Java基础之数组
1 定义
2 初始化
3 下标访问
4 常见操作
4.1 sort(排序操作)
4.2 binarySearch(二分查找)
4.3 equals(判断两个数组是否相等)
4.4 fill
4.5 copyOf(复制数组)
4.6 toString(相当于遍历,得到数组的字符串表示)
4.7 arraycopy
5 数组应用
5.1 实现数组的遍历
5.2 实现数组元素的交换
5.3 实现两个数组之间的交换
6 使用数组过程中常见的两个异常
6.1 下标越界异常(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException)
6.2 空指针异常(NullPointerException)
7 特殊事项
1 定义
数组是一组具有相同类型的元素的集合。
2 初始化
int[] a;
表示定义一个a,类型是存在int类型元素的数组,大小不确定。
int[] a = {1,2,3,4,5};
表示定义一个变量a,其类型是数组,该数组的元素类型是int,该数 组进行了初始化操作,数组大小确定为五个,元素分别是1,2,3,4,5.
int[] a =new int [] {1,2,3,4,5};
boolean[] a = {true,false};
String[] a = {"Hello ","World"};
String[] a = new String[] {"A","B"};
Random[] a = { new Random(),new Random(),new Random()};int[] a = new int[3];
定义一个数组,元素个数为三;该式等价于 int[] a = new int[] {0,0,0}
String[] a = new String[3];
该式等价于 String[] a = new String[] {null,null,null};
注意:int[] a; a = {1,2,3,4,5}; 这种用法是错误的,不能使用这个语法
int[] a; a = new int[] {1,2,3}; 而这种语法是正确的
注意:数组的长度一旦确定是无法更改的。
int[] a = new int[3]; //定义一个有三个元素的数组,让a引用指向该数组
a = new int[5]; //定义一个新的有五个元素的数组,让a引用指向新的数组
上面这种写法是可以的,本质上数组长度没有变,只是改变了a的引用指向。
int[] a = {1,2,3};
int[] b = new int[]{1,2,3,4};
b = new int[]{4,5};
int[] c = new int[5];
int[] c = new int[3]; //改变c的指向,并不意味着改变了数组的长度3 下标访问
- 数组下标的类型为int类型,其下标范围为[0,数组的长度)。
- 使用下标访问数组元素的具体代码:
a[下标] = 0; //将该位置的元素赋值为0;
b = a[下标]; //将该位置的元素赋值给另一个变量
4 常见操作
4.1 sort(排序操作)
4.1.1 Java实现
Arrays.sort(array);//实现对数组的全排操作
Arrays.sort(array,1,5);//将数组下标为一到4的元素进行排序,其余位置不变4.1.2 自实现
public static void MySort(long[] array,int fromIndex,int toIndex){
int size = toIndex - fromIndex;
for(int i = 0;i < size - 1;i++){
for(int j = fromIndex;j < toIndex - i - 1;j++){
if(array[j] > array[j + 1]){
swap(array,j,j+1);
}
}
// for(int j = 0;j < size - i - 1;j++){
// if(array[fromIndex + j] > array[fromIndex + j + 1]){
// swap(array,fromIndex + j,fromIndex + j + 1);
// }
// }
}
}
public static void swap(long[] array,int x,int y){
long t = array[x];
array[x] = array[y];
array[y] = t;
}
public static void Sort(long[] array){
//使用冒泡排序法
//外层循环代表一次冒泡
for(int i = 0;i < array.length - 1;i++){
//内层循环代表一次完整的冒泡过程
//array.length - 1 次冒泡过程
//无序区间为[0,len -i)
for(int j = 0;j < array.length - i - 1;j++){
if(array[j] > array[j+1]){
swap(array,j,j+1);
}
}
}
}4.2 binarySearch(二分查找)
4.2.1 Java实现
long[] array = {1,2,3,4,6,8,10};
long r = Arrays.binarySearch(array,6);
//经过查找,可以返回该数所在的下标;如果数组中没有这个数,返回一个负值,代表没找到4.2.2 自实现
public static int MyBinarySearch(long[] array,long key){
//待查找区间为左闭右闭
int fromIndex = 0;
int toIndex = array.length - 1;
while(toIndex >= fromIndex){
int midIndex = fromIndex + (toIndex - fromIndex) / 2;
if (key == array[midIndex]) {
return midIndex;
} else if (key < array[midIndex]) {
toIndex = midIndex - 1;
} else {
fromIndex = midIndex + 1;
}
}
return -1;
}
public static int binarySearch(long[] array,long key) {
//待查找区间为左闭右开
int fromIndex = 0;
int toIndex = array.length;
while (toIndex > fromIndex) {
int midIndex = fromIndex + (toIndex - fromIndex) / 2;
if (key == array[midIndex]) {
return midIndex;
} else if (key < array[midIndex]) {
toIndex = midIndex;
} else {
fromIndex = midIndex + 1;
}
}
return -1;
}注意:只有在数组有序的情况下,才可以进行二分查找。
4.3 equals(判断两个数组是否相等)
4.3.1 Java实现
long[] a = {1,2,3,4,5};
long[] b = {1,2,3,4,5};
System.out.println(a == b);
//不能这样判断两个数组中的元素是否相等,这判断的是两个数组的引用是否相等,那么其输出结果就是错误的
System.out.println(Arrays.equals(a,b));4.3.2 自实现
public static boolean equals(long[] a,long[] b){
//比较两个数组的长度
if(a.length == b.length){
return false;
}
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
if(a[i] != b[i]){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}4.4 fill
4.4.1 Java实现
long[] a = {1,2,3,4,5};
Arrays.fill(a,5);//将数组元素全部用5来填充
Arrays.fill(a,1,3,5);//将数组下标为1和2的元素用5填充4.4.2 自实现
public static void fill(long[] a, long key) {
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
a[i] = key;
}
}
public static void MyFill(long[] a,int fromIndex,int toIndex,long key){
for (int i = fromIndex; i < toIndex; i++) {
a[i] = key;
}
}4.5 copyOf(复制数组)
4.5.1 Java实现
long[] a = {1,2,3};
long[] a1 = Arrays.copyOf(a,2);//在这个情况下,复制的新长度是2,所以只复制1,2
long[] a2 = Arrays.copyOf(a,3);//在这个情况下,复制的新长度是3,刚好等于原长度,则复制出来的数组为1,2,3
long[] a3 = Arrays.copyOf(a,4);//在这个情况下,复制的新长度为4,超出原长度,则则在超出的地方补0
long[] a4 = Arrays.copyOfRange(a,1,2);//将数组下标为1的数组复制出来
long[] a5 = Arrays.copyOfRange(a,-1,2);//左边下标越界,异常
long[] a6 = Arrays.copyOfRange(a,1,4);//右边下标越界,在尾部自动补04.5.2 自实现
public static long[] copyOfRange(long[] original,int fromIndex,int toIndex){
long[] newArray = new long[toIndex - fromIndex];
//设置i为新数组的下标
//当toIndex < original.length 时,一共要复制toIndex - fromIndex个元素
//当toIndex == original.length 时,一共要复制toIndex - fromIndex个元素
//当toIndex > original.length 时,一共要复制original.length - fromIndex个元素
for(int i = 0;i < Math.min(original.length,toIndex) - fromIndex;i++){
newArray[i] = original[fromIndex + i];
}
return newArray;
}
public static long[] copyOf(long[] original,int newLength){
//定义一个新的长度的数组
long[] newArray = new long[newLength];
//三种情况:original.length > newLength
//original.length == newLength
//original.length < newLength
for(int i = 0;i < Math.min(original.length,newLength);i++){
newArray[i] = original[i];
}
return newArray;
}4.6 toString(相当于遍历,得到数组的字符串表示)
4.6.1 Java实现
long[] a = {1,2,3};
String s = Arrays.toString(a);4.6.2 自实现
public static String toString(long[] array){
String r = "[";
for(int i = 0;i < array.length - 1;i++){
r += (array[i] + ",");
}
if(array.length >= 1) {
r += array[array.length - 1];
}
r += "]";
return r;
}4.7 arraycopy
在使用时输入原数组、原数组复制的开始下标、目标数组,目标数组的开始下标,拷贝长度。
int[] a = {1,2,3,4,5};
int[] b = new int[7];
System.arraycopy(a,1,b,2,4);5 数组应用
5.1 实现数组的遍历
按照从前到后的顺序,访问数组中的每个元素(使用a.length来获取数组的长度)
for(int i = 0;i < a.length;i++){
System.out.println(a[i]);
}
//便捷的数组遍历方式
//遍历a中的每个元素,把元素的值赋予e
//下面这种方法虽然便捷,但不能从中间开始遍历
for(int e:a){
System.out.println(e);
}5.2 实现数组元素的交换
public static void swap(double[] array,int i ,int j){
double t = array[i];
array[i] = array[j];
array[j] = t;
}5.3 实现两个数组之间的交换
public static void swap(int[] a,int[] b){
int[] tmp = a;
a = b;
b = tmp;
}6 使用数组过程中常见的两个异常
6.1 下标越界异常(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException)
int[] a = {1,2,3};
System.out.println(a[3]);6.2 空指针异常(NullPointerException)
对一个值为null的引用做解引用操作时,会出现空指针异常。
int[] a = null;//null代表让a引用不关联任何对象,不能对其解引用
System.out.println(a.length);7 特殊事项
对于引用类型来说,形参的改变不影响实参(除通过引用改对象之外)。一个对象可以被多个引用指向,而一个引用只能指向一个或0个对象,不能指向多个。
注意:在下面这种情况下,a引用为空也不会出错。
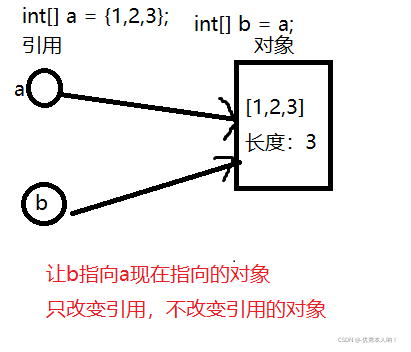
int[] a = {1,2,3};
int[] b = a;
b[1] = 5;从以上步骤可以看出,当执行了b[1] = 5时,a中的值发生了变化,a[1] = 5。
四、多维数组
二维数组实际上就是将多个一维数组整合在一起的一个数组,多(n)维数组是将多个(n-1)维数组整合到一起。下面通过对二维数组的相关操作来理解多维数组。
| 多维数组 | 形式 | 类型 |
| 一维数组 | long[] a; | long |
| 二维数组 | long[][] b; | long[],是引用类型 |
long[][] a = new long[10][];
因为类型为long[],是引用类型,引用类型的默认值是null,所以该数组十个元素的值都为null。a[3]得到的类型为long[],a[3][0]代表从a这个数组取出下标是3的元素,元素类型为long[],所以从语法上讲,这种情况下还可以取出元素中的元素,但是所有默认值都为null,对其解引用就会出现空指针异常。
long[][] a7 = {
{1,2,3},
{4},
{5,6,7,8,9},
null,
{10}
};
long[][] a8 = new long[][]{
new long[]{1,2,3},
new long[]{4,5}
};综上所述,数组的大部分知识就以归纳完毕,如有错误,请指正!