Microsoft NNI入门
【GiantPandaCV导语】Neural Network Intelligence 是一个工具包,可以有效帮助用户设计并调优汲取学习模型的神经网络架构,以及超参数。具有易于使用、可扩展、灵活、高效的特点。本文主要讲NNI基础的概念以及一个训练MNIST的入门教程。本文首发于GiantPandaCV,未经允许,不得转载。
1. 概述
NNI有以下几个特性:
- 易于使用:可以通过pip进行安装,通过命令行工具查看效果。
- 可扩展:支持不同计算资源,多种计算平台,可以在不同平台并行运行。
- 灵活:NNI内部有超参数调优算法、NAS算法、early stop算法等
- 高效:NNI在系统和算法级别上进行不断优化。
基础概念:
- Experiment:表示一次任务,比如寻找最好的神经网络架构。由automl算法+多个Trial构成。
- Search Space: 搜索空间,需要预定义的空间,比如超参数范围,block个数限制等。
- Configuration: 配置文件是搜索空间的实例化,比如从搜索空间中固定下来一定的超参数。
- Trial:独立尝试,基于某个Configuration来进行运行的一次实验。
- Tuner:调优器内含有automl算法,可以为下一个trial生成新的Configuration。
- Assessor: 评估器,分析trial的中间结果,来确定trial是否应该提前终止掉。
- 训练平台:Trial的具体执行环境,比如本机、远程服务器、集群等等。
体系结构如下图所示:
- nnictl: 这是命令行工具,用于控制web 服务器,和其他管理功能,用户可以使用这个命令来进行管理。
- NNI Core: 内部核心,实现了web UI, nnimanager控制器,训练服务等核心内容。
- Advisor: 包括Tuner和Assessor,分别负责生成下一个trial和评估该trial。
- 右侧代表训练平台,将许多trial进行分配到各个平台中,完成一次尝试。
2. 使用逻辑
一个Experiment的运行逻辑是:
- Tuner 接收搜索空间,生成configuration
- 将这些生成的configuration提交到很多训练平台上。
- 将各个平台上执行的训练结果返回给Tuner
- 继续生成新的configuration。
用户的使用逻辑是:
- 定义搜索空间,按照格式要求编写json文件
- 改动原有模型代码,添加上nni的api
- 定义实验配置,在config.yml文件中,根据要求,设置好对应的参数要求。
3. 功能
-
超参数调优:最核心的功能,提供了许多流行的自动调优算法和提前种猪算法。
-
通用NAS框架:指定候选的架构,并且可以为NAS的研究人员提供了简单的接口,便于开发新的NAS算法。NNI支持多种one-shot NAS算法,使用这些算法不需要启动NNI experiment,只需直接运行。但是如果需要调整超参数,就需要启动NNI experiement。
-
模型压缩:压缩后的网络通常具有更小的模型尺寸和更快的推理速度, 模型性能也不会有明显的下降。 NNI 上的模型压缩包括剪枝和量化算法
-
自动特征工程:为下游任务找到最有效的特征。
4. 安装
Linux下安装:
python3 -m pip install --upgrade nni
Docker中使用NNI:
docker pull msranni/nni:latest
Window下安装:
pip install cython wheel
python -m pip install --upgrade nni
5. 入门实验
用MNIST进行演示如何找到MNIST模型最佳超参数,官方教程以tensorflow1.x为例的,并且暂时还没有支持tensorflow2.x,笔者本地只有tf2和pytorch环境,所以选择pytorch进行演示。演示代码来自官方库:https://github.com/microsoft/nni/blob/master/examples/trials/mnist-pytorch
伪代码:
输出: 一组最优的参数配置
1: For t = 0, 1, 2, ..., maxTrialNum,
2: hyperparameter = 从搜索空间选择一组参数
3: final result = run_trial_and_evaluate(hyperparameter)
4: 返回最终结果给 NNI
5: If 时间达到上限,
6: 停止实验
7: 返回最好的实验结果
网络结构定义:
class Net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, hidden_size):
super(Net, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 20, 5, 1)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(20, 50, 5, 1)
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(4*4*50, hidden_size)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(hidden_size, 10)
def forward(self, x):
x = F.relu(self.conv1(x))
x = F.max_pool2d(x, 2, 2)
x = F.relu(self.conv2(x))
x = F.max_pool2d(x, 2, 2)
x = x.view(-1, 4*4*50)
x = F.relu(self.fc1(x))
x = self.fc2(x)
return F.log_softmax(x, dim=1)
基本上和pytorch网络是一样的,不过构建类的时候有一个超参数,hidden size是nni负责搜索的。
第一步: 搜索空间文件构建
{
"batch_size": {"_type":"choice", "_value": [16, 32, 64, 128]},
"hidden_size":{"_type":"choice","_value":[128, 256, 512, 1024]},
"lr":{"_type":"choice","_value":[0.0001, 0.001, 0.01, 0.1]},
"momentum":{"_type":"uniform","_value":[0, 1]}
}
可以看出,搜索对象有batch size、hidden size、lr、momentum等参数,里边涉及到几种类型 type。
choice代表从后边value中选择其中一个值,uniform代表生成一个均匀分布的超参数。
第二步:添加nni api从nni获取超参数,并返回运行结果
try:
# get parameters form tuner
tuner_params = nni.get_next_parameter()
logger.debug(tuner_params)
params = vars(merge_parameter(get_params(), tuner_params))
print(params)
main(params)
except Exception as exception:
logger.exception(exception)
raise
第三行,nni.get_next_parameter()就是tuner,获取下一个configuration,将参数传递给main(第七行)中,开始根据configuration执行一次trial。
在main函数中,通过args得到对应hidden_size、lr、momentum等的参数
def main(args):
use_cuda = not args['no_cuda'] and torch.cuda.is_available()
torch.manual_seed(args['seed'])
device = torch.device("cuda" if use_cuda else "cpu")
kwargs = {'num_workers': 1, 'pin_memory': True} if use_cuda else {}
data_dir = args['data_dir']
train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
datasets.MNIST(data_dir, train=True, download=True,
transform=transforms.Compose([
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.1307,), (0.3081,))
])),
batch_size=args['batch_size'], shuffle=True, **kwargs)
test_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
datasets.MNIST(data_dir, train=False, transform=transforms.Compose([
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.1307,), (0.3081,))
])),
batch_size=1000, shuffle=True, **kwargs)
hidden_size = args['hidden_size']
model = Net(hidden_size=hidden_size).to(device)
optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=args['lr'],
momentum=args['momentum'])
for epoch in range(1, args['epochs'] + 1):
train(args, model, device, train_loader, optimizer, epoch)
test_acc = test(args, model, device, test_loader)
# report intermediate result
nni.report_intermediate_result(test_acc)
logger.debug('test accuracy %g', test_acc)
logger.debug('Pipe send intermediate result done.')
# report final result
nni.report_final_result(test_acc)
logger.debug('Final result is %g', test_acc)
logger.debug('Send final result done.')
返回运行结果:
for epoch in range(1, args['epochs'] + 1):
train(args, model, device, train_loader, optimizer, epoch)
test_acc = test(args, model, device, test_loader)
# report intermediate result
nni.report_intermediate_result(test_acc)
logger.debug('test accuracy %g', test_acc)
logger.debug('Pipe send intermediate result done.')
# report final result
nni.report_final_result(test_acc)
logger.debug('Final result is %g', test_acc)
logger.debug('Send final result done.')
主要是nni.report_intermediate_result 返回中间结果 和 nni.report_final_result 返回最终结果。
第三步 定义配置文件,声明搜索空间和Trial
authorName: pprp
experimentName: example_mnist_pytorch
trialConcurrency: 1 # 设置并发数量
maxExecDuration: 1h # 每个trial 最长执行时间
maxTrialNum: 10 # 实验重复运行次数
#choice: local, remote, pai
trainingServicePlatform: local
searchSpacePath: search_space.json # 搜索空间对应json文件
#choice: true, false
useAnnotation: false
tuner:
#choice: TPE, Random, Anneal, Evolution, BatchTuner, MetisTuner, GPTuner
#SMAC (SMAC should be installed through nnictl)
builtinTunerName: TPE # 指定tuner算法
classArgs:
#choice: maximize, minimize
optimize_mode: maximize
trial:
command: python3 mnist.py # 命令行
codeDir: .
gpuNum: 1 # 使用gpu数目
一切准备就绪,在命令行启动MNIST Experiment:
nnictl create --config config.yml
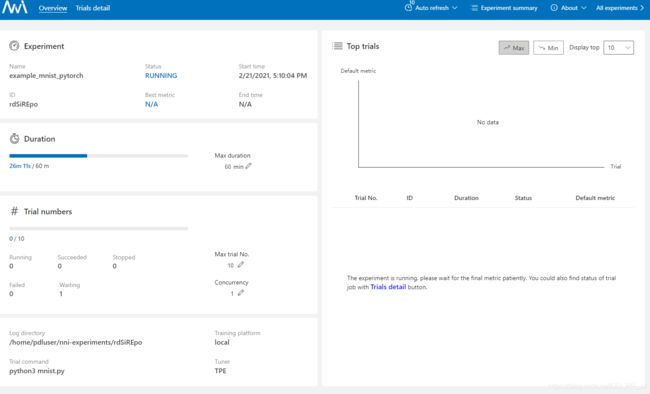
访问上图展示的连接,可以看到NNI Web UI界面。
官方提供的教程基于tensorflow 1.x,详细了解请看 https://nni.readthedocs.io/zh/stable/Tutorial/QuickStart.html
后续会陆陆续续出关于NAS使用教程,敬请期待。