【RPC 协议】序列化与反序列化 | lua-cjson | lua-protobuf
文章目录
-
- RPC 协议
-
- gRPC
- JSON-RPC
- 数据序列化与反序列化
-
- lua-cjson
- lua-protobuf
RPC 协议
在分布式计算,远程过程调用(英语:Remote Procedure Call,缩写为 RPC)是一个计算机通信协议。该协议允许运行于一台计算机的程序调用另一个地址空间(通常为一个开放网络的一台计算机)的子程序,而程序员就像调用本地程序一样,无需额外地为这个交互作用编程(无需关注细节)。RPC 是一种服务器-客户端(Client/Server)模式,经典实现是一个通过发送请求-接受回应进行信息交互的系统。
RPC 协议根据所使用的数据格式,可以分为有模式(schema)和无模式(schema-less)。
- 有模式(schema)
通讯双方需要提前定义协议模板,在数据传输过程中只传输值,无需传输数据结构,节省流量。典型的有模式 RPC 协议是基于 Protobuf 接口描述语言来实现的,例如 gRPC。
优点是协议结构明确,解析效率高;缺点是不够灵活,协议变更需要重新定义。
- 无模式(schema-less)
没有预定义数据结构,支持动态语言。无需协议模板,数据传输过程中需要带上数据结构。典型的无模式 RPC 协议是基于 JSON 来实现的, 例如 JSON-RPC 。
优点是协议灵活、易于扩展;缺点是解析效率较低。
通常我们会在数据序列化格式(如 Protobuf、JSON)的基础上,定制符合自己要求的 RPC 协议,灵活的在服务器和客户端之间通信。而不是采用通用的 RPC 框架,对于不需要的功能,增加了通信的开销。
gRPC
https://doc.oschina.net/grpc
JSON-RPC
https://wiki.geekdream.com/Specification/json-rpc_2.0.html
数据序列化与反序列化
lua-cjson
采用的 json for lua 库:https://github.com/cloudwu/lua-cjson
lua CJSON 网站: https://www.kyne.com.au/~mark/software/lua-cjson.php
安装步骤:
git clone https://github.com/cloudwu/lua-cjson.gitcd lua-cjson && sudo vim Makefile
修改如下:(版本 5.4,lua 文件前缀 /home/cauchy/.luaver/lua/5.4.6)
由于我使用 luaver 来管理,所以这里 lua 的路径可能不同。
make
执行完 Makefile,成功后会生成 cjson.so,我们只需要这个动态库。
mv cjson.so ../ && cd .. && sudo rm -rf lua-cjson
这一步可不执行,只需要 cjson.so 在 require "cjson" 时能找到即可,自己可以放置它的位置。
示例代码:
协议格式:
{
"fid": "c2s_hello",
"msg": "world"
}
{
"fid": "s2c_hello",
"succ": true,
"msg": "hello " .. "${msg}"
}
fid 用于映射 RPC 协议处理的函数名,fd 用于标识网络连接的文件描述符,JS_data 标识序列化后的 JSON 数据,data 是反序列化后的数据。
创建三个文件:libnet.lua,server.lua,client.lua。
libnet.lua
模拟网络库,简易实现网络数据的收发过程。提供三个接口,发送消息给服务端,发送消息给客户端,连接服务器。
local M = {}
local server, client
function M.send_to_server(fd, JS_data)
if not server then
server = require "server"
end
server.dispatch(fd, JS_data)
end
function M.send_to_client(fd, JS_data)
if not client then
client = require "client"
end
client.dispatch(fd, JS_data)
end
local fd = 0
function M.connect_server()
fd = fd + 1
return fd
end
return M
server.lua
模拟服务器业务逻辑,实现处理客户端的请求。
local cjson = require "cjson"
local libnet = require "libnet"
local M = {}
local RPC = {}
function RPC.c2s_hello(data)
return {
fid = "s2c_hello",
succ = true,
msg = "hello " .. data.msg
}
end
function M.dispatch(fd, JS_data)
local data = cjson.decode(JS_data)
local f = assert(RPC[data.fid], "Not exists Func: " .. data.fid)
local ok, r = pcall(f, data)
if ok then
libnet.send_to_client(fd, cjson.encode(r))
end
return ok
end
return M
client.lua
模拟客户端业务逻辑,实现处理服务端的请求。
local cjson = require "cjson"
local libnet = require "libnet"
local M = {}
local RPC = {}
function RPC.s2c_hello(data)
print(data.succ, data.msg)
end
function M.dispatch(fd, JS_data)
local data = cjson.decode(JS_data)
local f = assert(RPC[data.fid], "Not exists Func: " .. data.fid)
local ok, r = pcall(f, data)
return ok
end
return M
新建 main.lua,测试逻辑。
local cjson = require "cjson"
local libnet = require "libnet"
local function main()
local fd = libnet.connect_server()
local data = {
fid = "c2s_hello",
msg = "world"
}
local JS_data = cjson.encode(data)
libnet.send_to_server(fd, JS_data)
end
main()
lua-protobuf
lua-protobuf 库:https://github.com/starwing/lua-protobuf
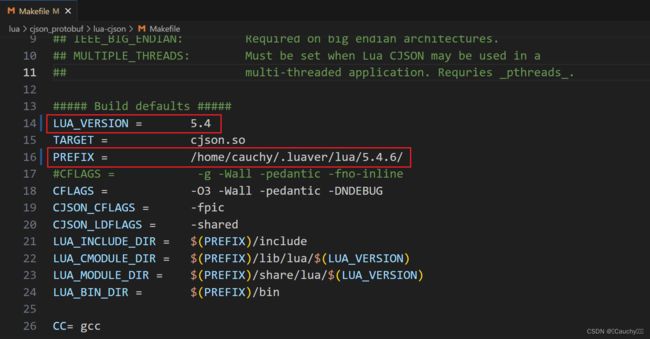
luaver use 5.4.6luaver use-luarocks 3.9.2luarocks install lua-protobuf
使用 luarocks 来管理安装 lua 包:

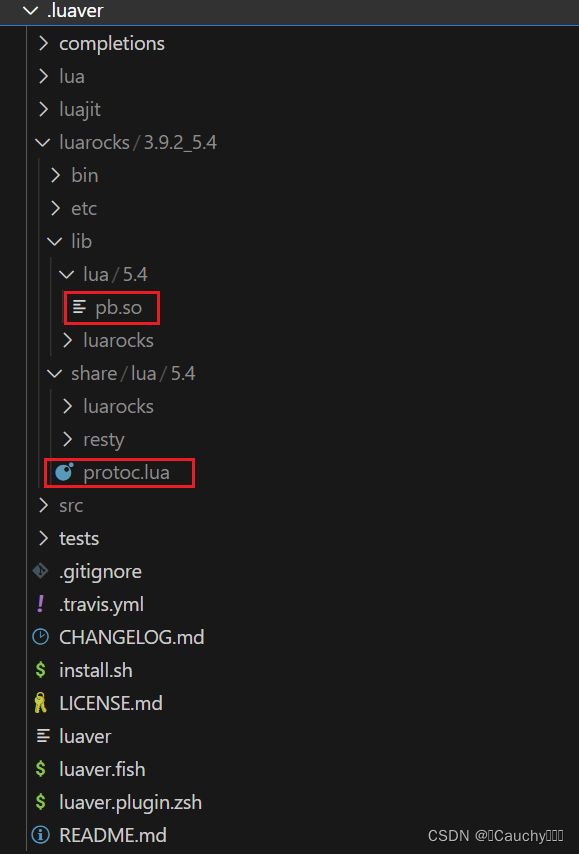
安装完后,可以查看需要的 pb.so 和 protoc.lua 两个文件的路径:
-
pb.so:Protocol Buffers 的 Lua 语言动态库文件,通过在 Lua 中require("pb")来加载该库。 -
protoc.lua:Protocol Buffers 的 Lua 描述文件编译器,将.proto文件编译生成对应的 Lua 代码,生成的 Lua 代码依赖 pb.so 库来实现序列化和反序列化。
示例代码:
local pb = require "pb"
local protoc = require "protoc"
-- 直接载入schema (这么写只是方便, 生产环境推荐使用 protoc.new() 接口)
assert(protoc:load [[
message Phone {
optional string name = 1;
optional int64 phonenumber = 2;
}
message Person {
optional string name = 1;
optional int32 age = 2;
optional string address = 3;
repeated Phone contacts = 4;
} ]])
-- lua 表数据
local data = {
name = "ilse",
age = 18,
contacts = {
{ name = "alice", phonenumber = 12312341234 },
{ name = "bob", phonenumber = 45645674567 }
}
}
-- 将Lua表编码为二进制数据
local bytes = assert(pb.encode("Person", data))
print(pb.tohex(bytes))
-- 再解码回Lua表
local data2 = assert(pb.decode("Person", bytes))
print(data2.name, data2.age, data2.contacts[1].name, data2.contacts[1].phonenumber, data2.contacts[2].name, data2.contacts[2].phonenumber)
使用 protoc.new() 创建一个编译器实例,加载 .proto 文件:
addressbook.proto
syntax = "proto3";
package cauchy;
message Person {
string name = 1;
int32 age = 2;
enum PhoneType {
MOBILE = 0;
HOME = 1;
WORK = 2;
}
message PhoneNumber {
string number = 1;
PhoneType type = 2;
}
repeated PhoneNumber phones = 3;
}
main.lua
local protoc = require "protoc"
local pb = require "pb"
local data = {
name = "cauchy",
age = 20,
phones = {
{ number = "1234567890", type = 1 },
{ number = "0987654321" }
}
}
local p = protoc.new()
local addressbook = io.open("addressbook.proto"):read("a")
p:load(addressbook)
local bytes = assert(pb.encode("cauchy.Person", data))
local data2 = assert(pb.decode("cauchy.Person", bytes))
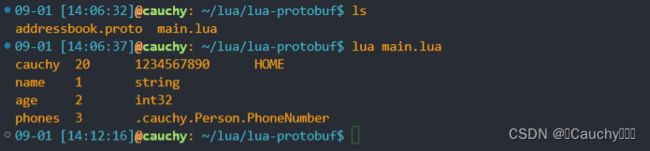
print(data2.name, data2.age, data2.phones[1].number, data2.phones[1].type)
for name, id, types in pb.fields("cauchy.Person") do
print(name, id, types)
end
由于我是通过 luaver 管理 luarocks 和 lua,使用 luarocks 分发 lua 模块,安装的 lua-protobuf。所以上述路径下,没有 pb.so 和 protoc.lua,直接找到安装路径下的,需要 luaver 使用 lua 和 luarocks。

不过使用者也可以直接拉取到执行脚本的路径下。
上述操作是在 lua 代码中,直接通过导入 protoc.lua 文件,来在运行时加载 .proto 文件的,无需提前编译,但是这样转换性能可能比较慢。
下面我们来安装 protoc 编译器:
sudo apt updatesudo apt install -y protobuf-compiler
protoc 默认安装在 /usr/bin/ 下。
执行 protoc -o addressbook.pb addressbook.proto 生成 .pb 文件。
.proto 文件:以 Protocol Buffers 语言编写的接口定义文件,用来定义数据结构、服务接口等。
.pb 文件:从 .proto 接口定义文件生成的目标语言代码文件,而没有指定目标语言,生成通用的二进制文件,包含了编码后的 Protocol Buffers 数据。
local pb = require "pb"
pb.loadfile("./addressbook.pb")
local data = {
name = "cauchy",
age = 20,
phones = {
{ number = "1234567890", type = 1 },
{ number = "0987654321"}
}
}
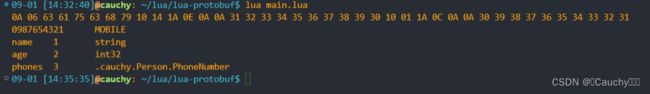
local bytes = pb.encode("cauchy.Person", data)
print(pb.tohex(bytes))
local data2 = pb.decode("cauchy.Person", bytes)
print(data2.phones[2].number, data2.phones[2].type)
for name, id, types in pb.fields("cauchy.Person") do
print(name, id, types)
end
更多具体的 API 操作,参考官方 GitHub:https://github.com/starwing/lua-protobuf