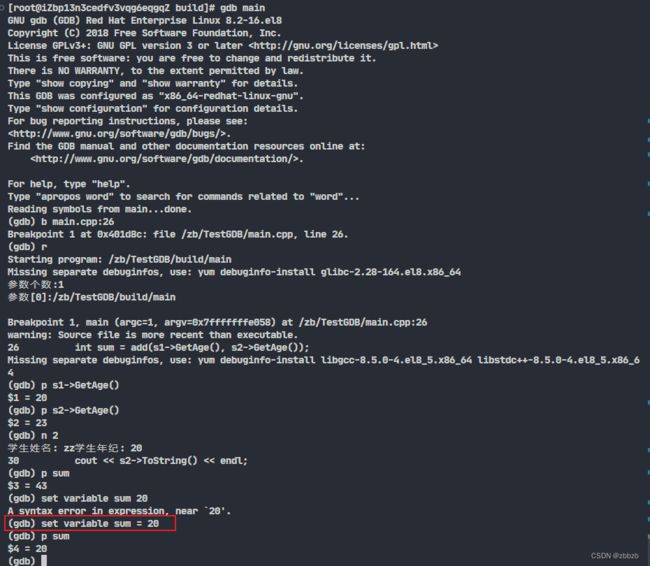
(set variable) 改变变量的值
set variable <变量> = <表达式>
可以在运行时随意修改变量的值
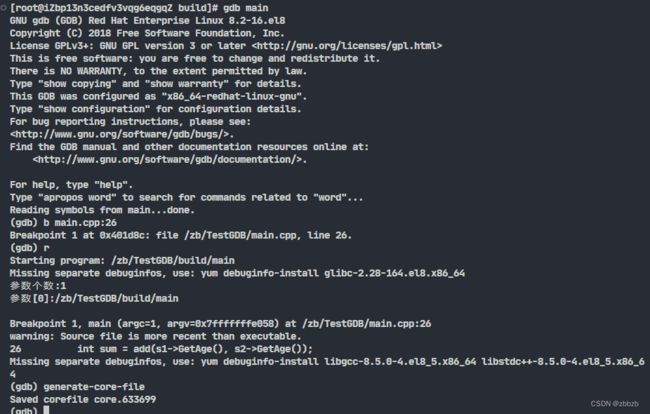
(generate-core-file) 生成内核转储文件
generate-core-file
生成在当前目录下
![]()
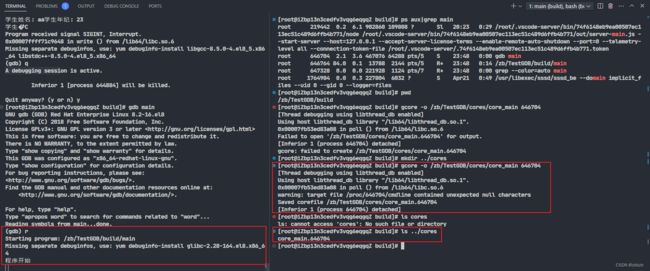
(gcore) linux工具生成内核转储文件
gcore -o 保存路径 pid
修改main.cpp
#include
#include
#include "student.h"
using namespace std;
int add(int a, int b)
{
return a + b;
}
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
std::cout << "程序开始" << std::endl;
while(true)
{
// cout << "参数个数:" << argc << endl;
// for(int i = 0; i < argc; i++)
// {
// cout << "参数[" << i << "]:" << argv[i] << endl;
// }
vector v = {1, 3};
Student* s1 = new Student("zz", 20);
Student* s2 = new Student("aa", 23);
Student* s3 = new Student("bb", 26);
int sum = add(s1->GetAge(), s2->GetAge());
// 显示Student信息
// cout << s1->ToString() << endl;
// cout << s2->ToString() << endl;
// cout << s3->ToString() << endl;
delete s1;
delete s2;
delete s3;
}
return 0;
}
从命令行直接生成内核转储文件
这里的路径需要是存在的
也可以 脚本每个多久生成一次core文件