Spring容器及实例化
一、前言
Spring 容器是 Spring 框架的核心部分,它负责管理和组织应用程序中的对象(Bean)。Spring 容器负责创建、配置和组装这些对象,并且可以在需要时将它们提供给应用程序的其他部分。
Spring 容器提供了两种主要类型的容器:BeanFactory 和 ApplicationContext。BeanFactory 是最基本的容器,提供了基本的 Bean 生命周期管理和依赖注入的功能。ApplicationContext 是 BeanFactory 的一个子接口,它提供了更多的企业级功能,例如国际化、事件传播、资源加载等。
在 Spring 中,通常通过配置文件或注解来定义和配置 Bean。当 Spring 容器启动时,它会根据配置的信息来实例化和初始化对象。
二、xml配置初步使用
2.1 添加依赖
创建maven项目,并在pom.xml中添加Spring的依赖。
4.0.0
org.example
spring_01
1.0
org.springframework
spring-context
5.3.22
junit
junit
4.11
test
ch.qos.logback
logback-classic
1.2.11
2.2 xml方式配置bean
新建bean.xml文件,目录结构
bean.xml
2.3 测试类查看效果
SpringTest.java
package com.demo;
/**
* @author zhe.han
* @date 2023/2/2 14:28
*/
public class SpringTest {
/**
* xml形式的简单入门
*
* 1:instantiation with a constructor 构造函数实例化
*/
@Test
public void test1() {
/**
* 加载文件的方式:使用resource加载文件
*
*/
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:/test1.xml");
// ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("file:E:\\study\\28spring\\spring_01\\src\\main\\resources\\test1.xml");
Emp employ = (Emp) context.getBean("employ");
final String password = employ.getPassword();
final String username = employ.getUsername();
System.out.println(username);
System.out.println(password);
}
}
三、实例化 Bean
官网中提到实例化bean,有三种方式
3.1 默认的无参构造函数
bean.xml
public class Emp {
final Log log = LogFactory.getLog(Emp.class);
private String username;
private String password;
public Emp(String username, String password) {
this.username = username;
this.password = password;
}
public Emp() {
log.info("构造方法实例化......");
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Emp{" +
"username='" + username + '\'' +
", password='" + password + '\'' +
'}';
}
}测试类:
@Test
public void test1() {
/**
* 加载文件的方式:使用resource加载文件
*
*/
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:/test1.xml");
Emp employ = context.getBean("employ", Emp.class);
log.info(employ);
}debug跟踪源码,了解实例化过程。
debug定位到这个方法中:
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#createBeanInstance
最终执行到这个方法:使用无参构造函数实例化bean
// No special handling: simply use no-arg constructor.
return instantiateBean(beanName, mbd);3.2 静态工程方法
/**
* Bean的实例化:
*
*
* 2:instantiation with a static Factory Method:静态工厂实例化
*
*/
@Test
public void test2() {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:/test2.xml");
// 静态工厂实例化
Emp2 employ = context.getBean("employ2_2", Emp2.class);
log.info(employ);
}
断点调试:
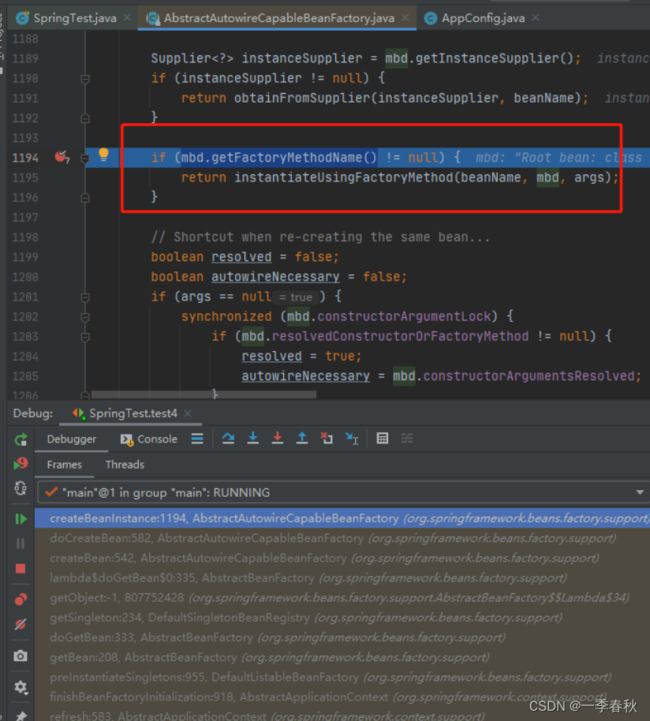
debug定位到这个方法中:‘
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#createBeanInstance
最终执行到这个方法:使用无参构造函数实例化bean
// 判断BeanDefination中是否有factory-method 这个属性
if (mbd.getFactoryMethodName() != null) {
return instantiateUsingFactoryMethod(beanName, mbd, args);
}3.3 实例工厂方法
test3.xml
DefaultServiceLocator
public class DefaultServiceLocator {
final static Log log = LogFactory.getLog(Emp2.class);
private static Emp2 employ = new Emp2();
public Emp2 createInstance() {
employ.setPassword("password");
employ.setUsername("username");
log.info("实例工厂方法");
return employ;
}
}断点发现实例化流程和静态工厂方法一样:
四、注解方式配置bean
4.1 使用Configuration 和Bean配置
// @Configuration 作为配置类,@Bean 用于实例化、配置、初始化Spring的bean对象AppConfig
@Configuration
public class AppConfig {
/**
* 等价于在xml中配置:
*
*
*
* @return
*/
@Bean
public Emp emp() {
return new Emp("zhang san", "123456");
}
}
/**
* 注解方式配置spring的bean
*/
@Test
public void test4() {
ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
Emp bean = context.getBean(Emp.class);
log.info(bean);
}最终的实例化方法和静态工厂、工厂实例化方法一致。
以上就是Spring的初步使用和Bean的实例化的方法的了解。