C语言中的数组使用方法及案例分享
1. 一维数组
1.1 一维数组的定义和初始化
1.1.1一维数组的定义
语法:
数据类型 数组名[数组长度]
解释说明:
- 数组的数据类型就是数组元素的数据类型
- 数组长度是数组能够包含的数组元素个数,为常量表达式
例子:
int a[10];
1.1.2 数值型一维数组的初始化
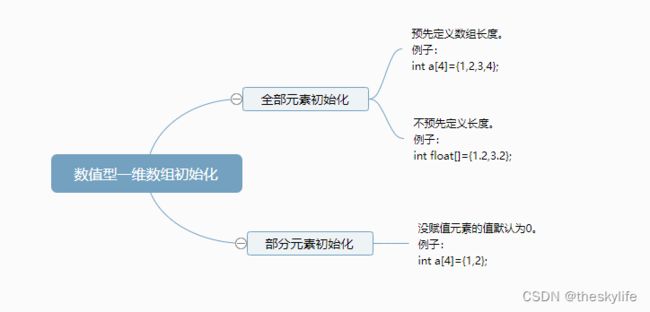
数组的初始化分为两种,一种为全部元素初始化,一种为部分元素初始化。详见下图:
1.1.3 字符串一维数组的初始化
字符型数组是:据类型为字符型的数组,可用于存储字符串,每一个元素存放一个字符常量。
对字符数组初始化时,可使用"\0"作为末尾元素值,存储字符串
char str[4]={'s','i','x','\0'};
也可以使用一个字符串常量为字符数组进行初始化,系统自动在字符串尾部增加一个结束标志’\0’
char str[4]='six';
如上,数组str的长度为4,内部占用5个字节空间。
1.2 一维数组的引用
数组元素的下标从0开始,当数组长度为n时,最末元素的下标是-1。
char str[4]的全部元素:str[0]、str[1]、str[2]、str[3]。
数组的输入和输出代码如下:
char str[4];
// 对第一个数组元素进行赋值
scanf("%c", &str[0]);
// 取第一个数组元素的值
printf("%c", str[0]);
2. 字符串
2.1 字符串拼接与复制
strcat(s1,s2):字符串拼接
strcpy(s1,s2) : 字符串复制
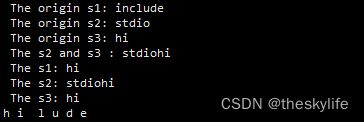
两个函数使用案例如下:
#include2.2 字符串比较函数
strcmp(s1,s2) :比较字符串s1和字符串s2的大小。
会自左至右逐个字符串比较字符串中个字符的ASCII码,遇到不同字符或’\0’时比较过程结束,此时,ASCII码值大的字符所在的字符串大。
该函数会返回一个数值.
- s1与s2相同:值为0
- s1大于s2:值为正数
- s1小于s2:值为负数
2.3 大小写转换与字符长度
strlwr(s):将大写转为小写
strupr(s):将小写转为大写
strlen(s): 求字符串的长度
3.二维数组
3.1 二维数组的定义
语法:
数据类型 数组名[表达式1][表达式2]:
以下形式都是正确的定义:
int a[3][5];
int b[][3];
3.2 二维数组的初始化
3.2.1 按行初始化
int a[2][3]={{1,2,3},{4,5,6}};
int a[2][3]={{1,2,3},{4}}; //实际为1,2,3 4,0,0
3.2.2 按列初始化
int a[2][3]={1,2,3,4,5,6};
int a[2][3]={1,2,3}; //实际为1,2,3 0,0,0
3.2.3 省略行数的初始化
int a[][4]={{1},{2,3}}; //实际为1,0,0,0 2,3,0,0
int a[][3]={1,2,3,4,5,6,7} //实际为1,2,3 4,5,6 7,0,0
4.相关应用案例
4.1 输出斐波那契序列
将Fibonacci数列的前20项存储于一维数组,并输出
#include4.2 字符串拼接
#include4.3 杨辉三角
实现完整C代码如下:
#include