64.C++运算符重载
目录
1.可重载\不可重载运算符
2.重载运算符:+
3.重载运算符:++
4.重载运算符:- -
5.重载运算符:<<
6.重载运算符:=
运算符重载是一种C++的特性,它允许重新定义或扩展已存在的运算符,以使其适用于用户自定义的数据类型。运算符重载使得您可以创建更直观、自然的操作符行为,从而增强代码的可读性和易用性。
1.可重载\不可重载运算符
2.重载运算符:+
class Point {
public:
// 定义属性
int x;
int y;
// 定义构造函数,⽤来初始化属性
Point() : x(0), y(0) {}
Point(int x, int y) : x(x), y(y) {}
// 在类内实现的运算符重载
Point operator+(const Point& p) const {
return { x + p.x, y + p.y };
}
};
// 全局函数实现运算符重载
Point operator-(const Point& p1, const Point& p2) {
return { p1.x - p2.x, p1.y - p2.y };
}
int main() {
Point p1(10, 20);
Point p2(15, 25);
Point res = p1 + p2;
cout << "res.x = " << res.x << ", res.y = " << res.y << endl;//输出 res.x=25,res.y=45
Point res2 = p1 - p2;
cout << "res2.x = " << res2.x << ", res2.y = " << res2.y << endl;//输出 res.x=-5,res.y=-5
return 0;
}3.重载运算符:++
class Point {
public:
// 定义属性
int x;
int y;
// 定义构造函数,⽤来初始化属性
Point() : x(0), y(0) {}
Point(int x, int y) : x(x), y(y) {}
// 运算符前置,先运算、后取值
Point operator++() {
x++;
y++;
return *this;
}
// 在类内实现的运算符重载,运算符后置
Point operator++(int) {
// 先创建⼀个对象,记录原来的值
Point tmp = *this;
// 属性⾃增
x++;
y++;
// 返回之前记录的值
return tmp;
}
};
int main() {
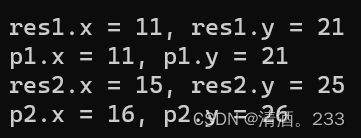
Point p1(10, 20);
Point p2(15, 25);
Point res1 = ++p1;
cout << "res1.x = " << res1.x << ", res1.y = " << res1.y << endl;
cout << "p1.x = " << p1.x << ", p1.y = " << p1.y << endl;
Point res2 = p2++;
cout << "res2.x = " << res2.x << ", res2.y = " << res2.y << endl;
cout << "p2.x = " << p2.x << ", p2.y = " << p2.y << endl;
return 0;
}4.重载运算符:- -
class Point {
public:
// 定义属性
int x;
int y;
// 定义构造函数,⽤来初始化属性
Point() : x(0), y(0) {}
Point(int x, int y) : x(x), y(y) {}
};
//类外实现 运算符前置 先运算再赋值
Point operator--(Point& point) {
point.x--;
point.y--;
return point;
}
//类外实现 运算符后置 先赋值再运算
Point operator--(Point& point, int) {
Point tmp = point;
point.x--;
point.y--;
return tmp;
}
int main() {
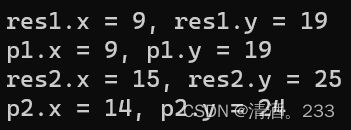
Point p1(10, 20);
Point p2(15, 25);
Point res1 = --p1;
cout << "res1.x = " << res1.x << ", res1.y = " << res1.y << endl;
cout << "p1.x = " << p1.x << ", p1.y = " << p1.y << endl;
Point res2 = p2--;
cout << "res2.x = " << res2.x << ", res2.y = " << res2.y << endl;
cout << "p2.x = " << p2.x << ", p2.y = " << p2.y << endl;
return 0;
}5.重载运算符:<<
class Point {
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, const Point& p);
public:
// 定义属性
int x;
int y;
// 定义构造函数,⽤来初始化属性
Point() : x(0), y(0), privateField(0) {}
Point(int x, int y) : x(x), y(y), privateField(0) {}
private:
int privateField;
};
// 在类外定义运算符重载,全局函数
// 我希望在这⾥能够将Point类中的私有属性也拼接起来,因此需要做成友元
ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, const Point& p) {
os << "x = " << p.x << ", y = " << p.y << ", privateField = " << p.privateField;
return os;
}
int main() {
Point p1(10, 20);
cout << "p1: " << p1 << endl;
return 0;
}6.重载运算符:=
class Person {
public:
int age;
int score;
int* p;
Person() : age(0), score(0), p(nullptr) {}
Person(const Person& person) {
cout << "拷贝构造函数执行了" << endl;
age = person.age;
score = person.score;
p = new int(*person.p);
}
// 重载赋值运算符
Person& operator=(const Person& person) {
cout << "重载赋值运算符执行了" << endl;
age = person.age;
score = person.score;
p = new int(*person.p);
return *this;
}
~Person() {
cout << "析构函数执行了" << endl;
if (p == nullptr) {
delete p;
p = nullptr;
}
}
};
int main() {
// 创建⼀个对象
Person p1;
p1.age = 18;
p1.score = 99;
p1.p = new int(100);
// 在这⾥,虽然是等号运算符,但是p2对象还没有完成空间开辟、实例化,那么在这⾥会调⽤拷⻉构造函数,⽽⾮重载的等号运算符
Person p2 = p1;
// 修改p2的属性值
p2.age = 20;
p2.score = 100;
p2.p = new int(200);
// 这⾥的p1已经开辟空间了,这⾥就会触发?载的等号运算符
p1 = p2;
cout << p1.age << ", " << p1.score << ", " << p1.p << " =>" << *p1.p << endl;
cout << p2.age << ", " << p2.score << ", " << p2.p << " =>" << *p2.p << endl;
return 0;
}