HTTPS协议工作流程(原理)
目录
前言
一、Http是什么?
1.1、 HTTP的数据传输过程
1.2、HTTP请求报文
1.3、HTTP响应报文
二、HTTPS(HTTP+SSL)
对称加密算法:
非对称加密算法
总结(原理)
前言
Http作为网络上的常用协议,主要用于浏览器端到服务器端的通信,是应用层的协议,在运输层基于TCP协议而完成数据的传输,而Https是安全的HTTP协议,在HTTP的基础上附加了SSL(安全套接层),通过一系列的机制实现了浏览器和服务器之间的安全数据传输。
一、Http是什么?
在介绍HTTPS之前,先要了解HTTP协议,HTTP协议又称超文本传输协议,用于在浏览器和服务器之间的数据传递,通过Http协议的特定需求生成特定格式的请求响应报文来DNS进行数据传递。
1.1、 HTTP的数据传输过程
- DNS(域名解析服务器)解析请求的域名将解析结果请求到指定服务器。
- 浏览器向服务器发起一个建立TCP连接的请求,进行TCP连接(三次握手,在上一篇中有解释详细一点2的过程)
- TCP连接建立后,浏览器端向服务器端发送一个HTTP格式的报文请求,
- 服务器端收到请求报文进行解析,并将解析的结果处理后,生成一个HTTP格式的响应报文,发送给浏览器端。
- 浏览器通过解析响应报文将响应结果渲染给用户
1.2、HTTP请求报文
POST http://www.example.com/ HTTP/1.1
Accept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,image/webp,image/apng,*/*;q=0.8,application/signed-exchange;v=b3;q=0.9
Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate
Accept-Language: zh-CN,zh;q=0.9,en;q=0.8
Cache-Control: max-age=0
Host: www.example.com
If-Modified-Since: Thu, 17 Oct 2019 07:18:26 GMT
If-None-Match: "3147526947+gzip"
Proxy-Connection: keep-alive
Upgrade-Insecure-Requests: 1
User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 xxx
param1=1¶m2=2- 请求报文的首行是请求方式 URL 协议版本
- 从第二行到空行属于请求报文头部
- 空行以下属于请求体
1.3、HTTP响应报文
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Age: 529651
Cache-Control: max-age=604800
Connection: keep-alive
Content-Encoding: gzip
Content-Length: 648
Content-Type: text/html; charset=UTF-8
Date: Mon, 02 Nov 2020 17:53:39 GMT
Etag: "3147526947+ident+gzip"
Expires: Mon, 09 Nov 2020 17:53:39 GMT
Keep-Alive: timeout=4
Last-Modified: Thu, 17 Oct 2019 07:18:26 GMT
Proxy-Connection: keep-alive
Server: ECS (sjc/16DF)
Vary: Accept-Encoding
X-Cache: HIT
Example Domain
// 省略...
- 响应报文的首行是 协议版本 请求状态码
- 从第二行到空行属于响应报文头部
- 空行以下属于响应体
存在问题
- HTTP协议的报文使用明文通信,在数据传输过程中,存在有报文被中途截获的问题,数据安全无法保证;
- 另外,http的请求容易被恶意的伪装
因此,在HTTP的原有基础上增加了新的安全机制,就有了https。
二、HTTPS(HTTP+SSL)
在前言中有提到,https是在http的基础之上附加了新的协议通过对传输过程数据进行加密进而实现数据的安全性,相比较HTTP,它具有以下几个特点:
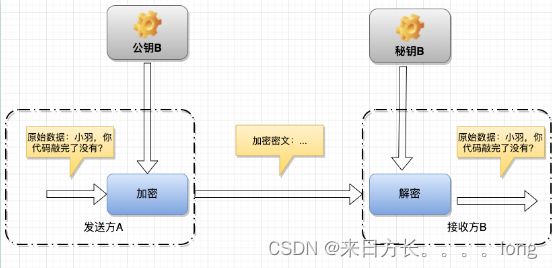
证书认证:凡是访问https的请求必须进行证书认证,当浏览器申请到一个https的域名时,会得到一个数据证书,这份数据证书中含有一份用于RAS的加密公钥,当用户获取到证书后可以使用公钥对自己自身生成的密钥进行一次加密,并将加密后的结果发送给服务器,服务器通过私钥进行解密,得到用户的密钥,这份密钥在整个传输中都保持安全状态,不会被他人读取,此后浏览器和服务器之间的数据发送可以使用此密钥进行加密,保证了数据的安全传输。
既HTTPS和HTTP不同之处主要体现在安全加密数据 上,那么,我们就要了解其中的加密算法。
加密算法可以分对称加密算法和非对称加密算法
对称加密算法:
以Java为例简单的通过代码实现以下
package 加密算法;
import java.security.InvalidAlgorithmParameterException;
import java.security.InvalidKeyException;
import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException;
import java.security.SecureRandom;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Base64;
import javax.crypto.BadPaddingException;
import javax.crypto.Cipher;
import javax.crypto.CipherInputStream;
import javax.crypto.IllegalBlockSizeException;
import javax.crypto.NoSuchPaddingException;
import javax.crypto.SecretKey;
import javax.crypto.spec.IvParameterSpec;
import javax.crypto.spec.SecretKeySpec;
public class AesKit {
public static String encrypt(String content,String key) {
String result = "";
try {
byte[] souces = content.getBytes();
//创建加密工具对象并设置加密方式,加密状态和填充方式NOPadding(为不填充)
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("AES/ECB/PKCS5Padding");
//创建该加密方式的密钥对象
SecretKey secreykey = new SecretKeySpec(key.getBytes(),"AES");
//初始化加密对象设置工具进行-加密,并传入密钥
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, secreykey);
//生成加密后字节数组
byte[] jiamiend = cipher.doFinal(souces);
result = Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(jiamiend);
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (NoSuchPaddingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalBlockSizeException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (BadPaddingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InvalidKeyException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return result;
}
public static String decrypt(String content,String key) {
String result = "";
try {
byte[] decode = Base64.getDecoder().decode(content);
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("AES/ECB/PKCS5Padding");
SecretKey secreykey = new SecretKeySpec(key.getBytes(),"AES");
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, secreykey);
byte[] jieiend = cipher.doFinal(decode);
result = new String(jieiend);
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (NoSuchPaddingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalBlockSizeException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (BadPaddingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InvalidKeyException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return result;
}
public static String encryptByCBC(String content,String key) {
String result = "";
try {
byte[] souces = content.getBytes();
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("AES/CBC/PKCS5Padding");
SecretKey secreykey = new SecretKeySpec(key.getBytes(),"AES");
SecureRandom instanceKey = SecureRandom.getInstanceStrong();
byte[] endkit = instanceKey.generateSeed(16);
System.out.println("加密随机数组"+Arrays.toString(endkit));
IvParameterSpec iv =new IvParameterSpec(endkit);
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, secreykey,iv);
byte[] jiamiend = cipher.doFinal(souces);
jiamiend = megerArray(endkit,jiamiend);
result = Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(jiamiend);
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (NoSuchPaddingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalBlockSizeException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (BadPaddingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InvalidKeyException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InvalidAlgorithmParameterException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return result;
}
public static String decryptByCBC(String content,String key) {
String result = "";
try {
byte[] decode = Base64.getDecoder().decode(content);
byte []ranarray = new byte[16];
System.arraycopy(decode, 0, ranarray, 0, ranarray.length);
byte[] input = new byte[decode.length-16];
System.arraycopy(decode, ranarray.length, input, 0, input.length);
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("AES/CBC/PKCS5Padding");
SecretKey secreykey = new SecretKeySpec(key.getBytes(),"AES");
IvParameterSpec iv =new IvParameterSpec(ranarray);
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, secreykey,iv);
byte[] jieiend = cipher.doFinal(input);
result = new String(jieiend);
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (NoSuchPaddingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalBlockSizeException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (BadPaddingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InvalidKeyException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InvalidAlgorithmParameterException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return result;
}
public static byte[] megerArray(byte []array1,byte [] array2) {
byte[] resultArray = new byte[array1.length+array2.length];
System.arraycopy(array1, 0, resultArray, 0, array1.length);
System.arraycopy(array2, 0, resultArray, array1.length, array2.length);
return resultArray;
}
}
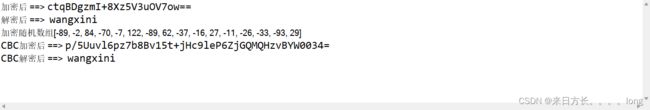
运行结果展示
在上面代码是对称型加密算法,只有一个密钥,使用了ECB模式简单的对称运算和CBC工作模式的加密,在ECB模式下,加密算法对称加密后每次加密的结果是相同的,而采用了CBC模式的对称AES加密每次加密后加密结果都不相同,这样的算法虽然增加了加密的复杂提高了资源消耗,但是安全性就大大的提高了。
非对称加密算法
一般的HTTPS都采用非对称式加密,常用的算法有RAS
Java的实现代码如下:
package 加密算法;
import java.security.InvalidKeyException;
import java.security.KeyPair;
import java.security.KeyPairGenerator;
import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException;
import java.security.PrivateKey;
import java.security.PublicKey;
import javax.crypto.BadPaddingException;
import javax.crypto.Cipher;
import javax.crypto.IllegalBlockSizeException;
import javax.crypto.NoSuchPaddingException;
public class RsaKit {
PublicKey pk;
PrivateKey sk;
public RsaKit() throws NoSuchAlgorithmException {
KeyPairGenerator kpg = KeyPairGenerator.getInstance("RSA");
kpg.initialize(1024);
KeyPair kp = kpg.generateKeyPair();
this.sk= kp.getPrivate();
this.pk= kp.getPublic();
}
public byte[] getPublicKey() {
return this.pk.getEncoded();
}
public byte[] getPivateKey() {
return this.sk.getEncoded();
}
public byte[] entrypt(byte[] content) throws Exception, NoSuchPaddingException {
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("RSA");
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, this.pk);
return cipher.doFinal(content);
}
public byte[] detrypt(byte[] content) throws NoSuchAlgorithmException, NoSuchPaddingException, InvalidKeyException, IllegalBlockSizeException, BadPaddingException {
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("RSA");
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, this.sk);
return cipher.doFinal(content);
}
}
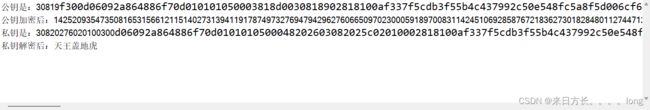
运行结果展示
RSA是非对称加密算法(又称公开密钥加密),采用RSA加密时,需要获取两把密钥(公钥和私钥),公钥加密私钥解密,只要私钥不被泄露就可以保证加密内容的安全。
总结(原理)
-
用户通过浏览器请求https网站,服务器收到请求,选择浏览器支持的加密和hash算法,同时返回数字证书给浏览器,包含颁发机构、网址、公钥、证书有效期等信息。 - 浏览器对证书的内容进行校验,如果有问题,则会有一个提示警告。否则,就生成随机秘钥
X,同时使用证书中的公钥进行加密,并且发送给服务器。 - 服务器收到之后,使用私钥解密,得到随机秘钥
X,然后使用随机秘钥X对网页内容进行加密,返回给浏览器。 - 浏览器则使用随机秘钥
X和之前约定的加密算法进行解密,得到最终的网页内容