c++(8.29)auto关键字,lambda表达式,数据类型转换,标准模板库,list,文件操作+Xmind
作业:
封装一个学生的类,定义一个学生这样类的vector容器, 里面存放学生对象(至少3个)
再把该容器中的对象,保存到文件中。
再把这些学生从文件中读取出来,放入另一个容器中并且遍历输出该容器里的学生。
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
class Stu
{
friend istream & operator>>(istream &cin,Stu &R);
friend ostream & operator<<(ostream &cout,const Stu &R);
private:
string name;
int age;
public:
Stu(){};
Stu(string name,int age):name(name),age(age){};
};
ostream & operator<<(ostream &cout,const Stu &R)
{
cout << R.name << " ";
cout << R.age << endl;
return cout;
}
istream & operator>>(istream &cin,Stu &R)
{
cin >> R.name;
cin >> R.age;
return cin;
}
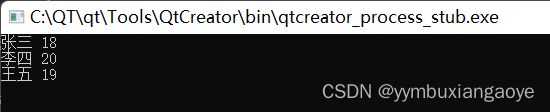
int main()
{
Stu s1("张三",18);
Stu s2("李四",20);
Stu s3("王五",19);
vector stu;
stu.push_back(s1);
stu.push_back(s2);
stu.push_back(s3);
ofstream ofs;
ofs.open("D:/2.txt",ios::out);
vector::iterator iter;
for(iter = stu.begin();iter!=stu.end();iter++)
{
ofs << *iter ;
}
ofs.close();
vectorstu1;
Stu s;
ifstream ifs;
ifs.open("D:/2.txt",ios::in);
while(ifs>>s)
{
stu1.push_back(s);
}
for(iter=stu1.begin();iter!=stu1.end();iter++)
{
cout << *iter ;
}
ifs.close();
return 0;
} 1.模板类
#include
using namespace std;
template < class T,class N>
class A
{
private:
T t;
N n;
public:
A(){};//无参构造
A(T t,N n):t(t),n(n){}//有参构造
void show()
{
cout << t << endl << n << endl;
}
};
int main()
{
A a("张三",18);
a.show();
return 0;
} 2.异常(异常情况为取钱时取的钱小于0或者大于余额)
#include
using namespace std;
class BankAccount
{
private:
double balance;
public:
BankAccount(){};
BankAccount(double balance):balance(balance){};
void withdraw(double money)
{
if(money<0)
{
throw(invalid_argument("取款金额不能为负数"));
}
else if(money>balance)
{
throw(runtime_error("余额不足"));
}
else
{
balance -= money;
cout << "余额为:" << balance << endl;
}
}
};
int main()
{
BankAccount account1(1000);
try {
account1.withdraw(-100);
} catch (invalid_argument &e)
{
cout << "Erro:" << e.what() << endl;
} catch (runtime_error &e)
{
cout << "Erro:" << e.what() << endl;
}
try {
account1.withdraw(1500);
} catch (invalid_argument &e)
{
cout << "Erro:" << e.what() << endl;
} catch (runtime_error &e)
{
cout << "Erro:" << e.what() << endl;
}
try {
account1.withdraw(500);
} catch (invalid_argument &e)
{
cout << "Erro:" << e.what() << endl;
} catch (runtime_error &e)
{
cout << "Erro:" << e.what() << endl;
}
return 0;
} 3.lambda表达式和auto的使用
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a=100;
double b=3.14;
char c='a';
auto fun=[a,b,c](){};//捕获外界a,b,c变量的值,fun函数中的a,b,c不是外界的a,b,c,地址不同,
//想要修改fun中的a,b,c的值,必须在()后加上mutable
auto fun1=[=](){};//捕获外界所有的变量值
auto fun2=[&a,&b](){};//捕获外界a,b变量的地址,fun函数中的a,b是外界的a,b,地址相同,
//想要修改fun2中的值,可以直接改变
auto fun3=[&](){};//捕获外界所有的变量的地址
auto fun4=[=,&a,&b](){};//捕获外界所有的值,但是变量a和变量b是引用捕获,
//fun函数中的a,b是外界的a,b,地址相同,可以直接修改,不用加上mutable
auto fun5=[&,a,b](){};//捕获外界所有变量的地址,但变量a,b捕获的是值,修改需要加mutable
return 0;
}
4.容器
#include
#include
using namespace std;
void printVector(vector &v)
{
vector ::iterator ite;//创建一个vector类型的迭代器ite
for(ite=v.begin();ite!=v.end();ite++)
{
cout << *ite << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
//容器
vectorv;//无参构造容器v
v.push_back(10);//尾插
v.push_back(20);
v.push_back(30);
v.push_back(40);
//算法
printVector(v);
vectorv2(v.begin(),v.end());//拷贝v中begin到end区间中的值
printVector(v2);
vectorv3(6,10);//拷贝构造,将6个10拷贝给v3
printVector(v3);
vectorv4=v2;//拷贝构造,将v2中的值拷贝给v4
printVector(v4);
vectorv5(v3);//拷贝构造,将v3中的值拷贝给v5
printVector(v5);
vectorv6;
v6=v5;//拷贝赋值,将v5的值拷贝一份给v6
v6.assign(v5.begin(),v5.end());//将v5begin到end区间的值拷贝一份赋值给v6
v6.assign(8,99);//将8个99拷贝一份赋值给v6
if(v6.empty())//判断v6是否为空
{
cout << "v6容器为空" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "v6容器的容量为:" << v6.capacity() << endl;
cout << "v6容器的大小(容器中的元素个数)为:" << v6.size() < 5.list链表
#include
#include
using namespace std;
void printList(list &v)
{
list ::iterator ite;//创建一个list类型的迭代器ite
for(ite=v.begin();ite!=v.end();ite++)
{
cout << *ite << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
}
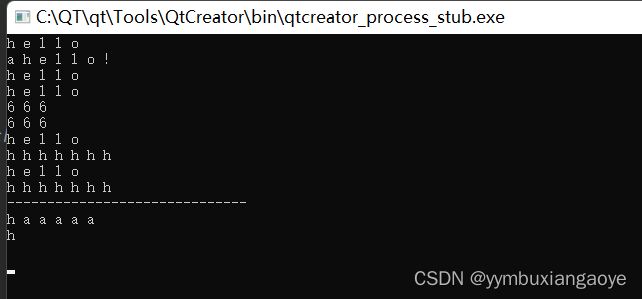
int main()
{
list lst;//定义一个链表,里面存放char类型元素
lst.push_back('h');//存放一个字符a
lst.push_back('e');
lst.push_back('l');
lst.push_back('l');
lst.push_back('o');
printList(lst);//输出lst中的所有元素
lst.push_front('a');//在lsit表头部插入字符'a'
lst.push_back('!');//在尾部插入元素'!'
printList(lst);//输出lst中的所有元素
lst.pop_front();//删除list表头部元素
lst.pop_back();//删除list表尾部元素
printList(lst);//输出lst中的所有元素
list lst2(lst.begin(),lst.end());//拷贝构造函数,将lst内从begin到end的元素拷贝到链表lst2中
printList(lst2);//输出lst2中的所有元素
list lst3(3,'6');//拷贝构造函数,将3个字符6存入链表lst3中
printList(lst3);//输出lst3中的所有元素
list lst4(lst3);//拷贝构造函数,将lst3中的元素拷贝到lst4中
printList(lst4);//输出lst4中的所有元素
list lst5;
lst5.assign(lst.begin(),lst.end());//拷贝赋值函数,将lst中begin到end区间的值拷贝一份赋值到lst5中
printList(lst5);//输出lst5中的所有元素,结果和lst结果一致
lst5.assign(7,'h');//将5个h赋值到lst5中
printList(lst5);//输出lst5中的所有元素,结构为7个h
lst5.swap(lst);//将lst中的元素和本身中的元素交换
printList(lst5);//输出lst5中的所有元素,因为交换,变成了lst中的元素
printList(lst);//输出lst中的所有元素,因为交换,变为之前lst5中的元素了
cout << "------------------------------" << endl;
list lstt(5,'a');//创建一个lstt链表,里面含有5个'a'
list ::iterator ite;
lstt.insert(lstt.begin(),'h');//在begin位置插入一个字符'h'
printList(lstt);//输出lstt链表中的所有元素
lstt.remove('a');//删除lstt链表中所有的字符'a'
printList(lstt);//输出lstt链表中的所有元素
lstt.clear();//删除lstt链表中的所有元素
printList(lstt);//输出lstt链表中的所有元素
return 0;
}