逻辑斯蒂回归 - 多项式回归
文章目录
-
- 一、预期结果
- 二、实验步骤
-
- 1)生成数据
- 2)算法实现
-
- 算法步骤:
-
- 1、获取规格化数据(系数矩阵、标签)
- 2、梯度上升法拟合系数
- 3、画图,看看拟合的准不准
- 结果
- 完整代码实现:
一、预期结果
训练一个基于逻辑斯蒂回归的机器学习模型,它能够训练出一条二次曲线,实现二分类问题。他不是线性的,而是多项式的。
二、实验步骤
1)生成数据
首先,我们预期得到的曲线是一个二次曲线,它的方程是这样的:
y = (x - 1)**2 - 1
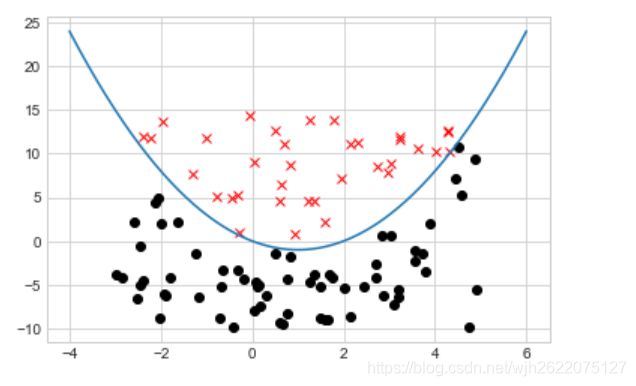
那么我们根据这个曲线生成一些数据,上下被分为两个类别
得到大概这样一张二分类图

代码实现:
import numpy as np
import random
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.style.use("seaborn-whitegrid")
# 数据有三维:(x,y,类别)
def fun(x): # 提前建立的二次曲线
y = (x - 1)**2 - 1
return y
def getData():
data = []
for i in range(100):
x = random.uniform(-3, 5)
# print(x)
y = fun(x)
alpha = random.uniform(-5, 5)
data.append([x, y + alpha, 0 if alpha < 0 else 1])
data = np.array(data)
return data
def draw(xlabel, ylabel, label):
index0 = np.argwhere(label == 0) # 获取值为0的数据的索引
index1 = np.argwhere(label == 1)
plt.plot(xlabel[index0], ylabel[index0], 'o', color='black')
plt.plot(xlabel[index1], ylabel[index1], 'x', color='red')
xs = np.linspace(-4, 6, 1000)
plt.plot(xs, fun(xs))
plt.show()
def main():
data = getData()
xlabel, ylabel, label = data[:, 0], data[:, 1], data[:, 2]
draw(xlabel, ylabel, label)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
想到另一种生成数据的方式,给出随机点,然后根据曲线划分类别,而不是在曲线上下生成点。
data = []
for i in range(1000):
x = random.uniform(-3, 5)
y = random.uniform(-10, 15)
data.append([x, y, 0 if fun(x) > y else 1])
data = np.array(data)
2)算法实现
下面就开始我们的逻辑斯谛回归算法进行回归拟合。
几个关键词:
1、sigmoid函数
2、梯度上升法
算法步骤:
1、获取规格化数据(系数矩阵、标签)
2、梯度上升法拟合系数
3、画图,看看拟合的准不准
结果
如图所示,蓝色的曲线为我们拟合到的二次曲线,而红色则为我们先前假定的曲线 在数据点不算很多的情况下,曲线也能基本拟合。
得到的方程为:y = 1.001488x^2 - 1.872946x + - 0.295519 和实际的方程y = x^2 - 2x相差不是很多。

完整代码实现:
import numpy as np
import random
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.style.use("seaborn-whitegrid")
# 数据有三维:(x,y,类别)
def fun(x): # 提前建立的二次曲线
y = (x - 1)**2 - 1
return y
def getData():
data = []
for i in range(100):
x = random.uniform(-3, 5)
y = random.uniform(-10, 15)
data.append([x, y, 0 if fun(x) > y else 1])
data = np.array(data)
return data
def draw(xlabel, ylabel, label):
index0 = np.argwhere(label == 0) # 获取值为0的数据的索引
index1 = np.argwhere(label == 1)
plt.plot(xlabel[index0], ylabel[index0], 'o', color='black')
plt.plot(xlabel[index1], ylabel[index1], 'x', color='red')
xs = np.linspace(-4, 6, 1000)
plt.plot(xs, fun(xs))
plt.show()
return
def sigmoid(inX):
return 1.0 / (1 + np.exp(-inX))
def gradAscent(dataMatIn, classLabels):
dataMatrix = np.mat(dataMatIn).transpose()
labelMat = np.mat(classLabels).transpose()
m, n = np.shape(dataMatrix)
alpha = 0.0001
maxCycles = 5000
weights = np.ones((n, 1))
# print(np.shape(dataMatrix)) # 100, 4
# print(np.shape(weights)) # 4, 1
for k in range(maxCycles):
h = sigmoid(dataMatrix*weights)
error = (labelMat - h) # 100, 1
weights = weights + alpha * dataMatrix.transpose() * error
return weights
def fun_model(weights, x):
return (-weights[0]*x*x-weights[1]*x) / weights[2]
def drawModel(weight, xlabel, ylabel, label): # 绘制模型训练出来的图
xs = np.linspace(-4, 6, 1000)
index0 = np.argwhere(label == 0) # 获取值为0的数据的索引
index1 = np.argwhere(label == 1)
plt.plot(xlabel[index0], ylabel[index0], 'o', color='black')
plt.plot(xlabel[index1], ylabel[index1], 'x', color='red')
plt.plot(xs, fun_model(weight, xs), color='blue') # 蓝色为训练出来的曲线
plt.plot(xs, fun(xs), color='red') # 红色为假定的曲线
plt.show()
return
def getEquation(weight): # 根据权重得到方程
x1 = -weight[0]/weight[2]
x2 = -weight[1]/weight[2]
x3 = -weight[3]/weight[2]
equation = "y = %fx^2 %s %fx + %s %f"%(x1, '+' if x2 >= 0 else '-', abs(x2), '+' if x3 >= 0 else '-', abs(x3))
return equation
def main():
data = getData()
xlabel, ylabel, label = data[:, 0], data[:, 1], data[:, 2]
# draw(xlabel, ylabel, label) # 绘制图形
xx = data[:, 0] ** 2
one = np.ones(len(xx))
new = np.array([xx, xlabel, ylabel, one])
weights = gradAscent(new, label)
weights = np.asarray(weights) # np.matrix类型真的是有大坑
# print(weights[0][0][0])
weight = []
for each in weights:
weight.append(each[0])
drawModel(weight, xlabel, ylabel, label)
equation = getEquation(weight)
print(equation)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()