类与对象(下)
类与对象(下)
- 一、初始化列表
-
- 1、构造函数与初始化
- 2、使用初始化列表的形式
- 3、注意点
- 4、代码
- 5、类需初始化列表但没使用初始化列表时报的错误
- 6、成员变量的初始化顺序
-
- (1)顺序
- (2)测试代码
- (3)运行结果
- 二、explicit关键字
-
- 1、作用
- 2、代码
- 3、讲解
- 4、运行结果与编译器报的错误
- 三、static成员
-
- 1、概念
- 2、特性
- 3、代码
- 4、运行结果
- 5、错误代码与编译器报的错误
- 四、友元
-
- 1、友元函数
-
- (1)概念
- (2)特性
- (3)测试代码
- (4)运行结果
- (5)说明
- 2、友元类
-
- (1)概念
- (2)特性
- (3)测试代码
- (4)运行结果
- (5)错误代码与编译器报的错误
- 五、内部类
-
- 1、概念
- 2、特性
- 3、代码
- 4、运行结果
- 5、错误代码与编译器报的错误
本文是接续文章 类与对象(上)和 类与对象(中)的。
一、初始化列表
1、构造函数与初始化
- 构造函数详情参见文章类与对象(中)。
- 在对象调用构造函数之后,对象中的成员变量虽然已经有了一个初始值,但是我们不能将这个操作称为对对象中成员变量的初始化,而是将其称为赋初值。因为初始化只能进行一次,而构造函数的函数体内可以对成员变量进行多次赋值。
2、使用初始化列表的形式
在构造函数后面,以一个冒号开始,接着是一个以逗号分隔的数据成员列表,每个“成员变量”后面跟一个放在括号中的初始值或表达式。
3、注意点
每个成员变量在初始化列表中只能出现一次,即初始化只能进行一次。
类中包含以下成员变量时,必须将其放在初始化列表位置进行初始化:
- 引用成员变量。
- const成员变量。
- 自定义类型成员变量(该类中没有默认构造函数)。
4、代码
#include- 类A是简单使用初始化列表,而类B则是注意点中的三种情况。
5、类需初始化列表但没使用初始化列表时报的错误
- 尽量使用初始化列表对成员变量进行初始化,因为不管是否使用初始化列表,对于自定义类型成员变量,一定会先使用初始化列表进行初始化。
- 内置类型也推荐使用初始化列表进行初始化,但内置类型在函数体内初始化也没有什么明显的问题,只不过内置类型的成员变量会先用初始化列表进行初始化。
- 对于类中的成员变量(代码中的private下),它们只是声明而已,可以认为在初始化列表中才是对它们进行定义,所以它们都会先用初始化列表进行初始化,再执行构造函数函数体内的内容。
- C++11中对内置类型的成员变量可以给初始值(缺省值)的补丁中,这个初始值(缺省值)是在初始化列表中对成员变量进行定义的。
6、成员变量的初始化顺序
(1)顺序
- 成员变量在类中的声明次序就是其在初始化列表中的初始化顺序,与其在初始化列表中的先后次序无关。
(2)测试代码
class A
{
public:
A(int n)
:_a1(n)
,_a2(_a1)
{}
void Print()
{
cout << _a1 << " " << _a2 << endl;
}
private:
int _a2;
int _a1;
};
int main()
{
A a(10);
a.Print();
return 0;
}
- _a2先用_a1进行初始化,但对_a2初始化时,_a1还未初始化为10,即_a1还是个随机值,所以_a2是用_a1这个随机值初始化的,然后_a1再初始化为10。
(3)运行结果
二、explicit关键字
1、作用
构造函数不仅可以初始化对象,对于单个参数或者除第一个参数无默认值(缺省值)且其余均有默认值(缺省值)的构造函数,还具有类型转换的作用。但当使用explicit修饰构造函数时,将会禁止构造函数的隐式转换。
2、代码
#include3、讲解
- d2为构造函数的隐式转换,即它是用一个int类型数据初始化创建的Date类型,它是由调用构造函数、拷贝构造函数和编译器优化实现的,但经过优化,它变成了和d1一样只调用构造函数。
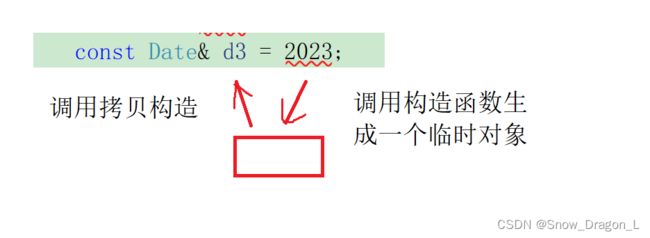
- d3则是对用int类型数据2023进行构造而产生的临时类的引用,但这个临时类具有常属性,需加const对d3进行修饰。
- 最后一个是匿名对象,因为它是匿名的,所以它的作用域只在那一行,出了那一行,这个匿名对象将被销毁。所以,下方运行结果中,最后一个构造函数和析构函数的打印就是它的。
4、运行结果与编译器报的错误
代码的运行结果

用explicit修饰构造函数时编译器报的错误

对象d3的原理图
三、static成员
1、概念
类成员的声明被static修饰就称它为类的静态成员,它的生命周期是整个程序。用static修饰的成员变量,称之为静态成员变量;用static修饰的成员函数,称之为静态成员函数。
2、特性
- 静态成员不属于某个具体的对象而是属于整个类,且它是存放在静态区中的,所以这个类和用这个类实例化出来的所有对象都是共享这些静态成员的。
- 静态成员变量必须在类外进行定义(初始化),定义时不能添加static关键字。因为类中只是声明,类成员的声明只有被static修饰才能称之为类的静态成员。
- 可以使用 类名::静态成员 或者 对象.静态成员 来访问类静态成员。
- 静态成员函数是属于所有类对象且是存在静态区中的,它不在类中,所以它的形参中没有隐藏的this指针,即它不能访问任何非静态成员;相反,非静态成员函数可以访问(调用)类的静态成员函数。
- 静态成员也是类的成员,受public、protected、private访问限定符的限制。
3、代码
下方的代码为计算程序中创建类对象的数量。
#include4、运行结果
5、错误代码与编译器报的错误
四、友元
1、友元函数
(1)概念
友元函数可以直接访问类的私有成员,它是定义在类外部的普通函数,不属于任何类,但需要在类的内部声明,声明时需要加friend关键字。
(2)特性
-
友元函数可以访问类的私有和保护成员,但它不是类的成员函数。
-
友元函数不能用const修饰。
-
友元函数可以在类定义的任何地方声明,不受类访问限定符的限制。
-
一个函数可以是多个类的友元函数。比如函数void func(const A& a, const B& b, const C& c),它的形参涉及A、B、C三个类,则可以把函数func同时弄成A、B、C三个类的友元。
-
友元函数的调用与普通函数的调用原理相同。
(3)测试代码
下方代码为<<的重载,<<的说明参见万字讲解C++基础
#include(4)运行结果
(5)说明
当在类内直接重载operator<<时,我们会发现没办法将operator<<重载成成员函数或者说是重载完要使用时会有点奇怪。因为_cout的输出流对象和隐含的this指针在抢占第一个形式参数的位置。this指针默认是第一个形式参数也就是左操作数。但在实际使用中cout需要是第一个形式参数对象,才是正常使用的方法。所以要将operator<<重载成全局函数。但将operator<<重载成全局函数又会导致类外没办法访问被private修饰的成员变量。operator>>同理。

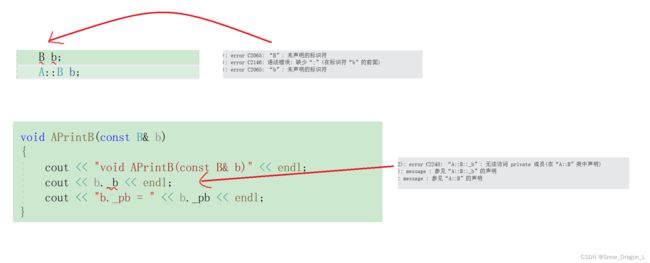
2、友元类
(1)概念
友元类的所有成员函数都是另一个类的友元函数,都可以访问另一个类中的隐藏信息(包括私有成员和保护成员)。 当希望一个类可以存取另一个类的私有成员时,可以将该类声明为另一个类的友元类。
(2)特性
- 友元类与另一个类的关系是单向的,不具有交换性。比如下面的Time类和Date类,在Time类中声明Date类为其友元类,那么在Date类中可以直接访问Time类的私有成员变量,但想在Time类中访问Date类中的私有成员变量则不行。
- 友元关系不能传递。即如果A是B的友元, B是C的友元,不能说明A是C的友元。
- 友元关系不能继承。
(3)测试代码
class Time
{
public:
friend class Date;
Time(int hour = 0, int minute = 0, int second = 0)
:_hour(hour)
,_minute(minute)
,_second(second)
{}
//void SetDateOfTime(int year, int month, int day)
//{
// //不能直接访问日期类私有的成员变量
// _d._year = year;
// _d._month = month;
// _d._day = day;
//}
private:
int _hour;
int _minute;
int _second;
//Date _d;
};
class Date
{
public:
Date(int year = 2023, int month = 8, int day = 25)
:_year(year)
, _month(month)
, _day(day)
{}
void SetTimeOfDate(int hour, int minute, int second)
{
//可以直接访问时间类私有的成员变量
_t._hour = hour;
_t._minute = minute;
_t._second = second;
}
void PrintT()
{
cout << _t._hour << ":" << _t._minute << ":" << _t._second << endl;
}
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
Time _t;
};
int main()
{
Date d;
d.SetTimeOfDate(18, 06, 0);
d.PrintT();
return 0;
}
(4)运行结果
(5)错误代码与编译器报的错误
五、内部类
1、概念
如果一个类定义在另一个类的内部,这个定义在内部的类就叫做内部类。内部类是一个独立的类,它不属于外部的类,更不能通过外部类的对象去访问内部类的成员。外部类对内部类没有任何特殊的访问权限;内部类天生就是外部类的友元类,友元类的详情参见上方的友元类,内部类可以通过外部类的对象参数去访问外部类中的所有成员。但外部类不是内部类的友元。
2、特性
- 内部类可以定义在外部类的public、protected、private中,即对访问限定符无要求。
- 内部类可以直接访问外部类中的static成员,不需要通过外部类的对象或类名去访问,当然,用它们去访问也没什么关系。
- 计算外部类的大小,即sizeof(外部类)时,计算结果是外部类的大小,内部类的大小对外部类的大小没有任何影响。
- 内部类定义在外部类的里面,内部类受外部类的类域、访问限定符限制。
3、代码
#include4、运行结果
5、错误代码与编译器报的错误
本文到这里就结束了,如有错误或者不清楚的地方欢迎评论或者私信
创作不易,如果觉得博主写得不错,请务必点赞、收藏加关注