webpack5学习笔记-3 打包优化的操作
一、打包环境区分优化
根据打包环境,写三个webpack配置文件webpack.comm.js,webpack.dev.js,webpcak.prod.js,然后通过webpack-merge包来进行合并
把公共的配置放在common文件,然后把开发环境和生产环境里的放在各自的文件
npm i webpack-merge -D

自己写个用node的path模块处理路径的js,paths.js
const path = require('path')
const appDir = process.cwd()
const resolveApp = (relativePath) => {
return path.resolve(appDir, relativePath)
}
module.exports = resolveApp
webpack.common.js
const resolveApp = require('./paths')
const HtmlWebpackPlugin = require('html-webpack-plugin')
const { merge } = require('webpack-merge')
// 导入其它的配置
const prodConfig = require('./webpack.prod')
const devConfig = require('./webpack.dev')
// 定义对象保存 base 配置信息
const commonConfig = {
entry: './src/index.js', // 反而没有报错( 相对路径 )
resolve: {
extensions: [".js", ".json", '.ts', '.jsx', '.vue'],
alias: {
'@': resolveApp('./src')
}
},
output: {
filename: 'js/main.js',
path: resolveApp('./dist')
},
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.css$/,
use: [
'style-loader',
{
loader: 'css-loader',
options: {
importLoaders: 1,
esModule: false
}
},
'postcss-loader'
]
},
{
test: /\.less$/,
use: [
'style-loader',
'css-loader',
'postcss-loader',
'less-loader'
]
},
{
test: /\.(png|svg|gif|jpe?g)$/,
type: 'asset',
generator: {
filename: "img/[name].[hash:4][ext]"
},
parser: {
dataUrlCondition: {
maxSize: 30 * 1024
}
}
},
{
test: /\.(ttf|woff2?)$/,
type: 'asset/resource',
generator: {
filename: 'font/[name].[hash:3][ext]'
}
},
{
test: /\.jsx?$/,
use: ['babel-loader']
}
]
},
plugins: [
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
title: 'copyWebpackPlugin',
template: './public/index.html'
})
]
}
module.exports = (env) => {
const isProduction = env.production
process.env.NODE_ENV = isProduction ? 'production' : 'development'
// 依据当前的打包模式来合并配置
const config = isProduction ? prodConfig : devConfig
const mergeConfig = merge(commonConfig, config)
return mergeConfig
}
webpcak.prod.js
const CopyWebpackPlugin = require('copy-webpack-plugin')
const { CleanWebpackPlugin } = require('clean-webpack-plugin')
module.exports = {
mode: 'production',
plugins: [
new CleanWebpackPlugin(),
new CopyWebpackPlugin({
patterns: [
{
from: 'public',
globOptions: {
ignore: ['**/index.html']
}
}
]
})
]
}
webpack.dev.js
const ReactRefreshWebpackPlugin = require('@pmmmwh/react-refresh-webpack-plugin')
module.exports = {
mode: 'development',
devtool: 'cheap-module-source-map',
target: 'web',
devServer: {
hot: true,
hotOnly: true,
port: 4000,
open: false,
compress: true,
historyApiFallback: true,
proxy: {
'/api': {
target: 'https://api.github.com',
pathRewrite: { "^/api": "" },
changeOrigin: true
}
}
},
plugins: [
new ReactRefreshWebpackPlugin()
]
}
babel.config.js
const presets = [
['@babel/preset-env'],
['@babel/preset-react'],
]
const plugins = []
// 依据当前的打包模式来决定plugins 的值
const isProduction = process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production'
if (!isProduction) {
plugins.push(['react-refresh/babel'])
}
module.exports = {
presets,
plugins
}
二、代码拆分
所有打包的模块代码都放到一个js中,是不合理的,一方面文件太大,影响加载速度,一方面是当前业务逻辑里没有用到全部代码
所有的代码都会被打包到一起,如果应用复杂,bundle会非常大。而并不是每个模块在启动时都是必要的,所以需要分包、按需加载
多入口
entry: {
//多个入口
// main1: './src/main1.js',
// main2: './src/main2.js'
//多个入口的单个依赖
// main1: { import: './src/main1.js', dependOn: 'lodash' },
// main2: { import: './src/main2.js', dependOn: 'lodash' },
// lodash: 'lodash',
// main1: { import: './src/main1.js', dependOn: 'shared' },
// main2: { import: './src/main2.js', dependOn: 'shared' },
// shared: ['lodash', 'jquery']
index: './src/index.js'
},
output: {
filename: 'js/[name].build.js',
path: resolveApp('./dist')
},
optimization: {
minimizer: [
new TerserPlugin({
extractComments: false,//去除额外的注释license的txt
}),
],
splitChunks: {
chunks: 'all'//全部拆包
}
}
splitchunks
optimization: {
splitChunks: {
chunks: 'initial', // async异步导入 initial同步导入 all全部分包
minSize: 20000, //被拆分出来的chunk最小体积
maxSize: 20000, //体积大于所设置值的进行拆分
minChunks: 1, //被拆分的包,至少被引用一次
cacheGroups: { //对拆包的结果进行分组,键值对,key可以自定义
syVendors: {
test: /[\\/]node_modules[\\/]/,
filename: 'js/[id]_vendor.js',
priority: -10, //优先级
},
default: {
minChunks: 2,
filename: 'js/syy_[id].js',
priority: -20,
}
}
}
}
动态导入
拆分代码
动态导入,webpack发现是异步的,就会自动分包,不需要配置

chunkIds:告知 webpack 当选择模块 id 时需要使用哪种算法
这里的id指的就是198
| 选项值 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| natural | 按使用顺序的数字 id。 |
| named | 对调试更友好的可读的 id。 |
| deterministic | 在不同的编译中不变的短数字 id。有益于长期缓存。在生产模式中会默认开启。 |
| size | 专注于让初始下载包大小更小的数字 id。 |
| total-size | 专注于让总下载包大小更小的数字 id。 |
output: {
filename: 'js/[name].bundle.js',
path: resolveApp('./dist'),
chunkFilename: 'js/chunk_[name].js'
},
optimization: {
// natural当前文件的名称是按自然数进行编号排序,如果某个文件当前次不再被依赖那么重新打包时序号都会变,会影响浏览器缓存
chunkIds: 'deterministic',
minimizer: [
new TerserPlugin({
extractComments: false,
}),
]
}
import(/*webpackChunkName: "title"*/'./title')
console.log('index.js代码')
通过动态导入生成的文件只是一个序号,可以使用魔法注释指定分包产生bundle的名称。相同的chunk名会被打包到一起。
魔法注释:在调用模块的之前增加行内注释
魔法注释修改的是图片中名字的bundle

懒加载
const oBtn = document.createElement('button')
oBtn.innerHTML = '点击加载元素'
document.body.appendChild(oBtn)
// 按需加载
oBtn.addEventListener('click', () => {
import('./utils').then(({ default: element }) => {
console.log(element)
document.body.appendChild(element)
})
})
utils.js
const oEle = document.createElement('div')
oEle.innerHTML = '前端开发'
module.exports = oEle
runtimeChunk
设置为 true 或 ‘multiple’,会为每个入口添加一个只含有 runtime 的额外 chunk,保存的是一些清单的信息,比如导入加载,方便浏览器做缓存
optimization: {
runtimeChunk: true,
minimizer: [
new TerserPlugin({
extractComments: false,
}),
]
},
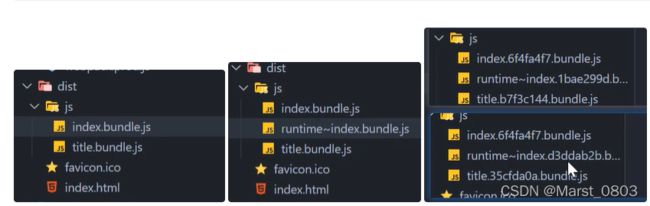
在被导入的文件中修改了内容,导入的文件没修改,可以看到contenthash值没有变化,所以方便做缓存
预加载/预获取
在声明 import 时,使用下面这些内置指令,可以让 webpack 输出 “resource hint(资源提示)”,来告知浏览器:
● prefetch(预获取):将来某些导航下可能需要的资源
● preload(预加载):当前导航下可能需要资源
● webpackPreLoad,webpackPrefetch
与 prefetch 指令相比,preload 指令有许多不同之处:
● preload chunk 会在父 chunk 加载时,以并行方式开始加载。prefetch chunk 会在父 chunk 加载结束后开始加载。
● preload chunk 具有中等优先级,并立即下载。prefetch chunk 在浏览器闲置时下载。
● preload chunk 会在父 chunk 中立即请求,用于当下时刻。prefetch chunk 会用于未来的某个时刻。
● 浏览器支持程度不同。
const oBtn = document.createElement('button')
oBtn.innerHTML = '点击加载元素'
document.body.appendChild(oBtn)
// 按需加载
oBtn.addEventListener('click', () => {
import(
/*webpackChunkName:'utils' */
/*webpackPreLoad:true */
'./utils').then(({ default: element }) => {
console.log(element)
document.body.appendChild(element)
})
})
三、CDN
cdn引入的方式是让webpack无需每次构建的时候都去打包第三方库或者插件
配置cdn是用 externals(外部的)选项,key表示的是包名,即package.json中包的名称,value表示的是包导出的类名。
如果有自己的CDN服务器,就在output里设置publicPath为CDN资源路径
如果没有,可以使用bootCDN,在externals里配置要排除打包的第三方库信息,然后在index.html模板文件中引入
output: {
filename: 'js/[name].[contenthash:8].bundle.js',
path: resolveApp('./dist'),
},
externals: {
lodash: '_'
},
public/index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width,initial-scale=1.0">
<title>
<%= htmlWebpackPlugin.options.title %>
</title>
</head>
<body>
<noscript>
<strong>We're sorry but <%= htmlWebpackPlugin.options.title %> doesn't work properly without JavaScript enabled.
Please enable it to continue.</strong>
</noscript>
<div id="app"></div>
<!-- built files will be auto injected -->
<script src="https://cdn.bootcdn.net/ajax/libs/lodash.js/4.17.21/lodash.min.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
四、Dll库(了解)
vue和react的脚手架中已经移除这个库,加快打包速度,具体的看webpack文档即可
五、压缩CSS
1、分离css
npm i mini-css-extract-plugin -D
webpack.prod.js
const MiniCssExtractPlugin = require("mini-css-extract-plugin")
module.exports = {
mode: 'production',
plugins: [
new MiniCssExtractPlugin({
filename: 'css/[name].[hash:8].css'
})
]
}
同时要修改css的loader处理,修改之前的webpack.common.js,改成方法,传入是否为开发环境的参数
const resolveApp = require('./paths')
const HtmlWebpackPlugin = require('html-webpack-plugin')
const { merge } = require('webpack-merge')
const TerserPlugin = require("terser-webpack-plugin");
const MiniCssExtractPlugin = require("mini-css-extract-plugin")
// 导入其它的配置
const prodConfig = require('./webpack.prod')
const devConfig = require('./webpack.dev')
// 定义对象保存 base 配置信息
const commonConfig = (isProduction) => {
return {
entry: {
index: './src/index.js'
},
resolve: {
extensions: [".js", ".json", '.ts', '.jsx', '.vue'],
alias: {
'@': resolveApp('./src')
}
},
output: {
filename: 'js/[name].[contenthash:8].bundle.js',
path: resolveApp('./dist'),
},
optimization: {
runtimeChunk: true,
minimizer: [
new TerserPlugin({
extractComments: false,
}),
]
},
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.css$/,
use: [
isProduction ? MiniCssExtractPlugin.loader : 'style-loader',
{
loader: 'css-loader',
options: {
importLoaders: 1,
esModule: false
}
},
'postcss-loader'
]
},
{
test: /\.less$/,
use: [
'style-loader',
'css-loader',
'postcss-loader',
'less-loader'
]
},
{
test: /\.(png|svg|gif|jpe?g)$/,
type: 'asset',
generator: {
filename: "img/[name].[hash:4][ext]"
},
parser: {
dataUrlCondition: {
maxSize: 30 * 1024
}
}
},
{
test: /\.(ttf|woff2?)$/,
type: 'asset/resource',
generator: {
filename: 'font/[name].[hash:3][ext]'
}
},
{
test: /\.jsx?$/,
use: ['babel-loader']
}
]
},
plugins: [
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
title: 'copyWebpackPlugin',
template: './public/index.html'
})
]
}
}
module.exports = (env) => {
const isProduction = env.production
process.env.NODE_ENV = isProduction ? 'production' : 'development'
// 依据当前的打包模式来合并配置
const config = isProduction ? prodConfig : devConfig
const mergeConfig = merge(commonConfig(isProduction), config)
return mergeConfig
}
2、压缩css
npm i css-minimizer-webpack-plugin -D
const CopyWebpackPlugin = require('copy-webpack-plugin')
const { CleanWebpackPlugin } = require('clean-webpack-plugin')
const MiniCssExtractPlugin = require("mini-css-extract-plugin")
const CssMinimizerPlugin = require("css-minimizer-webpack-plugin")
module.exports = {
mode: 'production',
optimization: {
minimizer: [
new CssMinimizerPlugin()
]
},
plugins: [
new CleanWebpackPlugin(),
new CopyWebpackPlugin({
patterns: [
{
from: 'public',
globOptions: {
ignore: ['**/index.html']
}
}
]
}),
new MiniCssExtractPlugin({
filename: 'css/[name].[hash:8].css'
})
]
}
六、Terserlugin压缩js
webpack5里面已经集成了,不用另外安装
const TerserPlugin = require('terser-webpack-plugin')
optimization: {
minimize: true, //允许使用TerserPlugin
minimizer: [
new TerserPlugin({ //压缩JS
extractComments: false
})
]
},
早期使用的uglify-js压缩,丑化Javascript代码如今已经不再维护且不支持ES6语法,Terser是uglify-es 复刻过来并且保留其原来大部分API
七、scope hoisting
基于esmodule的静态分析,来做作用域提升,把打包出来的js 文件,里面引用需要做好几层查找的东西,都放在了一个作用域下
打包体积变小,代码运行查找更快
生产模式下自动开启
八、TreeShaking
把不被使用的死代码去掉
usedExports
告知 webpack 去决定每个模块使用的导出内容,未使用的导出内容不会被生成,导出名称会被处理做单个标记字符
module.exports = {
//...
optimization: {
usedExports: true,
},
};

会标记出来foo2没有使用,terserPlugin就会把这些去除
sideEffect
针对某些模块,可以选择跳过,处理副作用代码,不进行使用
package.json
"sideEffects": [
"./src/title.js"
]
title.js
export function foo3() {
console.log('foo3')
}
window.title = '前端开发'
import './title'
console.log(window.title, '<------')
这个时候会发现输出的window.title是undefined
CSS
下面的css代码里,abc类没用到,配置好之后打包的css会自动去掉
body {
background-color: orange;
}
.abc {
font-size: 100px;
}
.ef {
background-color: #fff;
}
npm i purgecss-webpack-plugin -D
需要结合mini-css-extract-plugin
npm i glob -D
const MiniCssExtractPlugin = require("mini-css-extract-plugin")
const PurgeCSSPlugin = require('purgecss-webpack-plugin')
module.exports = {
mode: 'production',
plugins: [
new MiniCssExtractPlugin({
filename: 'css/[name].[hash:8].css'
}),
new PurgeCSSPlugin({
paths: glob.sync(`${resolveApp('./src')}/**/*`, { nodir: true }),
safelist: function () { //不被去除的css
return {
standard: ['body', 'html', 'ef']
}
}
})
]
}
九、压缩资源
开发模式可以在devServer里配置compress为true
生产模式使用compression-webpack-plugin
npm i compression-webpack-plugin -D
br的压缩方式兼容性不如gzip
minRatio:最小压缩比例,压缩后达不到就不压缩
threshold:体积大于值之后开始压缩
algorithm:指定压缩算法
const CompressionPlugin = require("compression-webpack-plugin")
module.exports = {
mode: 'production',
plugins: [
new CompressionPlugin({
test: /\.(css|js)$/,
minRatio: 0.8,
threshold: 0,
algorithm: 'gzip'
})
]
}
十、inlineChunkHtmlPlugin
配合htmlWebpackPlugin使用,在html中把文件内容少的资源压缩后直接注入进来
const InlineChunkHtmlPlugin = require('inline-chunk-html-plugin')
const HtmlWebpackPlugin = require('html-webpack-plugin')
module.exports = {
mode: 'production',
plugins: [
new InlineChunkHtmlPlugin(HtmlWebpackPlugin, [/runtime.*\.js/])
]
}
十一、打包library
打包自己开发的库
const foo1 = () => {
console.log('foo1函数')
}
const foo2 = () => {
console.log('foo2函数')
}
module.exports = {
foo1,
foo2
}
const path = require('path')
module.exports = {
mode: 'development',
devtool: false,
entry: './src/index.js',
output: {
filename: 'sy_utils.js',
path: path.resolve(__dirname, 'dist'),
libraryTarget: 'umd',
library: 'syUtil', //会把方法都放着这个对象上
globalObject: 'this'
}
}
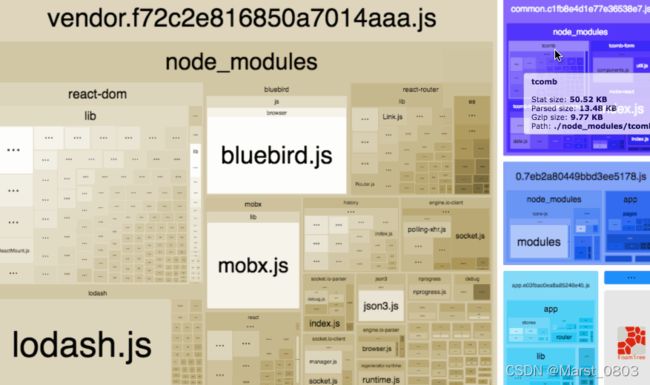
十二、打包分析
npm i speed-measure-webpack-plugin -D
// 时间分析
const SpeedMeasurePlugin = require("speed-measure-webpack-plugin")
const smp = new SpeedMeasurePlugin()
module.exports = (env) => {
const isProduction = env.production
process.env.NODE_ENV = isProduction ? 'production' : 'development'
const config = isProduction ? prodConfig : devConfig
const mergeConfig = merge(commonConfig(isProduction), config)
return smp.wrap(mergeConfig)
}
如果有兼容报错,一般是降级或者看issue里面的解决,无法兼容就不做了

官方分析工具 webpack --profile --json > stats.json
https://webpack.docschina.org/guides/code-splitting/#bundle-analysis
webpack-bundle-analyzer
npm install --save-dev webpack-bundle-analyzer
const BundleAnalyzerPlugin = require('webpack-bundle-analyzer').BundleAnalyzerPlugin;
module.exports = {
plugins: [
new BundleAnalyzerPlugin()
]
}