2.【Sharding-JDBC】快速入门
2.Sharding-JDBC快速入门
2.1 需求说明
本章节使用Sharding-JDBC完成对订单表的水平分表,通过快速入门程序的开发,快速体验Sharding-JDBC的使用方法。
人工创建两张表,t_order_1和t_order_2,这两张表是订单表拆分后的表,通过Sharding-Jdbc向订单表插入数据,按照一定的分片规则,主键为偶数的进入t_order_1,另一部分数据进入t_order_2,通过Sharding-Jdbc 查询数据,根据 SQL语句的内容从t_order_1或t_order_2查询数据。
2.2.环境搭建
2.2.1 环境说明
- 操作系统:Win10
- 数据库:MySQL-5.7.25
- JDK:64位 jdk1.8.0_201
- 应用框架:spring-boot-2.1.3.RELEASE,Mybatis3.5.0
- Sharding-JDBC:sharding-jdbc-spring-boot-starter-4.0.0-RC1
2.2.2 创建数据库
创建订单库order_db
CREATE DATABASE `order_db` CHARACTER SET 'utf8' COLLATE 'utf8_general_ci';
在order_db中创建t_order_1、t_order_2表
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `t_order_1`;
CREATE TABLE `t_order_1` (
`order_id` bigint(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '订单id',
`price` decimal(10, 2) NOT NULL COMMENT '订单价格',
`user_id` bigint(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '下单用户id',
`status` varchar(50) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NOT NULL COMMENT '订单状态',
PRIMARY KEY (`order_id`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE = InnoDB CHARACTER SET = utf8 COLLATE = utf8_general_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `t_order_2`;
CREATE TABLE `t_order_2` (
`order_id` bigint(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '订单id',
`price` decimal(10, 2) NOT NULL COMMENT '订单价格',
`user_id` bigint(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '下单用户id',
`status` varchar(50) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NOT NULL COMMENT '订单状态',
PRIMARY KEY (`order_id`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE = InnoDB CHARACTER SET = utf8 COLLATE = utf8_general_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic;
2.2.3.引入maven依赖
引入 sharding-jdbc和SpringBoot整合的Jar包:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shardingspheregroupId>
<artifactId>sharding‐jdbc‐spring‐boot‐starterartifactId>
<version>4.0.0‐RC1version>
dependency>
具体spring boot相关依赖及配置请参考资料中dbsharding/sharding-jdbc-simple工程,本指引只说明与ShardingJDBC相关的内容。
2.3 编写程序
2.3.1 分片规则配置
分片规则配置是sharding-jdbc进行对分库分表操作的重要依据,配置内容包括:数据源、主键生成策略、分片策略等。
在application.properties中配置
server.port=56081
spring.application.name = sharding‐jdbc‐simple‐demo
server.servlet.context‐path = /sharding‐jdbc‐simple‐demo
spring.http.encoding.enabled = true
spring.http.encoding.charset = UTF‐8
spring.http.encoding.force = true
spring.main.allow‐bean‐definition‐overriding = true
mybatis.configuration.map‐underscore‐to‐camel‐case = true
# 以下是分片规则配置
# 定义数据源
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.names = m1
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.type = com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.driver‐class‐name = com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.url = jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/order_db?useUnicode=true
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.username = root
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.password = root
# 指定t_order表的数据分布情况,配置数据节点
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.actual‐data‐nodes = m1.t_order_$‐>{1..2}
# 指定t_order表的主键生成策略为SNOWFLAKE
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.key‐generator.column=order_id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.key‐generator.type=SNOWFLAKE
# 指定t_order表的分片策略,分片策略包括分片键和分片算法
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.table‐strategy.inline.sharding‐column = order_id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.table‐strategy.inline.algorithm‐expression =
t_order_$‐>{order_id % 2 + 1}
# 打开sql输出日志
spring.shardingsphere.props.sql.show = true
swagger.enable = true
logging.level.root = info
logging.level.org.springframework.web = info
logging.level.com.itheima.dbsharding = debug
logging.level.druid.sql = debug
1.首先定义数据源m1,并对m1进行实际的参数配置。
2.指定t_order表的数据分布情况,他分布在m1.t_order_1,m1.t_order_2
3.指定t_order表的主键生成策略为SNOWFLAKE,SNOWFLAKE是一种分布式自增算法,保证id全局唯一
4.定义t_order分片策略,order_id为偶数的数据落在t_order_1,为奇数的落在t_order_2,分表策略的表达式为t_order_$->{order_id % 2 + 1}
2.3.2.数据操作
@Mapper
@Component
public interface OrderDao {
/**
* 新增订单
* @param price 订单价格
* @param userId 用户id
* @param status 订单状态
* @return
*/
@Insert("insert into t_order(price,user_id,status) value(#{price},#{userId},#{status})")
int insertOrder(@Param("price") BigDecimal price, @Param("userId") Long userId
, @Param("status") String status);
/**
* 根据id列表查询多个订单
* @param orderIds 订单id列表
* @return
*/
@Select({
""
})
List < Map > selectOrderbyIds(@Param("orderIds") List < Long > orderIds);
}
2.3.3.测试
编写单元测试:
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = {
ShardingJdbcSimpleDemoBootstrap.class
})
public class OrderDaoTest {
@Autowired
private OrderDao orderDao;
@Test
public void testInsertOrder() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
orderDao.insertOrder(new BigDecimal((i + 1) * 5), 1 L, "WAIT_PAY");
}
}
@Test
public void testSelectOrderbyIds() {
List < Long > ids = new ArrayList < > ();
ids.add(373771636085620736 L);
ids.add(373771635804602369 L);
List < Map > maps = orderDao.selectOrderbyIds(ids);
System.out.println(maps);
}
}
执行testInsertOrder:
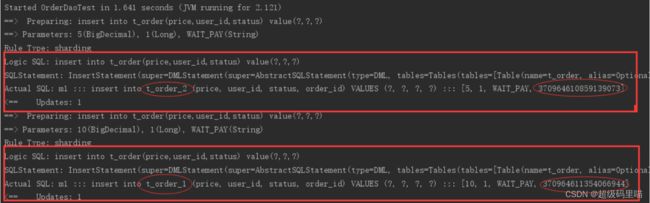
通过日志可以发现order_id为奇数的被插入到t_order_2表,为偶数的被插入到t_order_1表,达到预期目标。
执行testSelectOrderbyIds:

通过日志可以发现,根据传入order_id的奇偶不同,sharding-jdbc分别去不同的表检索数据,达到预期目标。
2.4.流程分析
通过日志分析,Sharding-JDBC在拿到用户要执行的sql之后干了哪些事儿:
(1)解析sql,获取片键值,在本例中是order_id
(2)Sharding-JDBC通过规则配置 t_order_$->{order_id % 2 + 1},知道了当order_id为偶数时,应该往t_order_1表插数据,为奇数时,往t_order_2插数据。
(3)于是Sharding-JDBC根据order_id的值改写sql语句,改写后的SQL语句是真实所要执行的SQL语句。
(4)执行改写后的真实sql语句
(5)将所有真正执行sql的结果进行汇总合并,返回。
2.5.其他集成方式
Sharding-JDBC不仅可以与spring boot良好集成,它还支持其他配置方式,共支持以下四种集成方式。
Spring Boot Yaml 配置
定义application.yml,内容如下:
server:
port: 56081
servlet:
context‐path: /sharding‐jdbc‐simple‐demo
spring:
application:
name: sharding‐jdbc‐simple‐demo
http:
encoding:
enabled: true
charset: utf‐8
force: true
main:
allow‐bean‐definition‐overriding: true
shardingsphere:
datasource:
names: m1
m1:
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
driverClassName: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/order_db?useUnicode=true
username: root
password: mysql
sharding:
tables:
t_order:
actualDataNodes: m1.t_order_$‐>{1..2}
tableStrategy:
inline:
shardingColumn: order_id
algorithmExpression: t_order_$‐>{order_id % 2 + 1}
keyGenerator:
type: SNOWFLAKE
column: order_id
props:
sql:
show: true
mybatis:
configuration:
map‐underscore‐to‐camel‐case: true
swagger:
enable: true
logging:
level:
root: info
org.springframework.web: info
com.itheima.dbsharding: debug
druid.sql: debug
如果使用application.yml则需要屏蔽原来的application.properties文件。
Java 配置
添加配置类:
@Configuration
public class ShardingJdbcConfig {
// 定义数据源
Map < String, DataSource > createDataSourceMap() {
DruidDataSource dataSource1 = new DruidDataSource();
dataSource1.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
dataSource1.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/order_db?useUnicode=true");
dataSource1.setUsername("root");
dataSource1.setPassword("root");
Map < String, DataSource > result = new HashMap < > ();
result.put("m1", dataSource1);
return result;
}
// 定义主键生成策略
private static KeyGeneratorConfiguration getKeyGeneratorConfiguration() {
KeyGeneratorConfiguration result = new
KeyGeneratorConfiguration("SNOWFLAKE", "order_id");
return result;
}
// 定义t_order表的分片策略
TableRuleConfiguration getOrderTableRuleConfiguration() {
TableRuleConfiguration result = new TableRuleConfiguration("t_order", "m1.t_order_$‐> {
1. .2
}
");
result.setTableShardingStrategyConfig(new InlineShardingStrategyConfiguration("order_id", "t_order_$‐>{order_id % 2 + 1}")); result.setKeyGeneratorConfig(getKeyGeneratorConfiguration());
return result;
}
// 定义sharding‐Jdbc数据源
@Bean
DataSource getShardingDataSource() throws SQLException {
ShardingRuleConfiguration shardingRuleConfig = new ShardingRuleConfiguration();
shardingRuleConfig.getTableRuleConfigs()
.add(getOrderTableRuleConfiguration());
//spring.shardingsphere.props.sql.show = true
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.put("sql.show", "true");
return ShardingDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(createDataSourceMap()
, shardingRuleConfig, properties);
}
}
}
由于采用了配置类所以需要屏蔽原来application.properties文件中spring.shardingsphere开头的配置信息。
还需要在SpringBoot启动类中屏蔽使用spring.shardingsphere配置项的类:
@SpringBootApplication(exclude = {SpringBootConfiguration.class})
public class ShardingJdbcSimpleDemoBootstrap {....}
Spring Boot properties配置
此方式同快速入门程序。
# 定义数据源
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.names = m1
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.type = com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.driver‐class‐name = com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.url = jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/order_db?useUnicode=true
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.username = root
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.m1.password = root
# 指定t_order表的主键生成策略为SNOWFLAKE
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.key‐generator.column=order_id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.key‐generator.type=SNOWFLAKE
# 指定t_order表的数据分布情况
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.actual‐data‐nodes = m1.t_order_$‐>{1..2}
# 指定t_order表的分表策略
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.table‐strategy.inline.sharding‐column = order_id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.table‐strategy.inline.algorithm‐expression = t_order_$‐>{order_id % 2 + 1}
Spring命名空间配置
此方式使用xml方式配置,不推荐使用。
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema‐instance"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:sharding="http://shardingsphere.apache.org/schema/shardingsphere/sharding"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring‐beans.xsd
http://shardingsphere.apache.org/schema/shardingsphere/sharding
http://shardingsphere.apache.org/schema/shardingsphere/sharding/sharding.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring‐context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring‐tx.xsd">
<context:annotation‐config />
<!‐‐定义多个数据源‐‐>
<bean id="m1" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource" destroy‐method="close">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" />
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/order_db_1?useUnicode=true" />
<property name="username" value="root" />
<property name="password" value="root" />
bean>
<!‐‐定义分库策略‐‐>
<sharding:inline‐strategy id="tableShardingStrategy" sharding‐column="order_id" algorithm‐
expression="t_order_$‐>{order_id % 2 + 1}" />
<!‐‐定义主键生成策略‐‐>
<sharding:key‐generator id="orderKeyGenerator" type="SNOWFLAKE" column="order_id" />
<!‐‐定义sharding‐Jdbc数据源‐‐>
<sharding:data‐source id="shardingDataSource">
<sharding:sharding‐rule data‐source‐names="m1">
<sharding:table‐rules>
<sharding:table‐rule logic‐table="t_order" table‐strategy‐
ref="tableShardingStrategy" key‐generator‐ref="orderKeyGenerator" />
sharding:table‐rules>
sharding:sharding‐rule>
sharding:data‐source>
beans>