算法思维总结
文章目录
-
- 1. 二分查找算法
- 2. 动态规划之0-1背包问题
- 3. 自定义乘法运算
- 4. 滑动窗口
- 5. 单链表反转
- 6. 字符串hash算法
- 7. DFS算法
- 8. 双指针算法去重复项(链表数组高效去重)
- 8. 双指针算法求唯一重复元素(快慢指针)
- 9. bit-map数据结构
- 10. 最大堆算法(优先队列)
- 11. 单调队列(滑窗最值)
- 12. xxx
- 参考文章链接
1. 二分查找算法
二分查找有三种算法,基本二分查找,左边界二分查找,右边界二分查找算法。
- 基本二分查找
思路:
每次查找,减半搜索区间(一般定为左右都为闭区间),如果找到target,返回目标,如果没有找到,返回-1,所以时间复杂度为logN。
易错点:
使用mid = left + (right - left) / 2, 可以防止溢出。
代码示例:
#include
#include
#include
#define LENGTH 5
uint16_t binarySearch(const uint16_t* const arr_p,
const uint16_t target)
{
assert(arr_p != NULL);
uint16_t left;
uint16_t right;
uint16_t mid;
left = 0;
right = LENGTH - 1;
//搜索区间[left, right]
while (left <= right)
{
mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (target == arr_p[mid])
return mid;
else if (target > arr_p[mid])
left = mid + 1;
else if (target < arr_p[mid])
right = mid -1;
}
return -1;
}
int main()
{
uint16_t array[LENGTH] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
uint16_t index = binarySearch(array, 3);
printf("find the target num of the index = %d\n", index);
return 0;
}
- 左边界二分查找
思路:
在找到目标值的时候,先不着急返回,先收紧右边界搜索区间。
易错点:
因为返回的是left,而当target > 所有的数值的时候,left有可能数组越界,所以需要做安全检查。
代码示例:
#include
#include
#include
#define LENGTH 5
#define INVALID_INDEX ~0
uint16_t leftBoundSearch(const uint16_t* const arr_p,
const uint16_t target)
{
assert(arr_p != NULL);
uint16_t left;
uint16_t right;
uint16_t mid;
left = 0;
right = LENGTH - 1;
//搜索区间[left, right]
while (left <= right)
{
mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (target == arr_p[mid])
right = mid - 1; //收紧右边界
else if (target > arr_p[mid])
left = mid + 1;
else if (target < arr_p[mid])
right = mid -1;
}
if (left >= LENGTH || arr_p[left] != target)
return INVALID_INDEX;
return left;
}
int main()
{
uint16_t array[LENGTH] = {1, 2, 2, 2, 5};
uint16_t index = leftBoundSearch(array, 2);
printf("find the target num of the index = %d\n", index);
return 0;
}
- 右边界二分查找
思路:
在找到目标值的时候,先不着急返回,先收紧左边界搜索区间。
代码示例:
#include
#include
#include
#define LENGTH 5
#define INVALID_INDEX ~0
uint16_t rightBoundSearch(const uint16_t* const arr_p,
const uint16_t target)
{
assert(arr_p != NULL);
uint16_t left;
uint16_t right;
uint16_t mid;
left = 0;
right = LENGTH - 1;
//搜索区间[left, right]
while (left <= right)
{
mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (target == arr_p[mid])
left = mid + 1; //收紧左边界
else if (target > arr_p[mid])
left = mid + 1;
else if (target < arr_p[mid])
right = mid -1;
}
if (right == -1 || arr_p[right] != target)
return INVALID_INDEX;
return right;
}
int main()
{
uint16_t array[LENGTH] = {1, 2, 2, 2, 5};
uint16_t index = rightBoundSearch(array, 2);
printf("find the target num of the index = %d\n", index);
return 0;
}
2. 动态规划之0-1背包问题
- 0-1背包问题描述
有N件物品和一个容量为V的背包。第i件物品的体积w[i],价值为v[i],求解将那些物品装入这个容量为V的背包,是的价值最大。 - 动态规划解题思路
- 问题分解:将问题分解为若干子问题
- 构造动态规划表:用一张表记录所有子问题的解,以便后边的问题用前边问题来更快求解。
- 状态转移方程
f[i][j] = MAX{f[i-1][j], f[i-1][j-w[i]] + v[i]}
问题实际上转化为:
求解装入第i件物品与不装入第i件物品的最大值。 - C代码的实现
#include
#include
#include
#include
#define MAX(a, b) ((a) > (b)) ? (a) : (b)
/**
*0-1背包问题(动态规划)
*/
const int oneZeroBackpack(const int numItem,
const int capa,
const int* const weight,
const int* const value)
{
assert(weight != NULL && value != NULL);
int row, col;
row = numItem + 1;
col = capa + 1;
//定义行列为row,col的状态转移表
int f[row][col];
memset(f, 0, sizeof(f));
//动态规划,求解最大值
//注意边界条件,可以取等号
for (int i = 1; i <= numItem; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= capa; j++)
{
if (weight[i] > j)
f[i][j] = f[i - 1][j];
else
f[i][j] = MAX(f[i - 1][j], f[i - 1][j - weight[i]] + value[i]);
}
}
return f[numItem][capa];
}
int main()
{
//numItem个商品,容量为capa
const int numItem = 3;
const int capa = 4;
//3个商品,每个商品重量weight数组,价值value数组,下标为0的不代表商品
int weight[3] = {2, 3, 5};
int value[3] = {3, 4, 5};
int result;
result = oneZeroBackpack(numItem, capa, weight, value);
printf("The max value is: %d\n", result);
}
3. 自定义乘法运算
描述
Note:为了简化,这里只考虑正整数相乘的情况。
在C语言的优化算法中,通常将除法运算转换为乘法运算,将取模运算转化为减法或者&运算。所以,自己研究下乘法运算的实现方式。
实现方式
- 转换为加法运算
- 如果被乘数是2^n,可以直接对乘数左移n位
- 直接转换为二进制相乘
二进制相乘的思路
将被乘数转化为二进制字符数据,从右->左 的遍历,如果当前位为temp[i] = 1, 则将乘数 左移 i位,最后循环累加。
例子:
3 * 3 = 11B * 11B
= 11B << 0 + 11B << 1
= 11B + 110B
= 3 + 6
= 9
易错点
被乘数转化为二进制字符后,需要从右 -> 左 遍历。
代码示例
#include
#include
#include
int multiply(const int x, const int y)
{
char tmp[10];
memset(tmp, 0, sizeof(tmp));
itoa(y, tmp, 2); //itoa(int value, char * string, int redix)
printf("The binary number of tmp = %s\n", tmp);
int ret = 0;
int length = strlen(tmp);
int shiftIndex = 0;
//note: loop start from right to left
for (int i = length - 1; i >= 0; --i)
{
//tmp[i] is a char type, tmp[0] = 49, tmp[1] = 49
if (tmp[i] == '1')
{
ret += x << shiftIndex; //x是乘数,y是被乘数
}
++shiftIndex;
}
return ret;
}
int main()
{
int val_1 = 3;
int val_2 = 4;
int val_3 = 5;
int val_4 = 6;
int result_12 = 0;
int result_13 = 0;
int result_14 = 0;
result_12 = multiply(val_1, val_2);
result_13 = multiply(val_1, val_3);
result_14 = multiply(val_1, val_4);
printf("The result of %d * %d = %d\n", val_1, val_2, result_12);
printf("The result of %d * %d = %d\n", val_1, val_3, result_13);
printf("The result of %d * %d = %d\n", val_1, val_4, result_14);
return 0;
}
- 优化
上边的算法,是先通过itoa()函数,将被乘数转为二进制再运算的。其实直接移位,取出最后一位就可以了。 - 代码示例
#include
#include
int multiply(const int x, int y)
{
int ret = 0;
int temp = 0;
int shiftIdx = 0;
while (y > 0)
{
temp = y & 0x01;
if (1 == temp)
{
ret += x << shiftIdx;
}
shiftIdx++;
y >>= 1;
}
return ret;
}
int main()
{
int a = 4;
int b = 5;
int c = multiply(a, b);
printf("%d * %d = %d\n", a, b, c);
return 0;
}
4. 滑动窗口
思路
动态调整窗口的左右边界。
应用场景
求一个字符串的最长子串的长度的时候,可以用到滑动窗口的算法。
代码示例
#include
#include
#include
#include
uint16_t slidingWindow(const char* const src_p)
{
assert(src_p != NULL);
uint16_t leftBound = 0;
uint16_t rightBound = 0;
uint16_t tempIndex = 0;
uint16_t maxLength = 0;
uint16_t length = strlen(src_p);
for (rightBound = 0; rightBound < length; rightBound++)
{
for (tempIndex = leftBound; tempIndex < rightBound; tempIndex++)
{
if (src_p[tempIndex] == src_p[rightBound])
{
leftBound = tempIndex + 1;
break;
}
}
maxLength = ((rightBound - leftBound) + 1) > maxLength ? (rightBound - leftBound) + 1 : maxLength;
}
return maxLength;
}
int main()
{
char *p = "guoxueping";
int ret = 0;
ret = slidingWindow(p);
printf("the length of the max sub string: %d\n", ret);
}
5. 单链表反转
文章参考自
单链表反转
原文有图,有助于理解。
思路
反转单链表有四种方式,分别为:
- 迭代反转
- 递归反转
- 头插法
- 就地逆置
方法一:迭代反转法
这种方式就是遍历整个链表节点,逐个反转当前节点,使其指向前一个节点指针域。
初始态:
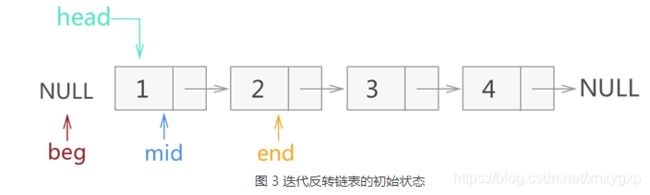
遍历一次的结果:

易错知识点
iteration_reverse()这个函数,形参是一级指针,而反转链表需要返回head的值,是个指针,所以函数调用的时候,需要把返回值重新赋给head.
e.g.
head = iteration_reverse(head)
代码示例
#include
#include
#define true 1
#define LENGTH 10
typedef struct LinkList {
int data;
struct LinkList* next;
}LinkList;
/**
*迭代反转链表
*迭代一次,移动mid = beg
*最后,head = mid
*/
LinkList * iteration_reverse(LinkList* head)
{
if (head == NULL || head->next == NULL)
{
return head;
}
LinkList* begin = NULL;
LinkList* middle = head;
LinkList* end = head->next;
while (true)
{
//modify the middle pointer area
middle->next = begin;
if (end == NULL)
{
break;
}
//right shift all 3 pointer area
begin = middle;
middle = end;
end = end->next;
}
//finally update the head pointer
head = middle;
return head;
}
int main()
{
LinkList linkList[LENGTH];
memset(linkList, 0, sizeof(linkList));
//define the head node
LinkList * head = &linkList[0];
//initialize the linkList expect the last node
int i;
for (i = 0; i < LENGTH - 1; i++)
{
linkList[i].data = i;
linkList[i].next = &linkList[i + 1];
}
//initialize the final node
linkList[i].data = i;
linkList[i].next = NULL;
//before reverse the link list
printf("Before reverse the link list:\n");
int j = 0;
while (NULL != head)
{
printf("linkList[%d].data = %d\n", j, head->data);
head = head->next;
j++;
}
//reallocate head to first node
head = &linkList[0];
//reverse the link list
//这个地方是需要改变head指针地址,所以一级指针形参head是不行的
//所以,要把返回值,重新赋给head
head = iteration_reverse(head);
printf("\nAfter reverse the link list:\n");
j = LENGTH - 1;
while (NULL != head)
{
printf("linkList[%d].data = %d\n", j, head->data);
--j;
head = head->next;
}
return 0;
}
- 结果输出
反转前的链表
Before reverse the link list:
linkList[0].data = 0
linkList[1].data = 1
linkList[2].data = 2
linkList[3].data = 3
linkList[4].data = 4
linkList[5].data = 5
linkList[6].data = 6
linkList[7].data = 7
linkList[8].data = 8
linkList[9].data = 9
反转后的链表
After reverse the link list:
linkList[9].data = 9
linkList[8].data = 8
linkList[7].data = 7
linkList[6].data = 6
linkList[5].data = 5
linkList[4].data = 4
linkList[3].data = 3
linkList[2].data = 2
linkList[1].data = 1
linkList[0].data = 0
方法二:递归反转法
- 思路
首先通过递归,找到最后一个节点,函数最终返回的是最后一个节点,作为新的头节点,每次退出递归,返回的是上一个节点,然后通过head->next->next = head将各个节点串在一起。
如下图:
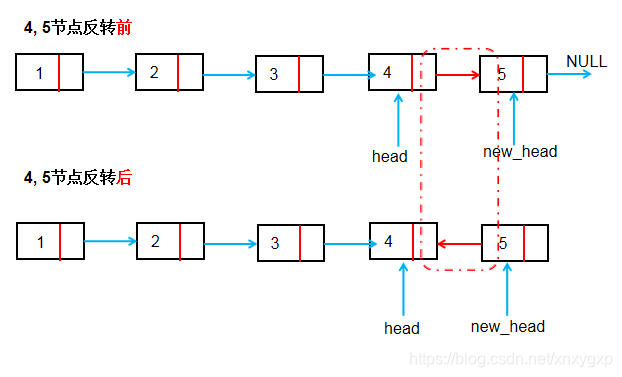
- 代码示例
LinkList * recursiveReverse(LinkList* head)
{
if (NULL == head || NULL == head->next)
{
return head;
}
LinkList* newHead = recursiveReverse(head->next);
head->next->next = head;
head->next = NULL;
return newHead;
}
方法三:头插法
#include
#include
#define true 1
#define LENGTH 10
typedef struct LinkList {
int data;
struct LinkList* next;
}LinkList;
/**
*head reverse the link list
*/
LinkList * headReverse(LinkList* head)
{
if (NULL == head || NULL == head->next)
{
return head;
}
LinkList* newHead = NULL;
LinkList* temp = NULL;
while (NULL != head)
{
//store the head node
temp = head;
head = head->next; //断开temp存储的节点
temp->next = newHead;
newHead = temp; //移动新的头结点
}
return newHead;
}
int main()
{
LinkList linkList[LENGTH];
memset(linkList, 0, sizeof(linkList));
//define the head node
LinkList * head = &linkList[0];
//initialize the linkList expect the last node
int i;
for (i = 0; i < LENGTH - 1; i++)
{
linkList[i].data = i;
linkList[i].next = &linkList[i + 1];
}
//initialize the final node
linkList[i].data = i;
linkList[i].next = NULL;
//before reverse the link list
printf("Before reverse the link list:\n");
int j = 0;
while (NULL != head)
{
printf("linkList[%d].data = %d\n", j, head->data);
head = head->next;
j++;
}
//reallocate head to first node
head = &linkList[0];
//reverse the link list
//这个地方是需要改变head指针地址,所以一级指针形参head是不行的
//所以,要把返回值,重新赋给head
head = headReverse(head);
printf("\nAfter reverse the link list:\n");
j = LENGTH - 1;
while (NULL != head)
{
printf("linkList[%d].data = %d\n", j, head->data);
--j;
head = head->next;
}
return 0;
}
方法四:就地逆置
-
思路
就地逆置,主要思路是,从第二个节点开始,依次取出来,然后插入原链表的头部。 -
与头插法的区别
头插法是插入新的链表,就地逆置是插入原链表。 -
代码示例
#include
#include
#define true 1
#define LENGTH 10
typedef struct LinkList {
int data;
struct LinkList* next;
}LinkList;
/**
*local reverse the link list
*/
LinkList * localReverse(LinkList* head)
{
if (NULL == head || NULL == head->next)
{
return head;
}
LinkList* begin = head;
LinkList* end = head->next;
while (NULL != end)
{
begin->next = end->next; //断开end存储的节点
//forward insert end node
end->next = head;
head = end;
//right shift the end node
end = begin->next;
}
return head;
}
int main()
{
LinkList linkList[LENGTH];
memset(linkList, 0, sizeof(linkList));
//define the head node
LinkList * head = &linkList[0];
//initialize the linkList expect the last node
int i;
for (i = 0; i < LENGTH - 1; i++)
{
linkList[i].data = i;
linkList[i].next = &linkList[i + 1];
}
//initialize the final node
linkList[i].data = i;
linkList[i].next = NULL;
//before reverse the link list
printf("Before reverse the link list:\n");
int j = 0;
while (NULL != head)
{
printf("linkList[%d].data = %d\n", j, head->data);
head = head->next;
j++;
}
//reallocate head to first node
head = &linkList[0];
//reverse the link list
//这个地方是需要改变head指针地址,所以一级指针形参head是不行的
//所以,要把返回值,重新赋给head
head = localReverse(head);
printf("\nAfter reverse the link list:\n");
j = LENGTH - 1;
while (NULL != head)
{
printf("linkList[%d].data = %d\n", j, head->data);
--j;
head = head->next;
}
return 0;
}
6. 字符串hash算法
-
思路
将每个字符乘以不同的权重,累计求和。为了避免hash冲突,前辈的经验,base的选择最好为奇数,hash长度最好为素数,因为素数只有1和本身可以除尽。
初步算法:
hash = hash + pow(base, index) * (*key)
由于幂函数的存在,效率不高,所以有了下边的优化代码。 -
算法的应用
hash算法的应用主要是实现hash表,hash表可以简单的看成数组+链表,同时 具备二者的优点。
hash表的实现可以参考如下链接,写得很好。
hash表的C实现 -
优化代码
#include
#include
#include
#define message(fmt, ...) do{\
printf("INFO: " fmt " [line: %d] [%s]\n", __VA_ARGS__, __LINE__, __FUNCTION__); \
}while(0);
/**
*字符串hash算法,BKDR
*/
unsigned int strHash(const char* key)
{
assert(NULL != key);
unsigned long long hash = 0; //define long long type, in case of buffer overflow
unsigned int seed = 131; //31, 131, 1313, 13131, etc...
unsigned int index = 0;
for (index = 0; index < strlen(key); key++, index++)
{
hash = seed * hash + *key;
}
return hash & (0x7FFFFFFFFFFFFFFF); //mod 2^64
}
int main()
{
char arrStr[20] = {"goodGoodStudy"};
unsigned int hashValue = strHash(arrStr);
message("hash value is = %u", hashValue);
return 0;
}
7. DFS算法
- 思路
深度优先搜索,简单理解就是一条道走到黑,就好比走迷宫,从迷宫入口一直靠着右手走,直到遇到了死胡同,然后返回,直到下一个岔路口,同样是顺着自己的右手走,直到走完所有的岔路口,最终肯定会走出迷宫。
实际上就是一个枚举算法。
这里用一个01背包问题,来应用DFS算法求解。也是枚举法的应用。
- 易错点
01背包问题,主要掌握两点:
- 不加入第i个物品,当前价值是否最大。
- 加入第i个物品,不超过容量的情况下,价值是否最大。
- 代码示例
#include
#define ARR_LENGTH 5
int totalNum = 5, capa = 5, maxValue = 0; //物品件数n,背包容量V,最大价值maxVallue
//int w[maxn], c[maxn];
int weight[ARR_LENGTH] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
int value[ARR_LENGTH] = {3, 4, 5, 6, 7};
void DFS(int index, int sumW, int sumV){
if(index == totalNum){
return;
}
DFS(index + 1, sumW, sumV); //不选第index件物品
//只有加入第index件物品后未超过容量V,才能继续
if(sumW + weight[index] <= capa){
if(sumV + value[index] > maxValue){
maxValue = sumV + value[index]; //更新最大价值maxValue
}
DFS(index + 1, sumW + weight[index], sumV + value[index]); //选择第index件物品
}
}
int main(){
DFS(0,0,0); //初始时为第0件物品,当前总重量和总价值都为0
printf("%d\n",maxValue);
return 0;
}
8. 双指针算法去重复项(链表数组高效去重)
-
思路
用两个指针(链表场景)或者索引(数组场景)分别记录两个位置,慢指针指示无重复数据的位置,快指针去遍历整组数据。如果遇到不重复的数据,就更新慢指针的指针域,使其指向下一个没有重复的数据。 -
易错点
这个方法只是适用于,有序数组,有序链表。 -
代码示例(针对数组)
#include
#include
#include
#define ARR_LEN 10
/**
*remove the duplicated item
*return the length of non-duplicated item
*/
int removeDuplicates(int * arr_p)
{
assert(NULL != arr_p);
//simulate the fast and slow pointer
int slow = 0;
int fast = 1;
int length = ARR_LEN;
if (0 == length)
return 0;
while (fast < length)
{
if (arr_p[fast] != arr_p[slow])
{
++slow;
arr_p[slow] = arr_p[fast];
}
++fast;
}
return slow + 1;
}
int main()
{
int array[ARR_LEN] = {1, 1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 4, 4, 5, 5};
int retLen = 0;
retLen = removeDuplicates(array);
for (int i = 0; i < retLen; ++i)
{
printf("array[%d] = %d\n", i, array[i]);
}
return 0;
}
- 代码示例(针对链表)
#include
#include
#include
typedef struct ListNode{
int data;
struct ListNode* next;
}ListNode;
/**
*@func: double pointer algorithm
*@parameter: return value
*/
ListNode* removeDuplicates(ListNode* head)
{
assert(NULL != head);
//define slow and fast pointer
ListNode* slow = head;
ListNode* fast = head->next;
while (NULL != fast)
{
if (slow->data != fast->data)
{
slow->next = fast;
slow = slow->next;
}
fast = fast->next;
}
//break with the duplicated item
slow->next = NULL;
return head;
}
int main()
{
ListNode node_1 = {1, NULL};
ListNode node_2 = {1, NULL};
ListNode node_3 = {2, NULL};
ListNode node_4 = {2, NULL};
ListNode node_5 = {3, NULL};
ListNode node_6 = {3, NULL};
//construct the link list
node_1.next = &node_2;
node_2.next = &node_3;
node_3.next = &node_4;
node_4.next = &node_5;
node_5.next = &node_6;
//define the head node
ListNode* head = &node_1;
//remove the duplicate item
removeDuplicates(head);
printf("After remove the duplicate item\n");
int index = 0;
while (head)
{
printf("node_%d.data = %d\n", index, head->data);
head = head->next;
++index;
}
return 0;
}
- 拓展:
如果题目变成
8. 双指针算法求唯一重复元素(快慢指针)
-
题目要求
快慢指针算法求数组中的某一个重复元素
数据范围:n + 1 个数,[1…n]闭区间 -
空间复杂度O(1) -->不能使用hash算法
-
时间复杂度小于O(n^2)
-
原数组只读 -->不能排序
-
只有一个元素重复,可能不止重复一次
-
思路
因为是唯一重复元素,并且可能重复多次,所以求和/异或法就不适用了。
这个题可以抽象成带环形的链表,将a[i]作为第i个元素a[a[i]]的索引,构建一个环形链表。那么环形入口就是需要求的重复元素。
代码中两次循环的作用:
- 找到环形链表的入口索引。
- 第二次相遇,slow指针刚好是重复的数据节点。
- 代码示例
#include
#include
#include
/**
*快慢指针算法求数组中的某一个重复元素
*数据范围:n + 1 个数,[1..n]闭区间
*1. 空间复杂度O(1) -->不能使用hash算法
*2. 时间复杂度小于O(n^2)
*3. 原数组只读 -->不能排序
*4. 只有一个元素重复,可能不止重复一次
*/
int findDuplicate(int* arr_p)
{
assert(NULL != arr_p);
int fast = arr_p[arr_p[0]];
int slow = arr_p[0];
//first encounter
while (fast != slow)
{
fast = arr_p[arr_p[fast]];
slow = arr_p[slow];
}
slow = 0;
while (fast != slow) //second encounter
{
fast = arr_p[fast];
slow = arr_p[slow];
}
return slow;
}
int main()
{
int array[] = {1, 3, 2, 5, 7, 6, 7, 4};
int retValue = findDuplicate(array);
printf("Find the duplicate number is: %d\n", retValue);
return 0;
}
- 拓展
如果题目变成,重复元素只有一个,并且只是重复一次。那么可以用求和或者异或求解。
算法思路
设 f(n-1) = {1, 2, 3, …, n-2, n -1}
假设[1…n]区间n+1个元素重复元素为k
f(n) = {1, 2, 3, …, k, k, … n-2, n-1} ==> 注意:这个地方比上边的数据多了一个。
所以,把f(n-1) 和f(n)求异或,就可以求解出重复的那个数据。
int findRepeat(const int arr[], const size_t len)
{
int res = arr[0];
for (int i = 1; i < len; i++)
{
res ^= i;
res ^= arr[i];
}
return res;
}
9. bit-map数据结构
- 什么是bit-map
bit-map就是用一个bit位来表示一个数据是否存在。 - 应用场景
在处理海量数据的时候,考虑到空间复杂度,bit-map的应用,可以大大减少内存开销。
海量数据找重,就是很好的应用。
- 代码示例
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
#define xxx ~0
class NBitMap
{
public:
NBitMap(size_t range)
{
_bitTable.resize((range >> 4) + 1);
}
void SetBit(size_t x)
{
size_t index = x >> 4;
size_t num = x % 16;
num *= 2;
bool first = _bitTable[index] & (1 << num);
bool second = _bitTable[index] & (1 << (num + 1));
if (!(first && second))
{
//if current bit is already set 1, set the (num + 1) is 1
if (_bitTable[index] >> num)
_bitTable[index] |= (1 << (num + 1));
else
_bitTable[index] |= (1 << num);
}
}
bool isDuplicate(size_t x)
{
size_t index = x >> 4;
size_t num = x % 16;
num *= 2;
//get the duplicated bit
return (_bitTable[index] >> num) & 0x02;
}
private:
vector _bitTable;
};
int main()
{
NBitMap * bitMap = new NBitMap(20);
bitMap->SetBit(2);
bitMap->SetBit(2);
bitMap->SetBit(2);
bitMap->SetBit(2);
bitMap->SetBit(5);
bitMap->SetBit(3);
bitMap->SetBit(3);
bitMap->SetBit(3);
bool isDuplicate = bitMap->isDuplicate(3);
cout << "isDuplicate = " << isDuplicate << endl;
return 0;
}
10. 最大堆算法(优先队列)
- 什么是最大堆
任意一层的父节点都大于叶子节点,这样的堆就是最大堆。
堆是二叉树的一个特例。 - 应用场景
堆排序,先构造一个最大堆或者最小堆,然后每次pop出最大值,最后所有pop出来的值就是一个有序数列。 - 参考链接
最小堆 构建、插入、删除的过程图解 - 代码示例
#include
#include
#define MAX_INT 0xFFFF
typedef int ElemType;
typedef struct Heap {
ElemType *elem_p;
int currentSize; //current item number
int maxSize; //max store capa
}Heap;
/**
*create a null max heap, and maxSize is maxCapa
*/
Heap * createNullMaxheap(const int maxCapa, Heap* const heap_p)
{
//valid data stored from index=1, so maxSize = maxCapa+1
heap_p->elem_p = (ElemType*)malloc((maxCapa + 1)*sizeof(ElemType));
heap_p->currentSize = 0; //valid data index from 1
heap_p->maxSize = maxCapa;
heap_p->elem_p[0] = MAX_INT; //定义哨兵大于堆中所有元素
return heap_p;
}
/**
*judge if maxHeap is full
*/
int isFullMaxheap(Heap* const heap_p)
{
return (heap_p->maxSize == heap_p->currentSize);
}
/**
*judege if max heap is empty
*/
int isEmptyMaxheap(Heap* const heap_p)
{
return heap_p->currentSize == 0; //if empty return 1, else return 0
}
/**
*insert item to max heap
*/
void insertMaxheap(ElemType insertValue, Heap* const heap_p)
{
int index = 0;
if (isFullMaxheap(heap_p))
{
printf("Max Heap is already full!\n");
return;
}
//increase the currentSize
++heap_p->currentSize;
//find the position which need to insert the data
index = heap_p->currentSize;
//if the insert value great than father node, index = index / 2;
//向上滤insertValue
for (; insertValue > heap_p->elem_p[index / 2]; index /= 2)
{
heap_p->elem_p[index] = heap_p->elem_p[index / 2];
}
heap_p->elem_p[index] = insertValue;
}
/**
*delete the item from max heap
*/
int deleteMaxheap(Heap* const heap_p)
{
int parent, child;
int maxData, temp;
if (isEmptyMaxheap(heap_p))
{
printf("Max heap is empty!!!\n");
return 0;
}
//retrive the root node
maxData = heap_p->elem_p[1];
//get the last item from max heap
temp = heap_p->elem_p[heap_p->currentSize--];
//从上至下,调整最大堆
for (parent = 1; parent*2 < heap_p->currentSize; parent <<= 1)
{
child = 2 * parent;
//find the greater child index
if (child != heap_p->currentSize && (heap_p->elem_p[child] < heap_p->elem_p[child + 1]))
{
++child;
}
if (temp >= heap_p->elem_p[child])
break;
else
heap_p->elem_p[parent] = heap_p->elem_p[child];
}
heap_p->elem_p[parent] = temp;
return maxData;
}
/**
*print the max heap
*/
void printMaxheap(Heap* const heap_p)
{
int index;
for (index = 1; index < heap_p->currentSize + 1; ++index)
{
printf("%d ", heap_p->elem_p[index]);
}
printf("\n");
}
int main()
{
ElemType arr[5] = {50, 60, 70, 80, 90};
int i, len = 5;
Heap* heap_p = (Heap*)malloc(sizeof(Heap));
heap_p = createNullMaxheap(len, heap_p);
printf("Add elements in order:\n");
for (i = 0; i < len; ++i)
{
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
insertMaxheap(arr[i], heap_p);
}
printf("\nPrint the max heap:\n");
printMaxheap(heap_p);
//delete the item from max heap
printf("delete the item from max heap: %d\n", deleteMaxheap(heap_p));
printf("After delete the item, the max heap is: \n");
printMaxheap(heap_p);
return 0;
}
11. 单调队列(滑窗最值)
- 单调队列
队列是先进先出的数据结构。
单调队列,分为单调递增或者单调递减队列。 - 应用场景
求滑动窗口中元素的最值。 - 题目描述
给定一个数组nums,滑窗大小为width,滑动窗口从数组的左端移动到数组的右端。每次移动一个元素位置。
返回滑动窗口中的最大值。
-
易错点
在移动右指针的时候,判断条件中left <= right一定要取等。 -
示例
输入:nums=[1, 3, -1, -3, 5, 3, 6, 7], width = 3
输出:[3, 3, 5, 5, 6, 7]
解释:
[1, 3, -1] -3, 5, 3, 6, 7 —> 3
1 [3, -1, -3] 5, 3, 6 ,7 —> 3
1, 3 [-1, -3, 5] 3, 6, 7 —> 5
1, 3, -1 [-3, 5, 3] 6, 7 —> 5
1, 3, -1, -3 [5, 3, 6] 7 —> 6
1, 3, -1, -3, 5 [3, 6, 7] —> 7 -
解体思路
用一个单调队列来存放滑窗大小的队列,这个地方因为是求最大值,所以采用单调递减队列,当队列元素个数大于width窗口大小,则pop出队首元素,当遍历的元素小于队尾元素,则加入队列。此题的关键就是,如何操作队列的队首 和队尾元素。
note:下边代码用vector来模拟了queue的特性。 -
代码示例
C++ Code
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
class Solution{
public:
vector maxSlidingWindow(vector& nums, int width)
{
int len = nums.size();
int left = 0;
int right = -1;
//define a queue list to store the item for sliding window
vector retList, queue(len, 0);
for (int index = 0; index < len; ++index)
{
//move right pointer
while (left <= right && nums[index] >= queue[right])
right--;
queue[++right] = nums[index];
//move left pointer
//元素长度超过width,移除left元素
if (right - left >= width)
left++;
//遍历的元素个数大于width,加入返回值
if (index + 1 >= width)
{
retList.push_back(queue[left]);
}
}
return retList;
}
};
int main()
{
int array[] = {1, 3, -1, -3, 5, 3, 6, 7};
vector srcList(array, array + 8);
vector ansList;
Solution * solution = new Solution();
ansList = solution->maxSlidingWindow(srcList, 3);
printf("The result of max num for sliding window\n");
for (vector::iterator it = ansList.begin(); it != ansList.end(); ++it)
{
printf("%d ", *it);
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
12. xxx
思路
易错点
代码示例
参考文章链接
labuladong手撕算法
程序员必须掌握哪些算法?
什么是B树?为啥文件索引要用B树而不用二叉查找树
什么是栈?
二叉树高频面试题和答案
二分查找树中的前、中、后序遍历动态图
二叉树遍历代码实现