浅谈C#方法调用方式
反射方式
在开发过程中对静态方法的调用是通过类型名后面加个点而后是调用方法的名称,对类型实例方法的调用是通过new一个对象,而后点加方法名称,这是最熟悉不过的两种方式。还可以通过读取CLR元数据,利用反射进行方法调用。在利用反射方式调用方法时,最重要的两个类是System.Type和System.Reflection.MethodInfo。用MethodInfo类型的Invoke方法调用方法,必须传入目标对象实例的引用。如下:
public class Calculate
{
//使用反射可以调用私有方法
private int Add(int leftNum, int rightNum)
{
return leftNum + rightNum;
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//用type.getmethod的方法获取类型方法,BindingFlags设置查找方法的范围
//本例是公有方法,私有方法而且是非静态的才被查找,如果要查找静态方法
//需要设置BindingFlags.Static
MethodInfo method = typeof(Calculate).GetMethod("Add", BindingFlags.Public
| BindingFlags.NonPublic
|BindingFlags.Instance);
if (method == null) return;
//调用方法的参数
object[] paras ={ 10, 20 };
//目标对象实例:new Calculate()
object result = method.Invoke(new Calculate(), paras);
Console.WriteLine(result);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
委托方式
任何对象都可以调用委托,只要方法返回值以及方法签名和委托声明一样就行。
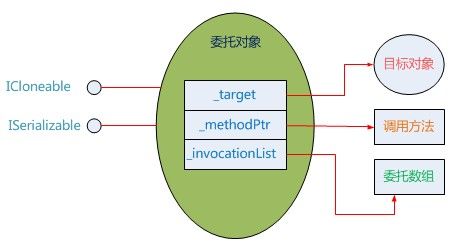
通过阅读CLR源代码,整理了委托类的重要字段和几个常用方法,自定义的委托类型都派生于MulticastDelegate。
public abstract class Delegate : ICloneable, ISerializable
{
// 调用目标对象,实例方法为类型实例引用,静态方法则为null
internal Object _target;
//指向调用方法
internal IntPtr _methodPtr;
//委托构造器
protected Delegate(Object target, String method)
{
//省略,具体看以查看clr源代码
}
public static Delegate CreateDelegate(Type type, Object target, String method)
{
//省略,具体看以查看clr源代码
}
public static Delegate CreateDelegate(Type type, Type target, String method)
{
//省略,具体看以查看clr源代码
}
public static Delegate Combine(params Delegate[] delegates) {}
public static Delegate Combine(Delegate a, Delegate b) {}
public static Delegate Remove(Delegate source, Delegate value){}
}
public abstract class MulticastDelegate : Delegate
{
private Object _invocationList;
protected MulticastDelegate(Object target, String method) : base(target, method) { }
protected MulticastDelegate(Type target, String method): base(target, method) { }
}
从源代码可以看出Delegate类提供了几个重载的静态方法CreateDelegate,方法返回值是Delegate类型。如果是实例方法则把对象引用传递给它,如是静态方法则传入对象类型。
public delegate int DelegateCaculate(int a,int b);
public class Caculate
{
public int Add(int num1, int num2)
{
return num1 + num2;
}
public static int Subtract(int num1, int num2)
{
return num2 - num1;
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Caculate caculate = new Caculate();
Type typeCaculate = typeof(Caculate);
Type typeDelegate = typeof(DelegateCaculate);
DelegateCaculate add = (DelegateCaculate)Delegate.CreateDelegate(typeDelegate, caculate, "Add");
DelegateCaculate subtract = (DelegateCaculate)Delegate.CreateDelegate(typeDelegate, typeCaculate, "Subtract");
Console.WriteLine("add:" + add(10, 20));
Console.WriteLine("subtract:" + subtract(10, 20));
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
CreateDelegate需要通过遍历元数据来获取方法句柄。C#语法提供了更便利的方法来调用委托,可以简单通过类型名或者对象名来限定方法,而且不需要通过遍历元数据,C#编译器使用底层CIL的ldftn或许ldvirtftn操作符获取方法地址,相对来说要比CreateDelegate快的多了。上面的Main方法可以改写为
static void Main(string[] args)
{
DelegateCaculate add = new DelegateCaculate(new Caculate().Add);
DelegateCaculate subtract = new DelegateCaculate(Caculate.Subtract);
Console.WriteLine("add:" + add(10, 20));
Console.WriteLine("subtract:" + subtract(10, 20));
Console.ReadLine();
}
可以将多个委托对象放到委托对象数组中,一旦对其调用,CLR将遍历委托数组,对其逐一调用。
public delegate void DelegateCaculate(int a,int b);
public class Caculate
{
public static void Add(int num1, int num2)
{
Console.WriteLine((num1 + num2));
}
public static void Subtract(int num1, int num2)
{
Console.WriteLine((num2- num1));
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
DelegateArray(new DelegateCaculate(Caculate.Add), new DelegateCaculate(Caculate.Subtract));
Console.ReadLine();
}
static void DelegateArray(DelegateCaculate a, DelegateCaculate b)
{
DelegateCaculate delChain = null;
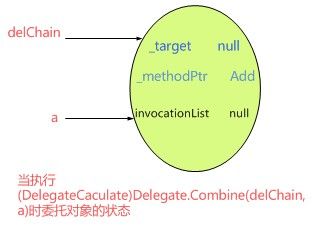
delChain = (DelegateCaculate)Delegate.Combine(delChain, a);
delChain = (DelegateCaculate)Delegate.Combine(delChain, b);
delChain(10, 20);
}
}
C#提供了更便捷的语法把委托对象添加到委托数组内,可以这样修改上面的DelegateArray方法,
static void DelegateArray(DelegateCaculate a, DelegateCaculate b)
{
DelegateCaculate delChain = null;
delChain += a;
delChain+=b;
delChain(10, 20);
}
当执行(DelegateCaculate)Delegate.Combine(delChain, a)时,因为委托数组中只有一个a对象,所以delChain也只是简单的指向a。示意图如下
当执行(DelegateCaculate)Delegate.Combine(delChain, b)是,因为委托数组已经有两个对象了,这时会生成一个新的MulticastDelegate对象让delChain指向它,而_invocationList指向一个委托数组对象,示意图如下
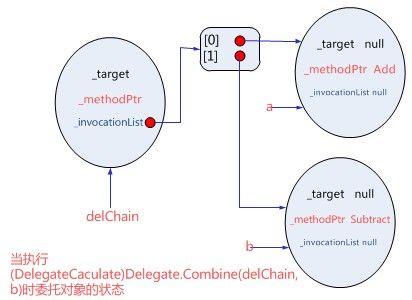
如果还有委托对象加入,将会再次生成一个新的MulticastDelegate对象让delChain指向这个新对象,原来的对象则等待垃圾回收器进行回收,这点可以查看CLR源代码,每添加一个委托对象就调用一次方法NewMulticastDelegate,这个方法返回值是MulticastDelegate。
委托与接口
接口与委托都拥有调用特定方法的能力,所以他们在这点很相像。但是接口需要目标方法的类型声明必须与该接口兼容,而委托可以被任何类型调用,只要该类型的目标方法签名和委托签名匹配即可。
那么何时用委托,何时用接口呢,msdn 总结的非常好,我就直接给粘贴过来了,
委托在以下情况很有用:
1、 调用单个方法。
2、 一个类希望有方法规范的多个实现。
3、 希望允许静态方法实现规范。
4、 希望类似事件的设计模式。
5、 调用方不需要知道或获得实现与委托签名匹配的方法的对象。
6、 实现的提供程序希望只对少数选择组件“分发”规范实现。
7、 需要方法的组合。
接口在以下情况很有用:
1、 规范定义一组相关方法。
2、 类通常只实现规范一次。
3、 接口的调用方希望转换为接口类型或从接口类型转换,以获得其他接口或类。