SpringBoot -> 自动装配初探,debug=ture判断配置类是否生效
文章目录
-
- 第一个注解:@SpringBootApplication
- 点进去有一堆注解:
- 1.这4个是元注解:
- 2.@SpringBootConfiguration @EnableAutoConfiguration @ComponentScan
- 3.@AutoConfigurationPackage @Import:
- 4.我们先进input的类里面看看
- 5.getCandidateConfigurations:翻译:获取候选配置
- 6.我们把方法拿下来这照着看
- 7.开始参数:第一个getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass():翻译 获取Spring Factory Loader Factory类
- 8.getBeanClassLoader():获取Bean类加载器 简洁,大气,一个加载器(我不懂,我猜他是自带的,应该也不需要我懂吧)
- 9.spring.factories:头皮发麻 好多东西
- 10.好了回到老地方
- 11.input走完了:总结就是获取到了"META-INF/spring.factories"配置文件中的所有自动配置类
- 12.回顾一下思路
- 13.差不多就springboot的流程了 ---自动配置
- 14.@AutoConfigurationPackage:现在看看这个
- 15.呦西,这里是扫描我们的jar包的地方吧
- 16.总结:
第一个注解:@SpringBootApplication
1.表示这是一个springboot的应用
2.指示一个配置类,该类声明一个或多个@Bean方法并触发自动配置和组件扫描。
这个类会触发自动配置和组件扫描。
3.这是一个方便的注释,相当于声明@Configuration、@EnableAutoConfiguration和@ComponentScan。
这是一个组合注解,就是@Configuration、@EnableAutoConfiguration和@ComponentScan的合并
@SpringBootApplication
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
}
}
点进去有一堆注解:
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan(excludeFilters = { @Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = TypeExcludeFilter.class),
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class) })
public @interface SpringBootApplication {
1.这4个是元注解:
@Target(ElementType.TYPE) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Inherited
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)表示这个自定义的注解(@interface SpringBootApplication)可以用在什么地方;
TYPE就是接口,类等上面,就不要用在属性上了
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME):就是会不会被编译器编译,比如@test是不会编译的
@Documented:就是可以做成doc文档
@Inherited:就是这个自定义的注解可以继承,父类用了这个注解,子类也生效
2.@SpringBootConfiguration @EnableAutoConfiguration @ComponentScan
@ComponentScan:这个就不说了,就是这个扫描包嘛,Filter过滤了一些包,其他的都可以注册到bean中
@SpringBootConfiguration :点进来就是这样,除了元注解就是一个@Configuration
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Configuration
public @interface SpringBootConfiguration {
@Configuration:这里面就是一个@Component,一个普通的注册到bean的类
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Component
public @interface Configuration {
@EnableAutoConfiguration:重点就是这个了,其他的都看完了,只剩这个了,点进去
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@AutoConfigurationPackage
@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)
public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration {
3.@AutoConfigurationPackage @Import:
@Import:
导入什么东西,在配置xml的时候也有,就是把什么东西连接到这里的意思嘛
这里肯定就是把AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class这个类都加载,
差不多就是给这个**@EnableAutoConfiguration**搞了个子类的意思
EnableAutoConfiguration有个子类是AutoConfigurationImportSelector
4.我们先进input的类里面看看
public class AutoConfigurationImportSelector implements DeferredImportSelector, BeanClassLoaderAware,
ResourceLoaderAware, BeanFactoryAware, EnvironmentAware, Ordered {
就是一个类AutoConfigurationImportSelector翻译英文就是自动配置导入选择器
名字的意思就是选择器,要导入哪个类型的自动配置类,应该有个相应的选择器去帮我们判断到底是哪个配置类
意思就是,我们maven导包了,他查看我们导的包,去加载对应的配置类嘛
看看到底是哪个方法搞的
protected List<String> getCandidateConfigurations(AnnotationMetadata metadata, AnnotationAttributes attributes) {
List<String> configurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(),
getBeanClassLoader());
Assert.notEmpty(configurations, "No auto configuration classes found in META-INF/spring.factories. If you "
+ "are using a custom packaging, make sure that file is correct.");
return configurations;
}
5.getCandidateConfigurations:翻译:获取候选配置
这不就是获取到底是那个配置类嘛
**理一下前面的思路先:**我们进了@SpringBootApplication注解看了他的注解只有一个有用
其他的元注解,扫描包什么都没什么大用,我们现在的位置就是@EnableAutoConfiguration 自动配置注解这里面
有@AutoConfigurationPackage @Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class) 我们在input类这里,还有个注解等会看
回到上面:getCandidateConfigurations方法
他的返回值是一个list,是configurations,看名字就是很多个配置类的意思好像
他用了SpringFactoriesLoader类里的方法loadFactoryNames:翻译加载工厂名称
听不懂哈,好像是要获得一些名字吧,我们去读一下这个方法的文档注释(就是点进去看看注释哈)
从“META-INF”加载给定类型的工厂实现的完全限定类名/春季工厂,使用给定的类装入器。
从springframework5.3开始,如果一个特定的实现类名对于给定的工厂类型被发现不止一次,那么重复的类名将被忽略。
参数:
表示工厂的接口或抽象类 类
加载器-用于加载资源的类加载器;可以为null以使用默认值
6.我们把方法拿下来这照着看
List<String> configurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(),
getBeanClassLoader());
读注释:
他会从“META-INF”什么东西里加载一个完全限定类名/春季工厂
大概就是从这“META-INF”找这些类吧(我连“META-INF”是啥都不知道)
然后用什么给定的类装入器,也听不懂哈,慢慢搞哈
5.3开始后,如果类重复了就忽略,就是不能重复加载类,我读懂了
7.开始参数:第一个getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass():翻译 获取Spring Factory Loader Factory类
哦,就是用这个方法去获取“META-INF”里面的类,我又懂了
后面的参数getBeanClassLoader等会再看,我们先进这里面看看;
protected Class<?> getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass() {
return EnableAutoConfiguration.class;
}
古德:非常简单,就是返回了一个EnableAutoConfiguration的class
哟咋这么眼熟;EnableAutoConfiguration
我们先进@SpringBootApplication,然后马上就来了个@EnableAutoConfiguration注解,我们点进去这里面才到input的
然后我们在input类里面点了方法,现在获取什么完全限定类名又绕回来了
现在他又给我返回来了咋回事,我思考下
我们是在input里面的,input相当于EnableAutoConfiguration的子类,也就是我们在子类中调用了父类,没毛病
我还发现了个秘密,你看没想到
protected List<String> getCandidateConfigurations(AnnotationMetadata metadata, AnnotationAttributes attributes) {
List<String> configurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(),
getBeanClassLoader());
Assert.notEmpty(configurations, "No auto configuration classes found in META-INF/spring.factories. If you "
+ "are using a custom packaging, make sure that file is correct.");
return configurations;
}
protected Class<?> getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass() {
return EnableAutoConfiguration.class;
}
getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass()方法就这这个获取候选配置方法的下面
接着前面我们讲了第一个参数,现在第二个
8.getBeanClassLoader():获取Bean类加载器 简洁,大气,一个加载器(我不懂,我猜他是自带的,应该也不需要我懂吧)
纳,现在好像什么都没得到;两个参数,一个返回了EnableAutoConfiguration,一个没啥用
我们进方法里看一下,到底是怎么获取到配置类,一堆配置类
private static Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(ClassLoader classLoader) {
// 搞了个map,不用懂太多,知道有个map就行
Map<String, List<String>> result = cache.get(classLoader);
//如果为空:就返回,猜猜意思
//大概就是,从这里就已经读到了上面“META-INF”里的配置类,如果什么都没读到,就返回空,正常
//现在还不知道“META-INF”里的东西是什么呢
if (result != null) {
return result;
}
//又new了一个map,这个就很明显了,重新高了一个空的,证明了上面确实应该读到了一些东西
result = new HashMap<>();
try {
//classLoader这个又来了,一个加载器,获取资源getResources,FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION一个常量
//点进常量看看,代码再下面;"META-INF/spring.factories"
//噢,"META-INF这个终于出现了,
//getResources就是获取META-INF/spring.factories,spring.properties里的东西
//我们也找找这个东西在那里,想进去看看,但是我发现,,我好像不知道它在哪里?尴尬...\
//想办法找,他没写绝对路径,肯定有个默认的路径,我们要找到那个默认的路径再找META-INF/spring.factories
//我猜默认的路径应该就是这个常量所在的类的包里面,因为配置文件properties肯定在包里了,反正正常的地方肯定没有的
//我点进去看了看,有META-INF文件夹,没有spring.factories文件,稳了,肯定在其中一个包里,要不要一个一个找一下
//不,我觉得肯定有准确的位置的,我想想,既然常量所在的类没有,我在这个方法里又调用了这个常量
//会不会在我这个方法所在的包中,我滑到最上面,找到package org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure;
//点进去,古德,我看见了META-INF/spring.factories,截图在下面,点进去spring.factories看看,截图也附加再下面
//现在就懂了,它把那个文件里那么多类似key=value的东西搞出来放在了这里Enumeration
Enumeration<URL> urls = classLoader.getResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION);
//hasMoreElements:翻译有更多元素 如果有更多,就继续循环
while (urls.hasMoreElements()) {
//下一个,这里就是把刚刚properties中的东西,一个一个的赋值
URL url = urls.nextElement();
//new一个UrlResource:把取出来的放进去
UrlResource resource = new UrlResource(url);
//又套娃,把在放进去的东西又放到一个Properties 中
//与前面不一样,前面应该每次循环都会创建new一个UrlResource,而这里只是放进去,应该可以放很多个
//配合他的名字properties,应该也是类似一个properties的文件,key-value
Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
//entrySet遍历,把东西分出来,用一个一个的set接收
for (Map.Entry<?, ?> entry : properties.entrySet()) {
//getKey,分出来key;trim修剪,刚刚spring.properties中有\,这些东西,感觉是去掉这些东西的
//修剪好了赋值string
String factoryTypeName = ((String) entry.getKey()).trim();
//getValue,这里是要把value也分出来
String[] factoryImplementationNames =
StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray((String) entry.getValue());
//又是一个遍历,变量分出来的value,刚刚在spring.properties中看到,一个key好像后面有很多value(xx=\,xx\,xx)
for (String factoryImplementationName : factoryImplementationNames) {
//result是上面的map,lambda,把factoryTypeName就是key存进去,用arraylist接收
//然后又add把factoryImplementationName就是value修剪一下也存进map中
//反正最后应该是把得到的所有配置类都放到了map中
result.computeIfAbsent(factoryTypeName, key -> new ArrayList<>())
.add(factoryImplementationName.trim());
}
}
}
//后面做了什么计算,就不懂了,就不看了,反正知道他把所有配置类都放到了map中返回了
// Replace all lists with unmodifiable lists containing unique elements
result.replaceAll((factoryType, implementations) -> implementations.stream().distinct()
.collect(Collectors.collectingAndThen(Collectors.toList(), Collections::unmodifiableList)));
cache.put(classLoader, result);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load factories from location [" +
FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION + "]", ex);
}
return result;
}
上面代码中的常量:
public static final String FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION = "META-INF/spring.factories";
找到了"META-INF/spring.factories"
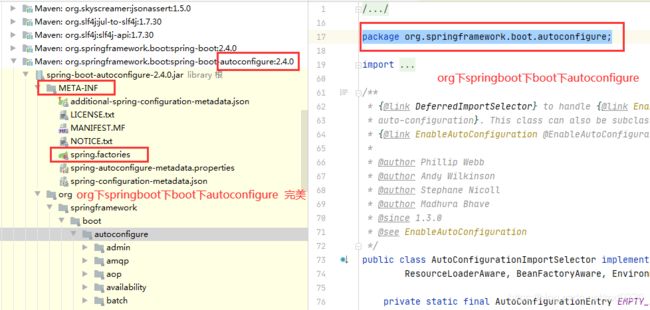
9.spring.factories:头皮发麻 好多东西
protected List<String> getCandidateConfigurations(AnnotationMetadata metadata, AnnotationAttributes attributes) {
List<String> configurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(),
getBeanClassLoader());
Assert.notEmpty(configurations, "No auto configuration classes found in META-INF/spring.factories. If you "
+ "are using a custom packaging, make sure that file is correct.");
return configurations;
}
loadFactoryNames:最后返回了一个map,咦它这里不是List configurations,list嘛
别搞我啊
噢噢噢,太绕了
List<String> configurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(),
getBeanClassLoader());
方法里面是:
```java
public static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryType, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
ClassLoader classLoaderToUse = classLoader;
if (classLoaderToUse == null) {
classLoaderToUse = SpringFactoriesLoader.class.getClassLoader();
}
String factoryTypeName = factoryType.getName();
return loadSpringFactories(classLoaderToUse).getOrDefault(factoryTypeName, Collections.emptyList());
}
return loadSpringFactories(classLoaderToUse):loadSpringFactories才是map,在loadFactoryNames后变成了list
private static Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(ClassLoader classLoader) {
Map<String, List<String>> result = cache.get(classLoader);
if (result != null) {
return result;
}
result = new HashMap<>();
try {
10.好了回到老地方
@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)
public class AutoConfigurationImportSelector implements DeferredImportSelector, BeanClassLoaderAware,
ResourceLoaderAware, BeanFactoryAware, EnvironmentAware, Ordered {
protected List<String> getCandidateConfigurations(AnnotationMetadata metadata, AnnotationAttributes attributes) {
List<String> configurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(),
getBeanClassLoader());
Assert.notEmpty(configurations, "No auto configuration classes found in META-INF/spring.factories. If you "
+ "are using a custom packaging, make sure that file is correct.");
return configurations;
}
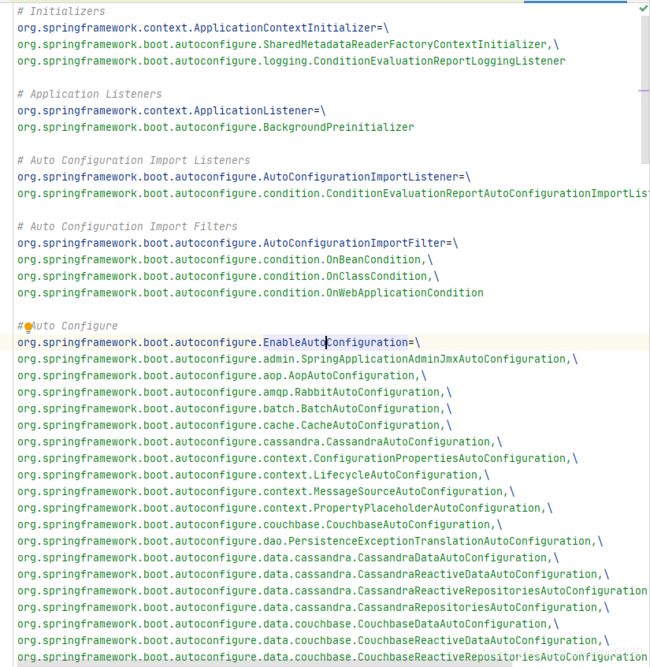
11.input走完了:总结就是获取到了"META-INF/spring.factories"配置文件中的所有自动配置类
...
# Auto Configuration Import Filters
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfigurationImportFilter=\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.OnBeanCondition,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.OnClassCondition,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.OnWebApplicationCondition
# Auto Configure
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.admin.SpringApplicationAdminJmxAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.aop.AopAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.amqp.RabbitAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.batch.BatchAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.CacheAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cassandra.CassandraAutoConfiguration,\
...
12.回顾一下思路
@SpringBootApplication
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
}
}
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan(excludeFilters = { @Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = TypeExcludeFilter.class),
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class) })
public @interface SpringBootApplication {
@AutoConfigurationPackage
@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)
public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration {
好:**@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)**走完了
其实也差不多了,springboot就是在input这里把我们所有的自动配置类都写好并且帮我们找到了
13.差不多就springboot的流程了 —自动配置
有始有终:
14.@AutoConfigurationPackage:现在看看这个
@Import(AutoConfigurationPackages.Registrar.class)
public @interface AutoConfigurationPackage {
AutoConfigurationPackages:自动配置包
Registrar:登记员
static class Registrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar, DeterminableImports {
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata metadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
register(registry, new PackageImports(metadata).getPackageNames().toArray(new String[0]));
}
@Override
public Set<Object> determineImports(AnnotationMetadata metadata) {
return Collections.singleton(new PackageImports(metadata));
}
}
自动配置包里面的一个静态内部类
看看注释:
importBeanDefinitionRegistrator存储导入配置中的基本包
15.呦西,这里是扫描我们的jar包的地方吧
16.总结:
@SpringBootApplication—>@EnableAutoConfiguration—>@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)
这一条路是找到自动配置类的
@SpringBootApplication—>@EnableAutoConfiguration—>
@AutoConfigurationPackage—>@Import(AutoConfigurationPackages.Registrar.class)
这一条路就扫描maven包的