3.springboot连接redis并完成缓存操作
目录:
1. java连接redis
2. springboot连接redis操作。
3. 完成缓存操作
默认有三种方式连接redis.
第一种:jedis---传统的项目--ssm
第二种:lettuce:---->刚出现没有多久就被springboot整合进来。
第三种:springboot连接redis
1 jedis操作redis服务器
(1)引入jedis依赖
redis.clients
jedis
4.3.1
(2)编写相关的代码,来试一下又没连接成功
每次使用jedis对象时 都需要自己创建,当使用完后,需要关闭该对象。===>jedis中也存在连接池.
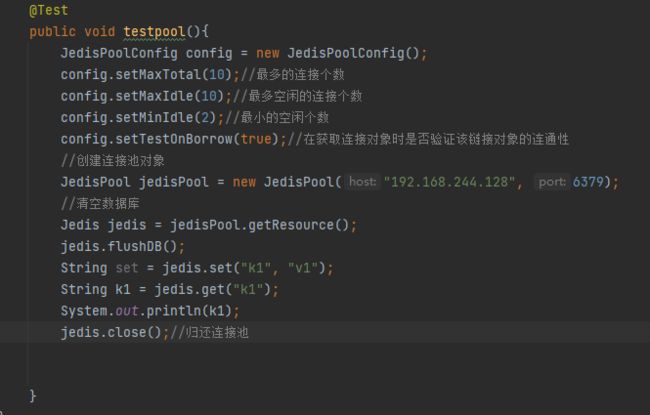
1.2 jedis连接池的使用
1.3测试jedis使用和不使用连接池的效率
@Test
public void test03(){
//连接池的配置信息
JedisPoolConfig config=new JedisPoolConfig();
config.setMaxTotal(100);//最多的连接个数
config.setMaxIdle(10); //最多空闲的连接个数
config.setMinIdle(2); //最小的空闲个数
config.setTestOnBorrow(true);//在获取连接对象时是否验证该连接对象的连通性
//创建连接池对象
JedisPool jedisPool=new JedisPool(config,"192.168.244.128",6379);
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for(int i=0;i<10000;i++){
Jedis jedis = jedisPool.getResource();
String ping = jedis.ping();
jedis.close();
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("耗时:"+(end-start));
}
@Test
public void test02(){
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
//Jedis(String host, int port)
for(int i=0;i<10000;i++){
Jedis jedis=new Jedis("192.168.244.128",6379);
String ping = jedis.ping();
jedis.close();
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("耗时:"+(end-start));
}2. springboot整合redis
springboot在整合redis时提高两个模板类,StringRedisTemplate和RedisTemplate.以后对redis的操作都在该模板类中。StringRedisTemplate是RedisTemplate的子类。
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-data-redis
org.apache.commons
commons-pool2
修改配置文件
spring.redis.host=192.168.244.128
spring.redis.port=6379
#最多获取数
spring.redis.lettuce.pool.max-active=8
spring.redis.lettuce.pool.max-wait=-1ms
spring.redis.lettuce.pool.max-idle=8
spring.redis.lettuce.pool.min-idle=0测试:
package com.hql;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.*;
import java.util.*;
@SpringBootTest
class SpringbootJedisApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@Test
void contextLoads() {
//关于key的操作
//keys *
Set keys = redisTemplate.keys("*");
System.out.println(keys);
//exists key
Boolean hasKey = redisTemplate.hasKey("k1");//判断是否存在指定的key
System.out.println("判断是否存在指定的key:"+hasKey);
//del key [key....]
Boolean k1 = redisTemplate.delete("k1");//删除指定的key
System.out.println("是否删除指定key成功:"+k1);
System.out.println("=================================================");
//操作字符串
ValueOperations forValue = redisTemplate.opsForValue();//专门操作字符串
//set key value
forValue.set("k1","v1");
//get key
String k11 = forValue.get("k1");
System.out.println(k11);
//mset key value
HashMap map= new HashMap<>();
map.put("k2","v2");
map.put("k3","v3");
map.put("k4","v4");
forValue.multiSet(map);
//mget key
List list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("k2");
list.add("k3");
list.add("k4");
List strings = forValue.multiGet(list);
System.out.println(strings);
//incr key
Long k5 = forValue.increment("k5", 50);
System.out.println(k5);
//decr key
Long k55 = forValue.decrement("k5",2);
System.out.println(k55);
//setnx key value
Boolean aBoolean = forValue.setIfAbsent("k6", "v6");
System.out.println("是否存入成功:"+aBoolean);
System.out.println("==================================================");
//Hash类型
//hset key filed value filed value ......
HashOperations forHash = redisTemplate.opsForHash();
HashMap hashmap = new HashMap<>();
hashmap.put("name","dong");
hashmap.put("age","10");
hashmap.put("sex","男");
forHash.putAll("k7",hashmap);
//hgetall key value
Map k7 = forHash.entries("k7");
System.out.println(k7);
//hkeys key
Set 2.2 RedisTemplate
它是StringRedisTemplate的父类,它类可以存储任意数据类型,但是任意类型必须序列化,默认采用的是jdk的序列化方式。jdk序列化方式阅读能力差,而且占用空间大. 我们在使用是一般需要人为指定序列化方式。
package com.hql;
import com.hql.pojo.User;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.ValueOperations;
import java.util.Set;
@SpringBootTest
class SpringbootJedisApplicationTests2 {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@Test
void contextLoads() {
redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
redisTemplate.setValueSerializer(new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer());
ValueOperations valueOperations = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
valueOperations.set("user",new User(1,"哈哈哈","北京"));
Object user = valueOperations.get("user");
System.out.println(user);
}
}
如果每次使用都人为指定序列化方式,比较麻烦所以统一设置redisTemplate的序列化
package com.hql.config;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonAutoDetect;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.PropertyAccessor;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.RedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer;
/**
* @program: springboot-jedis
* @description:
* @author:
* @create: 2023-04-24 16:26
**/
@Configuration
public class RedisConfig {
//比如验证码
@Bean //该方法的返回对象交于spring容器管理
public RedisTemplate redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory factory) {
RedisTemplate template = new RedisTemplate<>();
RedisSerializer redisSerializer = new StringRedisSerializer();
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer jackson2JsonRedisSerializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer(Object.class);
ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper();
om.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY);
om.enableDefaultTyping(ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL);
jackson2JsonRedisSerializer.setObjectMapper(om);
template.setConnectionFactory(factory);
//key序列化方式
template.setKeySerializer(redisSerializer);
//value序列化
template.setValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
//value hashmap序列化
template.setHashValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
return template;
}
}
上面的连接都是连接的单机版的redis,真实项目它们的redis都是集群模式.
2.3 springboot连接集群
配置文件
#最多获取数
spring.redis.lettuce.pool.max-active=8
spring.redis.lettuce.pool.max-wait=-1ms
spring.redis.lettuce.pool.max-idle=8
spring.redis.lettuce.pool.min-idle=0
# 设置redis重定向的次数---根据主节点的个数
spring.redis.cluster.max-redirects=3
spring.redis.cluster.nodes=192.168.244.128:6000,192.168.244.128:6001,192.168.244.128:6002,192.168.244.128:6003,192.168.244.128:6004,192.168.244.128:60053. redis的应用场景
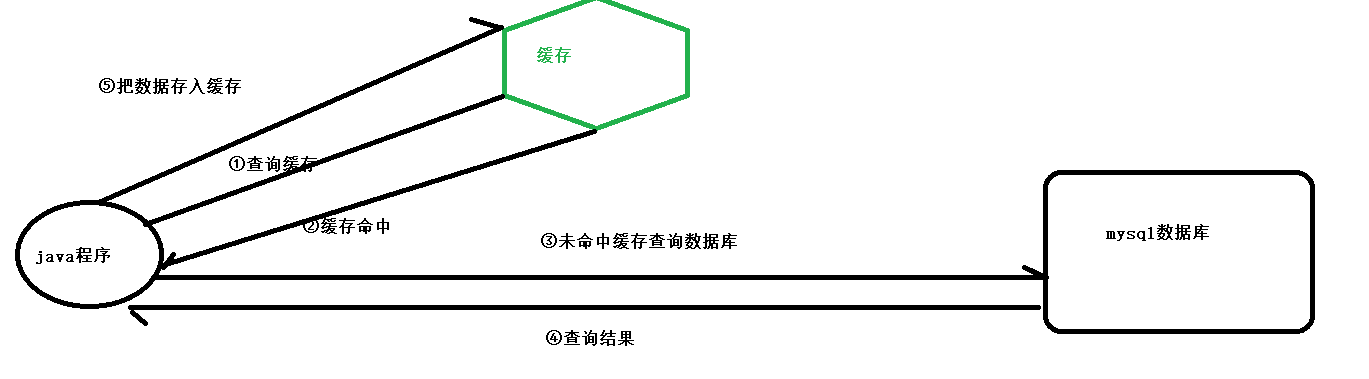
4.1 redis可以作为缓存
(1) 缓存的原理
(2)缓存的作用:
减少访问数据库的频率。--提高系统的性能
(3)什么样的数据适合放入缓存
-
查询频率高的
-
修改频率低的
-
数据安全性要求低的。
(4)用springboot 来使用缓存
1.引入依赖
4.0.0
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-parent
2.3.12.RELEASE
com.hql
springboot-jedis2
0.0.1-SNAPSHOT
springboot-jedis2
springboot-jedis2
1.8
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-data-redis
org.apache.commons
commons-pool2
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
mysql
mysql-connector-java
org.projectlombok
lombok
true
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-test
test
com.baomidou
mybatis-plus-boot-starter
3.5.1
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-maven-plugin
org.projectlombok
lombok
2.配置文件
server.port=8888
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/school?serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai
spring.datasource.password=
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
#mybatis-plus.configuration.log-impl=org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl
mybatis-plus.configuration.log-impl=org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl
spring.redis.host=192.168.244.128
spring.redis.port=6379
#最多获取数
spring.redis.lettuce.pool.max-active=8
spring.redis.lettuce.pool.max-wait=-1ms
spring.redis.lettuce.pool.max-idle=8
spring.redis.lettuce.pool.min-idle=0
pojo层
Student
package com.hql.pojo;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.IdType;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.TableId;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import lombok.ToString;
/**
* @program: springboot-jedis2
* @description:
* @author:
* @create: 2023-04-24 20:48
**/
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@ToString
public class Student {
@TableId(type = IdType.AUTO)
private Integer sid;
private String sname;
private Integer cid;
}
mapper层
StudentMapper
package com.hql.mapper;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.mapper.BaseMapper;
import com.hql.pojo.Student;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
/**
* @program: springboot-jedis2
* @description:
* @author:
* @create: 2023-04-24 20:50
**/
@Mapper
public interface StudentMapper extends BaseMapper {
}
service层
StudentService
package com.hql.service;
import com.hql.pojo.Student;
/**
* @program: springboot-jedis2
* @description:
* @author:
* @create: 2023-04-24 20:55
**/
public interface StudentService {
Student queryAllById(Integer id);
}
StudentServiceImpl
package com.hql.service.impl;
import com.hql.mapper.StudentMapper;
import com.hql.pojo.Student;
import com.hql.service.StudentService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.ValueOperations;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
/**
* @program: springboot-jedis2
* @description:
* @author:
* @create: 2023-04-24 20:56
**/
@Service
public class StudentServiceImpl implements StudentService {
@Autowired
private StudentMapper studentMapper;
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@Override
public Student queryAllById(Integer id) {
ValueOperations forValue = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
//1.查询缓存
Object o = forValue.get("student::" + id);
if(o!=null){ //缓存命中
return (Student) o;
}
Student student = studentMapper.selectById(id);
//2.查询到应该放入缓存
if(student!=null){
forValue.set("student::"+id,student);
}
return student;
}
}
controller层
StudentController
package com.hql.controller;
import com.hql.pojo.Student;
import com.hql.service.StudentService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* @program: springboot-jedis2
* @description:
* @author:
* @create: 2023-04-24 21:03
**/
@RestController
public class StudentController {
@Autowired
private StudentService studentService;
@GetMapping("getId/{id}")
public Student getAllId(@PathVariable Integer id){
Student student = studentService.queryAllById(id);
return student;
}
}
注意:这里我们用的是RedisTemplate,要序列化,引入config层
RedisConfig
package com.hql.config;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonAutoDetect;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.PropertyAccessor;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.RedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer;
/**
* @program: springboot-jedis
* @description:
* @author:
* @create: 2023-04-24 16:26
**/
@Configuration
public class RedisConfig {
//比如验证码
@Bean //该方法的返回对象交于spring容器管理
public RedisTemplate redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory factory) {
RedisTemplate template = new RedisTemplate<>();
RedisSerializer redisSerializer = new StringRedisSerializer();
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer jackson2JsonRedisSerializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer(Object.class);
ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper();
om.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY);
om.enableDefaultTyping(ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL);
jackson2JsonRedisSerializer.setObjectMapper(om);
template.setConnectionFactory(factory);
//key序列化方式
template.setKeySerializer(redisSerializer);
//value序列化
template.setValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
//value hashmap序列化
template.setHashValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
return template;
}
}
然后进行访问