嵌入式Linux驱动开发(I2C专题)(五)
I2C系统驱动程序模型
参考资料:
- Linux内核文档:
Documentation\i2c\instantiating-devices.rstDocumentation\i2c\writing-clients.rst
- Linux内核驱动程序示例:
drivers/eeprom/at24.c
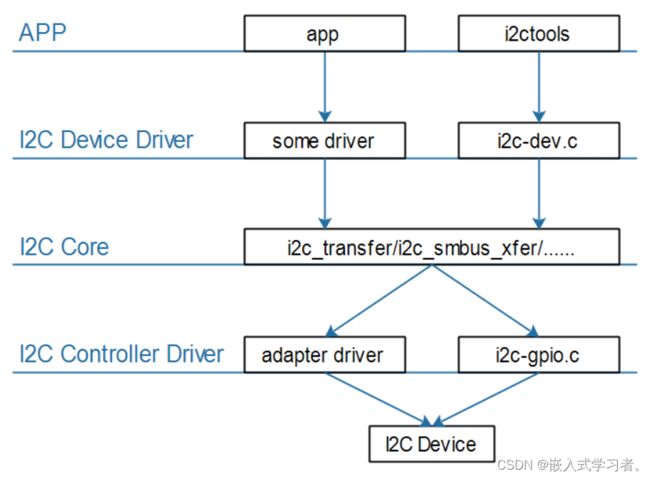
1. I2C驱动程序的层次
- 提供统一的访问函数,比如i2c_transfer、i2c_smbus_xfer等
- 实现
I2C总线-设备-驱动模型,管理:I2C设备(i2c_client)、I2C设备驱动(i2c_driver)、I2C控制器(i2c_adapter)
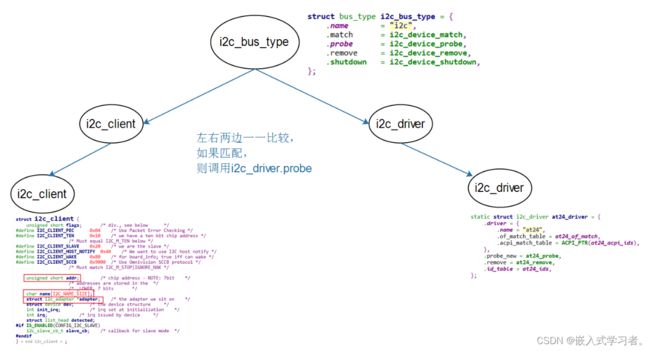
2. I2C总线-设备-驱动模型
2.1 i2c_driver
i2c_driver表明能支持哪些设备:
- 使用of_match_table来判断
- 设备树中,某个I2C控制器节点下可以创建I2C设备的节点
- 如果I2C设备节点的compatible属性跟of_match_table的某项兼容,则匹配成功
- i2c_client.name跟某个of_match_table[i].compatible值相同,则匹配成功
- 设备树中,某个I2C控制器节点下可以创建I2C设备的节点
- 使用id_table来判断
- i2c_client.name跟某个id_table[i].name值相同,则匹配成功
i2c_driver跟i2c_client匹配成功后,就调用i2c_driver.probe函数。
2.2 i2c_client
i2c_client表示一个I2C设备,创建i2c_client的方法有4种:
-
方法1
-
通过I2C bus number来创建
int i2c_register_board_info(int busnum, struct i2c_board_info const *info, unsigned len); -
通过设备树来创建
i2c1: i2c@400a0000 { /* ... master properties skipped ... */ clock-frequency = <100000>; flash@50 { compatible = "atmel,24c256"; reg = <0x50>; }; pca9532: gpio@60 { compatible = "nxp,pca9532"; gpio-controller; #gpio-cells = <2>; reg = <0x60>; }; };
-
-
方法2
有时候无法知道该设备挂载哪个I2C bus下,无法知道它对应的I2C bus number。
但是可以通过其他方法知道对应的i2c_adapter结构体。
可以使用下面两个函数来创建i2c_client:-
i2c_new_device
static struct i2c_board_info sfe4001_hwmon_info = { I2C_BOARD_INFO("max6647", 0x4e), }; int sfe4001_init(struct efx_nic *efx) { (...) efx->board_info.hwmon_client = i2c_new_device(&efx->i2c_adap, &sfe4001_hwmon_info); (...) } -
i2c_new_probed_device
static const unsigned short normal_i2c[] = { 0x2c, 0x2d, I2C_CLIENT_END }; static int usb_hcd_nxp_probe(struct platform_device *pdev) { (...) struct i2c_adapter *i2c_adap; struct i2c_board_info i2c_info; (...) i2c_adap = i2c_get_adapter(2); memset(&i2c_info, 0, sizeof(struct i2c_board_info)); strscpy(i2c_info.type, "isp1301_nxp", sizeof(i2c_info.type)); isp1301_i2c_client = i2c_new_probed_device(i2c_adap, &i2c_info, normal_i2c, NULL); i2c_put_adapter(i2c_adap); (...) } -
差别:
- i2c_new_device:会创建i2c_client,即使该设备并不存在
- i2c_new_probed_device:
- 它成功的话,会创建i2c_client,并且表示这个设备肯定存在
- I2C设备的地址可能发生变化,比如AT24C02的引脚A2A1A0电平不一样时,设备地址就不一样
- 可以罗列出可能的地址
- i2c_new_probed_device使用这些地址判断设备是否存在
-
-
方法3(不推荐):由i2c_driver.detect函数来判断是否有对应的I2C设备并生成i2c_client
-
方法4:通过用户空间(user-space)生成
调试时、或者不方便通过代码明确地生成i2c_client时,可以通过用户空间来生成。
// 创建一个i2c_client, .name = "eeprom", .addr=0x50, .adapter是i2c-3
# echo eeprom 0x50 > /sys/bus/i2c/devices/i2c-3/new_device
// 删除一个i2c_client
# echo 0x50 > /sys/bus/i2c/devices/i2c-3/delete_device
编写设备驱动之i2c_driver
参考资料:
Linux内核文档:
Documentation\i2c\instantiating-devices.rst
Documentation\i2c\writing-clients.rst
Linux内核驱动程序示例:
drivers/eeprom/at24.c
1. 套路
1.1 I2C总线-设备-驱动模型
1.2 示例
分配、设置、注册一个i2c_driver结构体,类似drivers/eeprom/at24.c:

2. 编写i2c_driver
2.1 先写一个框架
#include 2.2 在为AP3216C编写代码
百问网的开发板上有光感芯片AP3216C:

AP3216C是红外、光强、距离三合一的传感器,以读出光强、距离值为例,步骤如下:
复位:往寄存器0写入0x4
使能:往寄存器0写入0x3
读红外:读寄存器0xA、0xB得到2字节的红外数据
读光强:读寄存器0xC、0xD得到2字节的光强
读距离:读寄存器0xE、0xF得到2字节的距离值
AP3216C的设备地址是0x1E。
ap3216c_drv.c
#include ap3216c_client.c
#include APP
#include Makefile
# 1. 使用不同的开发板内核时, 一定要修改KERN_DIR
# 2. KERN_DIR中的内核要事先配置、编译, 为了能编译内核, 要先设置下列环境变量:
# 2.1 ARCH, 比如: export ARCH=arm64
# 2.2 CROSS_COMPILE, 比如: export CROSS_COMPILE=aarch64-linux-gnu-
# 2.3 PATH, 比如: export PATH=$PATH:/home/book/100ask_roc-rk3399-pc/ToolChain-6.3.1/gcc-linaro-6.3.1-2017.05-x86_64_aarch64-linux-gnu/bin
# 注意: 不同的开发板不同的编译器上述3个环境变量不一定相同,
# 请参考各开发板的高级用户使用手册
KERN_DIR = /home/book/100ask_imx6ull-sdk/Linux-4.9.88/
all:
make -C $(KERN_DIR) M=`pwd` modules
clean:
make -C $(KERN_DIR) M=`pwd` modules clean
rm -rf modules.order
obj-m += ap3216c_drv.o
obj-m += ap3216c_client.o
I2C_Adapter驱动框架讲解与编写
分配、设置、注册一个i2c_adpater结构体:
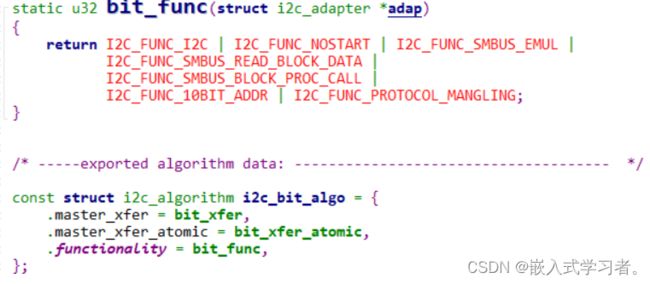
- i2c_adpater的核心是i2c_algorithm
- i2c_algorithm的核心是master_xfer函数
1. 所涉及的函数
-
分配
struct i2c_adpater *adap = kzalloc(sizeof(struct i2c_adpater), GFP_KERNEL); -
设置
adap->owner = THIS_MODULE; adap->algo = &stm32f7_i2c_algo; -
注册:i2c_add_adapter/i2c_add_numbered_adapter
ret = i2c_add_adapter(adap); // 不管adap->nr原来是什么,都动态设置adap->nr ret = i2c_add_numbered_adapter(adap); // 如果adap->nr == -1 则动态分配nr; 否则使用该nr -
反注册
i2c_del_adapter(adap);
2. i2c_algorithm示例
3. 编写一个框架程序
3.1 设备树
在设备树里构造I2C Bus节点:
i2c-bus-virtual {
compatible = "100ask,i2c-bus-virtual";
};
3.2 platform_driver
分配、设置、注册platform_driver结构体。
核心是probe函数,它要做这几件事:
- 根据设备树信息设置硬件(引脚、时钟等)
- 分配、设置、注册i2c_apdater
3.3 i2c_apdater
i2c_apdater核心是master_xfer函数,它的实现取决于硬件,大概代码如下:
static int xxx_master_xfer(struct i2c_adapter *adapter,
struct i2c_msg *msgs, int num)
{
for (i = 0; i < num; i++) {
struct i2c_msg *msg = msgs[i];
{
// 1. 发出S信号: 设置寄存器发出S信号
CTLREG = S;
// 2. 根据Flag发出设备地址和R/W位: 把这8位数据写入某个DATAREG即可发出信号
// 判断是否有ACK
if (!ACK)
return ERROR;
else {
// 3. read / write
if (read) {
STATUS = XXX; // 这决定读到一个数据后是否发出ACK给对方
val = DATAREG; // 这会发起I2C读操作
} else if(write) {
DATAREG = val; // 这会发起I2C写操作
val = STATUS; // 判断是否收到ACK
if (!ACK)
return ERROR;
}
}
// 4. 发出P信号
CTLREG = P;
}
}
return i;
}