javaee之黑马乐优商城2
简单分析一下商品分类表的结构
先来说一下分类表与品牌表之间的关系
再来说一下分类表和品牌表与商品表之间的关系
面我们要开始就要创建sql语句了嘛,这里我们分析一下字段
用到的数据库是heima->tb_category这个表
现在去数据库里面创建好这张表
下面我们再去编写一个实体类之前,我们去看一下这个类的请求方式,请求路径,请求参数,返回数据都是什么
下面再去编写实体类
实体都是放到
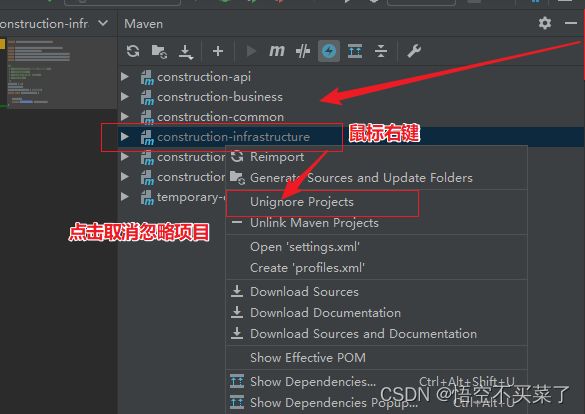
出现了一个小插曲,开始的时候,我maven项目右边的模块有些是灰色的,导致我导入依赖之后,所有的注解什么都不能用,解决方案如下
然后把依赖重新导入一下
我们先去完成我们商品分类表的一个实体类
Category.java
package com.leyou.item.pojo;
import lombok.Data;
import tk.mybatis.mapper.annotation.KeySql;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.Table;
/**
* Created by Administrator on 2023/8/28.
*/
@Table(name="tb_category")
@Data
public class Category {
@Id
@KeySql(useGeneratedKeys = true)
private Long id;
private String name;
private Long parentId;
private Boolean isParent;
private Integer sort;
}
然后去到ly-item-service去写具体的业务逻辑,比如mapper,service,web都在这里面
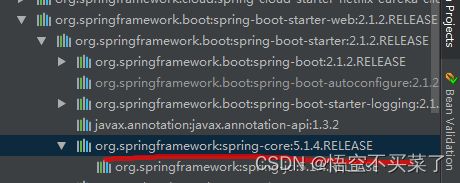
这里来说一个依赖问题
引入了spring-boot-starter-web这个依赖,也包含了spring的核心依赖
说一下在写这个controller类的时候,我们的路径是什么,路径就是我们访问每一个接口传递过来的url
ResponseEntity这个类是干嘛的
CollectionUtils工具类
这个是Spring给我们提供的一个工具类
我们可以来做如下检测
package com.leyou.item.web;
import com.leyou.item.pojo.Category;
import com.leyou.item.service.CategoryService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.util.CollectionUtils;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.List;
/**
* Created by Administrator on 2023/8/29.
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/category")
public class CategoryController {
@Autowired
private CategoryService categoryService;
/**
* 根据父节点的id查询商品分类
* @param pid
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("/list")
public ResponseEntity> queryCategoryListByPid(@RequestParam("pid")Long pid) {
try {
if(pid == null || pid.longValue() < 0) {
//会返回带着状态码的对象400 参数不合法
// return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST).build();
//可以做一格优化,下面的类似
return ResponseEntity.badRequest().build();
}
//开始利用service执行查询操作
List categoryList = categoryService.queryCategoryListByParentId(pid);
if(CollectionUtils.isEmpty(categoryList)) {
//如果结果集为空,响应404
return ResponseEntity.notFound().build();
}
//查询成功,响应200
return ResponseEntity.ok(categoryList);//这里才真正放了数据
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//自定义状态码,然后返回
//500返回一个服务器内部的错误
//这里也可以不返回,程序出错,本身就会返回500
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR).build()
}
}
下面我们去Service创建queryCategoryListByParentId这个方法
看一下完整代码
package com.leyou.item.service;
import com.leyou.item.mapper.CategoryMapper;
import com.leyou.item.pojo.Category;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.List;
/**
* Created by Administrator on 2023/8/29.
*/
@Service
public class CategoryService {
@Autowired
private CategoryMapper categoryMapper;
/**
* 根据父节点的id来查询子结点
* @param pid
* @return
*/
public List queryCategoryListByParentId(Long pid) {
Category category = new Category();
category.setParentId(pid);
return categoryMapper.select(category);
}
}
上面都做完了,现在去数据库操作把分类中的数据给插入一下,类似于如下这些数据
下面就是在数据中存在的数据
下面我开始去启动:
我们的数据肯定是去走网关的
但是在项目里面点击就出不来
上面明显就是出现了跨域的问题
跨域我们就是在服务端进行一个配置
说的简单点,服务器就给给我们配置如下信息
我们这里在服务器搭配一个类来配置这些信息就可以了
我们这里用SpringMVC帮我们写的一个cors跨域过滤器来做:CrosFilter
具体代码如下
package com.leyou.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.cors.CorsConfiguration;
import org.springframework.web.cors.UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource;
import org.springframework.web.filter.CorsFilter;
/**
* Created by Administrator on 2023/8/31.
*/
@Configuration
public class LeyouCorsConfiguration {
@Bean
public CorsFilter corsFilter() {
//1.添加CORS配置信息
CorsConfiguration config = new CorsConfiguration();
//1) 允许的域,不要写*,否则cookie就无法使用了
config.addAllowedOrigin("http://manage.leyou.com");
config.addAllowedOrigin("http://www.leyou.com");
//2) 是否发送Cookie信息
config.setAllowCredentials(true);
//3) 允许的请求方式
config.addAllowedMethod("OPTIONS");
config.addAllowedMethod("HEAD");
config.addAllowedMethod("GET");
config.addAllowedMethod("PUT");
config.addAllowedMethod("POST");
config.addAllowedMethod("DELETE");
config.addAllowedMethod("PATCH");
// 4)允许的头信息
config.addAllowedHeader("*");
//2.添加映射路径,我们拦截一切请求
UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource configSource = new UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource();
configSource.registerCorsConfiguration("/**", config);
//3.返回新的CorsFilter.
return new CorsFilter(configSource);
}
}
重新启动一下网关服务器
下面来讲品牌查询
我们现在要做的就是查询出上面的品牌
我们必须弄明白请求方式,请求路径,请求参数,响应数据决定返回值
一般来说如果页面要展示一个列表的话,就要返回一个List集合对象或者返回一个分页对象
我们就必须定义一个分页对象
分页对象后面大家都要用,我们就放到common里面去
先来把这个分页对象给做了
package com.leyou.common.pojo;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import java.util.List;
/**
* Created by Administrator on 2023/9/2.
*/
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class PageResult {
private Long total;//总条数
private Integer totalPage;//总页数
private List items;//当前页面数据对象
public PageResult(Long total,List items) {
this.total = total;
this.items = items;
}
}
下面我们来做一下前端页面
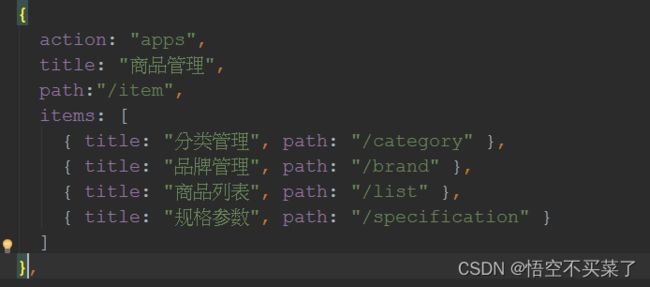
先去找这个页面,在menu.js里面,去查看商品的路径在什么位置
上面就是品牌的路径/item/brand,下面我们看组件在哪里
去到下面这个位置
这个位置去找我们的路由页面
所有的页面组件全部都在pages里面放着
我们这里自己来写一下组件
我们自己定义一个MyBrand1.vue组件
我们这个页面主要还是去做一个分页的表格
可以去Vuetify里面查找
我们这里应该去找从服务端就已经分页与排序好的数据
下面我们可以去看到这里面的模板代码
数据脚本当然是你在script里面,可以查看一下
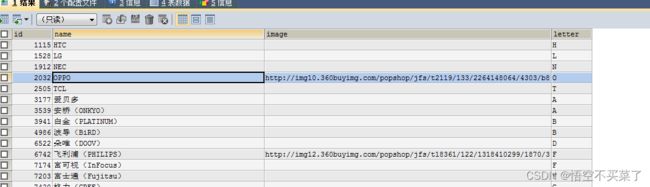
下面我们去看一下品牌表展示什么样的内容,我们看一下数据库里面的字段,先来创建一张产品表,然后把数据也给插入进去
下面我们把数据给插进去,类似于插入下面这些数据
看一下,很明显这个表的数据就已经存在了
我们表头我们直接可以从下面的位置修改
下面直接展示品牌页面前端所有代码
新增品牌
{{ props.item.id }}
{{ props.item.name }}
![]() 无
无
{{ props.item.letter }}
{{isEdit ? '修改' : '新增'}}品牌
close
下面开始写后台逻辑
开始写后台,先写一个产品类
Brand.java
package com.leyou.item.pojo;
import lombok.Data;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.Table;
/**
* Created by Administrator on 2023/9/2.
*/
@Data
@Table(name="tb_brand")
public class Brand {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy= GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
private String name;//品牌名称
private String image;//品牌图片
private Character letter;
}
接下来我们写上我们的通用Mapper类
下面我们去写service接口
下面去写Controller类
分析一下
返回的是什么:当前页的数据(list集合)和总条数
也就是上面返回的是如下一个分页对象,在ly-common模块里面,如果需要用到这个模块的对象,那么我们就需要把这个模块当成依赖引入到另外一个模块里面
这里是ly-item下面的模块ly-item-service需要用到PageResult对象
下面就是Controller中的代码
下面去完成Service中的方法
package com.leyou.item.service;
import com.github.pagehelper.Page;
import com.github.pagehelper.PageHelper;
import com.leyou.common.pojo.PageResult;
import com.leyou.item.mapper.BrandMapper;
import com.leyou.item.pojo.Brand;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import tk.mybatis.mapper.entity.Example;
/**
* Created by Administrator on 2023/9/2.
*/
@Service
public class BrandService {
//内部需要一个mapper调用
@Autowired
private BrandMapper brandMapper;
/**
*
* @param page 当前页
* @param rows 每页大小
* @param sortBy 排序字段
* @param desc 是否降序
* @param key 搜索关键字
* @return
*/
public PageResult queryBrandByPageAndSort(Integer page,Integer rows, String sortBy, Boolean desc, String key) {
//开启分页
//这个会自动拼接到后面的sql语句上面
PageHelper.startPage(page,rows);//传进来一个页码和展示多少行的数据,
//过滤
Example example = new Example(Brand.class);
if(key != null && !"".equals(key)) {
//进来有一模糊查询
//把这个语句拼接上
example.createCriteria().andLike("name","%" + key + "%").orEqualTo("letter",key);
}
if(sortBy != null && !"".equals(sortBy)) {
//根据sortBy字段进行排序
String orderByClause = sortBy + (desc ? " DESC " : " ASC ");
example.setOrderByClause(orderByClause);
}
//利用通用mapper进行查询
Page pageInfo = (Page) brandMapper.selectByExample(example);
//返回结果
//这里面传递总条数和页面信息
return new PageResult<>(pageInfo.getTotal(),pageInfo);
}
}
说一下,用Autowired注入Mapper的时候,提示注入不了,爆红