侯捷STL-容器deque、容器适配器stack、queue
容器deque、容器适配器stack、queue
一、使用deque
#include 二、queue源码解析
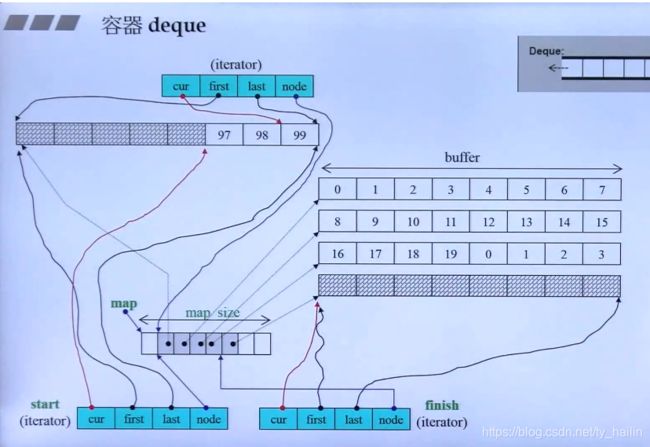
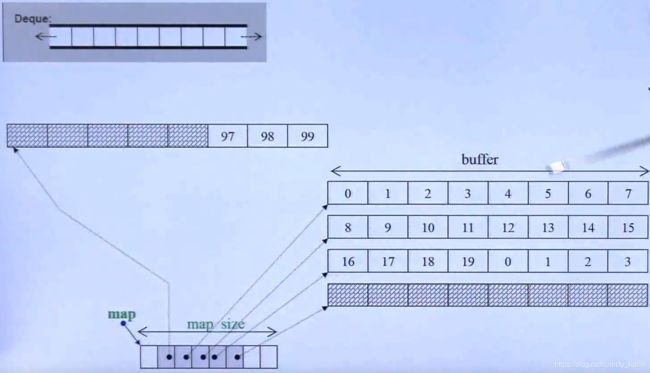
原理:分段连续空间:对外声称为连续空间,实际内部是以一个vector和若干数组组成,vector元素中存储每个连续空间地址
//deque源码
template <class T, class Alloc=alloc, size_t BufSize=0>
class deque{
public:
typedef T value_type;
typedef __deque_iterator<T,T&,T*,BufSize> iterator; //目前三个模板参数,新版本只有1个模板参数
protected:
typedef pointer* map_pointer; //T**
protected:
iterator start; //首元素迭代器
iterator finish;
map_pointer map
size_type map_size;
public:
iterator begin(){return start;};
iterator end() {return finish;}
size_type size() const {return finish - start;}
};
//计算buf_size大小
inline size_t __deque_buf_size(size_t n, size_t sz){
return n!=0 ? n : (sz<512 ? size_t(512/sz) : size_t(1));
}
//deque迭代器
template <class T, class Ref, class Ptr, size_t BufSize>
struct __deque_iterator{
typedef random_access_iterator_tag iterator_category; //随机访问迭代器
...
typedef T** map_pointer;
//成员
T* cur;
T* first;
T* last;
map_pointer node;
};
//deque::insert() 插入元素
iterator insert(iterator position, const value_type& x){
if (position.cur == start.cur){ //如果插入元素是deque最前端,则直接push_front()
push_front(x);
return start;
}
else if (position.cur == finish.cur){//如果插入元素是最尾端,则push_back()
push_back(x);
iterator tmp = finish;
--tmp;
return tmp;
}
else{
return insert_aux(position, x); //插入在中间
}
};
template<class T, class Alloc, size_t BufSize>
typename deque<T, Alloc, BufSize>::iterator
deque<T, Alloc, BufSize>::insert_aux(iterator pos, const value_type& x){
difference_type index = pos-start; //插入位置之前元素个数
value_type x_copy = x;
if (index < size()/2){ //如果插入点之前元素个数比之后元素个数少,则在最前端加入第1个元素,然后搬移插入位置之前数据往前一格
push_front(front());
...
copy(front2, pos1, front1);
}
else{ //如果插入点之后元素个数比之前元素个数少,则在最尾端加入第1个元素,然后搬移插入位置之前数据往后一格
push_back(back());
...
copy_backward(pos, back2, back1);
}
*pos = x_copy; //插入新元素
return pos;
}
三、deque怎么模拟连续空间
//deque模拟连续空间全是deque_iterator功劳
reference operator[size_type n](){
return start[difference_type[n];];
}
reference front(){ return *start;}
reference back() {
iterator tmp = finish;
--tmp;
return *tmp;
}
size_type size() const{return finish-start;}
bool empty const(){return finish == start;};
reference operator*() const{return *cur;}
pointer operator->() const{return &(operator*());}
//制造连续空间假象1
difference_type operator-(const self& x) const{
return difference_type(buffer_size()) * (node - x.node -1) + (cur-first) + (x.last - x.cur);
}
self& operator++(){
++cur; //移动元素
if (cur == last){
set_node(node+1):
cur = first;
}
return *this;
}
self operator++(int){
self tmp = *this;
++*this;
return tmp;
}
self& operator--(){
if (cur == first){
set_node(node-1):
cur = last;
}
--cur; //移动元素
return *this;
}
self operator--(int){
self tmp = *this;
--*this;
return tmp;
}
self& operator+=(difference_type n){
difference_type offset = n + (cur - first);
if (offset > 0 && offset < difference_type(buffer_size()))
cur += n; //在同一分段内
else{ //不在同一分段内
difference_type node_offset = offset > 0 ? offset / difference_type(buffer_size()) : -difference_type((-offset-1) / buffer_size()) -1;
set_node(node + node_offset);
cur = first + (offset - node_offset * difference_type(buffer_size()));
}
return *this;
}
self operator+(difference_type n) const {
self tmp = *this;
return tmp += n;
}
self& operator-=(difference_type n){
return (*this += -n);
}
self operator-(difference_type n) const{
self tmp = *this;
return tmp -= n;
}
reference operator[](difference_type n) const{
return *(*this+n);
}
四、使用stack
#include 五、stack源码解析
template<class T, class Sequence = deque<T>> //默认使用deque,可使用list和deque, deque效率更高
class stack{
protected:
Sequence c; //底层容器
public:
bool empty() const{return c.empty();}
size_type size() const {return c.size();}
reference top(){return c.back();};
void push(const value_type& x) {c.push_back();}
void pop(){c.pop_back();}
};
六、使用queue
#include 七、queue源码解析
```cpp
template<class T, class Sequence = deque<T>> //默认使用deque,可使用list和deque, deque效率更高
class queue{
protected:
Sequence c; //底层容器
public:
bool empty() const{return c.empty();}
size_type size() const {return c.size();}
reference front(){return c.front();}
reference back(){return c.back();}
void push(const value_type& x) {c.push_back();}
void pop(){c.pop_back();}
};
八、stack和queue底层容器选择
底层结构选择原则:stack和queue所有的接口转调用都能编译通过,都能适配,则可支持
1)stack和queue不允许遍历,则不提供iterator
2)stack和queue可以选择list或deque作底层结构
3)stack可以选择vector作底层结构,queue不能选择vector作底层结构
4)stack和queue都不可以选择set或map作底层结构