ReflectionUtils 工具类
ReflectionUtils是Spring框架中的反射工具类,它提供了一系列静态方法,可以方便地进行类、对象、方法、字段等反射操作。
1.shallowCopyFieldState(final Object src, final Object dest)
将源对象的属性值浅拷贝到目标对象中。
该方法会遍历源对象的所有可读属性,并将其值拷贝到目标对象的对应属性中。
拷贝的方式是通过直接赋值来实现的,因此是浅拷贝,即拷贝的是属性的引用而不是属性的副本。
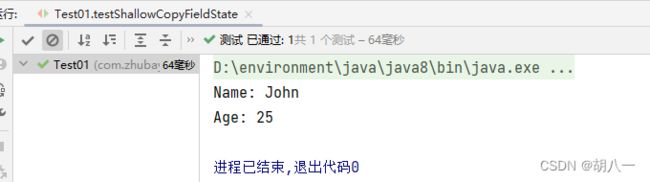
Person source = new Person();
source.setName("John");
source.setAge(25);
PersonVO target = new PersonVO();
// 浅拷贝
ReflectionUtils.shallowCopyFieldState(source, target);
System.out.println("Name: " + target.getName());
System.out.println("Age: " + target.getAge());
运行结果:
2.handleReflectionException(Exception ex)
用于处理反射操作中可能抛出的异常。
它接受一个Exception类型的参数ex,表示要处理的异常。
PersonVo example = new PersonVo();
try {
Method method = PersonVo.class.getMethod("nonExistingMethod");
ReflectionUtils.invokeMethod(method, example);
} catch (Exception ex) {
// 处理反射操作中的异常
ReflectionUtils.handleReflectionException(ex);
}
运行结果:
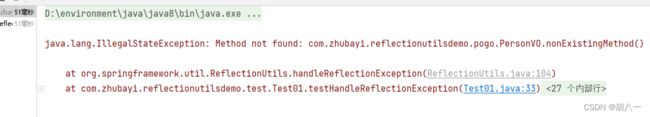
在示例中,我们调用了一个不存在的方法,固抛异常了。
3.handleInvocationTargetException(InvocationTargetException ex)
处理给定的调用目标异常,InvocationTargetException是Java反射中的一个异常类,它表示在调用方法时发生了异常。
通常情况下,我们可以使用getCause()方法获取原始的异常对象。
4.rethrowRuntimeException(Throwable ex)
重新抛出一个运行时异常。
5.rethrowException(Throwable ex)
重新抛出一个异常,重新抛出的异常分为三种类型:
运行时异常RuntimeException、Error、UndeclaredThrowableException。
6.ReflectionUtils.accessibleConstructor(Classclazz, Class... parameterTypes)
用于获取指定类的可访问构造函数。
try {
Constructor<Person> constructor = ReflectionUtils.accessibleConstructor(Person.class, String.class, int.class);
Person example = constructor.newInstance("John Doe", 25);
System.out.println("Name: " + example.getName());
System.out.println("Age: " + example.getAge());
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
运行结果:
7.Method findMethod(Class clazz, String name)
获取指定类的指定方法。
Method getNameMethod = ReflectionUtils.findMethod(Person.class, "getName");
System.out.println("getName method: " + getNameMethod);
8.findMethod(Class clazz, String name, @Nullable Class... paramTypes)
获取指定类的指定方法,该方法还有一个或多个参数类型。
Method setNameMethod = ReflectionUtils.findMethod(Person.class, "setName", String.class);
System.out.println("setName method: " + setNameMethod);
运行结果:

9.invokeMethod(Method method, @Nullable Object target)
用于调用指定方法,并传入目标对象(可选)。
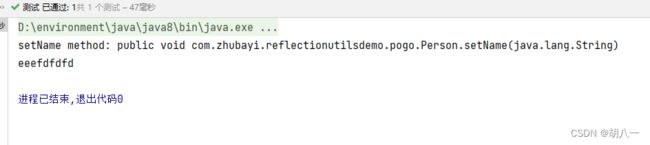
Method setNameMethod = ReflectionUtils.findMethod(Person.class, "setName", String.class);
System.out.println("setName method: " + setNameMethod);
Person example = new Person();
// 设置访问权限才可访问
setNameMethod.setAccessible(true);
ReflectionUtils.invokeMethod(setNameMethod, example, "eeefdfdfd");
System.out.println(example.getName());
运行结果:
10.declaresException(Method method, Class exceptionType)
用于检查指定方法是否声明了指定的异常类型。
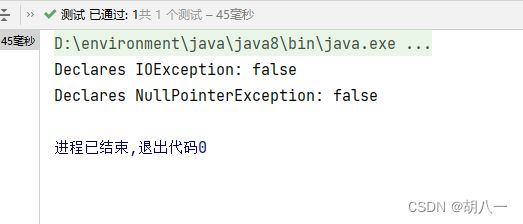
Method method = ReflectionUtils.findMethod(Person.class, "getName");
boolean declaresIOException = ReflectionUtils.declaresException(method, IOException.class);
System.out.println("Declares IOException: " + declaresIOException);
boolean declaresNullPointerException = ReflectionUtils.declaresException(method, NullPointerException.class);
System.out.println("Declares NullPointerException: " + declaresNullPointerException);
11.doWithLocalMethods(Class clazz, MethodCallback mc)
用于迭代指定类的所有本地方法,并对每个方法执行回调操作。
ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalMethods(Person.class, new PersonCallback());
回调类:
// 需要实现MethodCallback 方法
class PersonCallback implements MethodCallback {
@Override
public void doWith(Method method) throws IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException {
System.out.println("Method name: " + method.getName());
}
}
或者箭头函数
ReflectionUtils.doWithMethods(Person.class, (method)->{
System.out.println("Method name: " + method.getName());
});
12.doWithMethods(Class clazz, MethodCallback mc)
用于迭代指定类的所有方法,并对每个方法执行回调操作。
ReflectionUtils.doWithMethods(Person.class, new PersonCallback());
ReflectionUtils.doWithMethods(Person.class, (method)->{
System.out.println("Method name: " + method.getName());
});
过滤
ReflectionUtils.doWithMethods(Person.class, new PersonCallback(), new PersonMethodFilter());
ReflectionUtils.doWithMethods(Person.class, (method)->{
System.out.println("Method name: " + method.getName());
},method->Modifier.isPublic(method.getModifiers()));
// 需要实现MethodFilter接口
class PersonMethodFilter implements MethodFilter {
@Override
public boolean matches(Method method) {
return Modifier.isPublic(method.getModifiers());
}
}
运行结果:
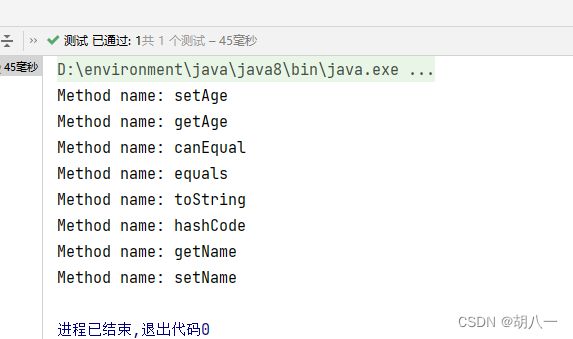
13.getAllDeclaredMethods(Class leafClass)
用于获取指定类及其所有父类中声明的所有方法。
Class<?> leafClass = Person.class;
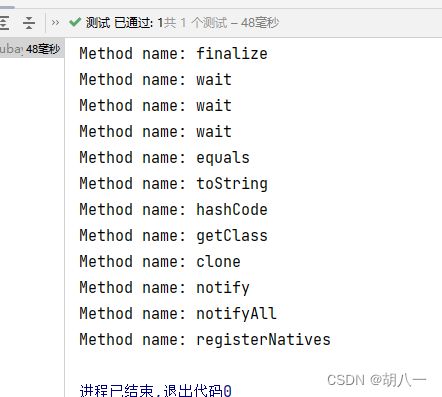
Method[] methods = ReflectionUtils.getAllDeclaredMethods(leafClass);
for (Method method : methods) {
System.out.println("Method name: " + method.getName());
}
运行结果:
Method name: equals
Method name: toString
Method name: hashCode
Method name: getName
Method name: setName
Method name: setAge
Method name: getAge
Method name: canEqual
Method name: finalize
Method name: wait
Method name: wait
Method name: wait
Method name: equals
Method name: toString
Method name: hashCode
Method name: getClass
Method name: clone
Method name: notify
Method name: notifyAll
Method name: registerNatives
进程已结束,退出代码0
14.getUniqueDeclaredMethods(Class leafClass)
用于获取指定类及其所有父类中声明的所有唯一方法。
Class<?> leafClass = Person.class;
Method[] methods = ReflectionUtils.getUniqueDeclaredMethods(leafClass);
for (Method method : methods) {
System.out.println("Method name: " + method.getName());
}
运行结果:
Method name: getAge
Method name: setAge
Method name: canEqual
Method name: equals
Method name: toString
Method name: hashCode
Method name: getName
Method name: setName
Method name: finalize
Method name: wait
Method name: wait
Method name: wait
Method name: getClass
Method name: clone
Method name: notify
Method name: notifyAll
Method name: registerNatives
进程已结束,退出代码0
15.isEqualsMethod(@Nullable Method method)
用于判断给定的方法是否是equals方法。
try {
Class<?> clazz = PersonVO.class;
Method method = clazz.getMethod("equals", Object.class);
boolean isEquals = ReflectionUtils.isEqualsMethod(method);
System.out.println("Is equals method: " + isEquals);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException | SecurityException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
运行结果:
Is equals method: true
进程已结束,退出代码0
16.isHashCodeMethod(@Nullable Method method)
用于判断给定的方法是否是hashCode方法。
17.isToStringMethod(@Nullable Method method)
用于判断给定的方法是否是toString方法。
18.isObjectMethod(@Nullable Method method)
用于判断给定的方法是否是Object类中的方法。
try {
Class<?> clazz = PersonVO.class;
Method method = clazz.getMethod("getName");
boolean isObjectMethod = ReflectionUtils.isObjectMethod(method);
System.out.println("Is Object method: " + isObjectMethod);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException | SecurityException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
运行结果:
Is Object method: false
进程已结束,退出代码0
19.isCglibRenamedMethod(Method renamedMethod)
用于判断给定的方法是否是Cglib的类中的renamed方法。
20.findField(Class clazz, String name)
用于在给定的类及其父类中查找指定名称的字段。
Class<?> clazz = Person.class;
Field field = ReflectionUtils.findField(clazz, "name");
System.out.println("Field name: " + field.getName());
运行结果:
Field name: name
进程已结束,退出代码0
findField(Class clazz, @Nullable String name, @Nullable Class type)
用于在给定的类及其父类中查找指定名称、类型的字段。
21.setField(Field field, @Nullable Object target, @Nullable Object value)
用于设置指定字段的值。
try {
Person myObject = new Person();
Field field = Person.class.getDeclaredField("name");
// 设置为可以访问
field.setAccessible(true);
ReflectionUtils.setField(field, myObject, "Hello, World!");
System.out.println("Field value: " + myObject.getName());
} catch (NoSuchFieldException | SecurityException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
运行结果:
Field value: Hello, World!
进程已结束,退出代码0
22.getField(Field field, @Nullable Object target)
用于获取指定字段的值。
try {
Person myObject = new Person("aaaa",10);
Field field = Person.class.getDeclaredField("name");
field.setAccessible(true);
Object value = ReflectionUtils.getField(field, myObject);
System.out.println("Field value: " + value);
} catch (NoSuchFieldException | SecurityException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
运行结果:
Field value: aaaa
进程已结束,退出代码0
23.doWithLocalFields(Class clazz, FieldCallback fc)
用于对指定类的本地字段(即不包括父类的字段)进行操作。
Class<?> clazz = PersonVO.class;
MyFieldCallback fieldCallback = new MyFieldCallback();
ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalFields(clazz, fieldCallback);
//FieldCallback 类
class MyFieldCallback implements FieldCallback {
@Override
public void doWith(Field field) throws IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException {
System.out.println("Field name: " + field.getName());
System.out.println("Field type: " + field.getType());
}
}
或者
ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalFields(Person.class, (field->{
System.out.println("Field name: " + field.getName());
System.out.println("Field type: " + field.getType());
}));
运行结果:
Field name: name
Field type: class java.lang.String
Field name: age
Field type: int
进程已结束,退出代码0
24.doWithFields(Class clazz, FieldCallback fc)
用于对指定类的字段(包括父类的字段)进行操作。
Class<?> clazz = Person.class;
MyFieldCallback fieldCallback = new MyFieldCallback();
ReflectionUtils.doWithFields(clazz, fieldCallback);
或者
ReflectionUtils.doWithFields(Person.class, (field->{
System.out.println("Field name: " + field.getName());
System.out.println("Field type: " + field.getType());
}));
运行结果:
Field name: name
Field type: class java.lang.String
Field name: age
Field type: int
进程已结束,退出代码0
25.doWithFields(Class clazz, FieldCallback fc, @Nullable FieldFilter ff)
用于对指定类的符合条件的字段进行操作。
Person myObject = new Person();
// 使用doWithFields方法对字段进行操作
ReflectionUtils.doWithFields(Person.class, new FieldCallback() {
@Override
public void doWith(Field field) throws IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException {
// 在这里可以对每个字段进行自定义操作
field.setAccessible(true); // 设置字段可访问,因为字段是私有的
Object value = field.get(myObject); // 获取字段的值
System.out.println("Field name: " + field.getName());
System.out.println("Field type: " + field.getType());
System.out.println("Field value: " + value);
}
}, new FieldFilter() {
@Override
public boolean matches(Field field) {
// 在这里可以定义过滤条件,只处理满足条件的字段
return field.getType() == String.class; // 只处理类型为String的字段
}
});
或者使用箭头函数
Person myObject = new Person();
// 使用doWithFields方法对字段进行操作
ReflectionUtils.doWithFields(Person.class, field-> {
// 在这里可以对每个字段进行自定义操作
field.setAccessible(true); // 设置字段可访问,因为字段是私有的
Object value = field.get(myObject); // 获取字段的值
System.out.println("Field name: " + field.getName());
System.out.println("Field type: " + field.getType());
System.out.println("Field value: " + value);
}, field-> {
// 在这里可以定义过滤条件,只处理满足条件的字段
return field.getType() == String.class; // 只处理类型为String的字段
});
使用匿名内部类实现了FieldCallback接口,并在doWith方法中定义了对每个字段的操作。
在doWith方法中,我们首先将字段设置为可访问状态,然后使用field.get(myObject)方法获取字段的值,并打印字段的名称、类型和值。
同时,我们还使用匿名内部类实现了FieldFilter接口,并在matches方法中定义了过滤条件。
在这个示例中,我们只处理类型为String的字段。
运行结果:
Field name: name
Field type: class java.lang.String
Field value: null
进程已结束,退出代码0
26.isPublicStaticFinal(Field field)
用于判断一个字段是否是public、static和final修饰的。
Field[] fields = Person.class.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : fields) {
if (ReflectionUtils.isPublicStaticFinal(field)) {
System.out.println(field.getName() + " is public, static, and final.");
}
}
由于在person对象中,并没有这样的字段,所以没有打印结果。
最后总结一下,ReflectionUtils工具类的作用:
获取类的信息:ReflectionUtils可以通过类的全限定名获取对应的Class对象,进而获取类的各种信息,如类名、包名、父类、接口等。
创建对象:ReflectionUtils可以通过Class对象创建实例,即通过反射实现动态创建对象的功能。
调用方法:ReflectionUtils可以通过Method对象调用类的方法,包括无参方法和有参方法,可以通过方法名和参数类型来定位方法。
访问字段:ReflectionUtils可以通过Field对象访问类的字段,包括获取字段值和设置字段值。
调用构造方法:ReflectionUtils可以通过Constructor对象调用类的构造方法,包括无参构造方法和有参构造方法