Hadoop源码阅读(二):DataNode启动
说明:
1.Hadoop版本:3.1.3
2.阅读工具:IDEA 2023.1.2
3.源码获取:Index of /dist/hadoop/core/hadoop-3.1.3 (apache.org)
4.工程导入:下载源码之后得到hadoop-3.1.3-src.tar.gz压缩包,在当前目录打开PowerShell,使用tar -zxvf指令解压即可,然后使用IDEA打开hadoop-3.1.3-src文件夹,要注意配置好Maven或Gradle仓库,否则jar包导入会比较慢
5.参考课程:尚硅谷大数据Hadoop教程,hadoop3.x搭建到集群调优,百万播放_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
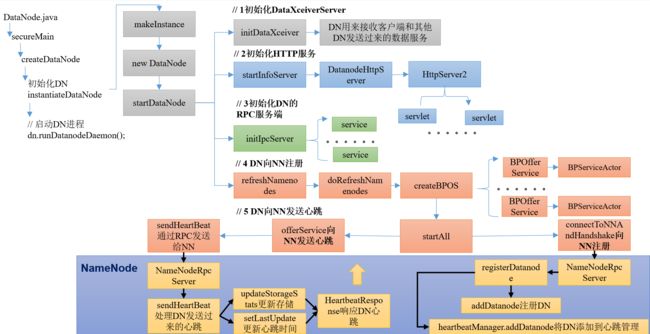
ctrl + n 全局查找datanode,进入DataNode.java
官方对其介绍如下:
/**********************************************************
* DataNode is a class (and program) that stores a set of
* blocks for a DFS deployment. A single deployment can
* have one or many DataNodes. Each DataNode communicates
* regularly with a single NameNode. It also communicates
* with client code and other DataNodes from time to time.
*
* DataNodes store a series of named blocks. The DataNode
* allows client code to read these blocks, or to write new
* block data. The DataNode may also, in response to instructions
* from its NameNode, delete blocks or copy blocks to/from other
* DataNodes.
*
* The DataNode maintains just one critical table:
* block-> stream of bytes (of BLOCK_SIZE or less)
*
* This info is stored on a local disk. The DataNode
* reports the table's contents to the NameNode upon startup
* and every so often afterwards.
*
* DataNodes spend their lives in an endless loop of asking
* the NameNode for something to do. A NameNode cannot connect
* to a DataNode directly; a NameNode simply returns values from
* functions invoked by a DataNode.
*
* DataNodes maintain an open server socket so that client code
* or other DataNodes can read/write data. The host/port for
* this server is reported to the NameNode, which then sends that
* information to clients or other DataNodes that might be interested.
*
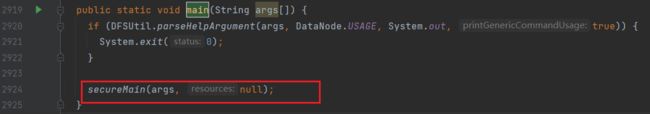
**********************************************************/找到main方法
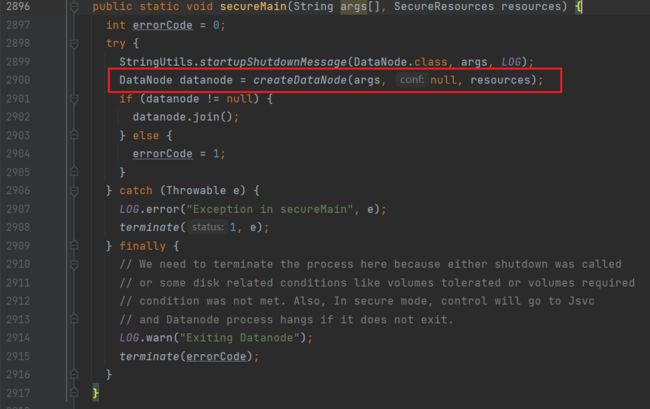
进入secureMain方法:
进入createDataNode方法:
- 进入
instantiateDataNode方法(初始化DN):
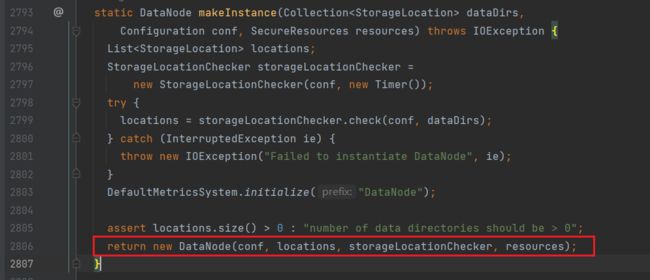
进入makeInstance方法(实例化对象):
进入DataNode类:
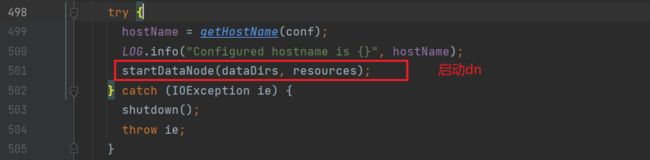
进入startDataNode方法,之后进行DN启动的一系列操作;
1.初始化DataXceiverServer(initDataXceiver)
在startDataNode方法中:
进入initDataXceiver方法:
dataXceiverServer是一个服务(线程),DN利用该服务来接收客户端和其他DN发送过来的数据服务
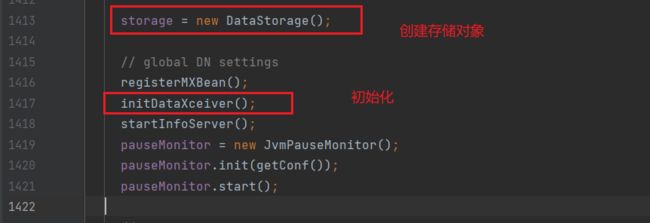
2.初始化HTTP服务(startInfoServer)
在startDataNode方法中:
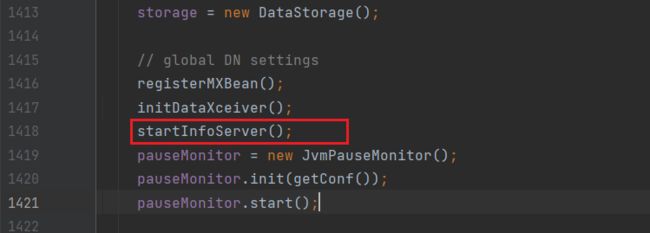
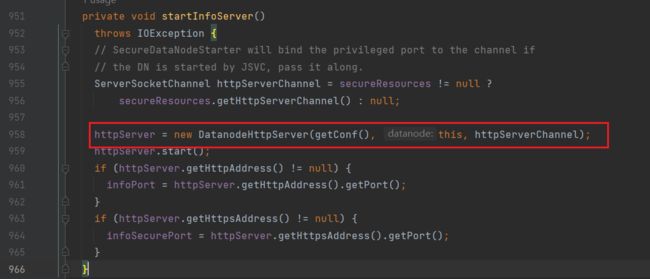
进入startInfoServer方法,实例化了一个httpserver
进入DatanodeHttpServer类:(DatanodeHttpServer.java)
也是通过builder构建了一个HTTP server
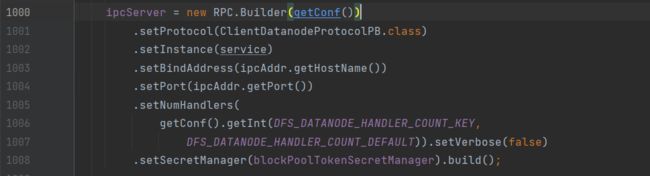
3.初始化RPC服务器(initIpcServer)
在startDataNode方法中:
进入initIpcServer,构建RPC服务器
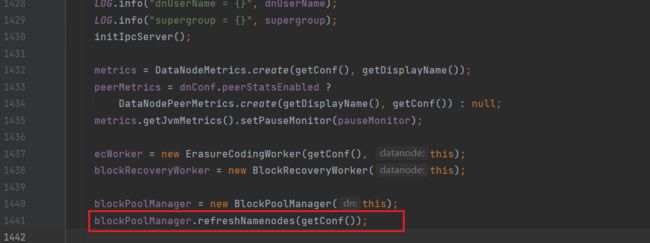
4.向NameNode注册(refreshNamenodes)
在startDataNode方法中:
进入refreshNamenodes(BlockPoolManager.java)
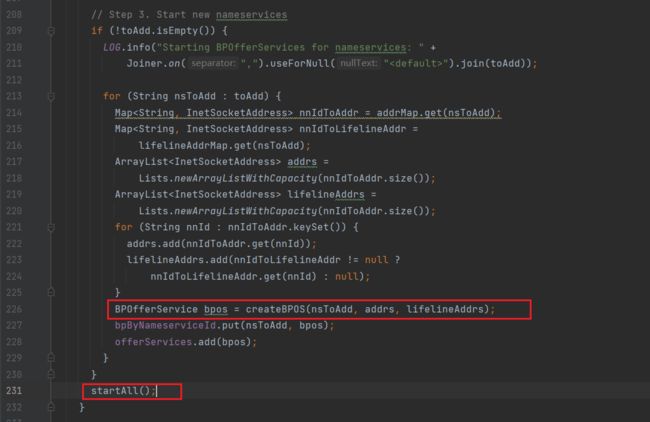
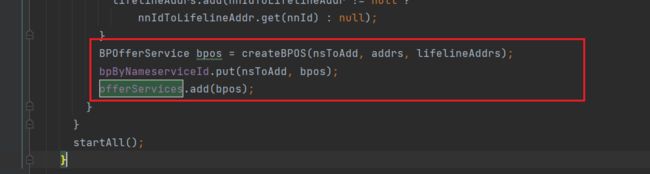
进入doRefreshNamenodes方法:
先是创建BPOS,然后启动所有的BPOS
- 接下来进入
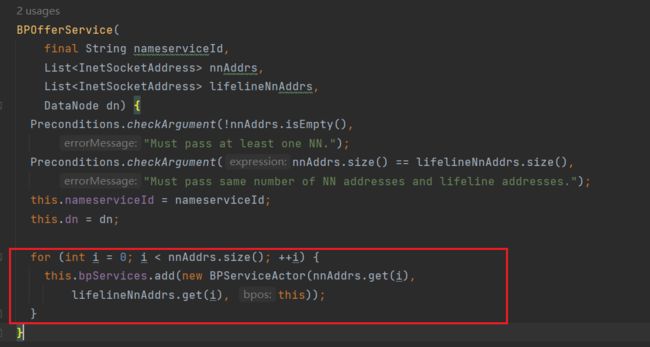
createBPOS方法
可以看到根据NameNode个数创建对应的服务:
有多少个NN就创建多少个对应的服务
- 进入
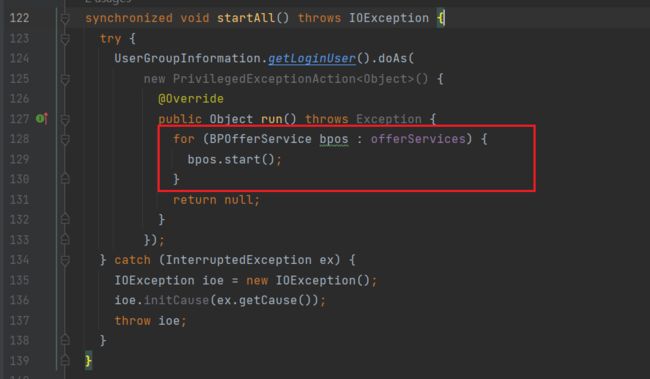
startAll方法
可以看到,遍历了所有的bpos,依次进行启动
这里的offerServices是存储所有通过createBPOS方法创建的bpos的集合:
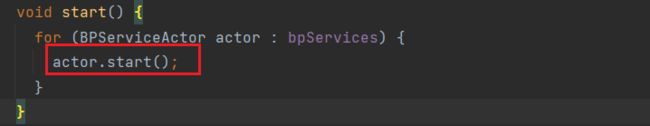
进入bpos.start()方法:
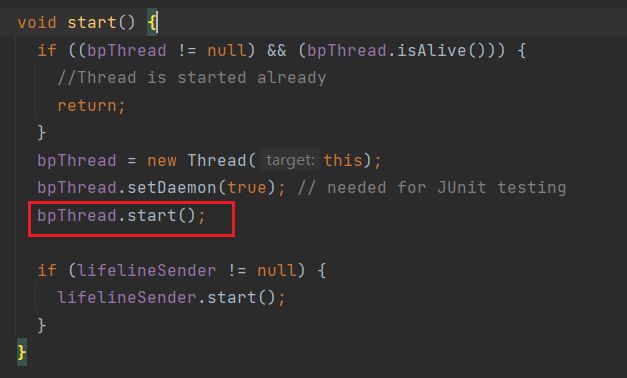
继续进入:
看到bpThread,表示开启一个线程,因此查找其run方法
可以看到通过connectToNNAndHandshake方法向NN进行注册:
- 通过
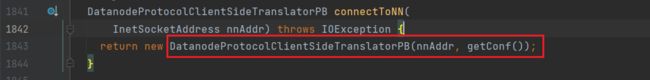
connectToNN方法来获取NN的RPC客户端对象,进入该方法:
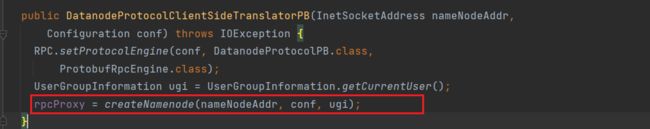
进入DatanodeProtocolClientSideTranslatorPB:
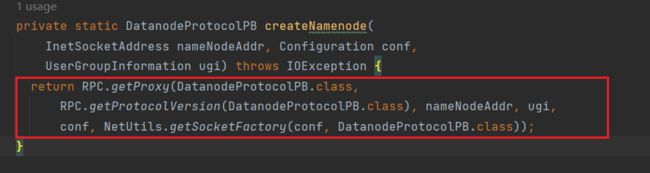
通过createNamenode方法来创建NN的RPC代理:
- 通过
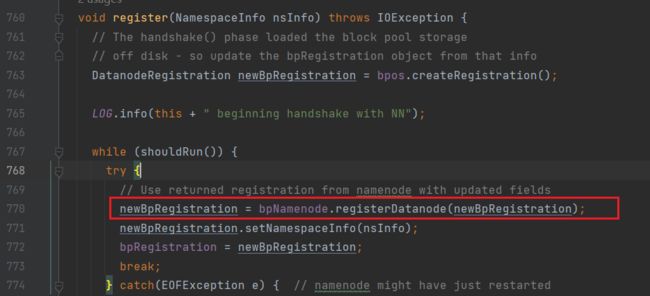
register方法来向NN进行注册:
通过bpNamenode.registerDatanode将注册信息发送给NN(bpNamenode即创建的NN RPC proxy)
注意:这里的registerDatanode方法,由DN调用,但执行在NN
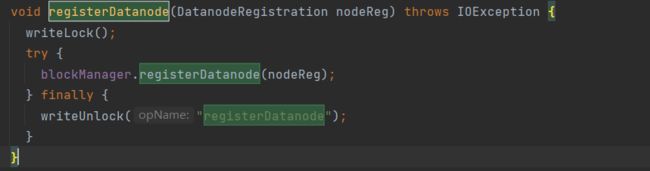
去FSNamesystem中查找:
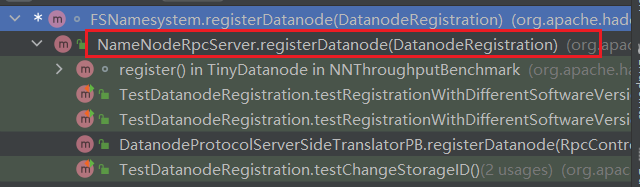
ctrl+alt+h查看该方法的调用:
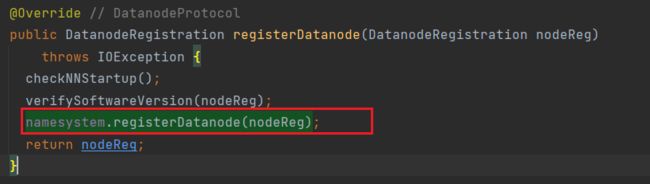
于是到NameNodeRpcServer中去查找:
可以看到,DN的信息向NN注册这一步骤是在该方法中完成的;
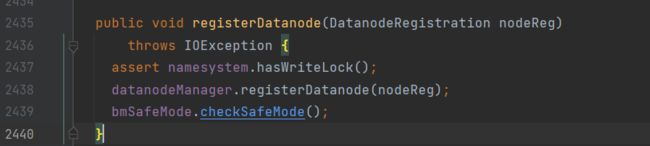
接下来回到FSNamesystem中,进入blockManager.registerDatanode方法:
进入datanodeManager.registerDatanode:(DatanodeManager.java)
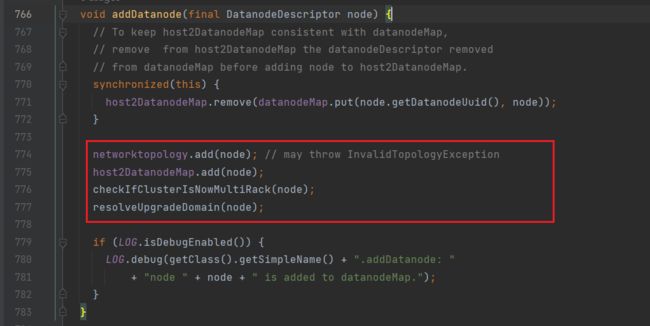
进入addDatanode
5.向NameNode发送心跳
回到startAll方法,再向前进入到BPServiceActor.java中的run方法
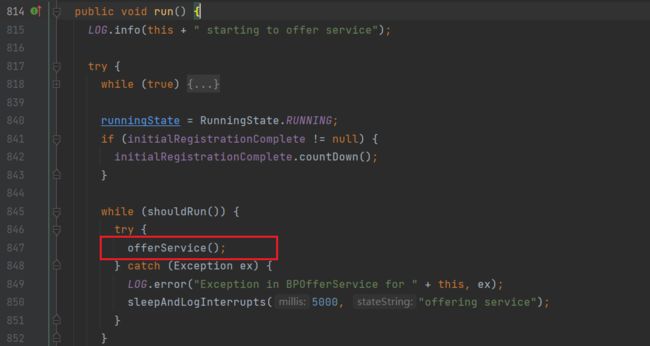
找到其中的offerService方法
进入offerService方法:
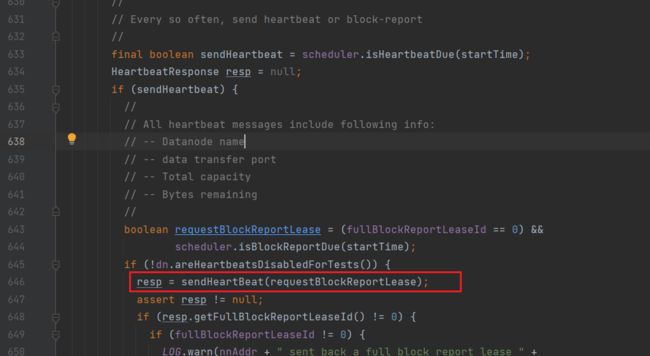
进入sendHeartBeat方法:
这里的bpNamenode是在connectToNNAndHandshake方法中获取到的NN的代理
因此该方法实际上是通过NN的RPC客户端将心跳信息发送给NN
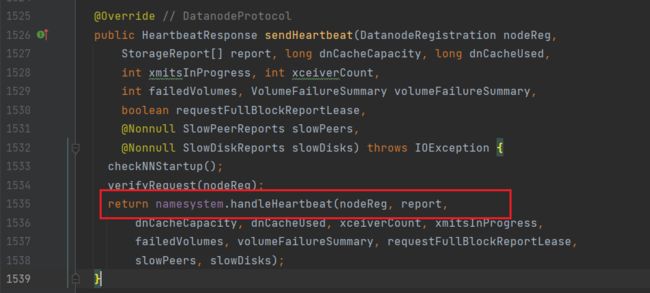
因此该方法实际的实现是在NN中,因此在NameNodeRpcServer.java中搜索sendHeartbeat:
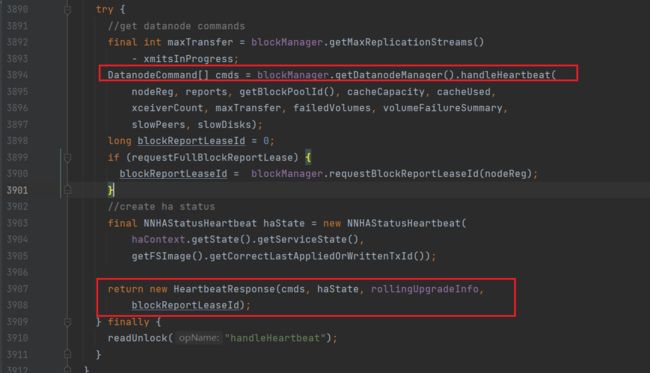
通过handleHeartbeat来处理DN的心跳信息,进入该方法:
处理DN发送过来的心跳并作出相应;
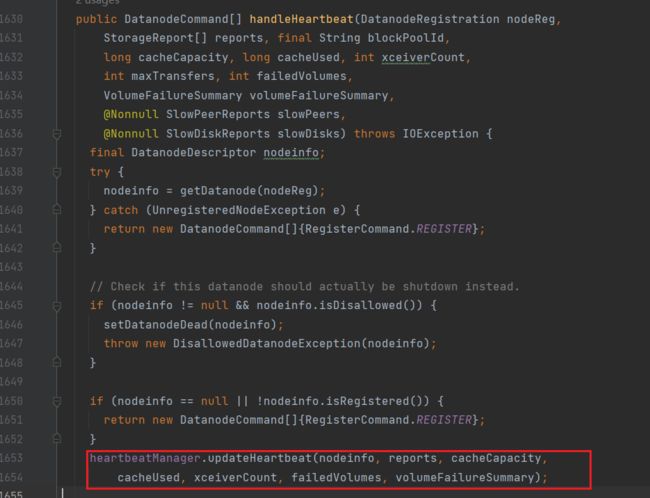
继续进入handleHeartbeat方法:(DatanodeManager.java)
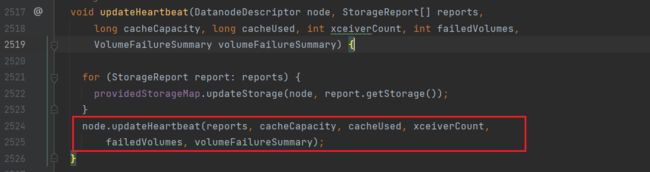
通过updateHeartbeat方法来更新心跳信息,进入该方法:(HeartbeatManager.java)
再次进入:(BlockManager.java)
继续进入:(DatanodeDescriptor.java)
进入updateHeartbeatState方法: