Code Lab - 3&4
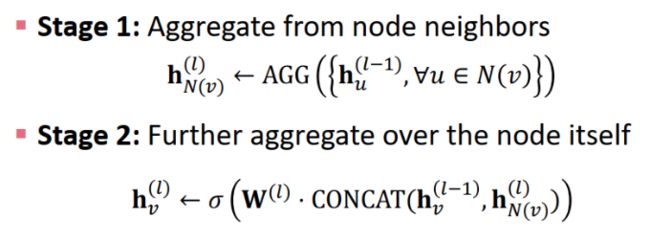
GAT里面有一些地方看的不是太懂(GAT里Multi Attention的具体做法),暂时找了参考代码,留一个疑问
1. 一个通用的GNN Stack
import torch_geometric
import torch
import torch_scatter
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch_geometric.nn as pyg_nn
import torch_geometric.utils as pyg_utils
from torch import Tensor
from typing import Union, Tuple, Optional
from torch_geometric.typing import (OptPairTensor, Adj, Size, NoneType,
OptTensor)
from torch.nn import Parameter, Linear
from torch_sparse import SparseTensor, set_diag
from torch_geometric.nn.conv import MessagePassing
from torch_geometric.utils import remove_self_loops, add_self_loops, softmax
class GNNStack(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_dim, hidden_dim, output_dim, args, emb=False):
super(GNNStack, self).__init__()
conv_model = self.build_conv_model(args.model_type)
self.convs = nn.ModuleList()
self.convs.append(conv_model(input_dim, hidden_dim))
#assert(断言) 用于判断一个表达式,在表达式条件为 false 的时候触发异常
assert (args.num_layers >= 1), 'Number of layers is not >=1'
for l in range(args.num_layers-1):
self.convs.append(conv_model(args.heads * hidden_dim, hidden_dim))
# post-message-passing
self.post_mp = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(args.heads * hidden_dim, hidden_dim), nn.Dropout(args.dropout),
nn.Linear(hidden_dim, output_dim))
self.dropout = args.dropout
self.num_layers = args.num_layers
self.emb = emb
def build_conv_model(self, model_type):
if model_type == 'GraphSage':
return GraphSage
elif model_type == 'GAT':
# When applying GAT with num heads > 1, you need to modify the
# input and output dimension of the conv layers (self.convs),
# to ensure that the input dim of the next layer is num heads
# multiplied by the output dim of the previous layer.
# HINT: In case you want to play with multiheads, you need to change the for-loop that builds up self.convs to be
# self.convs.append(conv_model(hidden_dim * num_heads, hidden_dim)),
# and also the first nn.Linear(hidden_dim * num_heads, hidden_dim) in post-message-passing.
return GAT
def forward(self, data):
x, edge_index, batch = data.x, data.edge_index, data.batch
for i in range(self.num_layers):
x = self.convs[i](x, edge_index)
x = F.relu(x)
x = F.dropout(x, p=self.dropout,training=self.training)
x = self.post_mp(x)
if self.emb == True:
return x
return F.log_softmax(x, dim=1)
def loss(self, pred, label):
return F.nll_loss(pred, label)2. 实现GraphSage和GAT
2.1 GraphSage
class GraphSage(MessagePassing):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, normalize = True,
bias = False, **kwargs):
super(GraphSage, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.in_channels = in_channels
self.out_channels = out_channels
self.normalize = normalize
# self.lin_l is the linear transformation that you apply to embedding for central node.
self.lin_l=Linear(in_channels,out_channels) #Wl
# self.lin_r is the linear transformation that you apply to aggregated message from neighbors.
self.lin_r=Linear(in_channels,out_channels) #Wr
self.reset_parameters()
def reset_parameters(self):
self.lin_l.reset_parameters()
self.lin_r.reset_parameters()
def forward(self, x, edge_index, size = None):
# 调用propagation函数进行消息传递:propagate(edge_index, x=(x_i, x_j), extra=(extra_i, extra_j), size=size)
# 我们将只使用邻居节点(x_j)的表示,因此默认情况下我们为中心节点和邻居节点传递与x=(x,x)相同的表示
out1 = self.lin_l(x)
out2 = self.propagate(edge_index,x = (x,x),size = size)
out2 = self.lin_r(out2)
out = out1 + out2
if self.normalize:
out = F.normalize(out)
return out
# 供propagate调用,对于所有(i,j)边,构造从邻点j到中心点i的信息
# x_j表示 所有邻点的特征嵌入矩阵
def message(self, x_j):
out = x_j
return out
# 聚合邻居信息
def aggregate(self, inputs, index, dim_size = None):
# The axis along which to index number of nodes.
node_dim = self.node_dim
out = torch_scatter.scatter(inputs,index,node_dim,dim_size=dim_size,reduce='mean')
return out
2.2 GAT
class GAT(MessagePassing):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, heads = 2,
negative_slope = 0.2, dropout = 0., **kwargs):
super(GAT, self).__init__(node_dim=0, **kwargs)
self.in_channels = in_channels
self.out_channels = out_channels
self.heads = heads
self.negative_slope = negative_slope
self.dropout = dropout
# self.lin_l is the linear transformation that you apply to embeddings
# Pay attention to dimensions of the linear layers, since we're using multi-head attention.
self.lin_l = Linear(in_channels,heads*out_channels) #W_l 这里的in_channels就是已经乘过heads的数字
self.lin_r = self.lin_l #W_r
# Define the attention parameters \overrightarrow{a_l/r}^T in the above intro.
self.att_l = Parameter(torch.Tensor(1, heads, out_channels))
self.att_r = Parameter(torch.Tensor(1, heads, out_channels))
self.reset_parameters()
def reset_parameters(self):
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(self.lin_l.weight)
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(self.lin_r.weight)
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(self.att_l)
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(self.att_r)
def forward(self, x, edge_index, size = None):
H, C = self.heads, self.out_channels
x_l = self.lin_l(x)
x_r = self.lin_r(x)
x_l = x_l.view(-1,H,C)
x_r = x_r.view(-1,H,C)
alpha_l = (x_l * self.att_l).sum(axis=1) #*是逐元素相乘(每个特征对应的所有节点一样处理?)。sum的维度是H(聚合)。
alpha_r = (x_r * self.att_r).sum(axis=1)
out = self.propagate(edge_index, x=(x_l, x_r), alpha=(alpha_l, alpha_r),size=size)
out = out.view(-1, H * C)
return out
def message(self, x_j, alpha_j, alpha_i, index, ptr, size_i):
#alpha:[E, C]
alpha = alpha_i + alpha_j #leakyrelu的对象
alpha = F.leaky_relu(alpha,self.negative_slope)
alpha = softmax(alpha, index, ptr, size_i)
alpha = F.dropout(alpha, p=self.dropout, training=self.training).unsqueeze(1) #[E,1,C]
out = x_j * alpha #通过计算得到的alpha来计算节点信息聚合值(得到h_i^') #[E,H,C]
return out
def aggregate(self, inputs, index, dim_size = None):
out = torch_scatter.scatter(inputs, index, dim=self.node_dim, dim_size=dim_size, reduce='sum')
return out3. 训练
3.1 优化器
import torch.optim as optim
def build_optimizer(args, params):
weight_decay = args.weight_decay
filter_fn = filter(lambda p : p.requires_grad, params)
if args.opt == 'adam':
optimizer = optim.Adam(filter_fn, lr=args.lr, weight_decay=weight_decay)
elif args.opt == 'sgd':
optimizer = optim.SGD(filter_fn, lr=args.lr, momentum=0.95, weight_decay=weight_decay)
elif args.opt == 'rmsprop':
optimizer = optim.RMSprop(filter_fn, lr=args.lr, weight_decay=weight_decay)
elif args.opt == 'adagrad':
optimizer = optim.Adagrad(filter_fn, lr=args.lr, weight_decay=weight_decay)
if args.opt_scheduler == 'none':
return None, optimizer
elif args.opt_scheduler == 'step':
scheduler = optim.lr_scheduler.StepLR(optimizer, step_size=args.opt_decay_step, gamma=args.opt_decay_rate)
elif args.opt_scheduler == 'cos':
scheduler = optim.lr_scheduler.CosineAnnealingLR(optimizer, T_max=args.opt_restart)
return scheduler, optimizer3.2 训练
import time
import networkx as nx
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.optim as optim
from tqdm import trange
import pandas as pd
import copy
from torch_geometric.datasets import TUDataset
from torch_geometric.datasets import Planetoid
from torch_geometric.data import DataLoader
import torch_geometric.nn as pyg_nn
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def train(dataset, args):
print("Node task. test set size:", np.sum(dataset[0]['test_mask'].numpy()))
print()
test_loader = loader = DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=args.batch_size, shuffle=False)
# build model
model = GNNStack(dataset.num_node_features, args.hidden_dim, dataset.num_classes,
args)
scheduler, opt = build_optimizer(args, model.parameters())
# train
losses = []
test_accs = []
best_acc = 0
best_model = None
for epoch in trange(args.epochs, desc="Training", unit="Epochs"):
total_loss = 0
model.train()
for batch in loader:
opt.zero_grad()
pred = model(batch)
label = batch.y
pred = pred[batch.train_mask]
label = label[batch.train_mask]
loss = model.loss(pred, label)
loss.backward()
opt.step()
total_loss += loss.item() * batch.num_graphs
total_loss /= len(loader.dataset)
losses.append(total_loss)
if epoch % 10 == 0:
test_acc = test(test_loader, model)
test_accs.append(test_acc)
if test_acc > best_acc:
best_acc = test_acc
best_model = copy.deepcopy(model)
else:
test_accs.append(test_accs[-1])
return test_accs, losses, best_model, best_acc, test_loader
def test(loader, test_model, is_validation=False, save_model_preds=False, model_type=None):
test_model.eval()
correct = 0
# Note that Cora is only one graph!
for data in loader:
with torch.no_grad():
# max(dim=1) returns values, indices tuple; only need indices
pred = test_model(data).max(dim=1)[1]
label = data.y
mask = data.val_mask if is_validation else data.test_mask
# node classification: only evaluate on nodes in test set
pred = pred[mask]
label = label[mask]
if save_model_preds:
print ("Saving Model Predictions for Model Type", model_type)
data = {}
data['pred'] = pred.view(-1).cpu().detach().numpy()
data['label'] = label.view(-1).cpu().detach().numpy()
df = pd.DataFrame(data=data)
# Save locally as csv
df.to_csv('CORA-Node-' + model_type + '.csv', sep=',', index=False)
correct += pred.eq(label).sum().item()
total = 0
for data in loader.dataset:
total += torch.sum(data.val_mask if is_validation else data.test_mask).item()
return correct / total
class objectview(object):
def __init__(self, d):
self.__dict__ = dfor args in [
{'model_type': 'GraphSage', 'dataset': 'cora', 'num_layers': 2, 'heads': 1, 'batch_size': 32, 'hidden_dim': 32, 'dropout': 0.5, 'epochs': 500, 'opt': 'adam', 'opt_scheduler': 'none', 'opt_restart': 0, 'weight_decay': 5e-3, 'lr': 0.01},
]:
args = objectview(args)
for model in ['GraphSage']:
args.model_type = model
# Match the dimension.
if model == 'GAT':
args.heads = 2
else:
args.heads = 1
if args.dataset == 'cora':
dataset = Planetoid(root='/tmp/cora', name='Cora')
else:
raise NotImplementedError("Unknown dataset")
test_accs, losses, best_model, best_acc, test_loader = train(dataset, args)
print("Maximum test set accuracy: {0}".format(max(test_accs)))
print("Minimum loss: {0}".format(min(losses)))
# Run test for our best model to save the predictions!
test(test_loader, best_model, is_validation=False, save_model_preds=True, model_type=model)
print()
plt.title(dataset.name)
plt.plot(losses, label="training loss" + " - " + args.model_type)
plt.plot(test_accs, label="test accuracy" + " - " + args.model_type)
plt.legend()
plt.show()