【业务功能88】微服务-springcloud-分布式锁-redis-redisson-可重入锁-读写锁-闭锁-信号量-缓存数据一致性问题-双写模式-失效模式-springcache
二、分布式锁
1.分布式锁的原理
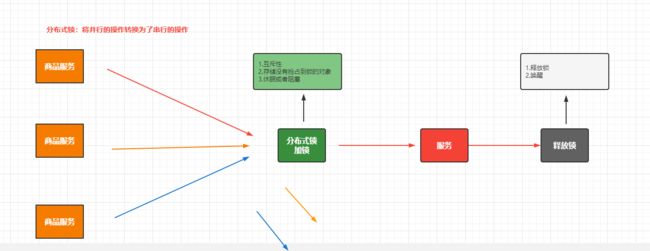
分布式锁或者本地锁的本质其实是一样的,都是将并行的操作转换为了串行的操作
2.分布式锁的常用解决方案
2.1 数据库
可以利用MySQL隔离性:唯一索引
use test;
CREATE TABLE `DistributedLock` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '主键',
`name` varchar(64) NOT NULL DEFAULT '' COMMENT '锁名',
`desc` varchar(1024) NOT NULL DEFAULT '备注信息',
`update_time` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '保存数据时间,自动生成',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
UNIQUE KEY `uidx_name` (`name`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COMMENT='锁定中的方法';
//数据库中的每一条记录就是一把锁,利用的mysql唯一索引的排他性
lock(name,desc){
insert into DistributedLock(`name`,`desc`) values (#{name},#{desc});
}
unlock(name){
delete from DistributedLock where name = #{name}
}
可以利用排他锁来实现 select … where … for update;
乐观锁:乐观的认为数据不会出现数据安全问题,如果出现了就重试一次
select ...,version;
update table set version+1 where version = xxx
2.2 Redis
setNX: setNX(key,value) :如果key不存在那么就添加key的值,否则添加失败,Redisson
2.3Zookeeper
3.Redis实现分布式锁
在Redis中是通过setNX指令来实现锁的抢占,那么利用这个命令实现分布式锁的基础代码为:
public Map<String, List<Catalog2VO>> getCatelog2JSONDbWithRedisLock() {
String keys = "catalogJSON";
// 加锁
Boolean lock = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().setIfAbsent("lock", "1111");
if(lock){
// 加锁成功
Map<String, List<Catalog2VO>> data = getDataForDB(keys);
// 从数据库中获取数据成功后,我们应该要释放锁
stringRedisTemplate.delete("lock");
return data;
}else{
// 加锁失败
// 休眠+重试
// Thread.sleep(1000);
return getCatelog2JSONDbWithRedisLock();
}
}
上面的代码其实是存在一些问题的,首先如果getDataForDB(keys)这个方法如果出现的异常,那么我们就不会删除该key也就是不会释放锁,从而造成了死锁,针对这个问题,我们可以通过设置过期时间来解决,具体代码如下:
public Map<String, List<Catalog2VO>> getCatelog2JSONDbWithRedisLock() {
String keys = "catalogJSON";
// 加锁
Boolean lock = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().setIfAbsent("lock", "1111");
if(lock){
// 给对应的key设置过期时间
stringRedisTemplate.expire("lock",20,TimeUnit.SECONDS);
// 加锁成功
Map<String, List<Catalog2VO>> data = getDataForDB(keys);
// 从数据库中获取数据成功后,我们应该要释放锁
stringRedisTemplate.delete("lock");
return data;
}else{
// 加锁失败
// 休眠+重试
// Thread.sleep(1000);
return getCatelog2JSONDbWithRedisLock();
}
}
上面虽然解决了getDataForDB方法出现异常的问题,但是如果在expire方法执行之前就中断呢?这样也会出现我们介绍的死锁的问题,那这个问题怎么办?这时我们就希望setNx和设置过期时间的操作能够保证原子性。
这时我们就可以在setIfAbsent方法中同时指定过期时间,保证这个原子性的行为
public Map<String, List<Catalog2VO>> getCatelog2JSONDbWithRedisLock() {
String keys = "catalogJSON";
// 加锁 在执行插入操作的同时设置了过期时间
Boolean lock = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().setIfAbsent("lock", "1111",30,TimeUnit.SECONDS);
if(lock){
// 给对应的key设置过期时间
stringRedisTemplate.expire("lock",20,TimeUnit.SECONDS);
// 加锁成功
Map<String, List<Catalog2VO>> data = getDataForDB(keys);
// 从数据库中获取数据成功后,我们应该要释放锁
stringRedisTemplate.delete("lock");
return data;
}else{
// 加锁失败
// 休眠+重试
// Thread.sleep(1000);
return getCatelog2JSONDbWithRedisLock();
}
}
如果获取锁的业务执行时间比较长,超过了我们设置的过期时间,那么就有可能业务还没执行完,锁就释放了,然后另一个请求进来了,并创建了key,这时原来的业务处理完成后,再去删除key的时候,那么就有可能删除别人的key,这时怎么办?针对这种情况我们可以查询的锁的信息通过UUID来区分,具体的代码如下:
public Map<String, List<Catalog2VO>> getCatelog2JSONDbWithRedisLock() {
String keys = "catalogJSON";
// 加锁 在执行插入操作的同时设置了过期时间
String uuid = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
Boolean lock = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().setIfAbsent("lock", uuid,30,TimeUnit.SECONDS);
if(lock){
// 给对应的key设置过期时间
stringRedisTemplate.expire("lock",20,TimeUnit.SECONDS);
// 加锁成功
Map<String, List<Catalog2VO>> data = getDataForDB(keys);
// 获取当前key对应的值
String val = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get("lock");
if(uuid.equals(val)){
// 说明这把锁是自己的
// 从数据库中获取数据成功后,我们应该要释放锁
stringRedisTemplate.delete("lock");
}
return data;
}else{
// 加锁失败
// 休眠+重试
// Thread.sleep(1000);
return getCatelog2JSONDbWithRedisLock();
}
}
上面查询key的值和删除key其实不是一个原子性操作,这就会出现我查询出来key之后,时间过期了,然后key被删除了,然后其他的请求创建了一个新的key,然后原来的执行删除了这个key,又出现了删除别人key的情况。这时我们需要保证查询和删除是一个原子性行为。
public Map<String, List<Catalog2VO>> getCatelog2JSONDbWithRedisLock() {
String keys = "catalogJSON";
// 加锁 在执行插入操作的同时设置了过期时间
String uuid = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
Boolean lock = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().setIfAbsent("lock", uuid,300,TimeUnit.SECONDS);
if(lock){
Map<String, List<Catalog2VO>> data = null;
try {
// 加锁成功
data = getDataForDB(keys);
}finally {
String srcipts = "if redis.call('get',KEYS[1]) == ARGV[1] then return redis.call('del',KEYS[1]) else return 0 end ";
// 通过Redis的lua脚本实现 查询和删除操作的原子性
stringRedisTemplate.execute(new DefaultRedisScript<Long>(srcipts,Long.class)
,Arrays.asList("lock"),uuid);
}
return data;
}else{
// 加锁失败
// 休眠+重试
// Thread.sleep(1000);
return getCatelog2JSONDbWithRedisLock();
}
}
https://space.bilibili.com/435498550 分布式锁的实现
4.Redisson分布式锁
4.1 Redisson的整合
添加对应的依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.redissongroupId>
<artifactId>redissonartifactId>
<version>3.16.1version>
dependency>
添加对应的配置类
@Configuration
public class MyRedisConfig {
@Bean
public RedissonClient redissonClient(){
Config config = new Config();
// 配置连接的信息
config.useSingleServer()
.setAddress("redis://192.168.56.100:6379");
RedissonClient redissonClient = Redisson.create(config);
return redissonClient;
}
}
4.2 可重入锁
/**
* 1.锁会自动续期,如果业务时间超长,运行期间Redisson会自动给锁重新添加30s,不用担心业务时间,锁自动过期而造成的数据安全问题
* 2.加锁的业务只要执行完成, 那么就不会给当前的锁续期,即使我们不去主动的释放锁,锁在默认30s之后也会自动的删除
* @return
*/
@ResponseBody
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello(){
RLock myLock = redissonClient.getLock("myLock");
// 加锁
myLock.lock();
try {
System.out.println("加锁成功...业务处理....." + Thread.currentThread().getName());
Thread.sleep(30000);
}catch (Exception e){
}finally {
System.out.println("释放锁成功..." + Thread.currentThread().getName());
// 释放锁
myLock.unlock();
}
return "hello";
}
4.3 读写锁
根据业务操作我们可以分为读写操作,读操作其实不会影响数据,那么如果还对读操作做串行处理,效率会很低,这时我们可以通过读写锁来解决这个问题
@GetMapping("/writer")
@ResponseBody
public String writerValue(){
RReadWriteLock readWriteLock = redissonClient.getReadWriteLock("rw-lock");
// 加写锁
RLock rLock = readWriteLock.writeLock();
String s = null;
rLock.lock(); // 加写锁
try {
s = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set("msg",s);
Thread.sleep(30000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
rLock.unlock();
}
return s;
}
@GetMapping("/reader")
@ResponseBody
public String readValue(){
RReadWriteLock readWriteLock = redissonClient.getReadWriteLock("rw-lock");
// 加读锁
RLock rLock = readWriteLock.readLock();
rLock.lock();
String s = null;
try {
s = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get("msg");
}finally {
rLock.unlock();
}
return s;
}
在读写锁中,只有读读的行为是共享锁,相互之间不影响,只要有写的行为存在,那么就是一个互斥锁(排他锁)
4.4 闭锁
基于Redisson的Redisson分布式闭锁(CountDownLatch)Java对象 RCountDownLatch采用了与 java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch相似的接口和用法。
@GetMapping("/lockDoor")
@ResponseBody
public String lockDoor(){
RCountDownLatch door = redissonClient.getCountDownLatch("door");
door.trySetCount(5);
try {
door.await(); // 等待数量降低到0
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "关门熄灯...";
}
@GetMapping("/goHome/{id}")
@ResponseBody
public String goHome(@PathVariable Long id){
RCountDownLatch door = redissonClient.getCountDownLatch("door");
door.countDown(); // 递减的操作
return id + "下班走人";
}
4.5 信号量(Semaphore)
基于Redis的Redisson的分布式信号量(Semaphore)Java对象
RSemaphore采用了与 java.util.concurrent.Semaphore相似的接口和用法。同时还提供了异步(Async)、反射式(Reactive)和RxJava2标准的接口。
@GetMapping("/park")
@ResponseBody
public String park(){
RSemaphore park = redissonClient.getSemaphore("park");
boolean b = true;
try {
// park.acquire(); // 获取信号 阻塞到获取成功
b = park.tryAcquire();// 返回获取成功还是失败
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "停车是否成功:" + b;
}
@GetMapping("/release")
@ResponseBody
public String release(){
RSemaphore park = redissonClient.getSemaphore("park");
park.release();
return "释放了一个车位";
}
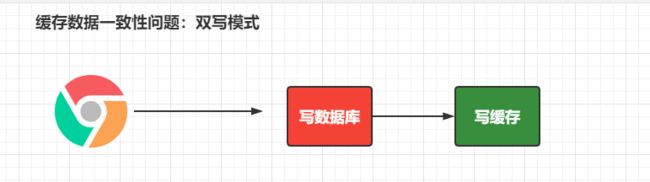
4.6 缓存数据一致性问题
针对于上的两种解决方案我们怎么选择?
- 缓存的所有数据我们都加上过期时间,数据过期之后主动触发更新操作
- 使用读写锁来处理,读读的操作是不相互影响的
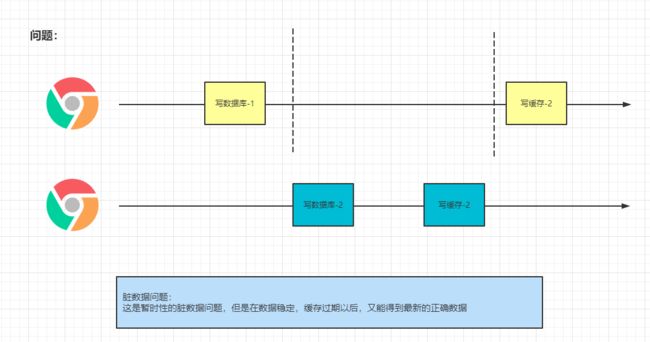
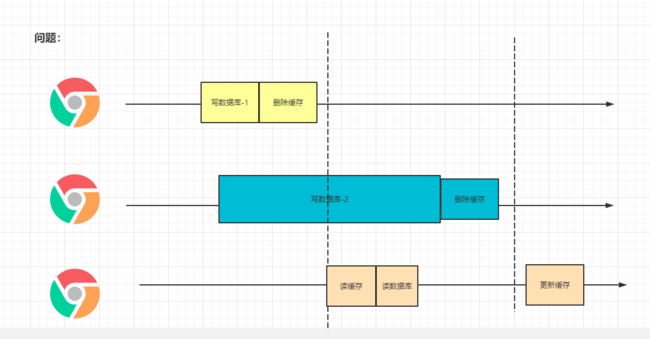
无论是双写模式还是失效模式,都会导致缓存的不一致问题。即多个实例同时更新会出事。怎么办?
- 如果是用户纬度数据(订单数据、用户数据),这种并发几率非常小,不用考虑这个问题,缓存数据加
上过期时间,每隔一段时间触发读的主动更新即可 - 如果是菜单,商品介绍等基础数据,也可以去使用canal订阅binlog的方式。
- 缓存数据+过期时间也足够解决大部分业务对于缓存的要求。
- 通过加锁保证并发读写,写写的时候按顺序排好队。读读无所谓。所以适合使用读写锁。(业务不关心
脏数据,允许临时脏数据可忽略)
总结:
- 我们能放入缓存的数据本就不应该是实时性、一致性要求超高的。所以缓存数据的时候加上过期时间,保证每天拿到当前最新数据即可。
- 我们不应该过度设计,增加系统的复杂性
- 遇到实时性、一致性要求高的数据,就应该查数据库,即使慢点。
三、SpringCache
相关依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cacheartifactId>
dependency>
配置类
- 指定自定义的序列化的方式 在redis客户端看value格式是json格式,比较方便
- 设置过期时间,除了在yaml配置文件中配置spring.cache.redis.time-to-live 指定过期时间,还需要配置文件进行相应方法的调用实现才能获取配置的过期时间
- 设置防止穿透,也就是缓存空值,防止大量空值查询绕过redis,cache-null-values: true # 是否缓存空值,防止缓存穿透,同样还需要配置文件进行相应方法的调用实现才能获得
- 设置key前缀,指定前缀 key-prefix:pro_ ; use-key-prefix: true(默认true) 同样要在配置类中对应的方法去调用实现
@Configuration
public class MyCacheConfig {
@Bean
public RedisCacheConfiguration redisCacheConfiguration(CacheProperties cacheProperties){
RedisCacheConfiguration config = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig();
// 指定自定义的序列化的方式
config = config.serializeKeysWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(new StringRedisSerializer()));
config = config.serializeValuesWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer()));
CacheProperties.Redis redisProperties = cacheProperties.getRedis();
if (redisProperties.getTimeToLive() != null) {
config = config.entryTtl(redisProperties.getTimeToLive());
}
if (redisProperties.getKeyPrefix() != null) {
config = config.prefixKeysWith(redisProperties.getKeyPrefix());
}
if (!redisProperties.isCacheNullValues()) {
config = config.disableCachingNullValues();
}
if (!redisProperties.isUseKeyPrefix()) {
config = config.disableKeyPrefix();
}
return config;
}
}
application.yml
spring:
redis:
host: 192.168.56.100
port: 6379
cache:
type: redis # SpringCache 缓存的类型是 Redis
redis:
time-to-live: 60000 # 指定缓存key的过期时间
# key-prefix: bobo_
use-key-prefix: true
cache-null-values: true # 是否缓存空值,防止缓存穿透
使用举例
/**
* 查询出所有的商品大类(一级分类)
* 在注解中我们可以指定对应的缓存的名称,起到一个分区的作用,一般按照业务来区分
* @Cacheable({"catagory","product"}) 代表当前的方法的返回结果是需要缓存的,
* 调用该方法的时候,如果缓存中有数据,那么该方法就不会执行,
* 如果缓存中没有数据,那么就执行该方法并且把查询的结果缓存起来
* 缓存处理
* 1.存储在Redis中的缓存数据的Key是默认生成的:缓存名称::SimpleKey[]
* 2.默认缓存的数据的过期时间是-1永久
* 3.缓存的数据,默认使用的是jdk的序列化机制
* 改进:
* 1.生成的缓存数据我们需要指定自定义的key: key属性来指定,可以直接字符串定义也可以通过SPEL表达式处理:#root.method.name
* 2.指定缓存数据的存活时间: spring.cache.redis.time-to-live 指定过期时间
* 3.把缓存的数据保存为JSON数据
* SpringCache的原理
* CacheAutoConfiguration--》根据指定的spring.cache.type=reids会导入 RedisCacheAutoConfiguration
* @return
*/
@Trace
@Cacheable(value = {"catagory"},key = "#root.method.name",sync = true)
@Override
public List<CategoryEntity> getLeve1Category() {
System.out.println("查询了数据库操作....");
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
List<CategoryEntity> list = baseMapper.queryLeve1Category();
System.out.println("查询消耗的时间:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start));
return list;
}
SpringCache的不足:
1).读模式
- 缓存穿透:查询一个null的数据。可以解决 cache-null-values=true
- 缓存击穿:大量并发进来同时查询一个正好过期的数据。解决方案:分布式锁 sync=true 本地锁
- 缓存雪崩:大量的key同一个时间点失效。解决方案:添加过期时间 time-to-live=60000 指定过期时间
2).写模式
- 读写锁
- 引入canal,监控binlog日志文件来同步更新数据
- 读多写多,直接去数据库中读取数据即可
总结:
- 常规数据(读多写少):而且对及时性和数据的一致性要求不高的情况,我们完全可以使用SpringCache
- 特殊情况:特殊情况特殊处理。