一、前言
- REmote DIctionary Server(Redis)是一个由 Salvatore Sanfilippo 写的 key-value 存储系统,是跨平台的非关系型数据库。
- Redis 有三种集群模式:主从模式,Sentinel(哨兵)模式,Cluster 模式,这三种模式环境编排部署都会在本文章介绍与实战操作。
- 想了解更多关于 redis 概念与原理介绍,请参考我之前的博客:云原生之深入解析Redis的原理分析与环境部署。
- Redis 的相关资料:Redis。
二、Redis 主从模式编排部署实战操作
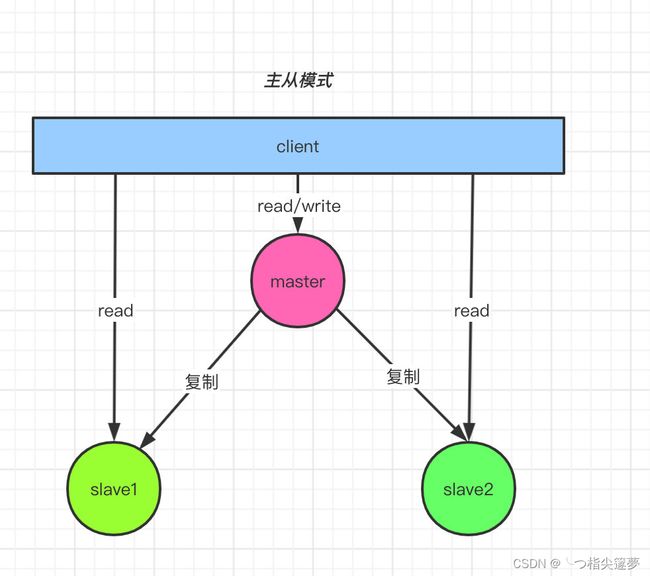
① 下载 chart 包
helm repo add bitnami https://charts.bitnami.com/bitnami
helm pull bitnami/redis --version 17.3.7
tar -xf redis-17.3.7.tgz
② 构建镜像
- 不重新构建镜像,只是把远程镜像 tag 一下,推到本地 harbor 仓库加速下载镜像:
docker pull docker.io/bitnami/redis:7.0.5-debian-11-r7
# tag
docker tag docker.io/bitnami/redis:7.0.5-debian-11-r7 myharbor.com/bigdata/redis:7.0.5-debian-11-r7
# 推送镜像到本地harbor仓库
docker push myharbor.com/bigdata/redis:7.0.5-debian-11-r7
③ 修改 yaml 编排
- redis/templates/master/pv.yaml,新增 pv.yaml 文件,内容如下:
{{- range .Values.master.persistence.local }}
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolume
metadata:
name: {{ .name }}
labels:
name: {{ .name }}
spec:
storageClassName: {{ $.Values.master.persistence.storageClass }}
capacity:
storage: {{ $.Values.master.persistence.size }}
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
local:
path: {{ .path }}
nodeAffinity:
required:
nodeSelectorTerms:
- matchExpressions:
- key: kubernetes.io/hostname
operator: In
values:
- {{ .host }}
---
{{- end }}
global:
redis:
password: "123456"
...
image:
registry: myharbor.com
repository: bigdata/redis
tag: 7.0. 5-debian-11-r7
master:
count: 1
persistence:
enabled: true
size: 8Gi
storageClass: "local-redis-storage"
local :
- name: redis-0
host: "local-168-182-110"
path: "/opt/bigdata/servers/redis/data/data1"
replica:
replicaCount: 2
persistence:
enabled: true
size: 8Gi
storageClass: "local-redis-storage "
local:
- name: redis-1
host: "local-168-182-111"
path: " /opt/bigdata/servers/redis/data/data1"
- name: redis-2
host: "local-168-182-112"
path: " /opt/bi gdata/servers/redis/data/data1"
④ 开始部署
#创建存储目录
mkdir /opt/bigdata/servers/redis/data/data1
#先检查语法
helm lint ./redis
#开始安装
helm install redis ./redis -n redis --create-namespace
REVISION: 1
TEST SUITE: None
NOTES:
CHART NAME: redis
CHART VERSION: 17.3.7
APP VERSION: 7.0.5
** Please be patient while the chart is being deployed **
Redis® can be accessed on the following DNS names from within your cluster:
redis-master .redis.svc.cluster. local for read/write operations (port 6379)
redis-replicas. redis.svc. cluster.local for read-only operations (port 6379)
Toget your password run:
export REDIS_ PASSWORD=$(kubectl get secret --namespace redis redis -o jsonpath="{data.redis-passwordf" | base64 -d)
To connect to your Redis® server:
1. Run a Redis® pod that you can use as a client:
kubectl run --namespace redis redis-client --restart='Never' --env REDIS_ PASSWORD=$REDIS_ PASSWORD --image myharbor.com/bigdata/redis:7.0.5-debian-11-r7 --command -- sleep infinity
Use the following command to attach to the pod:
kubectl exec --tty -i redis-client I
--namespace redis -- bash
2. Connect using the Redis® CLI:
REDISCLI_ AUTH=" $REDIS_ PASSWORD" redis-cli -h redis-master
REDISCLI_ AUTH=" $REDIS_ PASSWORD" redis-cli -h redis-replicas
To connect to your database from outside the cluster execute the following commands :
kubectl port-forward --namespace redis svc/redis-master 6379:6379 &
REDISCLI_ AUTH=" $REDIS_ PASSWORD" redis-cli -h 127.0.Ø.1 -p 6379
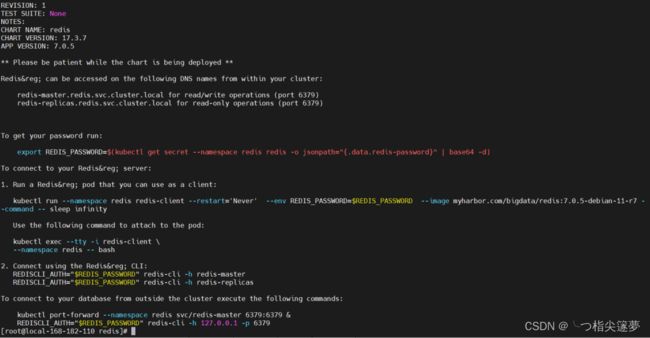
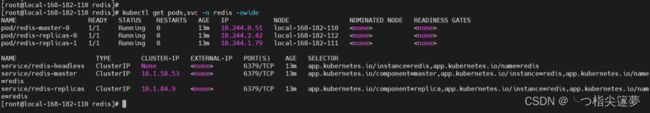
⑤ 测试验证
kubectl get pods,svc -n redis -owide
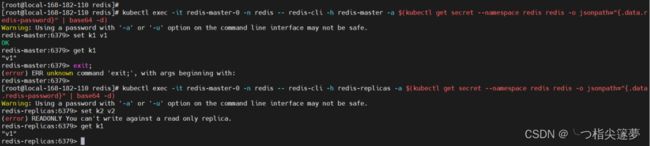
# 登录master,可读可写
kubectl exec -it redis-master-0 -n redis -- redis-cli -h redis-master -a $(kubectl get secret --namespace redis redis -o jsonpath="{.data.redis-password}" | base64 -d)
# 登录slave,只读
kubectl exec -it redis-master-0 -n redis -- redis-cli -h redis-replicas -a $(kubectl get secret --namespace redis redis -o jsonpath="{.data.redis-password}" | base64 -d)
⑥ 卸载
helm uninstall redis-sentinel -n redis-sentinel
# delete ns
kubectl delete ns redis-sentinel --force
# delete pv
kubectl delete pv `kubectl get pv|grep ^redis-|awk '{print $1}'` --force
rm -fr /opt/bigdata/servers/redis/data/data1/*
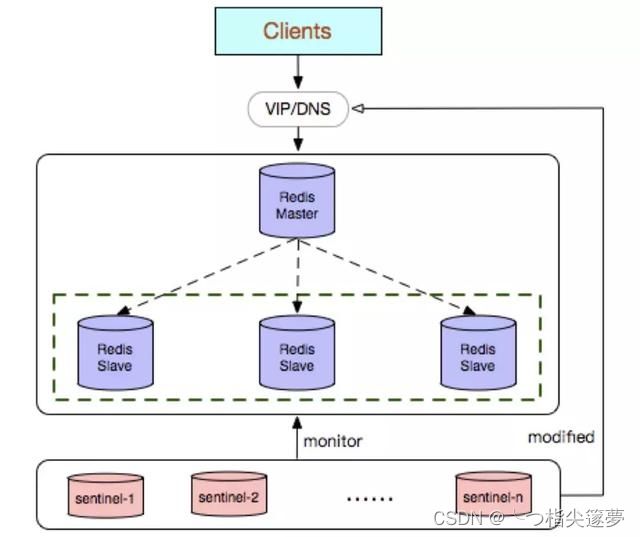
三、Redis 哨兵模式编排部署实战操作
- 主从模式的弊端就是不具备高可用性,当 master 挂掉以后,Redis 将不能再对外提供写入操作,因此 sentinel 应运而生。
① 构建镜像
- 这里重新构建镜像,也只是把远程的镜像推送到本地 harbor:
docker pull docker.io/bitnami/redis-sentinel:7.0.5-debian-11-r6
# tag
docker tag docker.io/bitnami/redis-sentinel:7.0.5-debian-11-r6 myharbor.com/bigdata/redis-sentinel:7.0.5-debian-11-r6
# push
docker push myharbor.com/bigdata/redis-sentinel:7.0.5-debian-11-r6
② 修改 yaml 编排:redis-sentinel/values.yaml
replica:
# replica. replicaCount与sentinel.quorumft一样
replicaCount: 3
storageClass: "local-redis-storage"
local :
- name: redis-0
host: "local-168-182-110"
path: "/opt/bigdata/servers/redis/data/data1"
- name: redis-1
host:
"local-168-182-111"
path: "/opt/bigdata/servers/redis/data/data1"
- name: redis-2
host:
"local-168-182-112"
path: "/opt/bigdata/servers/redis/data/data1"
sentinel:
enabled: true
image:
registry: myharbor.com
repository: bigdata/redis-sentinel
tag: 7.0.5-debian-11-r6
quorum: 3
- redis-sentinel/templates/replicas/pv.yaml,新增 pv.yaml 文件,内容如下:
{{- range .Values.master.persistence.local }}
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolume
metadata:
name: {{ .name }}
labels:
name: {{ .name }}
spec:
storageClassName: {{ $.Values.master.persistence.storageClass }}
capacity:
storage: {{ $.Values.master.persistence.size }}
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
local:
path: {{ .path }}
nodeAffinity:
required:
nodeSelectorTerms:
- matchExpressions:
- key: kubernetes.io/hostname
operator: In
values:
- {{ .host }}
---
{{- end }}
③ 开始部署
# 创建存储目录
mkdir -p /opt/bigdata/servers/redis/data/data1
helm install redis-sentinel ./redis-sentinel -n redis-sentinel --create-namespace
NAME: redis-sentinel
LAST DEPLOYED: Fri Nov 4 22:42:52 2023
NAMESPACE: redis-sentinel
STATUS: deployed
REVISION: 1
TEST SUITE: None
NOTES:
CHART NAME: redis
CHART VERSION: 17.3.7
APP VERSION: 7.0.5
** Please be patient while the chart is being deployed **
Redis® can be accessed via port 6379 on the following DNS name from within your cluster;
redis-sentinel.redis-sentinel.svc.cluster.local for read only operations
For read/write operations, first access the Redis® Sentinel cluster, which is available in port 26379 using the same domain name above.
To get your password run:
export REDIS_ _PASSWORD-$(kubectl get secret --namespace redis-sentinel redis-sentinel -O jsonpath="f.data.redis-password]" I base64 -d)
To connect to your Redis® server:
1. Run a Redis® pod that you can use as a client:
kubectl run --namespace redis-sentinel redis-client -- restart='Never' -env REDIS_ PASSWORD-=$REDIS_ PASSWORD -- image myharbor.com/bigdata/redis:7.0.5-debian-11-r7 --command -- sleep infinity
Use the following command to attach to the pod:
kubectl exec --tty -i redis-client \
-- namespace redis-sentinel -- bash
2. Connect using the Redis® CLI:
REDISCLI AUTH=" $REDIS_ PASSWORD" redis-cli -h redis-sentinel -p 6379 # Read only operations
REDISCLI_ AUTH=" $REDIS_ PASSWORD" redis-cli -h redis-sentinel -p 26379 # Sentinel access
To connect to your database from outside the cluster execute the fol lowing commands :
kubectl port-forward --namespace redis-sentinel svc/redis-sentinel 6379:6379 &
REDISCLI_AUTH=" $REDIS_PASSWORD" redis-cli -h 127.0.0.1 -p 6379
kubectl get pods,svc -n redis-sentinel -owide
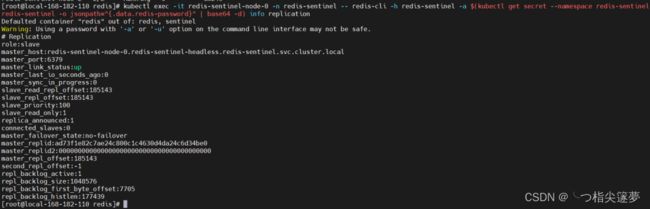
④ 模拟故障测试
# 查看
kubectl exec -it redis-sentinel-node-0 -n redis-sentinel -- redis-cli -h redis-sentinel -a $(kubectl get secret --namespace redis-sentinel redis-sentinel -o jsonpath="{.data.redis-password}" | base64 -d) info replication
kubectl delete pod redis-sentinel-node-0 -n redis-sentinel
- 再次查看 master 所在节点,master 节点已经切换到其它节点:
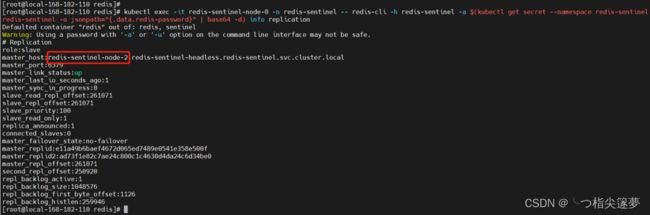
# 登录master节点
kubectl exec -it redis-sentinel-node-0 -n redis-sentinel -- redis-cli -h redis-sentinel-node-2.redis-sentinel-headless -a $(kubectl get secret --namespace redis-sentinel redis-sentinel -o jsonpath="{.data.redis-password}" | base64 -d)
# 登录slave节点
kubectl exec -it redis-sentinel-node-0 -n redis-sentinel -- redis-cli -h redis-sentinel-node-0.redis-sentinel-headless -a $(kubectl get secret --namespace redis-sentinel redis-sentinel -o jsonpath="{.data.redis-password}" | base64 -d)
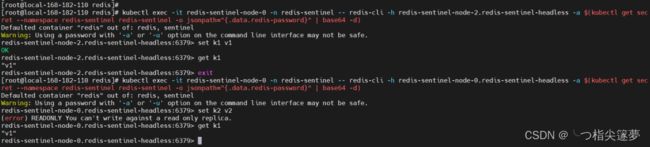
⑤ 卸载
helm uninstall redis-sentinel -n redis
# delete ns
kubectl delete ns redis --force
# delete pv
kubectl delete pv `kubectl get pv|grep ^redis-|awk '{print $1}'` --force
rm -fr /opt/bigdata/servers/redis/data/data1/*
四、Redis 集群模式编排部署实战操作
- 集群模式可以说是 sentinel+主从模式的结合体,通过 cluster 可以实现主从和 master 重选功能,所以如果配置两个副本三个分片的话,就需要六个 Redis 实例。因为 Redis 的数据是根据一定规则分配到 cluster 的不同机器的,当数据量过大时,可以新增机器进行扩容。
① 下载 chart 包
helm repo add bitnami https://charts.bitnami.com/bitnami
helm pull bitnami/redis-cluster --version 8.2.7
tar -xf redis-cluster-8.2.7.tgz
② 构建镜像
- 不重新构建镜像,只是把远程镜像 tag 一下,推到本地 harbor 仓库加速下载镜像:
docker pull docker.io/bitnami/redis-cluster:7.0.5-debian-11-r9
# tag
docker tag docker.io/bitnami/redis-cluster:7.0.5-debian-11-r9 myharbor.com/bigdata/redis-cluster:7.0.5-debian-11-r9
# 推送镜像到本地harbor仓库
docker push myharbor.com/bigdata/redis-cluster:7.0.5-debian-11-r9
③ 修改 yaml 编排
- redis-cluster/templates/pv.yaml,新增 pv.yaml 文件,内容如下:
{{- range .Values.master.persistence.local }}
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolume
metadata:
name: {{ .name }}
labels:
name: {{ .name }}
spec:
storageClassName: {{ $.Values.master.persistence.storageClass }}
capacity:
storage: {{ $.Values.master.persistence.size }}
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
local:
path: {{ .path }}
nodeAffinity:
required:
nodeSelectorTerms:
- matchExpressions:
- key: kubernetes.io/hostname
operator: In
values:
- {{ .host }}
---
{{- end }}
password: "123456"
...
image:
registry: myharbor . com
repository: bigdata/ redis-cluster
tag: 7. 0.5-debian-11-r9
...
persi stence:
storageClass: "local-redis-cluster- storage"
local:
- name: redis-cluster-0
host: "local-168 -182-110"
path: "/opt/bigdata/servers/redis-cluster/data/data1"
- name: redis-cluster-1
host: "local-168 -182-110"
path: " /opt/bigdata/servers/redis-cluster/data/data2"
- name: redis-cluster-2
host: "local-168-182-110"
path: "/opt/bigdata/servers/redis-cluster/data/data3"
- name: redis-cluster-3
host: "local-168-182-111"
path: " /opt/bigdata/servers/redis-cluster/data/data1"
- name: redis-cluster-4
host: "local-168-182-111"
path: " /opt/bigdata/servers/redis-cluster/data/data2"
- name: redis-cluster-5
host: "local-168 -182-111 "
path: "/opt/bigdata/servers/redis-cluster/data/data3"
- name: redis-cluster-6
host: "local-168 -182-112"
path: "/opt/bigdata/servers/redis-cluster/data/data1"
- name: redis-cluster-7
host: "local-168-182-112"
path: " /opt/bigdata/servers/redis-cluster/data/data2"
- name: redis-cluster-8
host: "local-168- 182- 112"
path: "/opt/bigdata/servers/redis-cluster/data/data3"
cluster:
init:
true
#一主两从(三组)
nodes: 9
replicas: 2
④ 开始部署
#创建存储目录
mkdir -p /opt/bigdata/ servers/ redis-cluster/ data/ dataf1. .3]
helm install redis-cluster ./redis-cluster -n redis-cluster --create-namespace
NOTES:
CHART NAME: redis-cluster
CHART VERSION: 8.2.7
APP VERSION: 7.0.5** Please be patient while the chart is being deployed **
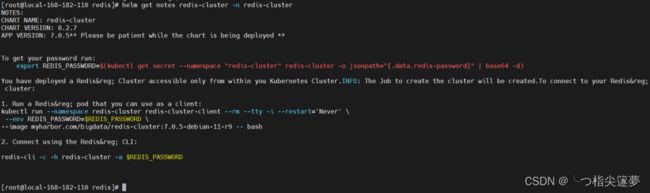
To get your password run:
export REDIS_ PAS SWORD-$( kubectl get secret -- namespace " redis-cluster" redis-cluster -O jsonpath-"f . data. redis-passwordf" I base64 -d)
You have deployed a Redi s® Cluster accessible only from within you Kubernetes Cluster.INFO: The job to creat the cluster will be creates. to connnet to your Redis&red;
1. Run a Redis® pod that you can use as a client:
kubectl run --namespace redis-cluster redis-cluster-client --rm --tty -i --restart='Never' \
-- env REDIS_ PASSWORD-$REDIS_ PASSWORD \
--image myharbor . com/bi gdata/ redis-cluster :7.0.5-debian-11-r9 -- bash
2. Connect using the Redis® CLI:
redis-cli -C -h redis-cluster -a $REDIS_ PASSWORD
kubectl getpods,svc -n redis-cluster -owide
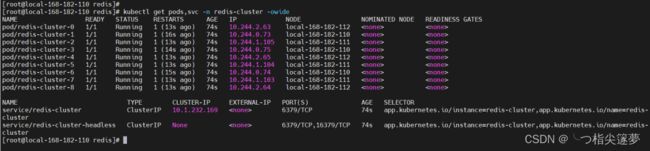
⑤ 故障测试
kubectl exec -it redis-cluster-0 -n redis-cluster -- redis-cli -c -h redis-cluster -a $(kubectl get secret --namespace "redis-cluster" redis-cluster -o jsonpath="{.data.redis-password}" | base64 -d) CLUSTER INFO
kubectl exec -it redis-cluster-0 -n redis-cluster -- redis-cli -c -h redis-cluster -a $(kubectl get secret --namespace "redis-cluster" redis-cluster -o jsonpath="{.data.redis-password}" | base64 -d) CLUSTER NODES
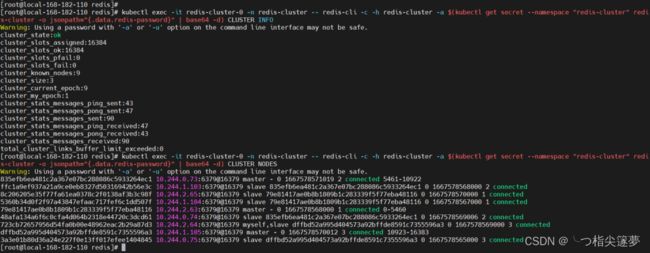
kubectl delete pod redis-cluster-1 -n redis-cluster
#再查看节点情况
kubectl exec -it redis-cluster-0 -n redis-cluster -- redis-cli -C -h redis-cluster -a $(kubectl get secret --namespace "redis-cluster" redis-cluster -o j sonpath="{.data.redis-password}" | base64 -d) CLUSTER NODES
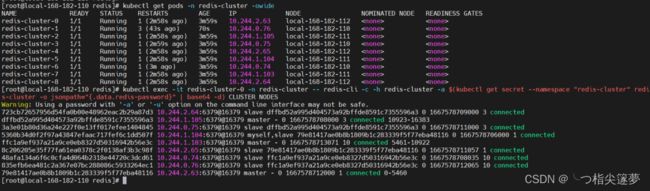
⑥ 卸载
helm uninstall redis-cluster -n redis-cluster
# delete ns
kubectl delete ns redis-cluster --force
# delete pv
kubectl delete pv `kubectl get pv|grep ^redis-cluster-|awk '{print $1}'` --force
rm -fr /opt/bigdata/servers/redis-cluster/data/data{1..3}/*














