【C++】异常
目录
- 一、概念
- 二、异常的使用
-
- 1、异常的抛出和捕获
- 2、异常的重新抛出
- 3、异常安全
- 4、异常规范
- 三、自定义异常体系
- 四、C++标准库的异常体系
- 五、异常的优缺点
一、概念
传统的错误处理机制:
- 终止程序,如assert,缺陷:用户难以接受。如发生内存错误,除0错误时就会终止程序。
- 返回错误码,缺陷:需要程序员自己去查找对应的错误。如系统的很多库的接口函数都是通过把错误码放到
errno中,表示错误
异常是一种处理错误的方式,当一个函数发现自己无法处理的错误时就可以抛出异常,让函数的直接或间接的调用者处理这个错误。
- throw:当问题出现时,程序就会抛出一个异常。这里是通过使用
throw关键字来完成的。 - catch: 在您想要处理问题的地方,通过异常处理程序捕获异常。
catch关键字用于捕获异常,可以有多个catch进行捕获。 - try: try块中的代码标识将被激活的特定异常。它后面通常跟着一个或多个 catch 块。
如果有一个块抛出一个异常,捕获异常的方法会使用 try 和 catch 关键字。try 块中放置可能抛出异常的代码,try 块中的代码被称为保护代码。使用 try/catch 语句的语法如下所示:
try
{
// 保护的标识代码
}
catch (ExceptionName e1)
{
// catch 块
}
catch (ExceptionName e2)
{
// catch 块
}
catch (ExceptionName eN)
{
// catch 块
}
二、异常的使用
1、异常的抛出和捕获
异常的抛出和匹配原则:
- 异常是通过抛出对象而引发的,该对象的类型决定了应该激活哪个catch的处理代码。
- 被选中的处理代码是调用链中与该对象类型匹配且离抛出异常位置最近的那一个。
- 抛出异常对象后,会生成一个异常对象的拷贝,因为抛出的异常对象可能是一个临时对象,所以会生成一个拷贝对象,这个拷贝的临时对象会在被catch以后销毁。(这里的处理类似于函数的传值返回)
- catch(…)可以捕获任意类型的异常,问题是不知道异常错误是什么。
- 实际中抛出和捕获的匹配原则有个例外,并不都是类型完全匹配,可以抛出的派生类对象,使用基类捕获,这个在实际中非常实用,我们后面会详细讲解这个。
在函数调用链中异常栈展开匹配原则:
6. 首先检查throw本身是否在try块内部,如果是再查找匹配的catch语句。如果有匹配的,则调到catch的地方进行处理。
7. 没有匹配的catch则退出当前函数栈,继续在调用函数的栈中进行查找匹配catch。
8. 如果到达main函数的栈,依旧没有匹配的,则终止程序。上述这个沿着调用链查找匹配的catch子句的过程称为栈展开。所以实际中我们最后都要加一个catch(…)捕获任意类型的异常,否则当有异常没捕获,程序就会直接终止。
9. 找到匹配的catch子句并处理以后,会继续沿着catch子句后面继续执行

double Division(int a, int b)
{
// 当b == 0时抛出异常
if (b == 0)
throw "Division by zero condition!";
else
return ((double)a / (double)b);
}
void Func()
{
int len, time;
cin >> len >> time;
cout << Division(len, time) << endl;
}
int main()
{
try
{
Func();
}
catch (const char* errmsg)
{
cout << errmsg << endl;
}
catch (...)
{
cout << "unkown exception" << endl;
}
return 0;
}
2、异常的重新抛出
有可能单个的catch不能完全处理一个异常,在进行一些校正处理以后,希望再交给更外层的调用链函数来处理,catch则可以通过重新抛出将异常传递给更上层的函数进行处理。
double Division(int a, int b)
{
// 当b == 0时抛出异常
if (b == 0)
{
throw "Division by zero condition!";
}
return (double)a / (double)b;
}
void Func()
{
// 这里可以看到如果发生除0错误抛出异常,另外下面的array没有得到释放。
// 所以这里捕获异常后并不处理异常,异常还是交给外面处理,这里捕获了再重新抛出去。
int* array = new int[10];
try {
int len, time;
cin >> len >> time;
cout << Division(len, time) << endl;
}
catch (...)
{
cout << "delete []" << array << endl;
delete[] array;
throw;
}
// ...
cout << "delete []" << array << endl;
delete[] array;
}
int main()
{
try
{
Func();
}
catch (const char* errmsg)
{
cout << errmsg << endl;
}
return 0;
}
3、异常安全
- 构造函数完成对象的构造和初始化,最好不要在构造函数中抛出异常,否则可能导致对象不完整或没有完全初始化。
- 析构函数主要完成资源的清理,最好不要在析构函数内抛出异常,否则可能导致资源泄漏(内存泄漏、句柄未关闭等)
- C++中异常经常会导致资源泄漏的问题,比如在new和delete中抛出了异常,导致内存泄漏,在lock和unlock之间抛出了异常导致死锁,C++经常使用RAII来解决以上问题。
4、异常规范
- 异常规格说明的目的是为了让函数使用者知道该函数可能抛出的异常有哪些。 可以在函数的后面接throw(类型),列出这个函数可能抛掷的所有异常类型。
- 函数的后面接throw(),表示函数不抛异常。
- 若无异常接口声明,则此函数可以抛掷任何类型的异常。
// 这里表示这个函数会抛出A/B/C/D中的某种类型的异常
void fun() throw(A,B,C,D);
// 这里表示这个函数只会抛出bad_alloc的异常
void* operator new (std::size_t size) throw (std::bad_alloc);
// 这里表示这个函数不会抛出异常
void* operator delete (std::size_t size, void* ptr) throw();
// C++11 中新增的noexcept,表示不会抛异常
thread() noexcept;
thread(thread&& x) noexcept;
三、自定义异常体系
实际使用中很多公司都会自定义自己的异常体系进行规范的异常管理,因为一个项目中如果大家随意抛异常,那么外层的调用者基本就没办法玩了,所以实际中都会定义一套继承的规范体系。这样大家抛出的都是继承的派生类对象,捕获一个基类就可以了。

// 服务器开发中通常使用的异常继承体系
class Exception
{
public:
Exception(int errid, const string& msg)
:_errid(errid)
, _errmsg(msg)
{}
virtual string what() const
{
return _errmsg;
}
int GetErrid() const
{
return _errid;
}
protected:
int _errid; // 错误码
string _errmsg; // 错误描述
};
class SqlException : public Exception
{
public:
SqlException(int errid, const string& msg, const string& sql)
:Exception(errid, msg)
, _sql(sql)
{}
virtual string what() const
{
string msg = "SqlException:";
msg += _errmsg;
msg += "->";
msg += _sql;
return msg;
}
private:
const string _sql;
};
class CacheException : public Exception
{
public:
CacheException(const string& errmsg, int id)
:Exception(id, errmsg)
{}
virtual string what() const
{
string msg = "CacheException:";
msg += _errmsg;
return msg;
}
};
class HttpServerException : public Exception
{
public:
HttpServerException(const string& errmsg, int id, const string& type)
:Exception(id, errmsg)
, _type(type)
{}
virtual string what() const
{
string msg = "HttpServerException:";
msg += _errmsg;
msg += "->";
msg += _type;
return msg;
}
private:
const string _type;
};
void SQLMgr()
{
srand(time(0));
if (rand() % 7 == 0)
{
throw SqlException(100, "权限不足", "select * from name = '张三'");
}
cout << "调用成功" << endl;
}
void CacheMgr()
{
srand(time(0));
if (rand() % 5 == 0)
{
throw CacheException("权限不足", 100);
}
else if (rand() % 6 == 0)
{
throw CacheException("数据不存在", 101);
}
SQLMgr();
}
void HttpServer()
{
// 模拟服务出错
srand(time(0));
if (rand() % 3 == 0)
{
throw HttpServerException("请求资源不存在", 100, "get");
}
else if (rand() % 4 == 0)
{
throw HttpServerException("权限不足", 101, "post");
}
CacheMgr();
}
int main()
{
while (1)
{
this_thread::sleep_for(chrono::seconds(1));
try
{
HttpServer();
}
catch (const Exception& e) // 这里捕获父类对象就可以
{
// 多态
cout << e.what() << endl;
}
catch (...)
{
cout << "Unkown Exception" << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
四、C++标准库的异常体系
C++ 提供了一系列标准的异常,定义在 中,我们可以在程序中使用这些标准的异常。它们是以父子类层次结构组织起来的,如下所示:
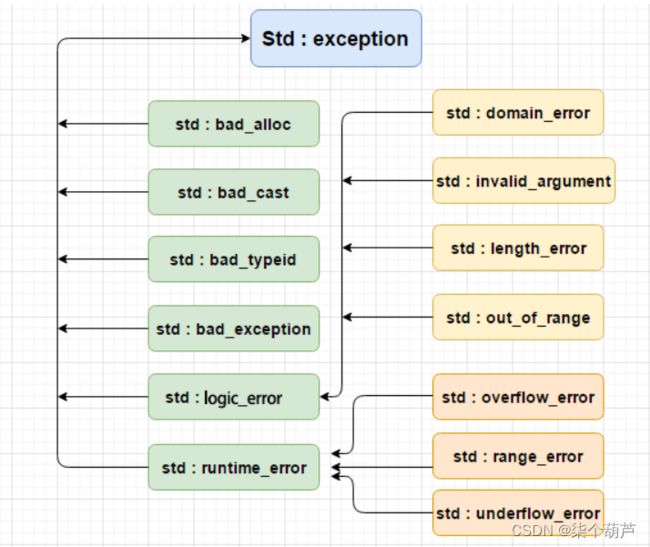

说明: 实际中我们可以可以去继承exception类实现自己的异常类。但是实际中很多公司像上面一样自己定义一套异常继承体系。因为C++标准库设计的不够好用。
int main()
{
try
{
vector<int> v(10, 5);
// 这里如果系统内存不够也会抛异常
v.reserve(1000000000);
// 这里越界会抛异常
v.at(10) = 100;
}
catch (const exception& e) // 这里捕获父类对象就可以
{
cout << e.what() << endl;
}
catch (...)
{
cout << "Unkown Exception" << endl;
}
return 0;
}
五、异常的优缺点
C++异常的优点:
- 异常对象定义好了,相比错误码的方式可以清晰准确的展示出错误的各种信息,甚至可以包含堆栈调用的信息,这样可以帮助更好的定位程序的bug。
- 返回错误码的传统方式有个很大的问题就是,在函数调用链中,深层的函数返回了错误,那么我们得层层返回错误,最外层才能拿到错误,具体看下面的详细解释。
// 1.下面这段伪代码我们可以看到ConnnectSql中出错了,先返回给ServerStart,
//ServerStart再返回给main函数,main函数再针对问题处理具体的错误。
// 2.如果是异常体系,不管是ConnnectSql还是ServerStart及调用函数出错,都不用检查,
//因为抛出的异常异常会直接跳到main函数中catch捕获的地方,main函数直接处理错误。
int ConnnectSql()
{
// 用户名密码错误
if (...)
return 1;
// 权限不足
if (...)
return 2;
}
int ServerStart() {
if (int ret = ConnnectSql() < 0)
return ret;
int fd = socket()
if(fd < 0)
return errno;
}
int main()
{
if (ServerStart() < 0)
...
return 0;
}
- 很多的第三方库都包含异常,比如boost、gtest、gmock等等常用的库,那么我们使用它们也需要使用异常。
- 部分函数使用异常更好处理,比如构造函数没有返回值,不方便使用错误码方式处理。比如T& operator这样的函数,如果pos越界了只能使用异常或者终止程序处理,没办法通过返回值表示错误。
C++异常的缺点:
- 异常会导致程序的执行流乱跳,并且非常的混乱,并且是运行时出错抛异常就会乱跳。这会导致我们跟踪调试时以及分析程序时,比较困难。
- 异常会有一些性能的开销。当然在现代硬件速度很快的情况下,这个影响基本忽略不计。
- C++没有垃圾回收机制,资源需要自己管理。有了异常非常容易导致内存泄漏、死锁等异常安全问题。这个需要使用RAII来处理资源的管理问题。学习成本较高。
- C++标准库的异常体系定义得不好,导致大家各自定义各自的异常体系,非常的混乱。
- 异常尽量规范使用,否则后果不堪设想,随意抛异常,外层捕获的用户苦不堪言。所以异常规范有两点:一、抛出异常类型都继承自一个基类。二、函数是否抛异常、抛什么异常,都使用 func() throw();的方式规范化。
总结: 异常总体而言,利大于弊,所以工程中我们还是鼓励使用异常的。另外OO的语言基本都是用异常处理错误,这也可以看出这是大势所趋。