LeetCode刷题之剑指offer
剑指 offer 题目目录
剑指 Offer 03. 数组中重复的数字
方法一:借助HashSet去重
class Solution {
public int findRepeatNumber(int[] nums) {
HashSet<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
for(int a : nums){
if(set.contains(a)){
return a;
}else{
set.add(a);
}
}
return -1;
}
}
方法二:此题数组有限制,数字在 0 ~ n-1 中国
class Solution {
public int findRepeatNumber(int[] nums) {
int i = 0;
while (i < nums.length){
if (nums[i] == i){
i++;
continue;
}
if (nums[nums[i]] == nums[i]) return nums[i];
//索引交换, 当前 i 位置上的数为 nums[i],放在它正确的位置上,加入 i = 0,nums[0] = 2,那就把 2 放在 nums[2] = 2 上
//把 nums[2] 位置的数字暂存 nums[0] 位置
int index = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[index];
nums[index] = index;
}
return -1;
}
}
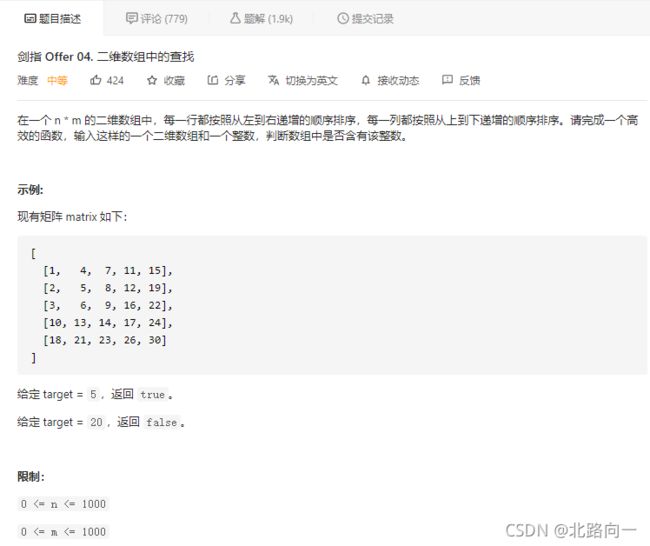
剑指 Offer 04. 二维数组中的查找
class Solution {
public boolean findNumberIn2DArray(int[][] matrix, int target) {
if(matrix == null || matrix.length < 1) return false;
int row = matrix.length;
int col = matrix[0].length;
int i = 0,j = col - 1;
while(i < row && j >= 0){
int a = matrix[i][j];
if(a == target){
return true;
}else if(a < target){
i++;
}else{
j--;
}
}
return false;
}
}
剑指 Offer 05. 替换空格
class Solution {
public String replaceSpace(String s) {
return s.replaceAll(" ","%20");
}
}
剑指 Offer 06. 从尾到头打印链表
2.先反转链表,则存储到集合中。
方法三:
借助递归的特性,当反转链表到末尾时候,用count记录当前链表的长度。
一切皆在代码中:
class Solution {
private int[] ans;
private int count;
private int index;
public int[] reversePrint(ListNode head) {
dfs(head);
return ans;
}
public void dfs(ListNode head){
if(head == null){
ans = new int[count];
return;
}
count++;
dfs(head.next);
ans[index++] = head.val;
}
}
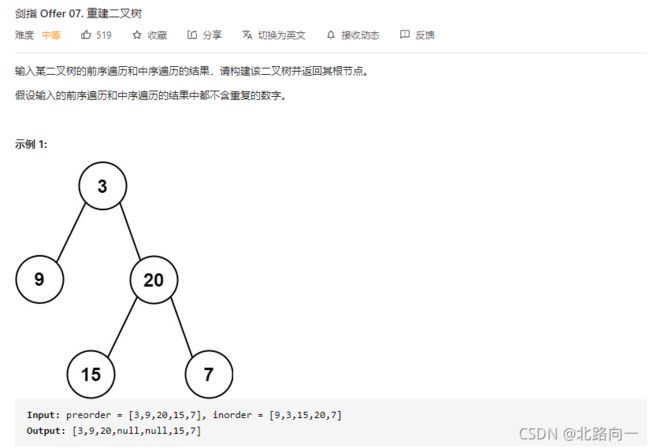
剑指 Offer 07. 重建二叉树
思路:
根据前序遍历:根左右,
中序遍历:左根右
可以根据前序遍历的根节点的值,在中序遍历中找到对应的index,从而将中序遍历的数组以 index 为界限,分成左子树,右子树。进而递归构建二叉树。
class Solution {
private int[] preorder;
//key 表示在中序遍历中对应的节点,value 为其索引
private Map<Integer,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
//前:根左右,中:左根右
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
this.preorder = preorder;
for(int i = 0;i < inorder.length;i++){
map.put(inorder[i],i);
}
return buildTree(0,0,inorder.length - 1);
}
/**
* rootIndex 前序遍历中跟节点的索引
* leftBound 递归树的左边界,即数组左边界
* rightBound 递归树的右边界,即数组右边界
*/
public TreeNode buildTree(int rootIndex,int leftBound,int rightBound){
if(leftBound > rightBound) return null;
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(preorder[rootIndex]);
//在中序遍历 map 中找到根节点的 index,根节点的左边为左子树,右边为右子树
int indx = map.get(root.val);
root.left = buildTree(rootIndex + 1,leftBound,indx - 1);
//需要确定前序遍历中,右子树的根节点的索引
root.right = buildTree(rootIndex + (indx - leftBound) + 1,indx + 1,rightBound);
return root;
}
}
剑指 Offer 09. 用两个栈实现队列
class CQueue {
private Stack<Integer> stack1;
private Stack<Integer> stack2;
public CQueue() {
stack1 = new Stack<>();
stack2 = new Stack<>();
}
public void appendTail(int value) {
stack1.push(value);
}
public int deleteHead() {
if(stack2.isEmpty()){
while(!stack1.isEmpty()){
stack2.push(stack1.pop());
}
}
if(stack2.isEmpty()){
return -1;
}
return stack2.pop();
}
}
剑指 Offer 10- I. 斐波那契数列
class Solution {
public int fib(int n) {
if(n < 2) return n;
int one = 1, two = 1;
for(int i = 2; i <= n; i++){
int temp = (one + two) % 1000000007;
one = two;
two = temp;
}
return one;
}
}
剑指 Offer 10- II. 青蛙跳台阶问题
class Solution {
public int numWays(int n) {
if(n == 0) return 1;
//其中 a1 表示第一次跳一阶,a2 表示第一次跳两阶 f(n-1) + f(n-2)
int a1 = 1, a2 = 1;
for(int i = 2; i <= n; i++){
int c = (a1 + a2) % 1000000007;
a1 = a2;
a2 = c;
}
return a2;
}
}
剑指 Offer 11. 旋转数组的最小数字
二分法的思想:直接以 mid 与 right向比较,判断函数的单调性
class Solution {
//二分法的思想
public int minArray(int[] numbers) {
if(numbers == null || numbers.length < 1) return 0;
int left = 0,right = numbers.length - 1;
while(left < right){
int mid = (left + right) / 2;
if(numbers[right] > numbers[mid]){
//右部分上升序列
right = mid;
}else if(numbers[mid] > numbers[right]){
//则一定在右边
left = mid + 1;
}else{
// right = mid, 2 3 3 3 这种情况
right--;
}
}
return numbers[left];
}
}
剑指 Offer 12. 矩阵中的路径
class Solution {
public boolean exist(char[][] board, String word) {
char[] words = word.toCharArray();
int row = board.length;
int col = board[0].length;
for(int i = 0;i < row;i++){
for(int j = 0;j < col;j++){
boolean result = dfs(board,words,0,i,j,new boolean[row][col]);
if(result) return true;
}
}
return false;
}
public boolean dfs(char[][] board,char[] words,int count,int i,int j,boolean[][] flag){
if(i < 0 || i >= board.length || j < 0 || j >= board[0].length || flag[i][j] || board[i][j] != words[count]){
return false;
}
if(count == words.length - 1) return true;
flag[i][j] = true;
//四个方向
if(dfs(board,words,count + 1,i - 1,j, flag) ||
dfs(board,words,count + 1,i + 1,j, flag) ||
dfs(board,words,count + 1,i,j - 1, flag) ||
dfs(board,words,count + 1,i ,j + 1, flag)){
return true;
}
flag[i][j] = false;
return false;
}
}
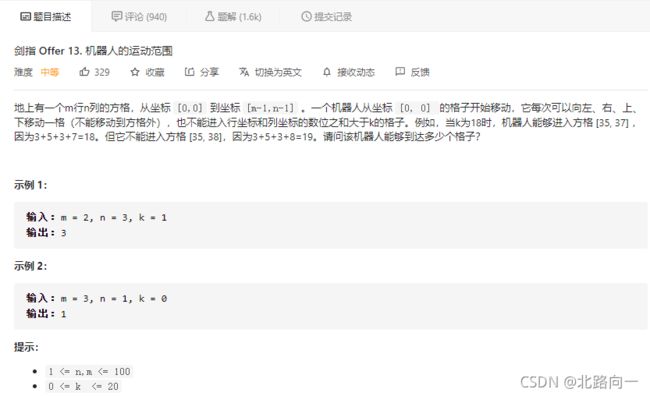
剑指 Offer 13. 机器人的运动范围
class Solution {
//回溯算法
public int movingCount(int m, int n, int k) {
return backtrack(new boolean[m * n],0,0,m,n,k);
}
//回溯算法,已经经过的位置需要编辑为true,但是可以重走这个位置,只是不计数而已
public int backtrack(boolean[] falg,int i,int j,int m,int n,int k){
if(i < 0 || i >= m || j < 0 || j >= n || falg[i * n + j] || (int2Sum(i) + int2Sum(j)) > k){
return 0;
}
falg[i * n + j] = true;
int sum = backtrack(falg,i + 1,j,m,n,k) +
backtrack(falg,i - 1,j,m,n,k) +
backtrack(falg,i,j + 1,m,n,k) +
backtrack(falg,i,j - 1,m,n,k);
//因为可以走原始的路,所以不需要回退
return sum + 1;
}
public int int2Sum(int i){
int ans = 0;
while(i > 0){
ans += i % 10;
i /= 10;
}
return ans;
}
}
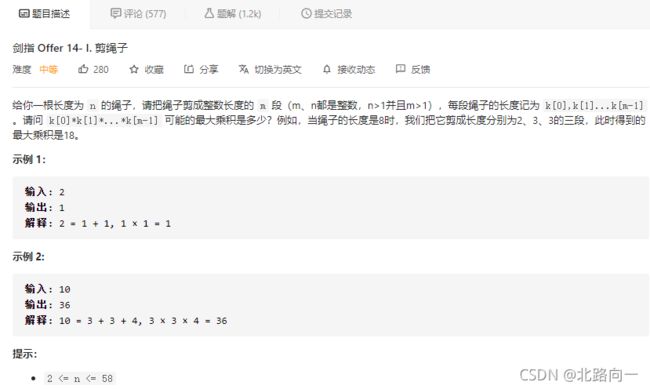
剑指 Offer 14- I. 剪绳子
f ( n ) = m a x ( f ( 1 ) ∗ f ( n − 1 ) , f ( 2 ) ∗ f ( n − 2 ) , . . . , f ( n / 2 − 1 ) ∗ f ( n / 2 ) ) f(n) = max(f(1)*f(n-1),f(2)*f(n-2),...,f(n/2 - 1)*f(n/2)) f(n)=max(f(1)∗f(n−1),f(2)∗f(n−2),...,f(n/2−1)∗f(n/2))
找到最大的值,但是需要注意题目限制, f ( 2 ) = 1 , f ( 3 ) = 2 , f ( 4 ) = m a x ( f ( 1 ) ∗ f ( 3 ) , f ( 2 ) ∗ f ( 2 ) ) f(2) =1,f(3) = 2,f(4) = max(f(1)*f(3),f(2)*f(2)) f(2)=1,f(3)=2,f(4)=max(f(1)∗f(3),f(2)∗f(2))
但是有: f ( 1 ) , f ( 2 ) , f ( 3 ) f(1),f(2),f(3) f(1),f(2),f(3)在参与结果计算的时候,不考虑拆分
代码:
class Solution {
//常规思路,动态规划
public int cuttingRope(int n) {
if(n == 2) return 1;
if(n == 3) return 2;
//定义 dp 数组
int[] dp = new int[n + 1];
//dp[1] = 1,dp[2] = 2,dp[3] = 3,取值问题,f(5) = max(f(1) * f(4),f(2) * f(3)), 从 f(4) 开始定义 dp 数组
for(int i = 0; i < 4;i++){
dp[i] = i;
}
//从 dp[4] 开始计算
for(int i = 4; i <= n; i++){
int max = 0;
//因为 f(2) * f(3) = f(3) * f(2)
for(int j = 1; j <= i / 2; j++){
max = Math.max(max,dp[j] * dp[i - j]);
}
dp[i] = max;
}
return dp[n];
}
}
方法二:数学证明
class Solution{
public int cuttingRope(int n){
if(n <= 3) return n - 1;
int a = n / 3,b = n % 3;
if(b == 0) return (int)Math.pow(3,a);
if(b == 1) return (int)Math.pow(3,a - 1) * 4;
return (int)Math.pow(3,a)*2;
}
}
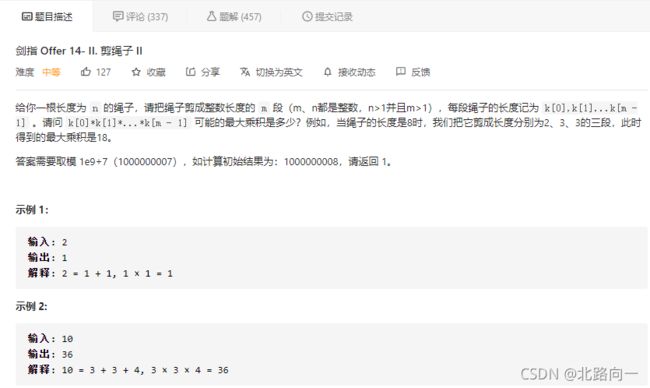
剑指 Offer 14- II. 剪绳子 II
class Solution {
//将绳子分成3 3 3 3 ,求结果
public int cuttingRope(int n) {
if (n < 4) return n - 1;
int p = 1000000007;
long result = 1;
//优先切 3
while (n > 4){
result = result * 3 % p;
n -= 3;
}
//循环完 只剩 n = 2 ,3,4,都是直接乘就可以
return (int) (result * n % p);
}
}
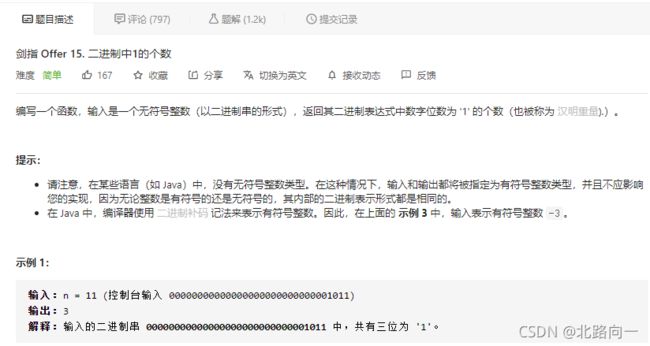
剑指 Offer 15. 二进制中1的个数
public class Solution {
// you need to treat n as an unsigned value
public int hammingWeight(int n) {
int count = 0;
while(n != 0){
count += n & 1;
//将 n 无符号右移
n >>>= 1;
}
return count;
}
}
剑指 Offer 16. 数值的整数次方
class Solution {
//去除边界条件,快速幂
public double myPow(double x, int n) {
if(x == 0) return 0;
long b = n;
if(n < 0) {
x = 1 / x;
b = -b;
}
double ans = 1.0d;
while(b > 0){
//当 b 的二进制当前位置是否为 1,需要乘以剩余的 x
if((b & 1) == 1) ans *= x;
x *= x;
b >>= 1;
}
return ans;
}
}
剑指 Offer 17. 打印从1到最大的n位数
class Solution {
public int[] printNumbers(int n) {
int count = 1;
while(n > 0){
count *= 10;
n--;
}
int[] ans = new int[count - 1];
for(int i = 1; i < count;i++){
ans[i - 1] = i;
}
return ans;
}
}
class Solution {
StringBuilder res;
int count = 0, n;
char[] num, loop = {'0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9'};
public String printNumbers(int n) {
this.n = n;
res = new StringBuilder(); // 数字字符串集
num = new char[n]; // 定义长度为 n 的字符列表
dfs(0); // 开启全排列递归
res.deleteCharAt(res.length() - 1); // 删除最后多余的逗号
return res.toString(); // 转化为字符串并返回
}
void dfs(int x) {
if(x == n) { // 终止条件:已固定完所有位
res.append(String.valueOf(num) + ","); // 拼接 num 并添加至 res 尾部,使用逗号隔开
return;
}
for(char i : loop) { // 遍历 ‘0‘ - ’9‘
num[x] = i; // 固定第 x 位为 i
dfs(x + 1); // 开启固定第 x + 1 位
}
}
}
输入:n = 3
输出:"000,001,002,...,100,101,102,...,997,998,999"
class Solution {
private int[] res;
private int nine = 0,count = 0,start,n;
char[] num,loop = {'0','1','2','3','4','5','6','7','8','9'};
//难点在大数问题上,用普通的数学计算无法组合到对应的排列。应用回溯算法的排列组合思想
public int[] printNumbers(int n) {
this.n = n;
res = new int[(int)Math.pow(10,n) - 1];
num = new char[n];
//起始位置
start = n - 1;
dfs(0);
return res;
}
public void dfs(int x){
if(x == n){
//start 表示左边的其实位置
String s = String.valueOf(num).substring(start);
if(!s.equals("0")) res[count++] = Integer.parseInt(s);
if(n - start == nine) start--;
return;
}
for(char i:loop){
//遇到 ‘9’ nine 的数量数量增加
if(i == '9') nine++;
num[x] = i;
dfs(x + 1);
}
nine--;
}
}
剑指 Offer 18. 删除链表的节点
class Solution {
//创建亚节点点出
public ListNode deleteNode(ListNode head, int val) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
dummy.next = head;
ListNode pre = dummy;
while(head != null && head.val != val){
pre = head;
head = head.next;
}
//断链
if(head != null){
pre.next = head.next;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
class Solution {
//创建哑节点防止删除头部
public ListNode deleteNode(ListNode head, int val) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
dummy.next = head;
ListNode pre = dummy;
while(head != null){
if(head.val == val){
pre.next = head.next;
break;
}else{
pre = head;
head = head.next;
}
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
递归版本:
class Solution {
public ListNode deleteNode(ListNode head, int val) {
if(head == null) return null;
if(head.val == val) return head.next;
head.next = deleteNode(head.next,val);
return head;
}
}
剑指 Offer 19. 正则表达式匹配
public class Solution139_10_正则表达式匹配 {
/**
* ⽅方法⼀一:回溯
*/
public static boolean isMatch(String s, String p) {
if (p.isEmpty()) return s.isEmpty();
boolean first_match = (!s.isEmpty() && (p.charAt(0) == s.charAt(0) || p.charAt(0) == '.'));
if (p.length() >= 2 && p.charAt(1) == '*') {
// isMatch(s,p.substring(2) 表示第⼀一个不不匹配 x*匹配s的零个字符
//(first_match && isMatch(s.substring(1),p)) 表示第⼀一个匹配
return (isMatch(s, p.substring(2)) || (first_match && isMatch(s.substring(1), p)));
} else {
return first_match && isMatch(s.substring(1), p.substring(1));
}
}
/**
* ⽅方法三:动态规划
* ⾃自低向上法 从最后向最前进⾏行行匹配
*/
public static boolean isMatch1(String s, String p) {
int n1 = s.length();
int n2 = p.length();
boolean[][] dp = new boolean[n1 + 1][n2 + 1];
dp[n1][n2] = true;
for (int i = n1; i >= 0; i--) {
for (int j = n2 - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
boolean first_match = (i < n1 && (p.charAt(j) == s.charAt(i) || p.charAt(j) == '.'));
if (j + 1 < n2 && p.charAt(j + 1) == '*') {
dp[i][j] = dp[i][j + 2] || first_match && dp[i + 1][j];
} else {
dp[i][j] = first_match && dp[i + 1][j + 1];
}
}
}
return dp[0][0];
}
}
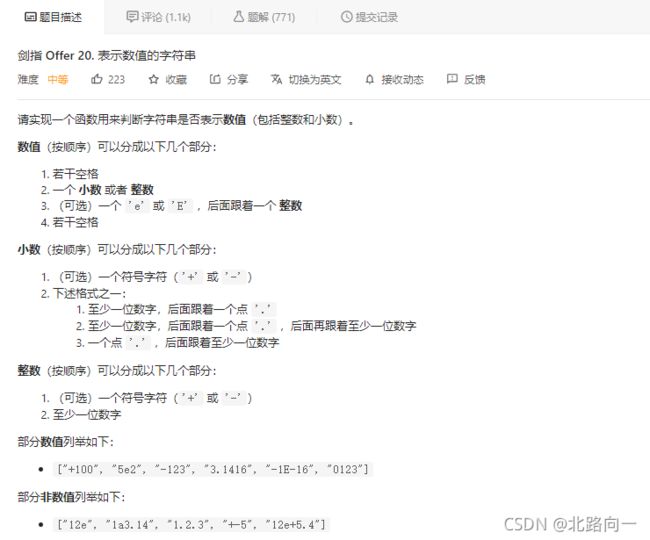
剑指 Offer 20. 表示数值的字符串
boolean isNum = false,isDot = false,ise_or_E = false;
1.当遇到 ‘.’ 时候
小数点之前可以没有整数,但是不能重复出现小数点、或出现‘e’、‘E’
if(str[i] == '.'){
// 小数点之前可以没有整数,但是不能重复出现小数点、或出现‘e’、'E'
if(isDot || ise_or_E) return false;
isDot = true;
}
2.当遇到 ‘e’ / ‘E’ 时候
‘e’ ‘E’ 前面必须有整数,且前面不能重复出现‘e’或’E’
if(str[i] == 'e' || str[i] == 'E'){
// ‘e’或'E'前面必须有整数,且前面不能重复出现‘e’或'E'
if(!isNum || ise_or_E) return false;
ise_or_E = true;
isNum = false; // 重置isNum,因为‘e’或'E'之后也必须接上整数,防止出现 123e或者123e+的非法情况
}
3.当遇到 ‘-’ ‘+’ 时候
正负号只可能出现在第一个位置,或者出现在‘e’或’E’的后面一个位置
if(str[i] == '-' || str[i] == '+'){
// 正负号只可能出现在第一个位置,或者出现在‘e’或'E'的后面一个位置
if(i != 0 && str[i - 1] != 'e' && str[i -1] != 'E') return false;
}
代码:
class Solution {
public boolean isNumber(String s) {
if(s == null || s.length() == 0) return false;
boolean isNum = false,isDot = false,ise_or_E = false; // 标记是否遇到数位、小数点、‘e’或'E'
char[] str = s.trim().toCharArray();
for(int i = 0 ; i < str.length; i++){
if(str[i] >= '0' && str[i] <= '9'){
isNum = true;
}else if(str[i] == '.'){
// 小数点之前可以没有整数,但是不能重复出现小数点、或出现‘e’、'E'
if(isDot || ise_or_E) return false;
isDot = true;
}else if(str[i] == 'e' || str[i] == 'E'){
// ‘e’或'E'前面必须有整数,且前面不能重复出现‘e’或'E'
if(!isNum || ise_or_E) return false;
ise_or_E = true;
isNum = false; // 重置isNum,因为‘e’或'E'之后也必须接上整数,防止出现 123e或者123e+的非法情况
}else if(str[i] == '-' || str[i] == '+'){
// 正负号只可能出现在第一个位置,或者出现在‘e’或'E'的后面一个位置
if(i != 0 && str[i - 1] != 'e' && str[i -1] != 'E') return false;
}else{
return false;
}
}
return isNum;
}
}
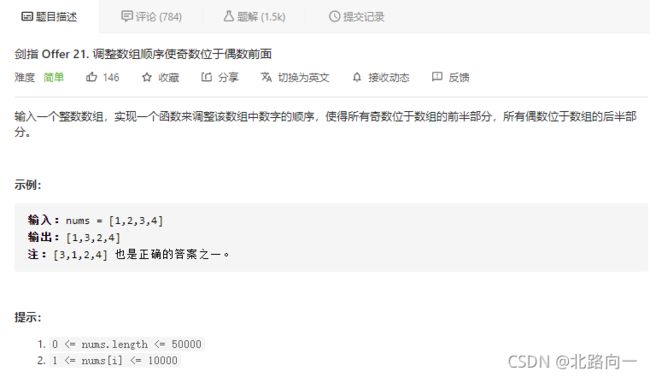
剑指 Offer 21. 调整数组顺序使奇数位于偶数前面
class Solution {
//首位双指针交换位置
public int[] exchange(int[] nums) {
int left = 0;
int right = nums.length - 1;
while(left < right){
while(left < right && (nums[left] & 1) == 1){
//奇数
left++;
}
while(left < right && (nums[right] & 1) == 0){
//偶数
right--;
}
if(left < right){
int temp = nums[left];
nums[left] = nums[right];
nums[right] = temp;
left++;
right--;
}
}
return nums;
}
}
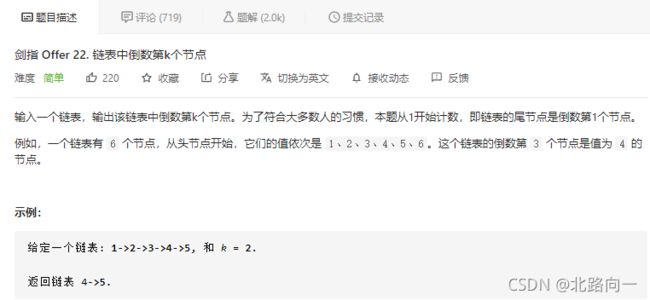
剑指 Offer 22. 链表中倒数第k个节点
思路:快慢链表指针
class Solution {
//快慢指针,让fast指针先走k步骤
public ListNode getKthFromEnd(ListNode head, int k) {
ListNode fast = head,slow = head;
while(k > 0 && fast != null){
fast = fast.next;
k--;
}
while(fast != null){
slow= slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
return slow;
}
}
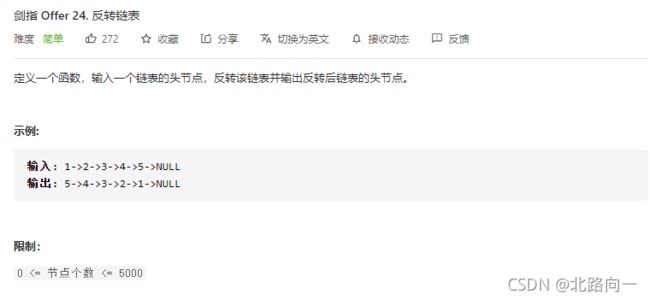
剑指 Offer 24. 反转链表
- 递归终止条件
- 当前操作的返回值
- 反转断链
class Solution {
//递归方法
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null) return head;
ListNode newHead = reverseList(head.next);
head.next.next = head;
head.next = null;
return newHead;
}
}
迭代:
class Solution {
//迭代,头插法,一次执行之后:
// -1->1->null 2->3->4->5->null(head = 2)
// -1->2->1->null 3->4->4->null (head = 3)
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
while(head != null){
ListNode next = head.next;
head.next = dummy.next;
dummy.next = head;
head = next;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
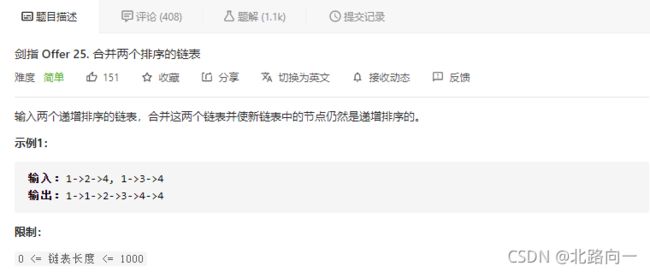
剑指 Offer 25. 合并两个排序的链表
- 找整个递归的终⽌条件:递归应该在什么时候结束?
- 找返回值:应该给上⼀级返回什么信息?
- 本级递归应该做什么:在这⼀级递归中,应该完成什么任务?
class Solution {
//递归
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
if(l1 == null) return l2;
if(l2 == null) return l1;
if(l1.val < l2.val){
l1.next = mergeTwoLists(l1.next,l2);
return l1;
}else{
l2.next = mergeTwoLists(l1,l2.next);
return l2;
}
}
}
方法二:迭代
class Solution {
//迭代
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode cur = dummy;
while(l1 != null && l2 != null){
if(l1.val < l2.val){
cur.next = l1;
l1 = l1.next;
}else{
cur.next = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
if(l1 != null) cur.next = l1;
if(l2 != null) cur.next = l2;
return dummy.next;
}
}
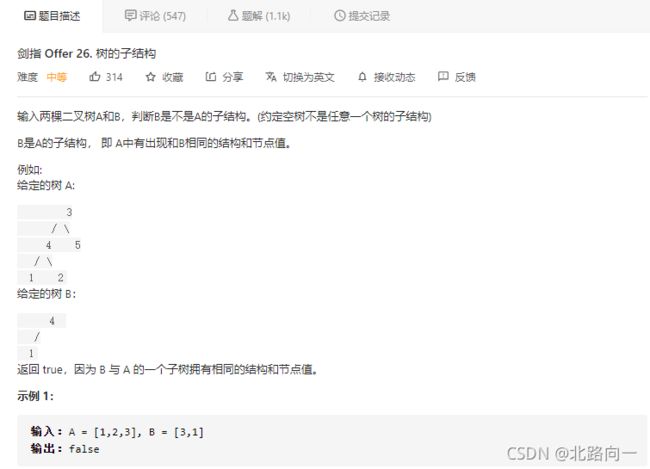
剑指 Offer 26. 树的子结构
class Solution {
public boolean isSubStructure(TreeNode A, TreeNode B) {
//包括根节点,不包括根节点,约定空树不是任意一个树的子结
if(B == null || A == null) return false;
return (isSame(A,B) || isSubStructure(A.left,B) || isSubStructure(A.right,B));
}
/** 终止条件:
当节点 B 为空:说明树 B 已匹配完成(越过叶子节点),因此返回 true ;
当节点 A 为空:说明已经越过树 A 叶子节点,即匹配失败,返回 false ;
当节点 A 和 B 的值不同:说明匹配失败,返回 false ;
返回值:
判断 A 和 B 的左子节点是否相等,即 isSame(A.left, B.left) ;
判断 A 和 B 的右子节点是否相等,即 isSame(A.right, B.right) ;
*/
public boolean isSame(TreeNode a,TreeNode b){
if(b == null) return true;
if(a == null) return false;
if(a.val != b.val) return false;
return isSame(a.left,b.left) && isSame(a.right,b.right);
}
}
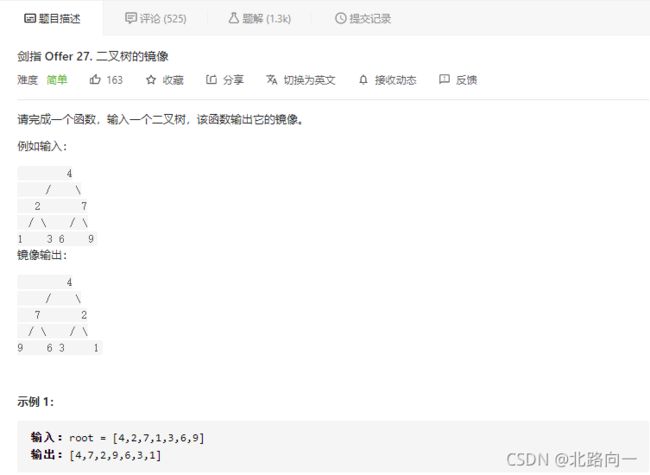
剑指 Offer 27. 二叉树的镜像
class Solution {
public TreeNode mirrorTree(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return null;
TreeNode left = root.left;
root.left = mirrorTree(root.right);
root.right = mirrorTree(left);
return root;
}
}
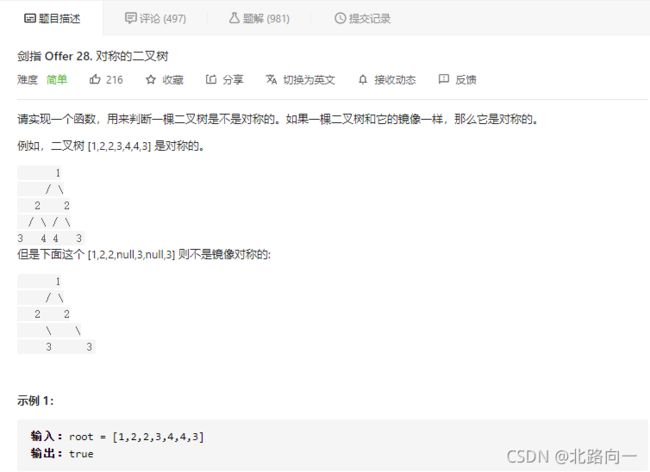
剑指 Offer 28. 对称的二叉树
左子树和右子树比较
class Solution {
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return true;
return isMerror(root.left,root.right);
}
public boolean isMerror(TreeNode a,TreeNode b){
if(a == null && b == null) return true;
if(a == null || b == null) return false;
if(a.val != b.val) return false;
return isMerror(a.left,b.right) && isMerror(a.right,b.left);
}
}
剑指 Offer 29. 顺时针打印矩阵
class Solution {
//从外层往内层打印
public static int[] spiralOrder(int[][] matrix) {
if(matrix == null || matrix.length == 0 || matrix[0].length == 0 ) return new int[0];
int row = matrix.length;
int col = matrix[0].length;
int count = 0;//打印指针
int[] ans = new int[row * col];
//圈数
int rip = (Math.min(row,col) + 1) / 2;
for(int i = 0;i < rip;i++){
//从左往右
for(int j = i;j < col - i;j++) ans[count++] = matrix[i][j];
//从上往下
for(int j = i + 1;j < row - i;j++) ans[count++] = matrix[j][col - i - 1];
//从左往右,并且判断是否是另起一行 row - 1 != 2i
for(int j = col - i - 2;j >= i && (row - i - 1) != i ;j--) ans[count++] = matrix[row - i - 1][j];
//从下往上
for(int j = row - i - 2;j > i && (col - i -1)!=i;j--) ans[count++] = matrix[j][i];
}
return ans;
}
}
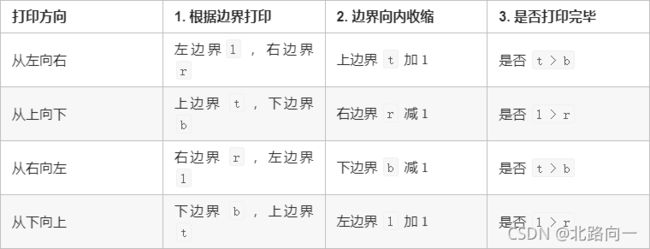
class Solution {
//定义打印的左边界,右边界,上边界和下边界,并且在每一个方向上打印完后进行边界条件判断
public int[] spiralOrder(int[][] matrix) {
if(matrix == null || matrix.length == 0) return new int[0];
int l = 0, r = matrix[0].length - 1,t = 0, b = matrix.length - 1,count = 0;
int[] ans = new int[(r + 1)*(b + 1)];
while(true){
//从左往右遍历
for(int i = l;i <= r; i++) ans[count++] = matrix[t][i];
//从上往下遍历,同时将 t 的值+1,判断是否超过了底部
if(++t > b) break;
for(int i = t; i <= b; i++) ans[count++] = matrix[i][r];
//从左往右遍历,同时将r的值-1,判断是否达到了左边界
if(--r < l) break;
for(int i = r;i >= l;i--) ans[count++] = matrix[b][i];
//从下往上,同时将b的值 -1 ,判断是否达到了上边界
if(--b < t) break;
for(int i = b;i >= t;i--) ans[count++] = matrix[i][l];
//从左往右,同时将l的值 + 1,同时判断左边界是否超出右边界
if(++l > r) break;
}
return ans;
}
}
剑指 Offer 30. 包含min函数的栈
class MinStack {
Stack<Integer> stack;
Stack<Integer> minStack;
/** initialize your data structure here. */
public MinStack() {
stack = new Stack<>();
minStack = new Stack<>();
}
public void push(int x) {
stack.push(x);
if(!minStack.isEmpty()){
int min = minStack.peek();
if(x < min){
minStack.push(x);
}else{
minStack.push(min);
}
}else{
minStack.push(x);
}
}
public void pop() {
stack.pop();
minStack.pop();
}
public int top() {
return stack.peek();
}
public int min() {
return minStack.peek();
}
}
剑指 Offer 31. 栈的压入、弹出序列
借助栈来判断:
1.每次先直接将入栈数据压入栈中,再判断当前压入的数据是否和出栈的数据相同,如果相同。则出栈,将出栈数组的指针右移。
class Solution {
//借助 stack 来判断
public boolean validateStackSequences(int[] pushed, int[] popped) {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
//第二个数组的指针
int p = 0;
for(int a : pushed){
//入栈
stack.push(a);
while(!stack.isEmpty() && stack.peek() == popped[p]){
stack.pop();
p++;
}
}
return stack.isEmpty();
}
}
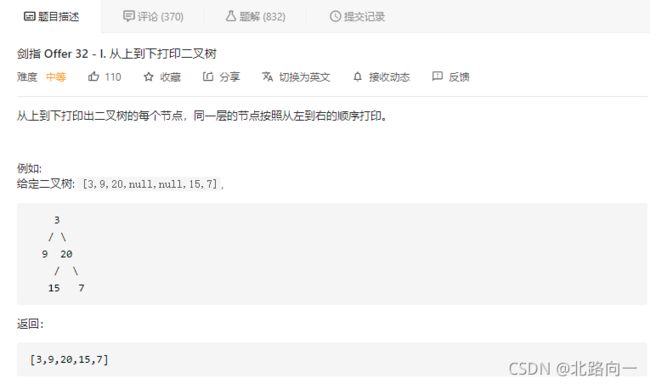
剑指 Offer 32 - I. 从上到下打印二叉树
class Solution {
//二叉树的层序遍历,借助队列
public int[] levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
//当前层有多少个节点
int size = queue.size();
while(size > 0){
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
size--;
if(node == null) continue;
ans.add(node.val);
//先添加左子树,再添加右子树
queue.add(node.left);
queue.add(node.right);
}
}
int[] result = new int[ans.size()];
for(int i = 0; i< ans.size(); i++){
result[i] = ans.get(i);
}
return result;
}
}
优化后的代码:
class Solution {
public int[] levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return new int[0];
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
queue.add(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
ans.add(node.val);
if(node.left != null) queue.add(node.left);
if(node.right != null) queue.add(node.right);
}
int[] reuslt = new int[ans.size()];
for(int i = 0; i < ans.size();i++){
reuslt[i] = ans.get(i);
}
return reuslt;
}
}
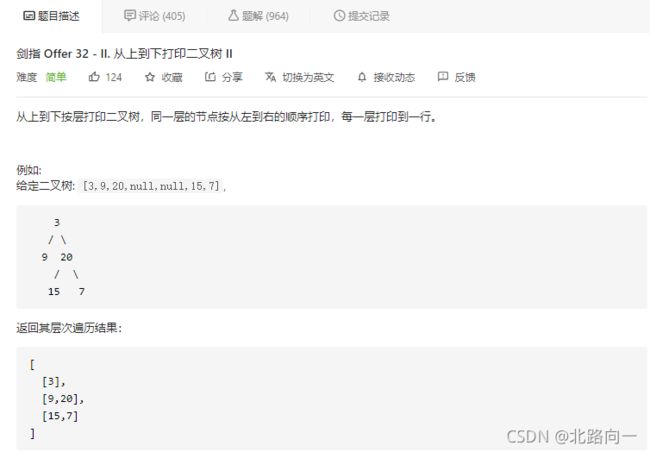
剑指 Offer 32 - II. 从上到下打印二叉树 II
class Solution {
//层序遍历
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null) return ans;
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int size = queue.size();
List<Integer> item = new ArrayList<>(size);
while(size > 0){
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
size--;
item.add(node.val);
if(node.left != null) queue.add(node.left);
if(node.right != null) queue.add(node.right);
}
ans.add(item);
}
return ans;
}
}
剑指 Offer 32 - III. 从上到下打印二叉树 III
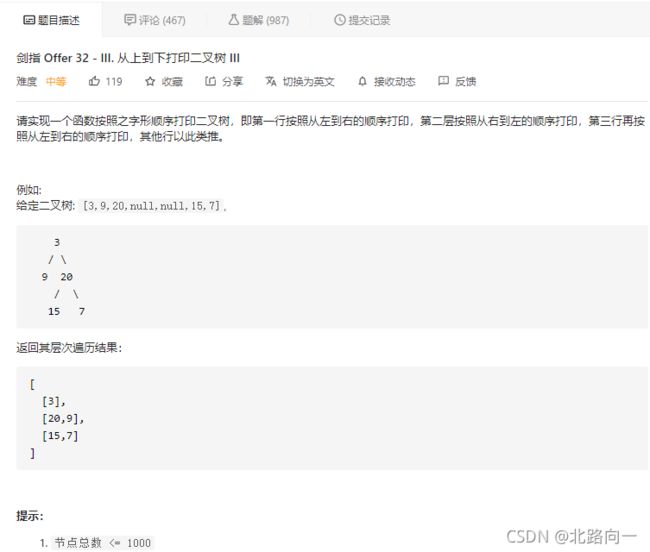
思路:奇数层正序遍历。偶数层反向遍历。
借助层序遍历的思路,判断当前是奇数层还是偶数层,从而将当前层数组进行反转
if(itemList.size() % 2 == 1) Collections.reverse(itemList);
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null) return ans;
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int size = queue.size();
List<Integer> item = new ArrayList<>(size);
while(size > 0){
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
size--;
item.add(node.val);
if(node.left != null) queue.add(node.left);
if(node.right != null) queue.add(node.right);
}
//根据是第奇数层还是偶数层,从而反转结果
if(ans.size() % 2 == 1) Collections.reverse(item);
ans.add(item);
}
return ans;
}
}
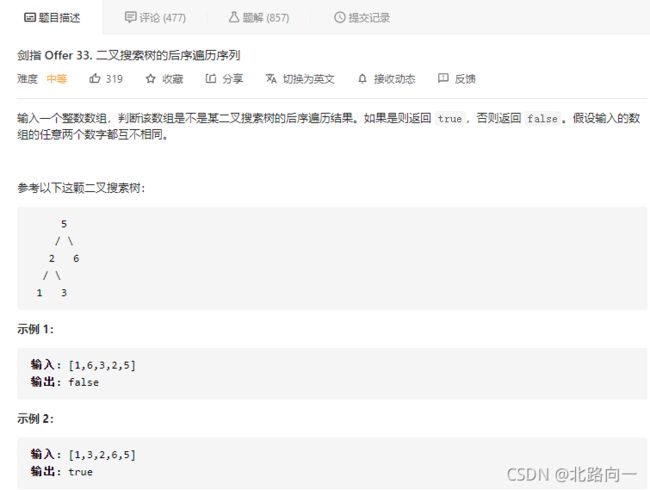
剑指 Offer 33. 二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列
class Solution {
//递归,分治法
public boolean verifyPostorder(int[] postorder) {
return isVerify(postorder,0,postorder.length - 1);
}
public boolean isVerify(int[] postorder,int l,int r){
if(l >= r) return true;
//寻找左子树的索引
int p = l;
while(postorder[p] < postorder[r]) p++;
//找到第一个大于跟节点的索引,则 p 左边的为左子树
int m = p;
//继续确定右子树的边界,因为右子树的值都比 根节点大
while(postorder[p] > postorder[r]) p++;
//最终一定找的是根节点,否则就不是后续遍历了
return p == r && isVerify(postorder,l,m - 1) && isVerify(postorder,m,r - 1);
}
}
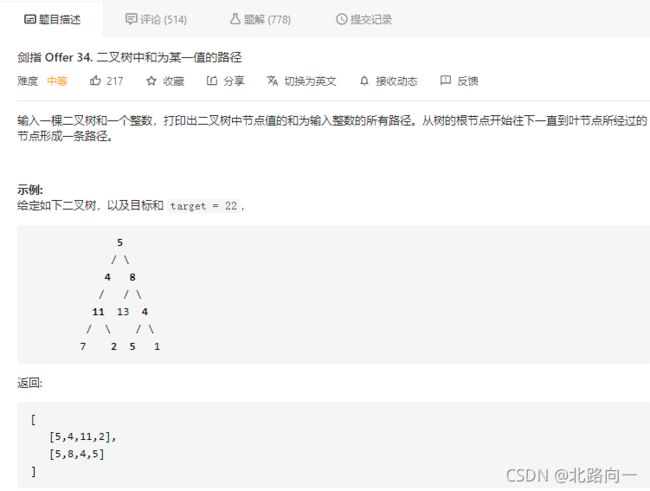
剑指 Offer 34. 二叉树中和为某一值的路径
求解路径问题,从跟节点到叶节点的满足条件的路径。回溯算法。
1、递归终止条件,当前节点为null直接返回。
2、判断当前路径是否满足条件
需要同时满足:当前路径的和以满足目标值。并且当前节点的left 和right 都为空。将当前 itemList 添加到集合中。不需要returen。因为接着会回溯,回到上一级节点。继续看看父节点的另外的子节点是否满足条件
class Solution {
private List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
private List<Integer> item = new ArrayList<>();
//回溯算法
public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int target) {
dfs(root,target);
return ans;
}
/**
* 1.递归终止条件
*/
public void dfs(TreeNode node,int target){
if(node == null) return;
target -= node.val;
item.add(node.val);
//判断当前是否满足条件
if(target == 0 && node.left == null && node.right == null){
//满足条件
ans.add(new ArrayList<>(item));
}
//还没找到,继续找
dfs(node.left,target);
dfs(node.right,target);
//回溯
item.remove(item.size() - 1);
}
}
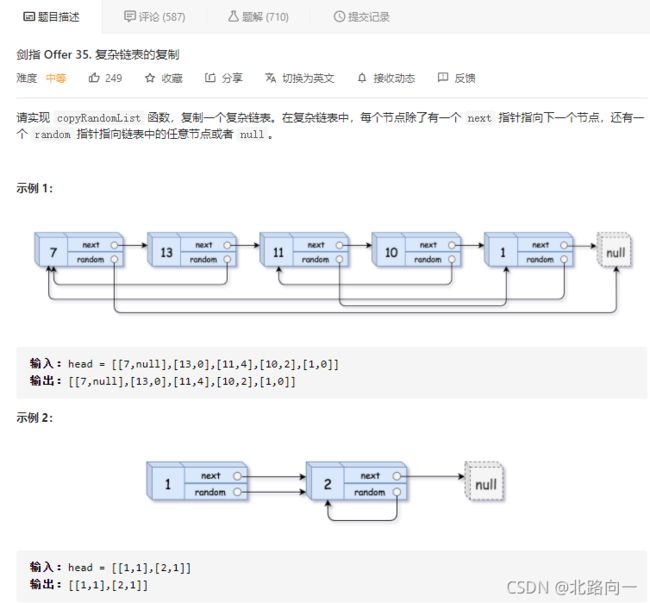
剑指 Offer 35. 复杂链表的复制
借助HashMap的快速访问特性。存储原链表的节点信息。
key : 原链表的节点
value : 新链表对应的节点
class Solution {
//借助Hash表来实现快速查询的效果
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
if(head == null ) return null;
Map<Node,Node> map = new HashMap<>();
//先构建原始节点和新链表节点的映射关系
Node cur = head;
while(cur != null){
map.put(cur,new Node(cur.val));
cur = cur.next;
}
//再来构建新链表的next指针和random指针
cur = head;
while(cur != null){
map.get(cur).next = map.get(cur.next);
map.get(cur).random = map.get(cur.random);
cur = cur.next;
}
return map.get(head);
}
}
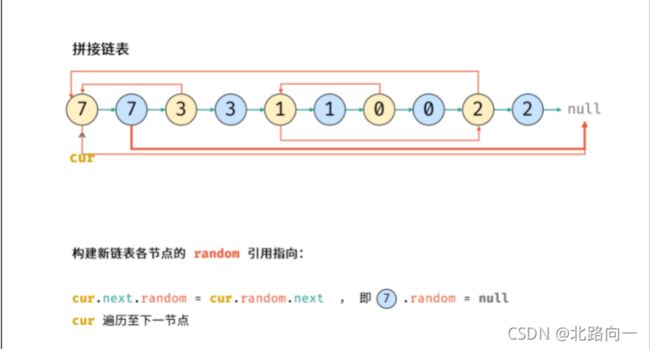
- 复制各个节点,并构建新链表
- 构建新链表的random指针
- 拆分链表
class Solution {
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
if(head == null) return null;
//1.拼接链表
Node cur = head;
while(cur != null){
Node temp = new Node(cur.val);
temp.next = cur.next;
cur.next = temp;
cur = temp.next;
}
//2.构建 random 指针
cur = head;
while(cur != null){
if(cur.random != null) cur.next.random = cur.random.next;
cur = cur.next.next;
}
//3.拆分链表
Node old = head;
cur = head.next;
Node newHead = cur;
//从下一个节点开始
while(cur.next != null){
old.next = old.next.next;
cur.next = cur.next.next;
old = old.next;
cur = cur.next;
}
//单独处理原链表的尾节点,因为我们是从第二个节点开始判断的
old.next = null;
return newHead;
}
}
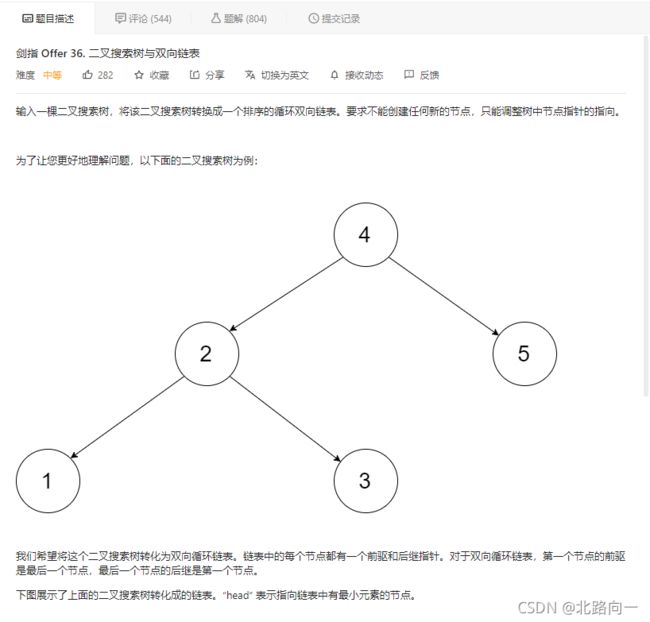
剑指 Offer 36. 二叉搜索树与双向链表
思路:二叉搜索树中序遍历有序
注意保存 head 节点和尾部节点。从而形成双向链表。
class Solution {
private Node pre,head;
//中序遍历有序,需要记录 pre 节点 和 cur 节点。并将 pre.right = cur,cur.left = pre
//当 pre 为 null 时,表示的是链表的头节点。保存。及中序遍历的第一个叶子节点
public Node treeToDoublyList(Node root) {
if(root == null) return null;
dfs(root);
//处理头节点和尾节点连起来
head.left = pre;
pre.right = head;
return head;
}
//中序遍历,根左右
public void dfs(Node node){
if(node == null) return;
dfs(node.left);
//链表 left 和 right 的拼接
if(pre != null){
pre.right = node;
}else{
//获取到了中序遍历的头节点
head = node;
}
node.left = pre;
//指针移动
pre = node;
dfs(node.right);
}
}
剑指 Offer 37. 序列化二叉树
1.序列化过程
- 将二叉树按照层序遍历,并且保存对应节点和其子节点。若子节点为null,则添加 “null” 字符串占位
2.反序列化过程
根据序列化的过程。构建二叉树
public class Codec {
// Encodes a tree to a single string.
public String serialize(TreeNode root) {
//1.异常处理
if(root == null) return "[]";
//2.借助队列实现层序遍历。
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append("[");
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
if(node != null){
sb.append(node.val + ",");
queue.add(node.left);
queue.add(node.right);
}else{
sb.append("null,");
}
}
//删除最后多余的,
sb.deleteCharAt(sb.length() - 1);
sb.append("]");
return sb.toString();
}
/**
* 1.特殊处理:data 为 "[]" ,返回 null
* 2.对上面序列化的字符串进行切割处理。去掉前后[,],同时以","切割字符串 ,字符串数据遍历指针 i = 1,跟节点root = value[0]
* 3.按照层序遍历构建二叉树
* 1.节点处队列记 为 node
* 2.构建 node 节点的左子节点的值为 value[i],入队里。同时 i++,继续操作右子节点。
*/
public TreeNode deserialize(String data) {
//1.空数据判断
if("[]".equals(data)) return null;
String[] str = data.substring(1,data.length() - 1).split(",");
//开始构建二叉树的根节点。同时创建队列
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(str[0]));
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
int i = 1;
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
//如果当前数组的值不为 null 就将它添加到 node的左子树中
if(!"null".equals(str[i])){
node.left = new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(str[i]));
queue.add(node.left);
}
i++;
//右子树
if(!"null".equals(str[i])){
node.right = new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(str[i]));
queue.add(node.right);
}
i++;
}
return root;
}
}
剑指 Offer 38. 字符串的排列
- 递归终止条件。即满足条件的排列。
- 记录当前字符是否选择过,减枝操作。
- 做选择(递归)
- 撤销选择。
class Solution {
private Set<String> ans;
//回溯算法
public String[] permutation(String s) {
if(s == null || s.length() == 0) return new String[0];
ans = new HashSet<>();
dfs(s.toCharArray(),new StringBuilder(),new boolean[s.length()]);
return ans.toArray(new String[0]);
}
public void dfs(char[] strs,StringBuilder sb,boolean[] flag){
//1.递归终止条件
if(sb.length() == strs.length){
ans.add(sb.toString());
return;
}
//2.做选择
for(int i = 0;i < strs.length;i++){
if(flag[i]) continue;
flag[i] = true;
sb.append(strs[i]);
//递归
dfs(strs,sb,flag);
//撤销选择
flag[i] = false;
sb.deleteCharAt(sb.length() - 1);
}
}
}
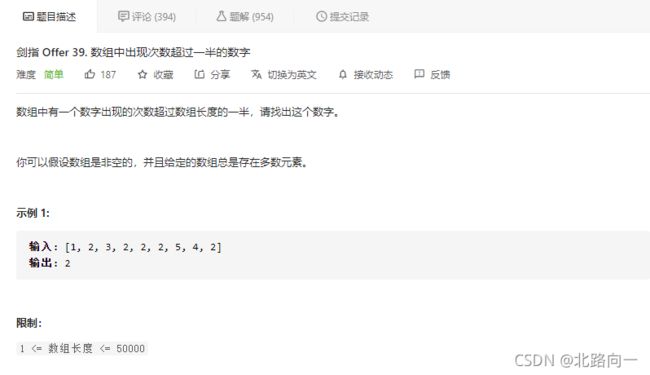
剑指 Offer 39. 数组中出现次数超过一半的数字
/*
采用阵地攻守的思想:
第一个数字作为第一个士兵,守阵地;times = 1;
遇到相同元素,times++;
遇到不相同元素,即为敌人,同归于尽,times--;
当遇到times为0的情况,又以新的i值作为守阵地的士兵,继续下去,到最后还留在阵地上的士兵,有可能是主元素。
再加一次循环,记录这个士兵的个数看是否大于数组一般即可。
*/
class Solution {
//投票法则,不同票数减一。相同票数加一
public int majorityElement(int[] nums) {
int a = nums[0];
int count = 1;
for(int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++){
if(nums[i] != a){
//不同
count--;
if(count == 0) {
a = nums[i];
count = 1;
}
}else{
count++;
}
}
//todo 判断结果是否满足条件,题目有说总是存在,异常情况下考虑找到的数据是否过半
return a;
}
}
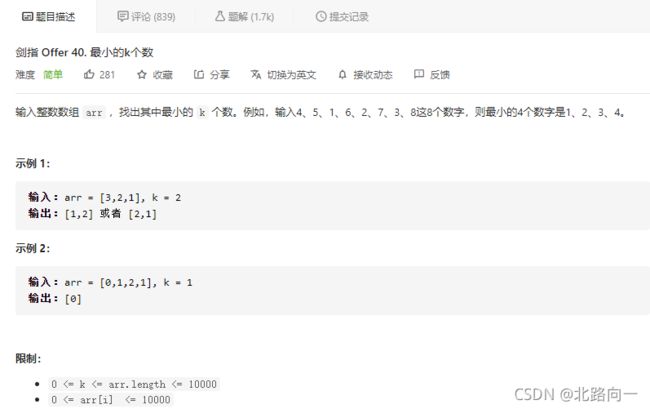
剑指 Offer 40. 最小的k个数
class Solution {
//1.借用大堆,每次拿到集合中的最大值.
public int[] getLeastNumbers(int[] arr, int k) {
int[] ans = new int[k];
if(k == 0 || arr == null || arr.length < k) return ans;
PriorityQueue<Integer> maxQueue = new PriorityQueue<>(k,(a,b)->{
return b - a;
});
for(int i = 0;i < k; i++){
maxQueue.add(arr[i]);
}
for(int i = k;i < arr.length;i++){
int a = maxQueue.poll();
if(a > arr[i]){
a = arr[i];
}
maxQueue.add(a);
}
int i = 0;
while(!maxQueue.isEmpty()){
ans[i] = maxQueue.poll();
i++;
}
return ans;
}
}
方法二:快排
利用快排的哨兵位置。从而提前找到前k个最小数
class Solution {
//快排
public int[] getLeastNumbers(int[] arr, int k) {
if(k >= arr.length) return arr;
return quickSort(arr,0,arr.length - 1,k);
}
//快排,找哨兵位置
public int[] quickSort(int[] arr,int l,int r,int k){
//以 l 为哨兵,进行排序,从右往左找到第一个比k晓得元素
int i = l, j = r;
while(i < j){
//找需要排到左边的第一个数字,第一个比l小的
while(i < j && arr[j] >= arr[l]) j--;
//从左往右找第一个比 r 大的
while(i < j && arr[i] <= arr[l]) i++;
swap(arr,i,j);
}
swap(arr,i,l);
//判断当前 i 的索引位置与 k 的关系
if(i < k){
//说明第 k + 1 小的元素在 i 在右子数组中
return quickSort(arr,i + 1,r,k);
}else if( i > k){
//说明第 k + 1小的元素在 i的左边
return quickSort(arr,l,i - 1,k);
}else{
//刚好
return Arrays.copyOf(arr,k);
}
}
public void swap(int[] arr,int i,int j){
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
}
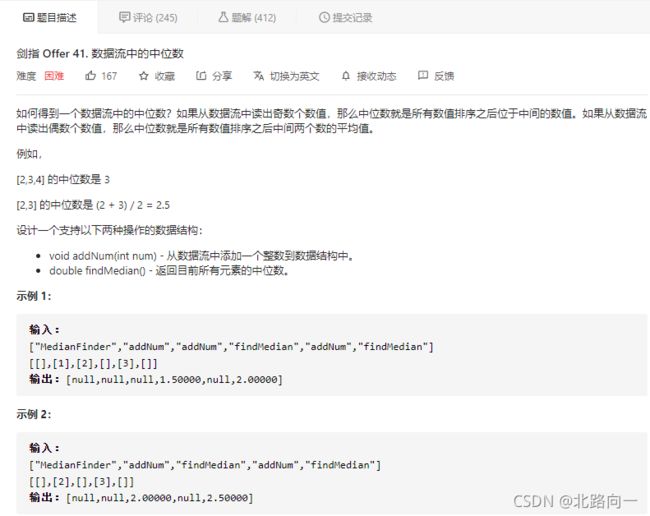
剑指 Offer 41. 数据流中的中位数
class MedianFinder {
/**
* min 小顶堆,保存大于中位数字的数字
* max 大顶堆,保存小于中位数字的数字
* 确保 Math.ads(min - max) <= 1。
* 当 length 为奇数时候,说明这个元素要添加到大堆中,但是为了确保大堆的元素都是小于小堆的,所以先把元素添加到小堆
* 在将小堆的最小元素poll到大堆中
*/
private PriorityQueue<Integer> min,max;
/** initialize your data structure here. */
public MedianFinder() {
//小堆
min = new PriorityQueue<>();
//大堆
max = new PriorityQueue<>((a,b) -> b - a);
}
public void addNum(int num) {
if(min.size() != max.size()){
//奇数,元素最终放到 max 中
min.add(num);
max.add(min.poll());
}else{
//偶数,元素最终需要被添加到 min 中
max.add(num);
min.add(max.poll());
}
}
public double findMedian() {
return min.size() != max.size() ? min.peek() : ((min.peek() + max.peek()) / 2.0);
}
}
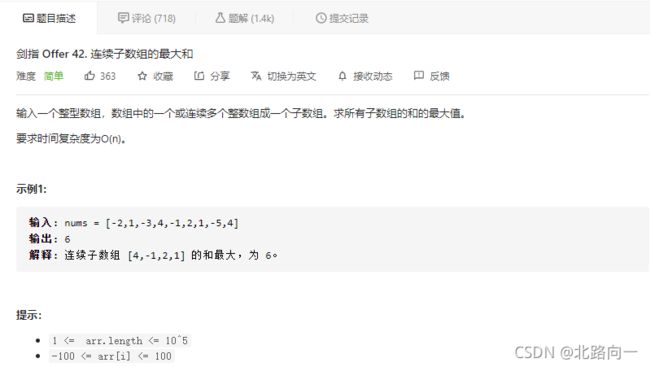
剑指 Offer 42. 连续子数组的最大和
class Solution {
//动态规划,抛弃之前的值
public int maxSubArray(int[] nums) {
int maxSum = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int curSum = 0;
for(int a : nums){
if(curSum <= 0){
curSum = a;
}else{
curSum += a;
}
maxSum = Math.max(maxSum,curSum);
}
return maxSum;
}
}
剑指 Offer 44. 数字序列中某一位的数字
class Solution {
/* 数字范围 数量 位数 占多少位
1-9 9 1 9
10-99 90 2 180
100-999 900 3 2700
1000-9999 9000 4 36000 ...
例如 2901 位 = 9 + 180 + 2700 + 12 即一定是4位数,第12位 n = 12;
数据位 = 1000 + (12 - 1)/ 4 = 1000 + 2 = 1002
定位1002中的位置 = (n - 1) % 4 = 3 s.charAt(3) = 2;
*/
public int findNthDigit(int n) {
//几位数,比如 2021 就是 4 位
int digit = 1;
//几位数的其实数字。例如 4位数的其实位置为 1000
long start = 1;
//达到x位数字一共占了多少个字符位置
long count = 9;//位数
while(n > count){
n -= count;
digit += 1;
start *= 10;
count = digit * start * 9;
}
//计算当前数字,n 为起始位置为 start 的第 n 个数字了,而每一个数有 digit 位,索引从 0 开始,所以可以求出该树
long num = start + (n - 1) / digit;
//再求出该数的具体位置的数字
return Long.toString(num).charAt((n - 1) % digit) - '0'; // 3.
}
}
剑指 Offer 45. 把数组排成最小的数
思路:比较字符串排列的大小:10,2比较,“102” 和"210"的大小
方法一:借助优先队列
class Solution {
//借助堆来实现字符串的排序,比较 10,2 的组合的大小: “102” 和 “210”的大小
public String minNumber(int[] nums) {
PriorityQueue<String> queue = new PriorityQueue<>((a,b)-> (a+b).compareTo(b+a));
for(int a : nums){
queue.add(String.valueOf(a));
}
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
sb.append(queue.poll());
}
return sb.toString();
}
}
方法二:Arrays.sort(numStr, (o1, o2) -> (o1 + o2).compareTo(o2 + o1));
class Solution {
public String minNumber(int[] nums) {
String[] numStr = new String[nums.length];
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
numStr[i] = String.valueOf(nums[i]);
}
Arrays.sort(numStr, (o1, o2) -> (o1 + o2).compareTo(o2 + o1));
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (String s : numStr) {
sb.append(s);
}
return sb.toString();
}
}
剑指 Offer 46. 把数字翻译成字符串
f ( n ) = f ( n − 1 ) + ( 10 = < x 1 x 2 < = 25 ) ? f ( n − 2 ) : 0 f(n) = f(n-1) + (10 =< x_1x_2 <= 25) ? f(n-2) :0 f(n)=f(n−1)+(10=<x1x2<=25)?f(n−2):0 判断最后两位数字是否满足条件在10和25之间
class Solution {
//动态规划
public int translateNum(int num) {
int dp0 = 1,dp1 = 1;
String str = String.valueOf(num);
//字符串substring为左闭右开
for(int i = 2; i <= str.length();i++){
String temp = str.substring(i-2,i);
int c = temp.compareTo("10") >= 0 && temp.compareTo("25") <= 0 ? dp0 + dp1 : dp0;
dp1 = dp0;
dp0 = c;
}
return dp0;
}
}
剑指 Offer 47. 礼物的最大价值
class Solution {
//原地修改,f(i,j) = grid[i][j] + max(f(i-1,j),f(i,j-1))
//矩阵的斜向遍历
public int maxValue(int[][] grid) {
if(grid == null || grid.length == 0) return 0;
int row = grid.length;
int col = grid[0].length;
//横向遍历填充举证
for(int i = 1; i < col;i++){
grid[0][i] += grid[0][i-1];
}
for(int i = 1;i < row; i++){
grid[i][0] += grid[i-1][0];
}
for(int i = 1;i < row;i++){
for(int j = 1; j < col;j++){
grid[i][j] += Math.max(grid[i-1][j],grid[i][j-1]);
}
}
return grid[row -1 ][col - 1];
}
}
剑指 Offer 48. 最长不含重复字符的子字符串
/**
* ⽅方法⼀一:滑动窗⼝口 左右指针
*/
public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {
int n = s.length();
Set<Character> set = new HashSet<>();
int ans = 0, i = 0, j = 1;
while (i < n && j < n) {
//扩展窗⼝口
if (!set.contains(s.charAt(j))) {
set.add(s.charAt(j++));
ans = Math.max(ans, j - i);//j⼜又指针
} else {
set.remove(s.charAt(i++));
}
}
return ans;
}
2.方法二:借助HashMap优化
方法一种,指针每次只移动一位,存在冗余操作
/**
* ⽅方法er:HashMap
* 优化的滑动窗⼝口
*/
public int lengthOfLongestSubstring1(String s) {
HashMap<Character, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
int left = 0, ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
if (map.containsKey(s.charAt(i))) {
left = Math.max(left, map.get(s.charAt(i)) + 1); //如果出现重复了了,则取其索引的下⼀一个位置重新开始
}
map.put(s.charAt(i), i);
ans = Math.max(ans, i - left + 1);
}
return ans;
}
3.对于简单的字符节后,用集合替代HashMap
/**
* 假设是ASCII 128 编码
* ⽤用整数数组替换hashmap
*/
public static int lengthOfLongestSubstring2(String s) {
int n = s.length(), ans = 0;
int[] index = new int[128];
//扩展[i,j]窗⼝口
for (int j = 0, i = 0; j < n; j++) {
i = Math.max(index[s.charAt(j)], i);//记录字符出现的最⼤大位置 j-i+1就是没有重复的⼦子串串⻓长度
ans = Math.max(ans, j - i + 1);
index[s.charAt(j)] = j + 1;
}
return ans;
}
剑指 Offer 49. 丑数
思想:田忌赛马:速度为2,3,5三匹马向前跑,跑一次就乘以速度
可以这样理解: 有三匹马在赛跑,a马跑的最慢,b马中等,c马跑的最快 遵循一个原则,跑的慢可以先跑,但是跑的远了,就得后跑 一开始a马速度慢,所以a先跑2米, 然后b马也慢,b马跑3米, 然后a马跑的太慢了,让他先跑也只跑了两米,所以再让他先跑,所以此时 a马跑了4米,b马跑了3米,c马原地不动 此时c马以及落后太多了,所以c马得到了先跑权力。 直到我们交出了10此跑步的权力之后,结束竞争。
class Solution {
//田忌赛马,有速度分别为 2,3,5 三匹马赛跑,a,b,c表示他们跑的次数
public int nthUglyNumber(int n) {
//存储数列
int[] dp = new int[n];
dp[0] = 1;//第一个丑数是1
int a = 0,b = 0, c = 0;
//第i个数一定是通过 2*a,3*b,5*c 中获取到的,我们取其中最小的一个,让其往前跑,但是会出现这样的情况:
//第 i 个数可能是都可以通过 2*a,3*b,5*c 生成,那么我们得让它们都向前跑。
for(int i = 1;i < n; i++){
int n2 = dp[a] * 2, n3 = dp[b] * 3, n5 = dp[c] * 5;
//寻找注销的那个数字作为下一个丑数
dp[i] = Math.min(Math.min(n2,n3),n5);
//如果该丑数与2,3,5匹配,则让马往前跑
if(dp[i] == n2) a++;
if(dp[i] == n3) b++;
if(dp[i] == n5) c++;
}
return dp[n - 1];
}
}
剑指 Offer 50. 第一个只出现一次的字符
class Solution {
//借助数组
public char firstUniqChar(String s) {
int[] map = new int[26];
char[] arr = s.toCharArray();
for(char a : arr){
map[a - 'a'] += 1;
}
for(char a : arr){
if(map[a - 'a'] == 1) return a;
}
return ' ';
}
}
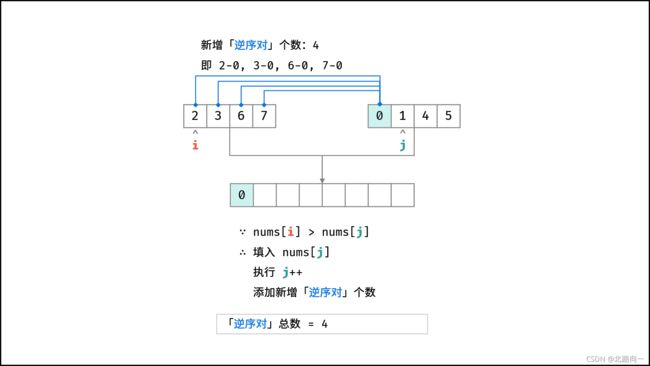
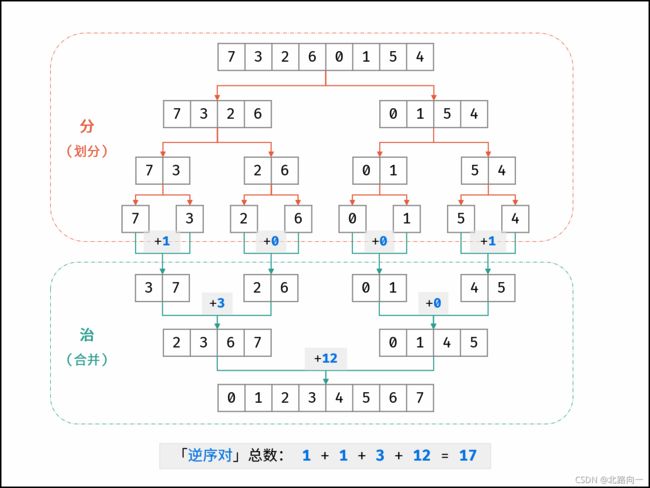
剑指 Offer 51. 数组中的逆序对
class Solution {
int count;
//归并排序,统计逆序对
public int reversePairs(int[] nums) {
int[] temp = new int[nums.length];
divideSort(nums,0,nums.length - 1, temp);
return count;
}
public void divideSort(int[] nums,int first,int last,int[] temp){
if(first < last){
int mid = (first + last) / 2;
divideSort(nums, first, mid, temp);
divideSort(nums, mid + 1, last, temp);
mergeTwo(nums,first,mid,last,temp);
}
}
//合并两个排序数组,最终放回原始数据,再归并的时候如果是逆序,则记录一下
public void mergeTwo(int[] nums,int first, int mid, int end, int[] temp){
int p1 = first, m = mid, p2 = mid + 1, n = end, p = 0;
while(p1 <= m && p2 <= n){
//归并比较
if(nums[p1] <= nums[p2]){
temp[p++] = nums[p1++];
}else{
//逆序了,这个时候需要记录,左边序列比右边的大,那么一共有的逆序对
count += (mid - p1 + 1);
temp[p++] = nums[p2++];
}
}
while (p1 <= m) temp[p++] = nums[p1++];
while (p2 <= n) temp[p++] = nums[p2++];
//将排序好的数组放入到 nums 中
for (int i = 0; i < p; i++) {
nums[first + i] = temp[i];
}
}
}
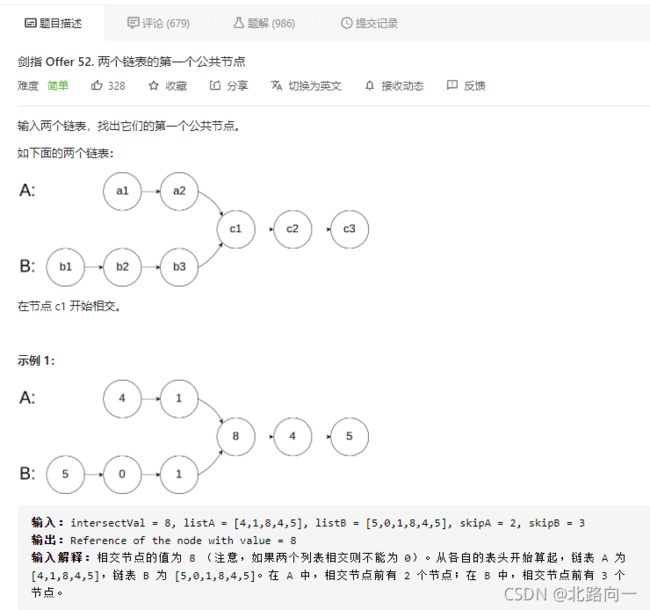
剑指 Offer 52. 两个链表的第一个公共节点
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
ListNode pointA = headA, pointB = headB;
while (pointA != pointB){
pointA = pointA == null ? headB : pointA.next;
pointB = pointB == null ? headA : pointB.next;
}
return pointA;
}
}
剑指 Offer 53 - I. 在排序数组中查找数字 I
思路:二分查找
1.查找左边界
class Solution {
//二分查找左边界点
public int search(int[] nums, int target) {
if(nums.length == 0 || nums[0] > target || nums[nums.length - 1] < target) return 0;
int len = nums.length;
int left = 0;
int right = len - 1;
//二分法找左边界
while(left < right){
int mid = (left + right) / 2;
if(nums[mid] >= target){
right = mid;
}else{
left = mid + 1;
}
}
//找到左边界后以此继续找
int count = 0;
while(left < len && nums[left] == target){
count++;
left++;
}
return count;
}
}
2.查找右边界
或者通过查找 target + 0.5 的方式
//查找右边界
public static int search1(int[] nums, int target) {
int left = 0,right = nums.length - 1;
while (left <= right){
int mid = (left + right) / 2;
if(nums[mid] <= target){
left = mid + 1;
}else {
right = mid - 1;
}
}
return left;
}
剑指 Offer 53 - II. 0~n-1中缺失的数字
注意:left <= right,初始数组为 nums[0] = 0; 输出为 1
class Solution {
public int missingNumber(int[] nums) {
int left = 0,right = nums.length - 1;
while(left <= right){
int mid = (left + right) / 2;
if(nums[mid] == mid){
left = mid + 1;
}else{
right = mid - 1;
}
}
return left;
}
}
剑指 Offer 54. 二叉搜索树的第k大节点
思路:利用中序遍历的递增性。第K大的点就说明是倒数第k个点。所有需要降序查找
利用二叉树中序遍历的反向遍历
class Solution {
int res,k;
//第 k 大的节点,中序遍历有序递增,反着就递减,这样就方便找到第k大(倒是第k个)的节点
public int kthLargest(TreeNode root, int k) {
this.k = k;
dfs(root);
return res;
}
//中序遍历的反向
public void dfs(TreeNode node){
if(node == null) return;
dfs(node.right);
if(k == 0) return;
if(--k == 0) res = node.val;
dfs(node.left);
}
}
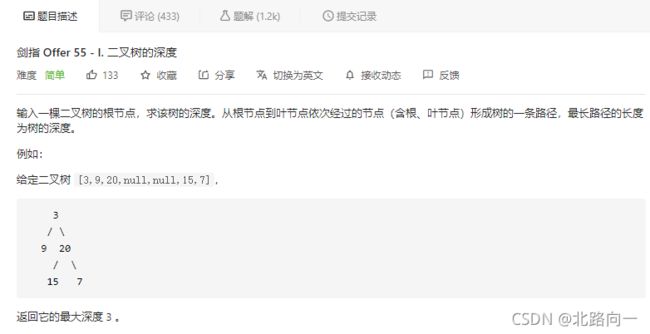
剑指 Offer 55 - I. 二叉树的深度
class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return 0;
return Math.max(maxDepth(root.left),maxDepth(root.right)) + 1;
}
}
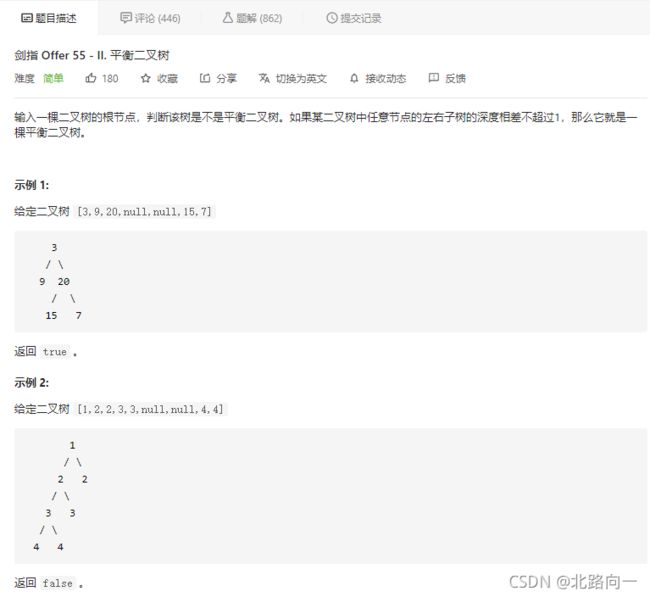
剑指 Offer 55 - II. 平衡二叉树
思路:递归判定两个树的深度是够超过了 1.
class Solution {
boolean isBalanced = true;
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return true;
dpth(root);
return isBalanced;
}
public int dpth(TreeNode node){
if(node == null) return 0;
int left = dpth(node.left);
int right = dpth(node.right);
if(Math.abs(left - right) > 1) isBalanced = false;
return Math.max(left,right) + 1;
}
}
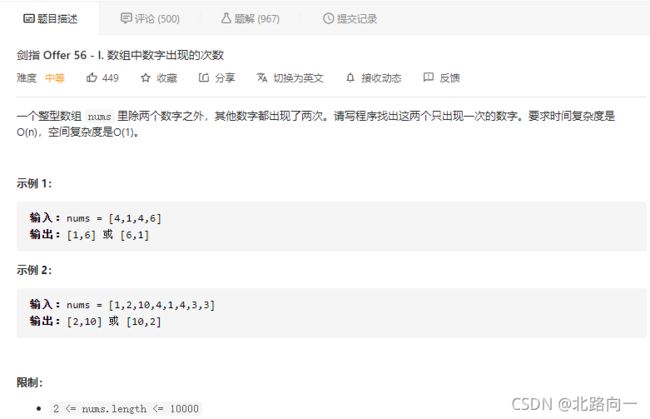
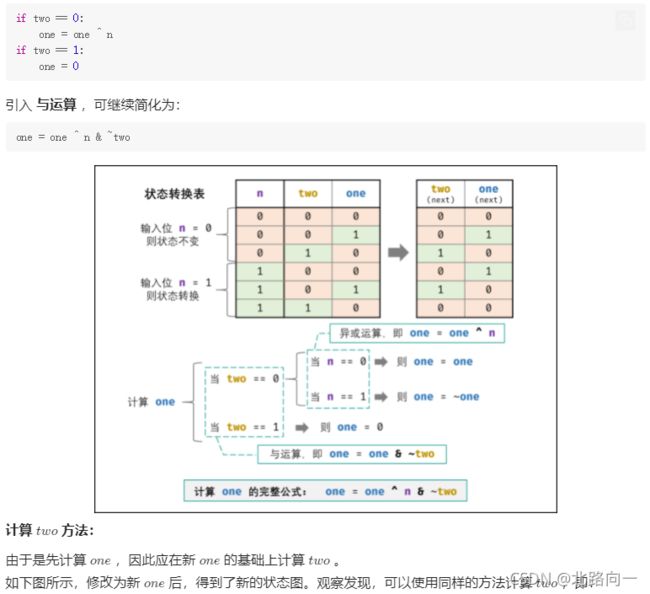
剑指 Offer 56 - I. 数组中数字出现的次数
public int[] singleNumber(int[] nums) {
int x = 0;
for(int num : nums) // 1. 遍历 nums 执行异或运算
x ^= num;
return x; // 2. 返回出现一次的数字 x
}
for(int num: nums) {
if((num & m) != 0) x ^= num; // 若 num & m != 0 , 划分至子数组 1 ,执行遍历异或
else y ^= num; // 若 num & m == 0 , 划分至子数组 2 ,执行遍历异或
}
return new int[] {x, y}; // 遍历异或完毕,返回只出现一次的数字 x 和 y
因为相同的元素异或一定会被分到同一组,并不是平均划分
代码:
class Solution {
//异或运算可以找到只出现一次的树,
public int[] singleNumbers(int[] nums) {
int ans = 0, x = 0, y = 0, m = 1;
for(int a : nums){
ans ^= a;
}
//ans 为最终两个数的异或结果,找到右边第一个为 1 的数字,因为只有当前两个元素此位不同才会出现1
while((ans & m) == 0){
m <<= 1;
}
//以 m 为分组将数组分成两部分,一部分包涵 x,一部分包涵 y,反正相同的元素肯定被分到了一组
for(int a : nums){
if( (a & m) != 0 ) x ^= a;
else y ^= a;
}
return new int[]{x,y};
}
}
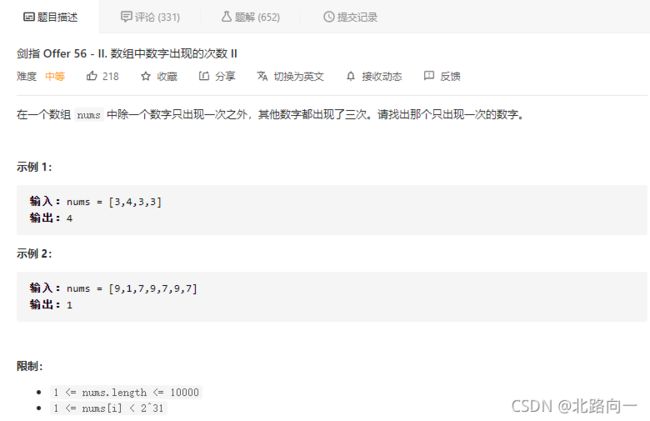
剑指 Offer 56 - II. 数组中数字出现的次数 II
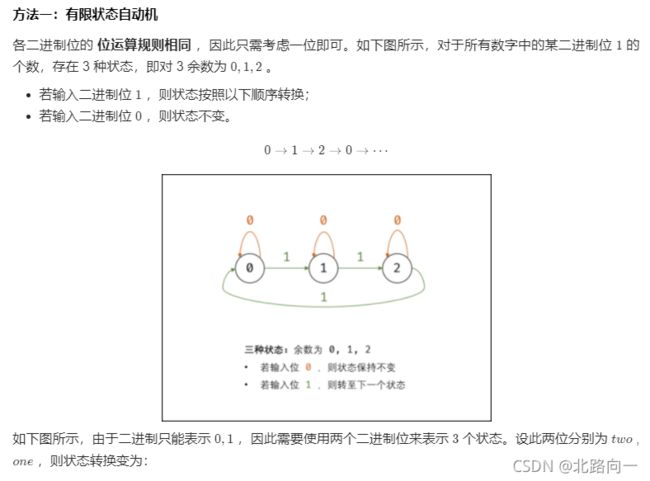
思路:一个数字出现1次,其他出现m次的通用方法
位运算,整数转正二进制的形式看待,则出现3次的话,各个位置出现1的次数都是3的倍数,余数就是只出现一次的那个数
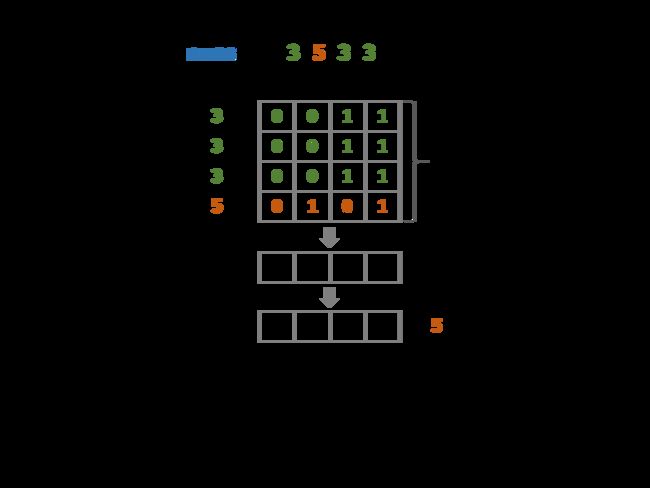
class Solution {
//位运算,变成二进制,则每个数对应的第n个位置1出现的次数。每个位置1出现的次数对3取余就是哪个唯一出现一次的数字了
//这种方法可以求出通用的m个数问题
public int singleNumber(int[] nums) {
int[] count = new int[32];
for(int a : nums){
//统计数字a中二进制1的个数
for(int i = 0; i < 32;i++){
count[i] += a & 1;
a >>>= 1;
}
}
int res = 0;
for(int i = 0;i < 32;i++){
res <<= 1;
res |= count[31 - i] % 3;
}
return res;
}
}
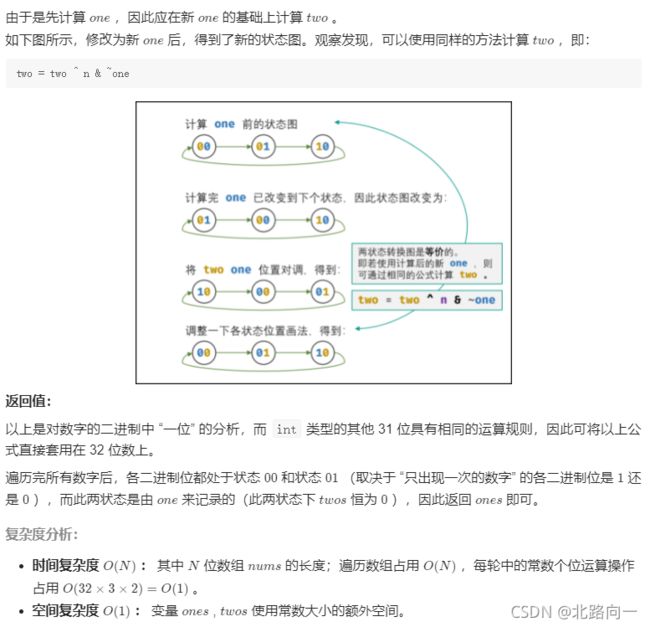
class Solution {
public int singleNumber(int[] nums) {
int ones = 0, twos = 0;
for(int num : nums){
ones = ones ^ num & ~twos;
twos = twos ^ num & ~ones;
}
return ones;
}
}
剑指 Offer 57 - II. 和为s的连续正数序列
class Solution {
//滑动窗口
public int[][] findContinuousSequence(int target) {
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
int sum = 0;
int left = 1, right = 1;
while (left <= target / 2) {
//只能右移
if (sum < target) {
sum += right;
right++;
} else if (sum > target) {
sum -= left;
left++;
} else {
List<Integer> item = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = left; i < right; i++) {
item.add(i);
}
ans.add(item);
sum -= left;
left++;
}
}
int[][] result = new int[ans.size()][1];
for (int i = 0; i < ans.size(); i++) {
List<Integer> list = ans.get(i);
int[] item = new int[list.size()];
for (int j = 0; j < list.size(); j++) {
item[j] = list.get(j);
}
result[i] = item;
}
return result;
}
}
剑指 Offer 57. 和为s的两个数字
class Solution {
//双指针,从两端向中间遍历
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
int left = 0,right = nums.length - 1;
while(left < right){
int sum = nums[left] + nums[right];
if(sum == target){
return new int[]{nums[left],nums[right]};
}else if(sum > target){
right--;
}else{
left++;
}
}
return new int[0];
}
}
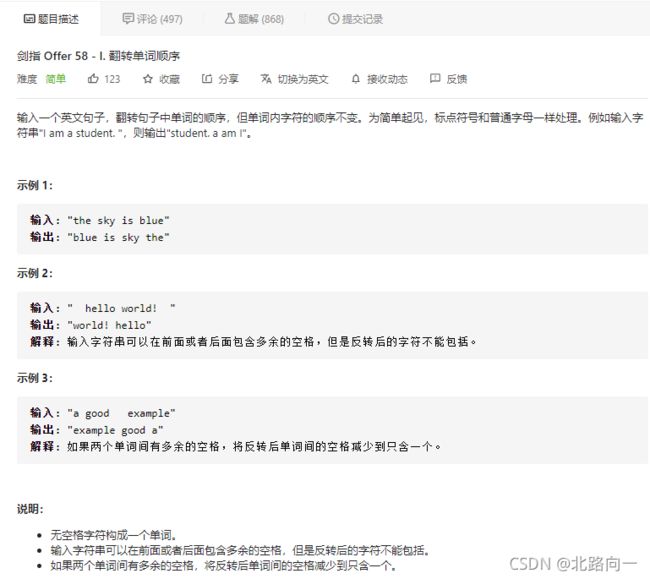
剑指 Offer 58 - I. 翻转单词顺序
class Solution {
public String reverseWords(String s) {
String[] strs = s.trim().split(" ");
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for(int i = strs.length - 1; i >= 0;i--){
if(strs[i].equals("")) continue;
sb.append(strs[i]).append(" ");
}
return sb.toString().trim();
}
}
剑指 Offer 58 - II. 左旋转字符串
思路:反转字符串,直接 s + s,切割n 到 len + n
class Solution {
public String reverseLeftWords(String s, int n) {
if(s.length() <= n) return s;
String ans = s + s;
return ans.substring(n,s.length()+n);
}
}
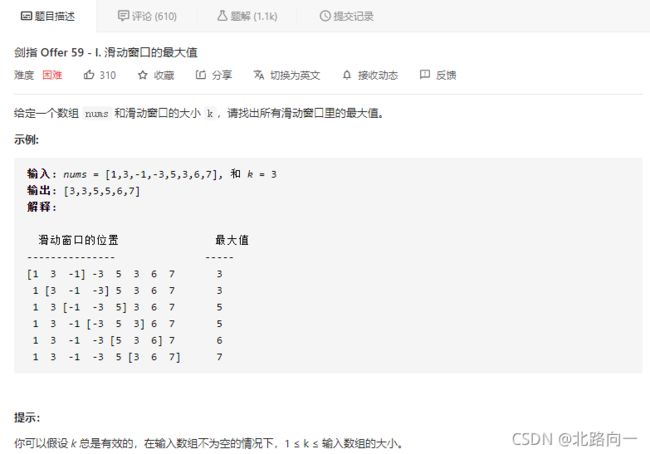
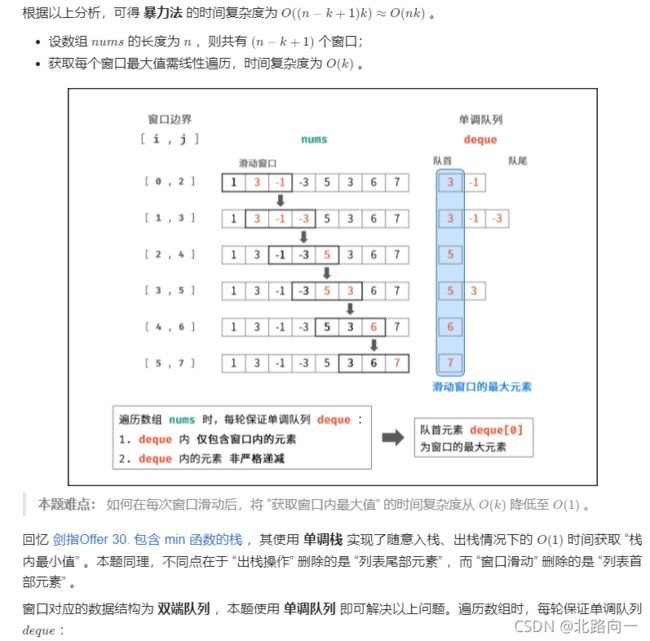
剑指 Offer 59 - I. 滑动窗口的最大值
class Solution {
//滑动窗口,利用单调队列,保证队列是对头最大
public int[] maxSlidingWindow(int[] nums, int k) {
int len = nums.length;
if(len == 0 || k == 0) return new int[0];
int[] ans = new int[len - k + 1];
Deque<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
//未形成窗口前
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++){
//找到窗口内的最大的值,从最后开始添加元素
while(!queue.isEmpty() && queue.peekLast() < nums[i])
queue.removeLast();
queue.addLast(nums[i]);
}
ans[0] = queue.peekFirst();
//开始移动窗口
for(int i = k; i < len; i++){
//如果队头元素比窗口内的第一个元素相等,说明即将将该元素移除了
if(queue.peekFirst() == nums[i - k]) queue.removeFirst();
while(!queue.isEmpty() && queue.peekLast() < nums[i])
queue.removeLast();
queue.addLast(nums[i]);
ans[i - k + 1] = queue.peekFirst();
}
return ans;
}
}
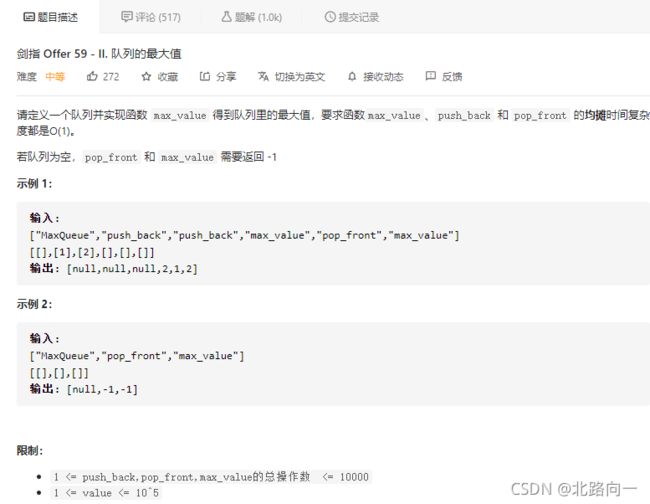
剑指 Offer 59 - II. 队列的最大值
-
一个队列用于存储原始存入的数据 q,另一个队列改造成一个单调递减队列 d,每次获取最大值的时候就从这个单调队列中获取。
-
每次向 d 的末尾添加元素的时候,都会移除掉队尾比 value 小的元素,从而保证 d 是单调的。因为小的元素不影响获取最大值。
-
当取 q 中的元素时候,判断当前元素是否与 d 的队头(及最大)元素相等,如果相等,则将 d 中的队头也一并弹出。这样确保每次都能获取到最大值
class MaxQueue {
private Deque<Integer> queue,maxqueue;
public MaxQueue() {
//保存输入值
queue = new LinkedList<>();
//保存最大值
maxqueue = new LinkedList<>();
}
public int max_value() {
if(maxqueue.isEmpty()) return -1;
return maxqueue.peekFirst();
}
public void push_back(int value) {
//确保maxqueue 倒序排列的,这样每次弹出最大
while(!maxqueue.isEmpty() && maxqueue.peekLast() < value){
maxqueue.pollLast();
}
maxqueue.addLast(value);
queue.addLast(value);
}
public int pop_front() {
if(queue.isEmpty()) return -1;
int a = queue.pollFirst();
if(maxqueue.peekFirst() == a){
maxqueue.pollFirst();
}
return a;
}
}
剑指 Offer 60. n个骰子的点数
只有一个骰子的概率: f ( 1 ) = [ 1 / 6 , 1 / 6 , 1 / 6 , 1 / 6 , 1 / 6 , 1 / 6 ] f(1) = [1/6,1/6,1/6,1/6,1/6,1/6] f(1)=[1/6,1/6,1/6,1/6,1/6,1/6] 和为 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 1,2,3,4,5,6, 1,2,3,4,5,6,
两个骰子时候:和的取值范围为 s u m = [ 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 11 , 12 ] sum =[2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12] sum=[2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12],那么 d p [ 0 ] = 2 = f ( 1 ) ∗ 1 / 6 + f ( 2 ) dp[0] = 2 = f(1)*1/6 + f(2) dp[0]=2=f(1)∗1/6+f(2)
class Solution {
//动态规划,一个筛子每个1-6出现的概率为1/6
public double[] dicesProbability(int n) {
double[] dp = new double[6];
Arrays.fill(dp, 1.0 / 6.0);
//从第二个筛子开始,前面出现的概率会对后面的值有影响,比如第一个筛子是 2,
//第二个筛子的和为 3,4,5,6,7,8概率分别 1/6 *(1/6,1/6,1/6,1/6,1/6,1/6),n 个筛子的所有和为 6 * n - n + 1 = 5n+1
for(int i = 2; i <= n;i++){
//i个筛子出现的所有和的概率dp数组
double[] temp = new double[5 * i + 1];
//当前 i 个筛子的取值概率跟 i- 1 有关
for(int j = 0;j < dp.length; j++){
//计算 temp 概率值,次筛子只能出现 1-6
for(int k = 0; k < 6; k++){
//之前dp[1] = 1/6,表示1个筛子 和为 2 的概率,现在最新的筛子为 k,则当前和为 j + k
temp[j + k] += dp[j] * (1.0 / 6.0);
}
}
dp = temp;
}
return dp;
}
}
剑指 Offer 61. 扑克牌中的顺子
思路:判断顺子就是 m a x − m i n < 5 max - min < 5 max−min<5 才能构成顺子,并且出现重复数字直接返回false
class Solution {
//最大值和最小值只差 >= 5就不能构成顺子
public boolean isStraight(int[] nums) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
int count = 0;//小王的个数
for(int i = 0; i < 4;i++){
if(nums[i] == 0){
count++;
} else if( nums[i] == nums[i + 1]){
//出现重复的数字,直接返回,注意这里只遍历到 i = 3
return false;
}
}
return nums[4] - nums[count] < 5;
}
}
剑指 Offer 62. 圆圈中最后剩下的数字
class Solution {
//约瑟夫环问题
public int lastRemaining(int n, int m) {
int dp = 0;
for(int i = 2; i <= n;i++){
dp = (dp + m) % i;
}
return dp;
}
}
剑指 Offer 63. 股票的最大利润
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
if(prices.length < 2) return 0;
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
int ans = 0;
stack.push(prices[0]);
for(int i = 1; i < prices.length; i++){
if(!stack.isEmpty() && stack.peek() > prices[i]){
stack.pop();
stack.push(prices[i]);
}else{
ans = Math.max(ans,prices[i] - stack.peek());
}
}
return ans;
}
}
思路二:动态规划,记录之前的最小值
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE, ans = 0;
for(int a : prices){
min = Math.min(min,a);
ans = Math.max(ans, a - min);
}
return ans;
}
}
剑指 Offer 64. 求1+2+…+n
思路:不能用各种运算符,递归做加法需要有终止条件,用逻辑运算符起到短路的作用

class Solution {
//逻辑元起到短路的效果
public int sumNums(int n) {
boolean x = (n > 1) && (n += sumNums(n - 1)) > 0;
return n;
}
}
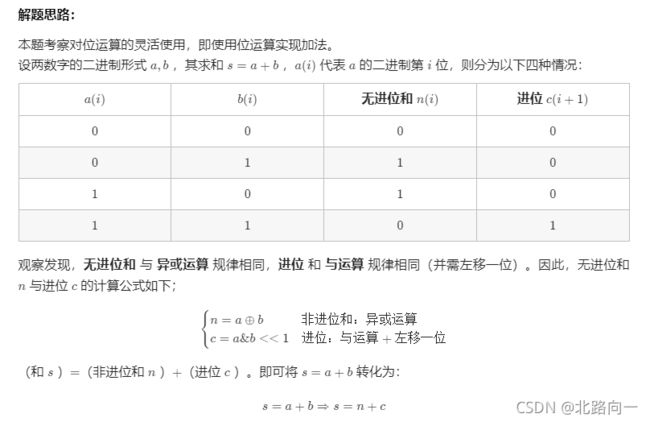
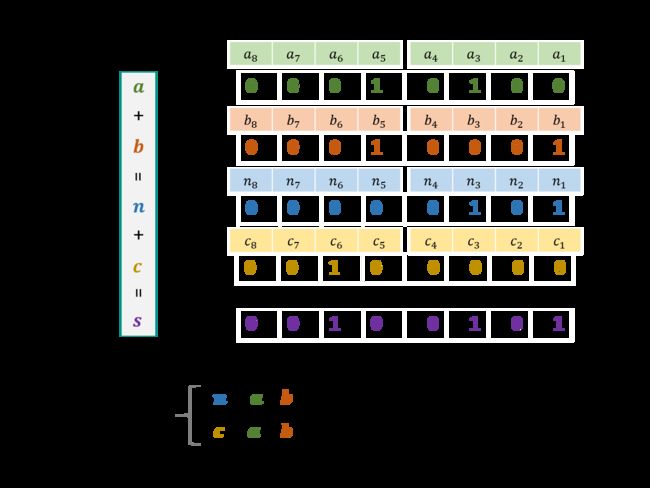
剑指 Offer 65. 不用加减乘除做加法
负数: 负数的二进制表示形式,二进制取反加1: e g : 8 = 00001000 − > − 8 = 11110111 + 1 = 11111000 eg: 8 = 00001000 -> -8 = 11110111+1 = 11111000 eg:8=00001000−>−8=11110111+1=11111000
class Solution {
//二进制运算,定义 c 为进位,n为和,分别用 b 和 a 来表示
public int add(int a, int b) {
//进位存在
while(b != 0){
int c = (a & b) << 1;
a ^= b;
b = c;
}
return a;
}
}
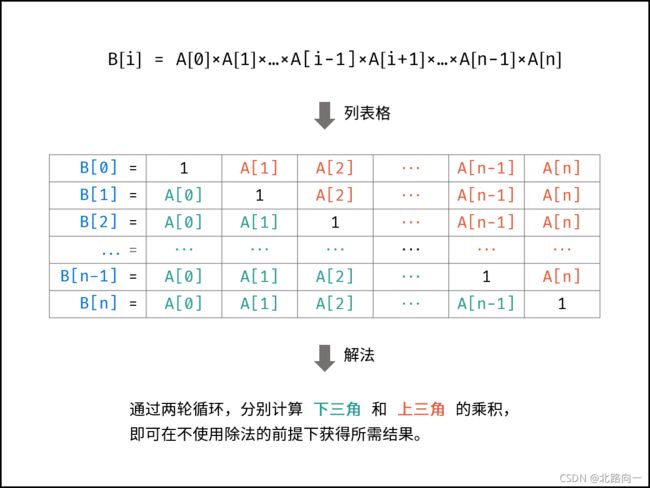
剑指 Offer 66. 构建乘积数组
class Solution {
//维护左右两个dp数组,分别保存,dpL[i] 为 1 * 2* 3... i -1 的和
//同理右边也为:dpR[i] 为 n * n- 2 * ... n - i + 1的和。
//那么 B[i] = dpL[i] * dpR[i]
public int[] constructArr(int[] a) {
if(a == null || a.length == 0) return new int[0];
int len = a.length;
int[] dpL = new int[len];
int[] dpR = new int[len];
//构建左右dp数组
dpL[0] = 1;
dpR[len - 1] = 1;
for(int i = 1; i < len ;i++ ){
dpL[i] = dpL[i - 1] * a[i - 1];
}
for(int i = len - 2; i >=0;i--){
dpR[i] = dpR[i + 1] * a[i + 1];
}
for(int i = 0; i < len;i++){
a[i] = dpL[i] * dpR[i];
}
return a;
}
}
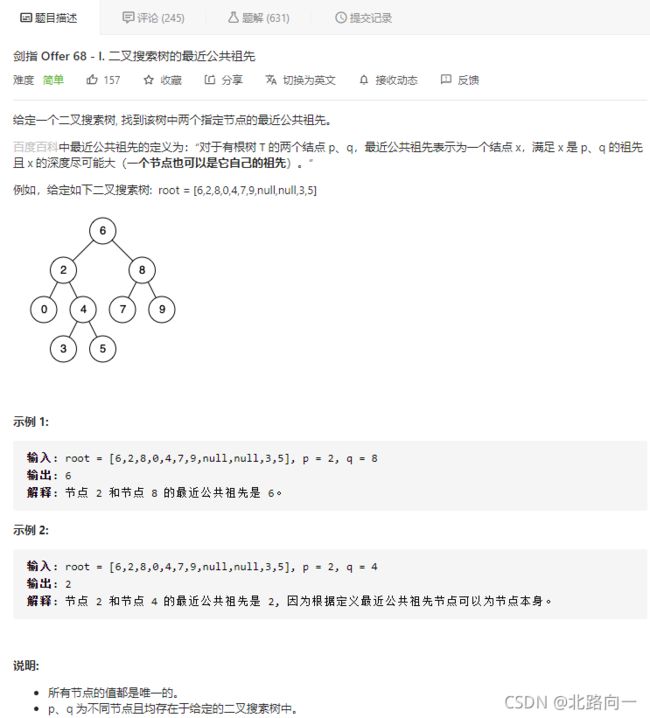
剑指 Offer 68 - I. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
题解:二叉搜索树的性质,要么当前node节点为祖先,要么它的子节点
class Solution {
//本题为二叉搜索树,并且值唯一,无论怎样,一定存在公共祖先,最起码root是的
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(root.val > p.val && root.val > q.val){
//给定当前的节点,发现p,p都比他小,那么只能往左子树递归了
return lowestCommonAncestor(root.left,p,q);
}else if(root.val < p.val && root.val < q.val){
return lowestCommonAncestor(root.right,p,q);
}else{
return root;
}
}
}
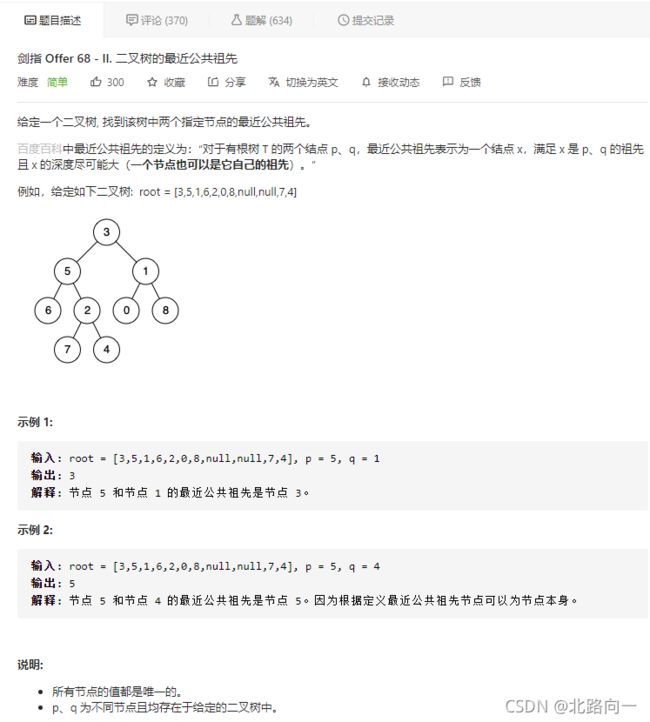
剑指 Offer 68 - II. 二叉树的最近公共祖先
class Solution {
//与二叉搜索树不同的是,这个递归的条件结束不同,需要持续往左右子树去找公共祖先,要么找到相等的,直接返回,要么p,q在node的两侧
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(root == null) return null;
if(root.val == p.val || root.val == q.val) return root;
//都没找到,递归左右子树
TreeNode left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left,p,q);
TreeNode right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right,p,q);
if(left == null) return right;
if(right == null) return left;
//不在左右子树中,那就在两边
return root;
}
}