【数据结构】ArrayList和顺序表
文章目录
- 1.线性表
- 2.顺序表
-
- 2.1 接口的实现
- 3. ArrayList简介
- 4. ArrayList使用
-
- 4.1 ArrayList的构造
- 4.2 ArrayList常见操作
- 4.3 ArrayList的遍历
- 4.4 ArrayList的扩容机制
- 5. ArrayList的具体使用
- 5.1 简单的洗牌算法
-
- 5.2 杨辉三角
- 6. ArrayList的问题及思考
1.线性表
线性表(linear list)是n个具有相同特性的数据元素的有限序列。 线性表是一种在实际中广泛使用的数据结构,常见的线性表:顺序表、链表、栈、队列…
线性表在逻辑上是线性结构,也就说是连续的一条直线。但是在物理结构上并不一定是连续的,线性表在物理上存储时,通常以数组和链式结构的形式存储
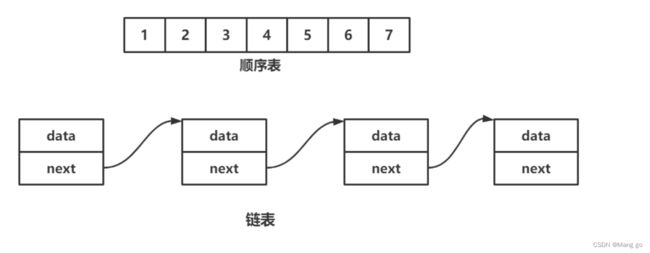
2.顺序表
顺序表是用一段物理地址连续的存储单元依次存储数据元素的线性结构,一般情况下采用数组存储。在数组上完成数据的增删查改。
2.1 接口的实现
public class SeqList {
private int[] array;
private int size;
// 默认构造方法
SeqList(){ }
// 将顺序表的底层容量设置为initcapacity
SeqList(int initcapacity){ }
// 新增元素,默认在数组最后新增
public void add(int data) { }
// 在 pos 位置新增元素
public void add(int pos, int data) { }
// 判定是否包含某个元素
public boolean contains(int toFind) { return true; }
// 查找某个元素对应的位置
public int indexOf(int toFind) { return -1; }
// 获取 pos 位置的元素
public int get(int pos) { return -1; }
// 给 pos 位置的元素设为 value
public void set(int pos, int value) { }
//删除第一次出现的关键字key
public void remove(int toRemove) { }
// 获取顺序表长度
public int size() { return 0; }
// 清空顺序表
public void clear() { }
// 打印顺序表,注意:该方法并不是顺序表中的方法,为了方便看测试结果给出的
public void display() { }
}
下一篇文章将会详细讲到如何自定义实现顺序表
3. ArrayList简介
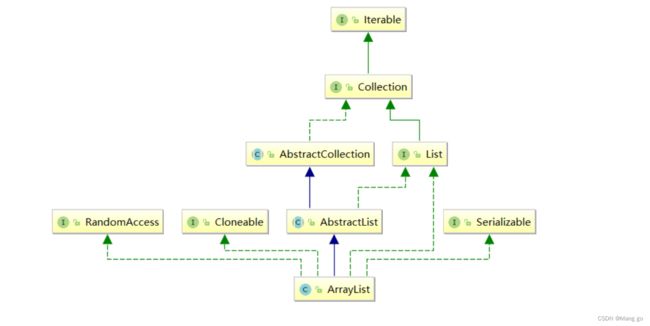
在集合框架中,ArrayList是一个普通的类,实现了List接口,具体框架图如下
【说明】
- ArrayList是以泛型方式实现的,使用时必须要先实例化
- ArrayList实现了RandomAccess接口,表明ArrayList支持随机访问
- ArrayList实现了Cloneable接口,表明ArrayList是可以clone的
- ArrayList实现了Serializable接口,表明ArrayList是支持序列化的
- 和Vector不同,ArrayList不是线程安全的,在单线程下可以使用,在多线程中可以选择Vector或者CopyOnWriteArrayList
- ArrayList底层是一段连续的空间,并且可以动态扩容,是一个动态类型的顺序表
4. ArrayList使用
4.1 ArrayList的构造
ArrayList一共有三个构造方法
| 方法 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| ArrayList() | 无参构造 |
| ArrayList(int initialCapacity) | 指定顺序表初始容量 |
| ArrayList(Collection c) | 利用其他 Collection 构建 ArrayList |
解释:
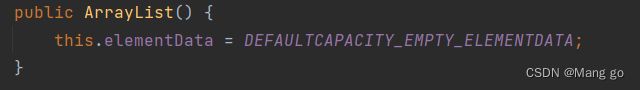
1.ArrayList()
ArrayList创建,推荐写法
构造了一个空的列表
public static void main(String[] args) {
// ArrayList创建,推荐写法
// 构造一个空的列表
List<Integer> list1 = new ArrayList<>();
}
2.ArrayList(int initialCapacity)
可以自定义顺序表长度
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 构造一个具有10个容量的列表
List<Integer> list2 = new ArrayList<>(10);
list2.add(1);
list2.add(2);
list2.add(3);
}
源码如下:
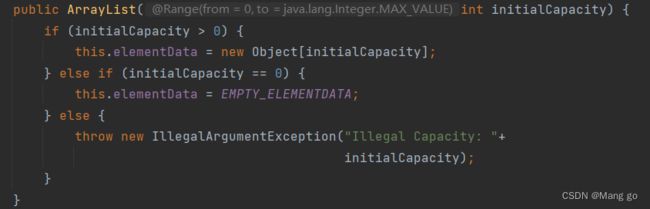
3.ArrayList(Collection c)
public static void main2(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(1);
list.add(2);
list.add(3);
//相当于进行了扩充
ArrayList<Number> list1 = new ArrayList<>(list);
list1.add(99.1);
list1.add(88.2);
System.out.println(list);
System.out.println(list1);
LinkedList<Integer> linkedList = new LinkedList<>();
ArrayList<Number> arrayList = new ArrayList<>(linkedList);
}
输出结果:
[ 1 , 2 , 3 ]
[ 1 , 2 , 3 ,99.1 , 88.2 ]
4.2 ArrayList常见操作
ArrayList虽然提供的方法比较多,但是常用方法如下所示,需要用到其他方法时,同学们自行查看ArrayList的帮助文档
| 方法 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| boolean add(E e) | 尾插 e |
| void add(int index, E element) | 将 e 插入到 index 位置 |
| boolean addAll(Collection c) | 尾插 c 中的元素 |
| E remove(int index) | 删除 index 位置元素 |
| boolean remove(Object o) | 删除遇到的第一个 o |
| E get(int index) | 获取下标 index 位置元素 |
| E set(int index, E element) | 将下标 index 位置元素设置为 element |
| void clear() | 清空 |
| boolean contains(Object o) | 判断 o 是否在线性表中 |
| int indexOf(Object o) | 返回第一个 o 所在下标 |
| int lastIndexOf(Object o) | 返回最后一个 o 的下标 |
| List |
截取部分 list |
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("JavaSE");
list.add("JavaWeb");
list.add("JavaEE");
list.add("JVM");
list.add("测试课程");
System.out.println(list);
// 获取list中有效元素个数
System.out.println(list.size());
// 获取和设置index位置上的元素,注意index必须介于[0, size)间
System.out.println(list.get(1));
list.set(1, "JavaWEB");
System.out.println(list.get(1));
// 在list的index位置插入指定元素,index及后续的元素统一往后搬移一个位置
list.add(1, "Java数据结构");
System.out.println(list);
// 删除指定元素,找到了就删除,该元素之后的元素统一往前搬移一个位置
list.remove("JVM");
System.out.println(list);
// 删除list中index位置上的元素,注意index不要超过list中有效元素个数,否则会抛出下标越界异常
list.remove(list.size()-1);
System.out.println(list);
// 检测list中是否包含指定元素,包含返回true,否则返回false
if(list.contains("测试课程")){
list.add("测试课程");
}
// 查找指定元素第一次出现的位置:indexOf从前往后找,lastIndexOf从后往前找
list.add("JavaSE");
System.out.println(list.indexOf("JavaSE"));
System.out.println(list.lastIndexOf("JavaSE"));
// 使用list中[0, 4)之间的元素构成一个新的SubList返回,但是和ArrayList共用一个elementData数组
List<String> ret = list.subList(0, 4);
System.out.println(ret);
list.clear();
System.out.println(list.size());
}
4.3 ArrayList的遍历
ArrayList 可以使用三方方式遍历:for循环+下标、foreach、使用迭代器
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(1);
list.add(2);
list.add(3);
list.add(4);
list.add(5);
// 使用下标+for遍历
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
System.out.print(list.get(i) + " ");
}
System.out.println();
// 借助foreach遍历
for (Integer integer : list) {
System.out.print(integer + " ");
}
System.out.println();
Iterator<Integer> it = list.listIterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
System.out.print(it.next() + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
注意:
- ArrayList最长使用的遍历方式是:for循环+下标 以及 foreach
- 迭代器是设计模式的一种,后序容器接触多了再给大家铺垫
4.4 ArrayList的扩容机制
下面代码有缺陷吗?为什么?
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
list.add(i);
}
}
ArrayList是一个动态类型的顺序表,即:在插入元素的过程中会自动扩容。以下是ArrayList源码中扩容方式
Object[] elementData; // 存放元素的空间
private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; // 默认空间
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10; // 默认容量大小
public boolean add(E e) {
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
ensureExplicitCapacity(calculateCapacity(elementData, minCapacity));
}
private static int calculateCapacity(Object[] elementData, int minCapacity) {
if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {
return Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);
}
return minCapacity;
}
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {
modCount++;
// overflow-conscious code
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}
private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// 获取旧空间大小
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
// 预计按照1.5倍方式扩容
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
// 如果用户需要扩容大小 超过 原空间1.5倍,按照用户所需大小扩容
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
// 如果需要扩容大小超过MAX_ARRAY_SIZE,重新计算容量大小
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// 调用copyOf扩容
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) {
// 如果minCapacity小于0,抛出OutOfMemoryError异常
if (minCapacity < 0)
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
}
【总结】
- 检测是否真正需要扩容,如果是调用grow准备扩容
- 预估需要库容的大小
初步预估按照1.5倍大小扩容
如果用户所需大小超过预估1.5倍大小,则按照用户所需大小扩容
真正扩容之前检测是否能扩容成功,防止太大导致扩容失败 - 使用copyOf进行扩容
5. ArrayList的具体使用
5.1 简单的洗牌算法
public class Card {
public int rank; // 牌面值
public String suit; // 花色
@Override
public String toString() {
return String.format("[%s %d]", suit, rank);
}
}
import java.util.List;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Random;
public class CardDemo {
public static final String[] SUITS = {"♠", "♥", "♣", "♦"};
// 买一副牌
private static List<Card> buyDeck() {
List<Card> deck = new ArrayList<>(52);
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= 13; j++) {
String suit = SUITS[i];
int rank = j;
Card card = new Card();
card.rank = rank;
card.suit = suit;
deck.add(card);
}
}
return deck;
}
private static void swap(List<Card> deck, int i, int j) {
Card t = deck.get(i);
deck.set(i, deck.get(j));
deck.set(j, t);
}
private static void shuffle(List<Card> deck) {
Random random = new Random(20190905);
for (int i = deck.size() - 1; i > 0; i--) {
int r = random.nextInt(i);
swap(deck, i, r);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Card> deck = buyDeck();
System.out.println("刚买回来的牌:");
System.out.println(deck);
shuffle(deck);
System.out.println("洗过的牌:");
System.out.println(deck);
// 三个人,每个人轮流抓 5 张牌
List<List<Card>> hands = new ArrayList<>();
hands.add(new ArrayList<>());
hands.add(new ArrayList<>());
hands.add(new ArrayList<>());
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
hands.get(j).add(deck.remove(0));
}
}
System.out.println("剩余的牌:");
System.out.println(deck);
System.out.println("A 手中的牌:");
System.out.println(hands.get(0));
System.out.println("B 手中的牌:");
System.out.println(hands.get(1));
System.out.println("C 手中的牌:");
System.out.println(hands.get(2));
}
}
运行结果
刚买回来的牌:
[[♠ 1], [♠ 2], [♠ 3], [♠ 4], [♠ 5], [♠ 6], [♠ 7], [♠ 8], [♠ 9], [♠ 10], [♠ 11], [♠ 12], [♠ 13], [♥ 1], [♥ 2], [♥ 3], [♥ 4], [♥ 5], [♥ 6], [♥ 7],
[♥ 8], [♥ 9], [♥ 10], [♥ 11], [♥ 12], [♥ 13], [♣ 1], [♣ 2], [♣ 3], [♣ 4], [♣ 5], [♣ 6], [♣ 7], [♣ 8], [♣ 9], [♣ 10], [♣ 11], [♣ 12], [♣
13], [♦ 1], [♦ 2], [♦ 3], [♦ 4], [♦ 5], [♦ 6], [♦ 7], [♦ 8], [♦ 9], [♦ 10], [♦ 11], [♦ 12], [♦ 13]]
洗过的牌:
[[♥ 11], [♥ 6], [♣ 13], [♣ 10], [♥ 13], [♠ 2], [♦ 1], [♥ 9], [♥ 12], [♦ 5], [♥ 8], [♠ 6], [♠ 3], [♥ 5], [♥ 1], [♦ 6], [♦ 13], [♣ 12], [♦ 12],
[♣ 5], [♠ 4], [♣ 3], [♥ 7], [♦ 3], [♣ 2], [♠ 1], [♦ 2], [♥ 4], [♦ 8], [♠ 10], [♦ 11], [♥ 10], [♦ 7], [♣ 9], [♦ 4], [♣ 8], [♣ 7], [♠ 8], [♦ 9], [♠
12], [♠ 11], [♣ 11], [♦ 10], [♠ 5], [♠ 13], [♠ 9], [♠ 7], [♣ 6], [♣ 4], [♥ 2], [♣ 1], [♥ 3]]
剩余的牌:
[[♦ 6], [♦ 13], [♣ 12], [♦ 12], [♣ 5], [♠ 4], [♣ 3], [♥ 7], [♦ 3], [♣ 2], [♠ 1], [♦ 2], [♥ 4], [♦ 8], [♠ 10], [♦ 11], [♥ 10], [♦ 7], [♣ 9], [♦
4], [♣ 8], [♣ 7], [♠ 8], [♦ 9], [♠ 12], [♠ 11], [♣ 11], [♦ 10], [♠ 5], [♠ 13], [♠ 9], [♠ 7], [♣ 6], [♣ 4], [♥ 2], [♣ 1], [♥ 3]]
A 手中的牌:
[[♥ 11], [♣ 10], [♦ 1], [♦ 5], [♠ 3]]
B 手中的牌:
[[♥ 6], [♥ 13], [♥ 9], [♥ 8], [♥ 5]]
C 手中的牌:
[[♣ 13], [♠ 2], [♥ 12], [♠ 6], [♥ 1]]
5.2 杨辉三角
杨辉三角
给定一个非负整数 numRows,生成「杨辉三角」的前 numRows 行。
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> generate(int numRows) {
List<List<Integer>> ret = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> list1 = new ArrayList<>();
list1.add(1);
ret.add(list1);
for(int i = 1; i < numRows ; i++){
List<Integer> curRow = new ArrayList<>();
curRow.add(1);
List<Integer> preRow = ret.get(i-1);
for(int j = 1;j<i;j++ ){
int val = preRow.get(j) + preRow.get(j-1);
curRow.add(val);
}
curRow.add(1);
ret.add(curRow);
}
return ret;
}
}
6. ArrayList的问题及思考
- ArrayList底层使用连续的空间,任意位置插入或删除元素时,需要将该位置后序元素整体往前或者往后搬移,故时间复杂度为O(N)
- 增容需要申请新空间,拷贝数据,释放旧空间。会有不小的消耗。
- 增容一般是呈2倍的增长,势必会有一定的空间浪费。例如当前容量为100,满了以后增容到200,我们再继续插入了5个数据,后面没有数据插入了,那么就浪费了95个数据空间。