JavaIO流
JavaIO流
- 一、概念
- 二、File类
- 三、File类的使用
-
- 1、File文件/文件夹类的创建
- 2、File类的获取操作
- 3、File类判断操作 - boolean
- 4、File类对文件/文件夹的增删改
- 5、File类的获取子文件夹以及子文件的方法
- 四、Java中IO流多种维度的维度
-
- 1、按照流向 - Java程序
- 2、按照流的大小分类
- 3、按照流的功能分类
- 五、JavaIO流的四大基类
-
- 1、InputStream
- 2、OutputStream
- 3、Reader
- 4、Writer
- 5、补充知识点——方法递归
- 六、JavaIO流中的常用实现类
-
- 1、节点流
- 2、处理流
一、概念
Java Input/Output,一般情况指的是Java操作一些外部数据时,使用IO流的形式进行操作,外部数据主要包括文件、网络等等。
二、File类
JavaIO既可以操作文件外部数据,还可以操作网络端口这种外部数据,如果Java要操作文件外部数据,必须要借助一个类File文件对象类。
File类是Java中对文件/文件夹的抽象表示,通过这个File类,我们可以将操作系统本地的一个文件/文件夹加载到Java程序当中,随后通过File对象可以对文件进行增删改查等操作。
File类只能操作文件的外部内容、而文件当中有哪些数据,这个操作File类做不到。
三、File类的使用
1、File文件/文件夹类的创建
根据全路径创建
File file = new File("d:" + File.separator + "桌面" + File.separator + "a");
根据父子路径创建
File file = new File("d:\\桌面" ,"a");
根据父子路径创建,只不过父路径也是File对象
File file = new File(new File("d:\\桌面") ,"a");
2、File类的获取操作
//在eclipse中,因为创建的时Java项目,Java项目中所有的相对路径,指的都是项目名下的某个路径 而非Java源文件的同级路径
File file1 = new File("a/a.txt");
//获取文件名 路径最后一个文件/文件夹的名字
String fileName = file.getName();
System.out.println(fileName);
//获取文件的父路径 取决于你再构建File对象时有没有传入父路径
String parent = file.getParent();
System.out.println(parent);
//获取文件的路径 ---传入的路径
String path = file.getPath();
System.out.println(path);
//获取文件的绝对的路径--传入路径没有关系的
String absolutePath = file1.getAbsolutePath();
System.out.println(absolutePath);
3、File类判断操作 - boolean
System.out.println(file1.exists());//判断路径是否存在
System.out.println(file1.isFile());//判断是否是文件
System.out.println(file1.isDirectory());//判断是否是目录
System.out.println(file1.isHidden());//判断是否是隐藏文件
System.out.println(file1.canRead());//可读
System.out.println(file1.canWrite());//可写
System.out.println(file1.canExecute());//可执行
4、File类对文件/文件夹的增删改
创建:
-
创建文件createNewFile():要求父目录必须存在
-
创建文件夹mkdir()创建单层目录/mkdirs()创建多层目录
删除:
- delete()–如果是目录,目录必须空目录
修改:
- renameTo(File):boolean
boolean mkdir = file1.mkdirs();//创建文件夹
System.out.println(mkdir);
boolean creatNewFile = file1.createNewFile();//创建文件
System.out.println(creatNewFile);
boolean delete = file1.delete();
System.out.println(delete);
//重命名要求两个路径必须在同一个路径下
boolean result = file1.renameTo(new File("KK"));
System.out.println(result);
5、File类的获取子文件夹以及子文件的方法
listFiles()
list():返回指定目录下的下一级的文件或者文件夹
四、Java中IO流多种维度的维度
1、按照流向 - Java程序
输入流 Input/Reader
输出流 Output/Writer
2、按照流的大小分类
字节流:Stream——什么样的数据都可以处理
字符流:Reader/Writer——只能处理纯文本类型的数据
3、按照流的功能分类
节点流:直接对接到数据源上的流
常用的节点流:文件流、数组流、网络流
处理流:无法直接对接到数据源上,而是包装了节点流,在节点流基础之上提供了更加强大的功能
五、JavaIO流的四大基类
Javaio流中所有的流都有四个顶尖父类,四个顶尖父类是四个抽象类,四个抽象类当中封装了和流有关的很多的公用方法。
1、InputStream
Java中所有字节输入流的顶尖父类 —— 一个字节一个字节的读取文件中的数据
read:int——读取的字节,全部读取完成后返回-1
available:int——可利用的字节数,还能读取的字节数
close()——关闭IO流,任何IO流都需要手动关闭
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
/**
* InputStream:是一个字节输入流
*/
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
InputStream is = null;
try {
is = new FileInputStream(new File("kl/a.txt"));
//读取数据源的一个字节,read每一次读取完成,下一次再进行读取,基于上一次的结果向后读取
int read = is.read();
System.out.println(read);
//返回值,如果是read()方法,代表的是每一次读取完成的字节的值,read(byte[])的话返回值不做研究
//不管什么情况下,read的返回值一旦为-1,那么代表数据与没数据了
int read2 = is.read();
System.out.println(read2);
byte[] array = new byte[12];
int read3 = is.read(array);
String string = new String(array,"UTF-8");
System.out.println(string);
//字节流中可以利用的字节数有多少
int available = is.available();
System.out.println(available);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(is!=null) {
try {
is.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
2、OutputStream
Java中所有字节输出流的顶尖父类
write:写出的字节
close()
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream;
/**
* OutputStream基类提供的常用方法:
* write(int字节)
*/
public class Demo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
OutputStream os = null;
try {
os = new FileOutputStream(new File("kl/a.txt"));
os.write(97);//a 覆盖写
os.write("中国加油".getBytes("UTF-8"));//中国加油
//os.write("中国加油".getBytes("UTF-8"),0,6);//中国
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(os != null) {
try {
os.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
复制照片到指定路径
package com.nuc.kl.file.io;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
/**
*
* @author 冰霜中的独舞
* @version 2023年7月7日 上午9:15:11
*
*/
public class FileCopy {
public static void main(String[] args) {
InputStream is = null;
OutputStream os = null;
try {
is = new FileInputStream(new File("D:\\2023PracticalTraining\\software\\workspace\\eclipseworkspace\\java-study-619\\picture\\c.png"));
os = new FileOutputStream(new File("D:\\2023PracticalTraining\\software\\workspace\\eclipseworkspace\\java-study-619\\picture\\d.png"));
//byte[] buf = new byte[1024 * 1024];
int read;
while((read = is.read()) != -1) {
os.write(read^5);
}
// while((read = is.read(buf)) != -1) {
// os.write(buf);
// }
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(os != null) {
try {
os.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(is != null) {
try {
is.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
/**
* 循环读取加密文件的1024个字节,然后对下一个字节进行解密操作^5
* 输入流(加密文件) 输出流(解密文件路径)
* 每隔1024个字节,对下一个字节进行^5运算进行加密
*/
public class Homework {
public static void main(String[] args) {
InputStream is =null;
OutputStream os =null;
try {
is = new FileInputStream(new File("D:\\Desktop\\a.png"));
os = new FileOutputStream(new File("D:\\Desktop\\b.png"));
//循环读取is中的数据,一次读取1024个字节
byte[] by = new byte[1024];
while(is.read(by) != -1) {
os.write(by);
int r = is.read()^5;
os.write(r);
}
System.out.println("解密完成!");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(os != null) {
try {
os.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(is != null) {
try {
is.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
3、Reader
Java中所有字符输入流的顶尖父类
因为要根据编码集进行数据的读取,一次要读取一个字符,而一个字符对应了多个字节。编码集只有纯文本才有编码集。
- read()
- close()
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.Reader;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* Read的常用方法
* close()
*/
public class Demo03 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Reader r = new FileReader(new File("kl/a.txt"));
int read = r.read();
System.out.println(read);
int read1 = r.read();
System.out.println(read1);
char c = (char)read1;
System.out.println(c);
char[] buf = new char[10];
r.read(buf);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(buf));
System.out.println(buf);
r.close();
}
}
a中国加油
4、Writer
Java中所有字符输出流的顶尖父类
- write
- close —— 底层调用了flush
- flush —— 字符流一次输出多个字节,先把多个字节缓存起来,直到遇到flush方法才会把缓存起来的结果输出
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.Writer;
public class Demo04 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Writer w = new FileWriter(new File("kl/a.txt"));
w.append('a');
w.write("zs12333");
w.write("ls12333");
w.flush();
w.close();
}
}
5、补充知识点——方法递归
方法迭代其实就是一种循环,只不过这个循环比较特殊,循环我们只知道循环的终止条件,而循环的次数我们是不太清楚的
使用方法:
1、将需要重复性执行的代码抽取到一个方法中
2、方法中需要对重复性执行的代码进行改造,有一个递归入口(自己调用自己的一个逻辑)、递归出口
/**
* 使用方法递归计算 ∑100
*/
public class RecursionStudy {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num = 0;
//for循环
for (int i = 0; i <= 100; i++) {
num = i + num;
}
System.out.println(num);
//迭代
System.out.println(sum(100));
}
public static int sum(int num) {
if(num == 1) {
return 1;
}else {
return num + sum(num-1);
}
}
}
六、JavaIO流中的常用实现类
1、节点流
直接连接数据源的流
-
数组流:连接的数据源是一个数组
- 字节数组流
- ByteArrayInputStream——字节数组输入流
- ByteArrayOutputStream——字节数组输出流-----输出的目的地是一个字节数组,只不过这个字节数组不需要我们创建传递,因为这个流底层封装了一个字节数组用于接收字节数据的输出
import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream; import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; public class Dmeo01 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException { ByteArrayInputStream basi =new ByteArrayInputStream("中国加油".getBytes("UTF-8")); byte[] by = new byte[12]; basi.read(by); System.out.println(new String(by,"UTF-8")); ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); System.out.println(baos); baos.write("中国加油!".getBytes("UTF-8")); System.out.println(baos); String string = baos.toString("UTF-8"); System.out.println(string); } }- 字符数组流
- CharArrayReader——字符数组输入流
- CharArrayWriter——字符数组输出流
- 字节数组流
-
文件流:连接的数据源是一个文件
- 字节流——什么文件都可以处理
- FileInputStream
- new FileInputStream(File)
- new FileInputStream(String path)
- 【注意】:文件必须存在,不存在报错
- FileOutputStream
- new FileOutputStream(File|String)——默认是覆盖写,因为boolean append默认为false
- new FileOutputStream(File|String,boolean append)——追加写
- 【注意】:文件可以不用提前存在,如果文件不存在会自动创建
- FileInputStream
- 字符流——只能处理纯文本文件
- FileReader
- new FileReader(String|File)
- FileWriter
- new FileWriter(File|String)—默认是覆盖写
- new FileWriter(File|String,boolean append)
- 写出数据之后,必须flush()刷新
- FileReader
- 字节流——什么文件都可以处理
-
网络流
2、处理流
处理流:对节点流进行包装,提供一些更加强大的功能——处理速度快。
- 缓冲流:缓冲流包装另外一个流,缓冲流内部维护一个缓冲池,使用了缓冲流,一次读取多个字节、多个字符到缓冲流的内部的缓冲池当中。—— 不管是字节的还是字符的缓冲流,一定要flush。
- 字节缓冲流 —— 缓冲了一个8192的字节数组
- BufferedInputStream
- BufferedOutputStream
- 字符缓冲流
- BufferedReader——提供了一个特殊的方法:readLine()
- BufferedWriter——提供了一个特殊的方法:newLine()
- 字节缓冲流 —— 缓冲了一个8192的字节数组
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.Writer;
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("wc.txt"));
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("wc_n.txt"));
String line = null;
while((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
line = line.toUpperCase();
bw.write(line);
bw.newLine();
bw.flush();
}
bw.close();
br.close();
System.out.println("输出完成!");
}
}
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.Writer;
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("wc.txt"));
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("wc_n.txt"));
String line = null;
while((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
line = line.toUpperCase();
bw.write(line);
bw.newLine();
bw.flush();
}
bw.close();
br.close();
System.out.println("输出完成!");
}
}
-
字节转字符流:以指定的编码集将一个字节流转换为字符流进行处理,加快我们的处理速度—纯文本类型的IO流有效
- InputStreamReader(InputStream,charset)
- OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream,charset)
-
对象流——只有字节流
-
Java中的序列化(Java对象转换成二进制编码)和反序列化(Java二进制编码转换为Java对象)机制的问题
-
序列化和反序列化需要用到Java的两个IO流
- ObjectInputStream
- ObjectOutputStream
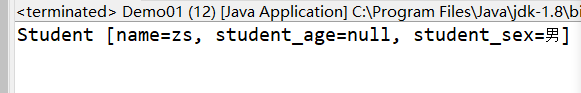
import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.ObjectInputStream; import java.io.ObjectOutputStream; public class Demo01 { public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException, IOException, ClassNotFoundException { /** * 序列化的代码 */ // Student s = new Student("zs",20,"男"); // ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("student.txt")); // oos.writeObject(s); // oos.flush(); // oos.close(); // System.out.println("对象序列化完成!"); /** * 反序列化的代码 */ ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("student.txt")); Object object = ois.readObject(); System.out.println(object); } } -
我们的Java对象如果想要序列化,那么必须得声明它能序列化,Java中对象默认不具备序列化的能力。如果想要具备,那么必须实现两个接口其中一个即可,序列化就是把对象的属性值转换成为二进制
- Serializable:static或者transient修饰的属性不会序列化
import java.io.Externalizable; import java.io.Serializable; import java.util.Objects; /** * JavaBean:只要私有化的属性和公开的get和set方法还有hashCode、equals、toString以及构造器 */ public class Student implements Serializable { private String name; private transient Integer student_age; private String student_sex; public Student() { super(); } public Student(String name, Integer student_age, String student_sex) { super(); this.name = name; this.student_age = student_age; this.student_sex = student_sex; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public Integer getStudent_age() { return student_age; } public void setStudent_age(Integer student_age) { this.student_age = student_age; } public String getStudent_sex() { return student_sex; } public void setStudent_sex(String student_sex) { this.student_sex = student_sex; } @Override public int hashCode() { return Objects.hash(name, student_age, student_sex); } @Override public boolean equals(Object obj) { if (this == obj) return true; if (obj == null) return false; if (getClass() != obj.getClass()) return false; Student other = (Student) obj; return Objects.equals(name, other.name) && Objects.equals(student_age, other.student_age) && Objects.equals(student_sex, other.student_sex); } @Override public String toString() { return "Student [name=" + name + ", student_age=" + student_age + ", student_sex=" + student_sex + "]"; } }- Externalizable:必须重写两个方法,一个序列化写出的方法,一个反序列化读取的方法
import java.io.Externalizable; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.ObjectInput; import java.io.ObjectOutput; import java.io.Serializable; import java.util.Objects; /** * JavaBean:只要私有化的属性和公开的get和set方法还有hashCode、equals、toString以及构造器 */ public class Student implements Externalizable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; private String name; private transient Integer student_age; private String student_sex; public Student() { super(); } public Student(String name, Integer student_age, String student_sex) { super(); this.name = name; this.student_age = student_age; this.student_sex = student_sex; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public Integer getStudent_age() { return student_age; } public void setStudent_age(Integer student_age) { this.student_age = student_age; } public String getStudent_sex() { return student_sex; } public void setStudent_sex(String student_sex) { this.student_sex = student_sex; } @Override public int hashCode() { return Objects.hash(name, student_age, student_sex); } @Override public boolean equals(Object obj) { if (this == obj) return true; if (obj == null) return false; if (getClass() != obj.getClass()) return false; Student other = (Student) obj; return Objects.equals(name, other.name) && Objects.equals(student_age, other.student_age) && Objects.equals(student_sex, other.student_sex); } @Override public String toString() { return "Student [name=" + name + ", student_age=" + student_age + ", student_sex=" + student_sex + "]"; } @Override public void writeExternal(ObjectOutput out) throws IOException { out.writeUTF(name); out.writeInt(student_age); } @Override public void readExternal(ObjectInput in) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException { name = in.readUTF(); student_age = in.readInt(); } }- 序列化版本id,是为了告诉编译器,序列化的二进制和我们当前项目中的类是否为同一个版本,如果是不同的版本,那么报错。
-
-
打印流——只有输出流——提供了一系列重载的print和println方法用于输出数据
- PrintStream
- PrintWriter
-
Java中标准输入和标准输出流
- System.in
- System.out
- System.setIn(InputStream)
- System.setOut(OutputStream)