Python实现Excel生成汇总直方图
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import geohash as geohash
import xlwt # 写入excel文件的库
import xlrd #读取Excel
import time
import datetime
import geohash #把经纬度转换为geohash
import random
start_time=datetime.datetime.now()
hang=0
lie=0
#以下为读取Excel
myWorkbook = xlrd.open_workbook('001.xls')
mySheets = myWorkbook.sheets()#获取工作表list。
table=myWorkbook.sheets()[0] #获取表的总行数
mySheets_rows=table.nrows
print(mySheets_rows)
#mySheets_rows为获取"sales"工作表中的总行数
mySheet = mySheets[0] # 通过索引顺序获取。
#table.cell(rowx, colx)
#以下为写入Excel
myWorkbook2 = xlwt.Workbook() #创建Excel工作表
mySheet2 = myWorkbook2.add_sheet('Test_Sheet') #添加Excel工作表,mySheet2为新建Excel
while hang<mySheets_rows: #只要没有最后一行
myRowValues = mySheet.row_values(hang) #lie是行数,从0开始计数,返回list对象。
geoGps = geohash.encode(float(myRowValues[4]), float(myRowValues[3]), precision=6) # 第4列和第5列为经纬度
# data = geohash.encode(116.255421,40.201209,precision=7),输出uzuxfzc
startTime = datetime.datetime.fromtimestamp(float(myRowValues[1]))
#把Unix时间戳转换为正常时间
endTime = datetime.datetime.fromtimestamp(float(myRowValues[2]))
for i in range(len(myRowValues)):
mySheet2.write(hang, lie, myRowValues[i])
lie+=1
mySheet2.write(hang, lie, geoGps) #最后一列插入geohash6
mySheet2.write(hang, lie+1, startTime) #最后一列插入startTime
mySheet2.write(hang, lie+2, startTime.weekday()) #最后一列插入startTime的星期几
mySheet2.write(hang, lie+3, endTime) #最后一列插入endTime
mySheet2.write(hang, lie+4, random.randint(1,7)) #最后一列插入endTime
mySheet2.write(hang, lie+5, round(random.uniform(0.01, 0.05),6)) #最后一列插入随机小数
i=0
lie=0
hang+=1
print('共改变'+str(hang)+'行')
myWorkbook2.save('test02.xls')
end_time = datetime.datetime.now()
speed = end_time - start_time
print('一共用时:'+str(speed))
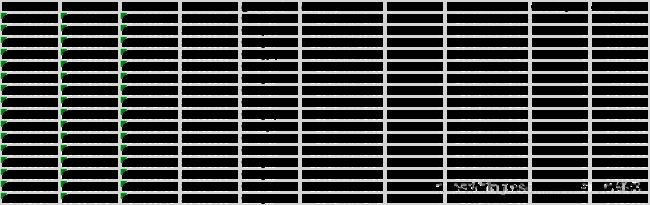
生成Excel如图 weekday和demand都是随机生成的数字
 |
|
|---|---|
# Import of all packages needed over this notebook
import json
import random # For sampling
import datetime as dt
from time import sleep
import pandas as pd
import seaborn as sns # Standard visualisations
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # For sub- and wider plots
from socket import timeout # Using timeout error for exceptions on geohash
import swifter # For easy parallelization of panda applys
import geohash # To decode Geohashes
from geopy.geocoders import Nominatim # To convert lat/long to addresses
from geopy.distance import distance # For distance between two coordinates
sns.set() # For prettier plots
geolocator = Nominatim(user_agent="hQ0PeXSNGppwoFjrtOUhJW95G5URrD8p")
df_train = pd.read_excel('test02.xls')
df_train.head(2)
# Plot aggregated demand per weekday and through the day
#绘制每个工作日和一天中的总需求
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(15,5))
#fig, ax = plt.subplots(1,3,figsize=(15,7)),这样就会有1行3个15x7大小的子图。
df_train.groupby(['weekday']).sum().demand.plot(kind='bar', ax=ax[0]) #第一个直方图
df_train.groupby(df_train['datetime'].dt.hour).sum().demand.plot(kind='bar', ax=ax[1])
#第2个直方图,画出每小时的需求量
plt.show()
#fig, ax = pyplot.subplots(figsize=(16,4))
#sns.barplot(data=df_sample, x='weekday', y='demand', ax=ax)
生成如下图

把两个结果合并groupby([df_train[‘weekday’],df_train[‘datetime’].dt.hour]
每周每小时进行group by
# Lastly, let's look at those two charts combined
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(20,5))
df_train.groupby([df_train['weekday'], df_train['datetime'].dt.hour]).sum().demand.plot(kind='bar', ax=ax)
plt.show()
当移动5小时时的需求图
# Demand plots when shifted by 5 hours#当移动5小时时的需求图
df_temp = df_train.copy()
df_temp['datetime'] = df_temp['datetime'] + dt.timedelta(hours=8)
#print( dt.timedelta(hours=8)) 结果8:00:00
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(15,5))
df_temp.groupby(['weekday']).sum().demand.plot(kind='bar', ax=ax[0])
df_temp.groupby(df_temp['datetime'].dt.hour).sum().demand.plot(kind='bar', ax=ax[1])
plt.show()
import pandas as pd
import seaborn as sns # Standard visualisations
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # For sub- and wider plots
from socket import timeout # Using timeout error for exceptions on geohash
import swifter # For easy parallelization of panda applys
import geohash # To decode Geohashes
from geopy.geocoders import Nominatim # To convert lat/long to addresses
from geopy.distance import distance # For distance between two coordinates
sns.set() # For prettier plots
geolocator = Nominatim(user_agent="hQ0PeXSNGppwoFjrtOUhJW95G5URrD8p")
df_train = pd.read_excel('test02.xls')
geo_cache = [{'geohash6': ghash, 'lat': geohash.decode(ghash)[0], 'lon': geohash.decode(ghash)[1]} for ghash in df_train.geohash6.unique()]
#读取Excel的geohash6这一列,转换为经纬度放到geo_cache
# print(geo_cache)结果:[{'geohash6': 'wm6n8t', 'lat': 30.70404052734375, 'lon': 104.0899658203125}, {'geohash6': 'wm6p03', 'lat': 30.76995849609375, 'lon': 104.0789794921875}
df_train = df_train.merge(pd.DataFrame(geo_cache), how='left', on='geohash6')
#合并
lat_dist = distance((df_train['lat'].max(), 0), (df_train['lat'].min(), 0))
lon_dist = distance((0, df_train['lon'].max()), (0, df_train['lon'].min()))
print(f"All geo-locations are within an area of {round(lat_dist.meters, 2)}m x {round(lon_dist.meters, 2)}m")
输出
All geo-locations are within an area of 24359.69m x 17121.89m
进程已结束,退出代码 0
绘制坐标散点图
import pandas as pd
import seaborn as sns # Standard visualisations
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # For sub- and wider plots
from socket import timeout # Using timeout error for exceptions on geohash
import swifter # For easy parallelization of panda applys
import geohash # To decode Geohashes
from geopy.geocoders import Nominatim # To convert lat/long to addresses
from geopy.distance import distance # For distance between two coordinates
sns.set() # For prettier plots
geolocator = Nominatim(user_agent="hQ0PeXSNGppwoFjrtOUhJW95G5URrD8p")
df_train = pd.read_excel('test02.xls')
geo_cache = [{'geohash6': ghash, 'lat': geohash.decode(ghash)[0], 'lon': geohash.decode(ghash)[1]} for ghash in df_train.geohash6.unique()]
#读取Excel的geohash6这一列,转换为经纬度放到geo_cache
# print(geo_cache)结果:[{'geohash6': 'wm6n8t', 'lat': 30.70404052734375, 'lon': 104.0899658203125}, {'geohash6': 'wm6p03', 'lat': 30.76995849609375, 'lon': 104.0789794921875}
df_train = df_train.merge(pd.DataFrame(geo_cache), how='left', on='geohash6')
#合并
def aggregate_demand(x):
x['demand'] = x['demand'].sum()
x['lat'] = x['lat'].min()
x['lon'] = x['lon'].min()
return x
# Plot general demand aggregated by location over the full time
df_temp = df_train.groupby(['geohash6']).apply(aggregate_demand).drop_duplicates(subset=['geohash6'])
#把Excel中的geohash6列应用aggregate_demand()函数,
# Pandas之drop_duplicates:去除重复项
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(7,7)) # Not true to scale
sns.scatterplot(x='lon', y='lat', size='demand', data=df_temp)
plt.show()
# scatterplot() 散点图
其中 查看df_temp变量,里面多出一个lat一个lon列,demand也是汇总过的



