SSM - Springboot - MyBatis-Plus 全栈体系(四)
第二章 SpringFramework
四、SpringIoC 实践和应用
1. SpringIoC / DI 实现步骤
1.1 配置元数据(配置)
- 配置元数据,既是编写交给SpringIoC容器管理组件的信息,配置方式有三种。
- 基于 XML 的配置元数据的基本结构:
<bean id="..." [1] class="..." [2]>
<!-- collaborators and configuration for this bean go here -->
</bean>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="..." [1] class="..." [2]>
bean>
<bean id="..." class="...">
bean>
beans>
-
Spring IoC 容器管理一个或多个组件。这些 组件是使用你提供给容器的配置元数据(例如,以 XML
-
标签 == 组件信息声明 id属性是标识单个 Bean 定义的字符串。class属性定义 Bean 的类型并使用完全限定的类名。
1.2 实例化IoC容器
- 提供给
ApplicationContext构造函数的位置路径是资源字符串地址,允许容器从各种外部资源(如本地文件系统、JavaCLASSPATH等)加载配置元数据。 - 我们应该选择一个合适的容器实现类,进行IoC容器的实例化工作:
//实例化ioc容器,读取外部配置文件,最终会在容器内进行ioc和di动作
ApplicationContext context =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("services.xml", "daos.xml");
1.3 获取Bean(组件)
- ApplicationContext 是一个高级工厂的接口,能够维护不同 bean 及其依赖项的注册表。通过使用方法 T getBean(String name, Class
requiredType) ,您可以检索 bean 的实例。 - 允许读取 Bean 定义并访问它们,如以下示例所示:
//创建ioc容器对象,指定配置文件,ioc也开始实例组件对象
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("services.xml", "daos.xml");
//获取ioc容器的组件对象
PetStoreService service = context.getBean("petStore", PetStoreService.class);
//使用组件对象
List<String> userList = service.getUsernameList();
2. 基于 XML 配置方式组件管理
2.1 实验一:组件(Bean)信息声明配置(IoC)
2.1.1 目标
- Spring IoC 容器管理一个或多个 bean。这些 Bean 是使用您提供给容器的配置元数据创建的(例如,以 XML
- 如何通过定义XML配置文件,声明组件类信息,交给 Spring 的 IoC 容器进行组件管理?
2.1.2 思路
2.1.3 准备项目
2.1.3.1 创建maven工程(spring-ioc-xml-01)
2.1.3.2 导入SpringIoC相关依赖
- pom.xml
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-contextartifactId>
<version>6.0.6version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.jupitergroupId>
<artifactId>junit-jupiter-apiartifactId>
<version>5.3.1version>
dependency>
dependencies>
2.1.4 基于无参数构造函数
- 当通过构造函数方法创建一个 bean(组件对象) 时,所有普通类都可以由 Spring 使用并与之兼容。也就是说,正在开发的类不需要实现任何特定的接口或以特定的方式进行编码。只需指定 Bean 类信息就足够了。但是,默认情况下,我们需要一个默认(空)构造函数。
2.1.4.1 准备组件类
package com.alex.ioc;
public class HappyComponent {
//默认包含无参数构造函数
public void doWork() {
System.out.println("HappyComponent.doWork");
}
}
2.1.4.2 xml配置文件编写
<!-- 实验一 [重要]创建bean -->
<bean id="happyComponent" class="com.alex.ioc.HappyComponent"/>
- bean标签:通过配置bean标签告诉IOC容器需要创建对象的组件信息
- id属性:bean的唯一标识,方便后期获取Bean!
- class属性:组件类的全限定符!
- 注意:要求当前组件类必须包含无参数构造函数!
2.1.5 基于静态工厂方法实例化
- 除了使用构造函数实例化对象,还有一类是通过工厂模式实例化对象。如何定义使用静态工厂方法创建Bean的配置?
2.1.5.1 准备组件类
public class ClientService {
private static ClientService clientService = new ClientService();
private ClientService() {}
public static ClientService createInstance() {
return clientService;
}
}
2.1.5.2 xml配置文件编写
- 文件:resources/spring-bean-01.xml
<bean id="clientService"
class="examples.ClientService"
factory-method="createInstance"/>
- class属性:指定工厂类的全限定符!
- factory-method: 指定静态工厂方法,注意,该方法必须是static方法。
2.1.6 基于实例工厂方法实例化
2.1.6.1 准备组建类
public class DefaultServiceLocator {
private static ClientServiceImplclientService = new ClientServiceImpl();
public ClientService createClientServiceInstance() {
return clientService;
}
}
2.1.6.2 xml配置文件编写
- 文件:resources/spring-bean-01.xml
<bean id="serviceLocator" class="examples.DefaultServiceLocator">
bean>
<bean id="clientService"
factory-bean="serviceLocator"
factory-method="createClientServiceInstance"/>
- factory-bean属性:指定当前容器中工厂Bean 的名称。
- factory-method: 指定实例工厂方法名。注意,实例方法必须是非static的!
2.1.7 图解IoC配置流程
2.2 实验二:组件(Bean)依赖注入配置(DI)
2.2.1 目标
- 通过配置文件,实现IoC容器中Bean之间的引用(依赖注入DI配置)。
- 主要涉及注入场景:基于构造函数的依赖注入和基于 Setter 的依赖注入。
2.2.2 思路
2.2.3 基于构造函数的依赖注入(单个构造参数)
2.2.3.1 介绍
- 基于构造函数的 DI 是通过容器调用具有多个参数的构造函数来完成的,每个参数表示一个依赖项。
- 下面的示例演示一个只能通过构造函数注入进行依赖项注入的类!
2.2.3.2 准备组件类
public class UserDao {
}
public class UserService {
private UserDao userDao;
public UserService(UserDao userDao) {
this.userDao = userDao;
}
}
2.2.3.3 编写配置文件
- 文件:resources/spring-02.xml
<beans>
<bean id="userService" class="x.y.UserService">
<constructor-arg ref="userDao"/>
bean>
<bean id="userDao" class="x.y.UserDao"/>
beans>
- constructor-arg标签:可以引用构造参数 ref 引用其他bean的标识。
2.2.4 基于构造函数的依赖注入(多构造参数解析)
2.2.4.1 介绍
- 基于构造函数的 DI 是通过容器调用具有多个参数的构造函数来完成的,每个参数表示一个依赖项。
- 下面的示例演示通过构造函数注入多个参数,参数包含其他bean和基本数据类型!
2.2.4.2 准备组件类
public class UserDao {
}
public class UserService {
private UserDao userDao;
private int age;
private String name;
public UserService(int age , String name ,UserDao userDao) {
this.userDao = userDao;
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
}
}
2.2.4.3 编写配置文件
<beans>
<bean id="userService" class="x.y.UserService">
<constructor-arg value="18"/>
<constructor-arg value="赵伟风"/>
<constructor-arg ref="userDao"/>
bean>
<bean id="userDao" class="x.y.UserDao"/>
beans>
<beans>
<bean id="userService" class="x.y.UserService">
<constructor-arg name="name" value="赵伟风"/>
<constructor-arg name="userDao" ref="userDao"/>
<constructor-arg name="age" value="18"/>
bean>
<bean id="userDao" class="x.y.UserDao"/>
beans>
<beans>
<bean id="userService" class="x.y.UserService">
<constructor-arg index="1" value="赵伟风"/>
<constructor-arg index="2" ref="userDao"/>
<constructor-arg index="0" value="18"/>
bean>
<bean id="userDao" class="x.y.UserDao"/>
beans>
- constructor-arg标签:指定构造参数和对应的值
- constructor-arg标签:name属性指定参数名、index属性指定参数角标、value属性指定普通属性值
2.2.5 基于Setter方法依赖注入
2.2.5.1 介绍
- 开发中,除了构造函数注入(DI)更多的使用的Setter方法进行注入!
- 下面的示例演示一个只能使用纯 setter 注入进行依赖项注入的类。
2.2.5.2 准备组件类
public Class MovieFinder{
}
public class SimpleMovieLister {
private MovieFinder movieFinder;
private String movieName;
public void setMovieFinder(MovieFinder movieFinder) {
this.movieFinder = movieFinder;
}
public void setMovieName(String movieName){
this.movieName = movieName;
}
// business logic that actually uses the injected MovieFinder is omitted...
}
2.2.5.3 编写配置文件
<bean id="simpleMovieLister" class="examples.SimpleMovieLister">
<property name="movieFinder" ref="movieFinder" />
<property name="movieName" value="消失的她"/>
bean>
<bean id="movieFinder" class="examples.MovieFinder"/>
- property标签:可以给setter方法对应的属性赋值
- property标签:name属性代表set方法标识、ref代表引用bean的标识id、value属性代表基本属性值
总结:
-
依赖注入(DI)包含引用类型和基本数据类型,同时注入的方式也有多种!主流的注入方式为setter方法注入和构造函数注入!
-
需要特别注意:引用其他bean,使用ref属性。直接注入基本类型值,使用value属性。
2.3 实验三:IoC 容器创建和使用
2.3.1 介绍
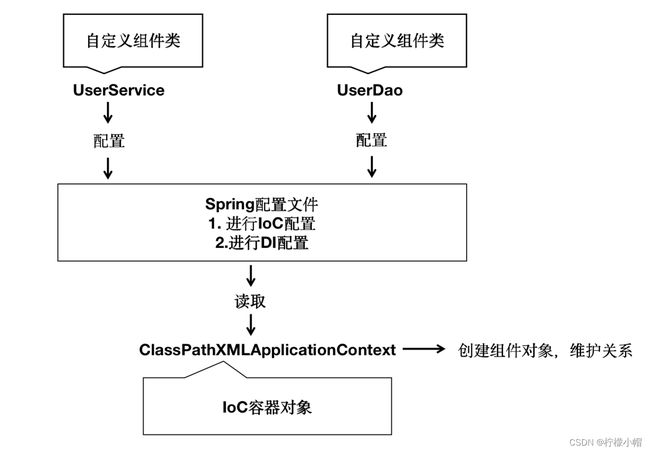
- 上面的实验只是讲解了如何在XML格式的配置文件编写IoC和DI配置!
- 如图:

- 想要配置文件中声明组件类信息真正的进行实例化成Bean对象和形成Bean之间的引用关系,我们需要声明IoC容器对象,读取配置文件,实例化组件和关系维护的过程都是在IoC容器中实现的!
2.3.2 容器实例化
//方式1:实例化并且指定配置文件
//参数:String...locations 传入一个或者多个配置文件
ApplicationContext context =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("services.xml", "daos.xml");
//方式2:先实例化,再指定配置文件,最后刷新容器触发Bean实例化动作 [springmvc源码和contextLoadListener源码方式]
ApplicationContext context =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext();
//设置配置配置文件,方法参数为可变参数,可以设置一个或者多个配置
context.setConfigLocations("services.xml", "daos.xml");
//后配置的文件,需要调用refresh方法,触发刷新配置
context.refresh();
2.3.3 Bean对象读取
//方式1: 根据id获取
//没有指定类型,返回为Object,需要类型转化!
HappyComponent happyComponent =
(HappyComponent) iocContainer.getBean("bean的id标识");
//使用组件对象
happyComponent.doWork();
//方式2: 根据类型获取
//根据类型获取,但是要求,同类型(当前类,或者之类,或者接口的实现类)只能有一个对象交给IoC容器管理
//配置两个或者以上出现: org.springframework.beans.factory.NoUniqueBeanDefinitionException 问题
HappyComponent happyComponent = iocContainer.getBean(HappyComponent.class);
happyComponent.doWork();
//方式3: 根据id和类型获取
HappyComponent happyComponent = iocContainer.getBean("bean的id标识", HappyComponent.class);
happyComponent.doWork();
// 根据类型来获取bean时,在满足bean唯一性的前提下,其实只是看:『对象 instanceof 指定的类型』的返回结果,
// 只要返回的是true就可以认定为和类型匹配,能够获取到。
2.4 实验四:高级特性:组件(bean)作用域和周期方法配置
2.4.1 组件周期方法配置
2.4.1.1 周期方法概念
- 我们可以在组件类中定义方法,然后当IoC容器实例化和销毁组件对象的时候进行调用!这两个方法我们成为生命周期方法!
- 类似于Servlet的init/destroy方法,我们可以在周期方法完成初始化和释放资源等工作。
2.4.1.2 周期方法声明
public class BeanOne {
//周期方法要求: 方法命名随意,但是要求方法必须是 public void 无形参列表
public void init() {
// 初始化逻辑
}
}
public class BeanTwo {
public void cleanup() {
// 释放资源逻辑
}
}
2.4.1.3 周期方法配置
<beans>
<bean id="beanOne" class="examples.BeanOne" init-method="init" />
<bean id="beanTwo" class="examples.BeanTwo" destroy-method="cleanup" />
beans>
2.4.2 组件作用域配置
2.4.2.1 Bean作用域概念
- 在IoC容器中,这些
BeanDefinition对象,BeanDefinition对象内,包含定义的信息(id,class,属性等等)! - 这意味着,
BeanDefinition与类概念一样,SpringIoC容器可以根据BeanDefinition对象反射创建多个Bean对象实例。 - 具体创建多少个Bean的实例对象,由Bean的作用域Scope属性指定!
2.4.2.2 作用域可选值
| 取值 | 含义 | 创建对象的时机 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| singleton | 在 IOC 容器中,这个 bean 的对象始终为单实例 | IOC 容器初始化时 | 是 |
| prototype | 这个 bean 在 IOC 容器中有多个实例 | 获取 bean 时 | 否 |
- 如果是在WebApplicationContext环境下还会有另外两个作用域(但不常用):
| 取值 | 含义 | 创建对象的时机 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| request | 请求范围内有效的实例 | 每次请求 | 否 |
| session | 会话范围内有效的实例 | 每次会话 | 否 |
2.4.2.3 作用域配置
- 作用域配置
<bean id="happyMachine8" scope="prototype" class="com.alex.ioc.HappyMachine">
<property name="machineName" value="happyMachine"/>
bean>
<bean id="happyComponent8" scope="singleton" class="com.alex.ioc.HappyComponent">
<property name="componentName" value="happyComponent"/>
bean>
2.4.2.4 作用域测试
@Test
public void testExperiment08() {
ApplicationContext iocContainer = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("配置文件名");
HappyMachine bean = iocContainer.getBean(HappyMachine.class);
HappyMachine bean1 = iocContainer.getBean(HappyMachine.class);
//多例对比 false
System.out.println(bean == bean1);
HappyComponent bean2 = iocContainer.getBean(HappyComponent.class);
HappyComponent bean3 = iocContainer.getBean(HappyComponent.class);
//单例对比 true
System.out.println(bean2 == bean3);
}