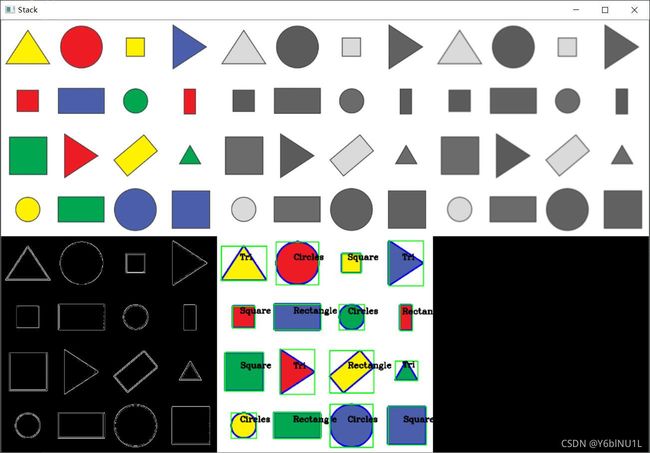
python识别图形形状
代码
import cv2
import numpy as np
"""
查找图像轮廓,计算图像矩,根据公式计算轮廓周长和面积
面积:cv2.contourArea()|M['m00']
周长:cv2.arcLength()
有两类边界矩形,直边界矩形,旋转边界矩形。
直边界矩形(就是没有旋转的矩形),使用函数cv2.boundingRect()可以查找到,
因为直边界矩形不考虑矩形旋转,所以直边界矩形的面积不是最小。
旋转矩形,这个矩形的面积最小,因为他考虑了矩形的旋转。
使用函数cv2.minAreaRect可以得到,函数返回一个Box2D结构,
其中包含旋转矩形左上角坐标(x, y),矩形的宽高(w, h),以及旋转角度。
但是绘制一个矩形需要四个角点,可以通过函数cv2.boxPoints()获得。
approxPolyDP(curve, epsilon, closed[, approxCurve]) -> approxCurve
第二个参数epsilon:指定原始轮廓到近似轮廓的最大距离,函数返回拟合的多边形边数。
"""
def stackImages(scale, imgArray):
rows = len(imgArray)
cols = len(imgArray[0])
rowsAvailable = isinstance(imgArray[0], list)
width = imgArray[0][0].shape[1]
height = imgArray[0][0].shape[0]
if rowsAvailable:
for x in range(0, rows):
for y in range(0, cols):
if imgArray[x][y].shape[:2] == imgArray[0][0].shape[:2]:
imgArray[x][y] = cv2.resize(imgArray[x][y], (0, 0), None, scale, scale)
else:
imgArray[x][y] = cv2.resize(imgArray[x][y], (imgArray[0][0].shape[1], imgArray[0][0].shape[0]),
None, scale, scale)
if len(imgArray[x][y].shape) == 2: imgArray[x][y] = cv2.cvtColor(imgArray[x][y], cv2.COLOR_GRAY2BGR)
imageBlank = np.zeros((height, width, 3), np.uint8)
hor = [imageBlank] * rows
hor_con = [imageBlank] * rows
for x in range(0, rows):
hor[x] = np.hstack(imgArray[x])
ver = np.vstack(hor)
else:
for x in range(0, rows):
if imgArray[x].shape[:2] == imgArray[0].shape[:2]:
imgArray[x] = cv2.resize(imgArray[x], (0, 0), None, scale, scale)
else:
imgArray[x] = cv2.resize(imgArray[x], (imgArray[0].shape[1], imgArray[0].shape[0]), None, scale, scale)
if len(imgArray[x].shape) == 2: imgArray[x] = cv2.cvtColor(imgArray[x], cv2.COLOR_GRAY2BGR)
hor = np.hstack(imgArray)
ver = hor
return ver
def getContours(img):
# 查找轮廓,cv2.RETR_ExTERNAL=获取外部轮廓点, CHAIN_APPROX_NONE = 得到所有的像素点
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(img, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE)
# 循环轮廓,判断每一个形状
for cnt in contours:
# 获取轮廓面积
area = cv2.contourArea(cnt)
print(area)
# 当面积大于500,代表有形状存在
if area > 500:
# 绘制所有的轮廓并显示出来
cv2.drawContours(imgContour, cnt, -1, (255, 0, 0), 3)
# 计算所有轮廓的周长,便于做多边形拟合
peri = cv2.arcLength(cnt, True)
# 多边形拟合,获取每个形状的 边
approx = cv2.approxPolyDP(cnt, 0.02 * peri, True)
print(len(approx))
objCor = len(approx)
# 获取每个形状的x,y,w,h
x, y, w, h = cv2.boundingRect(approx)
# 计算出边界后,即边数代表形状,如三角形边数=3
if objCor == 3:
objectType = "Tri"
elif objCor == 4:
# 判断是矩形还是正方形
aspRatio = w / float(h)
if aspRatio > 0.98 and aspRatio < 1.03:
objectType = "Square"
else:
objectType = "Rectangle"
# 大于4个边的就是圆形
elif objCor > 4:
objectType = "Circles"
else:
objectType = "None"
# 绘制文本时需要绘制在图形附件
cv2.rectangle(imgContour, (x, y), (x + w, y + h), (0, 255, 0), 2)
cv2.putText(imgContour, objectType,
(x + (w // 2) - 10, y + (h // 2) - 10), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_COMPLEX, 0.7,
(0, 0, 0), 2)
path = 'Resources/shapes.png'
img = cv2.imread(path)
imgContour = img.copy()
# 灰度化
imgGray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# 高斯平滑
imgBlur = cv2.GaussianBlur(imgGray, (7, 7), 1)
# 边缘检测
imgCanny = cv2.Canny(imgBlur, 50, 50)
# 获取轮廓特征点
getContours(imgCanny)
imgBlank = np.zeros_like(img)
imgStack = stackImages(0.6, ([img, imgGray, imgBlur],
[imgCanny, imgContour, imgBlank]))
cv2.imshow("Stack", imgStack)
cv2.waitKey(0)
效果图
原图链接:
百度网盘链接: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1rTqz1hr0BY2u7Qmjw66VDQ 提取码:j34c