VPP启动流程分析
今天我们介绍一下VPP的启动流程。如果把vpp看成一个应用程序,那么他是怎么工作的呢:
首先,vpp有许多插件so,每个插件下面有许多node,比如我们如果要新加一个功能为ip地址过滤,那么我们其实就是加一个node,当数据经过node时,调用我们提前注册的function函数就实现了我们的功能。接下来就理一下vpp从启动后到node生效的过程是怎样的。
开始之前先说下DPDK是怎么和vpp交互的。从vpp看来,dpdk就是一个插件,只不过这个插件运行得比较靠前,当数据包到来之后,dpdk将其收到rte_mbuf中,后面再将rte_mbuf转化为vlib_buf,后面的node就是从vlib_buf中取出数据再来处理,简单讲下rte_mbuf和vlib_buf的关系,以及他们是如何转化的:
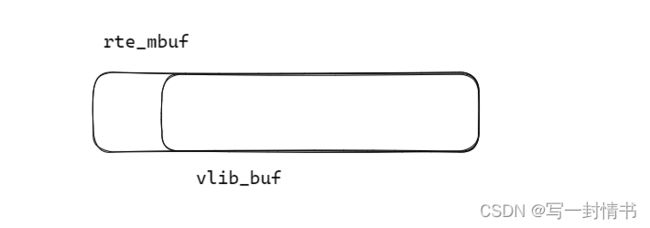
#define rte_mbuf_from_vlib_buffer(x) (((struct rte_mbuf *)x) - 1)
#define vlib_buffer_from_rte_mbuf(x) ((vlib_buffer_t *)(x+1))
这两个宏定义用于在vlib buffer和DPDK的rte_mbuf之间进行转换。rte_mbuf 是DPDK中用于表示数据包的结构体,而 vlib_buffer_t 是VPP中用于表示数据包的结构体。以下是对这两个宏的解释:
rte_mbuf_from_vlib_buffer(x): 这个宏将一个 vlib_buffer_t 转换成对应的 rte_mbuf。vlib_buffer_t 中的数据的指针指向 rte_mbuf 的后一个字节,所以通过将 x 强制转换为 struct rte_mbuf *,然后减去1,就可以得到对应的 rte_mbuf。
vlib_buffer_from_rte_mbuf(x): 这个宏将一个 rte_mbuf 转换成对应的 vlib_buffer_t。由于上面的宏中的指针偏移关系,将 x 强制转换为 vlib_buffer_t * 之后,可以得到指向 vlib_buffer_t 数据部分的指针
VPP 初始化
初始化里面主要做了四件事
1、load so //加载静态库
2、register node //注册处理节点
3、function init (cmd init,feture init) //注册处理函数
先上个伪代码简单看下流程
int main(){
//VPP 程序的入口函数,它初始化全局状态、配置、插件以及其他运行时环境,并最终进入主循环以运行网络处理和其他功能
vlib_unix_main();
//执行了插件的早期初始化,设置了插件路径、日志等,并准备加载新的插件
vlib_plugin_early_init();
//加载新插件,并进行相应的管理和处理,确保只加载有效的插件,并进行了排序、覆盖等操作
vlib_load_new_plugins();
//加载插件并进行一系列的检查,确保插件可以正确加载和初始化
load_one_plugin();
//通过协程跳转到thread0执行
clib_calljmp();
//线程函数,作为独立线程的入口点
thread0();
//各种初始化操作,调用初始化函数、配置函数、主循环函数、以及一系列的清理操作
vlib_main();
//调用所有初始化函数
vlib_call_all_init_functions();
vlib_call_init_exit_functions
//遍历所有的节点注册(node_registrations 链表),并将这些注册的节点全部注册到 VLIB 中
vlib_register_all_static_nodes();
//
vlib_main_loop (vm);
//VLIB 主循环或工作线程循环的核心部分。它处理节点的调度和执行,以及一些循环计数和时间间隔的计算
vlib_main_or_worker_loop (vm, /* is_main */ 1);
//负责管理进程的调度、执行和暂停等。根据进程的状态和标志,它会判断是否继续执行进程,
//启动定时器等。执行完毕后,会更新性能计数器、事件日志以及进程的统计信息
dispatch_process();
//责将进程切换到新的堆栈并执行其启动函数
vlib_process_startup
//进程启动的具体逻辑,包括在进程的堆栈上调用进程函数并处理返回值
vlib_process_bootstrap
// 这里就调用到了我们注册一个node之后,真正的处理函数
n = node->function (vm, node, f);
}
接下来对上面伪代码中的函数进行详细分析下:
从main函数开始,main函数中其实都是配置和初始化VPP环境的相关东西,大概就是下面这样:
int main(){
//创建主堆,使用了之前设置的 main_heap_size 和 main_heap_log2_page_sz
main_heap = clib_mem_init_with_page_size(main_heap_size, main_heap_log2_page_sz);
//初始化VLIB库,初始化VPE(VPP Environment)库
//将一个VLIB主要实例传递给了 vpe_main_init() 函数,以便VPE库能够与VLIB库进行集成
vlib_main_init();
vpe_main_init(vlib_get_first_main());
//进入VLIB的主循环并开始执行网络处理程序。这是整个程序的核心部分,处理数据包、事件和各种网络功能
return vlib_unix_main(argc, argv);
}
vlib_unix_main函数解析:
int
vlib_unix_main (int argc, char *argv[])
{
//初始化时间库
clib_time_init (&vm->clib_time);
//初始化并启用事件日志,用于记录系统中的事件
elog_init (vlib_get_elog_main (), vgm->configured_elog_ring_size);
elog_enable_disable (vlib_get_elog_main (), 1);
//初始化插件的配置,通过调用插件的配置函数来加载和处理插件特定的配置信息
if ((e = vlib_plugin_config (vm, &input)))
{
clib_error_report (e);
return 1;
}
unformat_free (&input);
//这里是各种so插件初始化的地方
i = vlib_plugin_early_init (vm);
if (i)
return i;
//调用注册的配置函数,这些函数在插件中注册,用于配置程序的各种功能
e = vlib_call_all_config_functions (vm, &input, 1 /* early */ );
if (e != 0)
{
clib_error_report (e);
return 1;
}
unformat_free (&input);
//加载 ELF 格式文件的符号,用于处理信号处理程序和内存分配追踪
clib_elf_main_init (vgm->exec_path);
vec_validate (vlib_thread_stacks, 0);
vlib_thread_stack_init (0);
__os_thread_index = 0;
vm->thread_index = 0;
//启动主循环,将堆栈切换到主线程的堆栈,然后使用 clib_calljmp 调用主循环
vlib_process_start_switch_stack (vm, 0);
i = clib_calljmp (thread0, (uword) vm,
(void *) (vlib_thread_stacks[0] +
VLIB_THREAD_STACK_SIZE));
return i;
}
这里我们再看看插件是如何被加载的,通过vlib_plugin_early_init
int
vlib_plugin_early_init (vlib_main_t * vm)
{
plugin_main_t *pm = &vlib_plugin_main;
pm->logger =
vlib_log_register_class_rate_limit ("plugin", "load",
0x7FFFFFFF /* aka no rate limit */ );
//如果插件路径未设置,则使用默认的插件路径 vlib_plugin_path
if (pm->plugin_path == 0)
pm->plugin_path = format (0, "%s", vlib_plugin_path);
//如果有额外的插件路径附加,将其添加到插件路径中
if (pm->plugin_path_add)
pm->plugin_path = format (pm->plugin_path, ":%s", pm->plugin_path_add);
//在插件路径的末尾添加一个 null 字节,以便可以在字符串中找到插件路径的终止
pm->plugin_path = format (pm->plugin_path, "%c", 0);
PLUGIN_LOG_DBG ("plugin path %s", pm->plugin_path);
//创建两个哈希表,用于存储插件的信息和覆盖信息
pm->plugin_by_name_hash = hash_create_string (0, sizeof (uword));
pm->plugin_overrides_by_name_hash = hash_create_string (0, sizeof (uword));
//设置插件主结构体的 vlib_main 字段,以指向 VLIB 主结构体
pm->vlib_main = vm;
//加载新的插件
return vlib_load_new_plugins (pm, 1 /* from_early_init */ );
}
插件的加载就是vlib_load_new_plugins 函数,它做了哪些事呢:加载新插件,并进行相应的管理和处理,确保只加载有效的插件,并进行了排序、覆盖等操作。我们如果自己新定制了plugin插件,也是在这里处理
int
vlib_load_new_plugins (plugin_main_t * pm, int from_early_init)
{
DIR *dp;
struct dirent *entry;
struct stat statb;
uword *p;
plugin_info_t *pi;
u8 **plugin_path;
uword *not_loaded_indices = 0;
int i;
//根据插件路径字符串生成一个字符串数组,每个元素表示一个路径
plugin_path = split_plugin_path (pm);
for (i = 0; i < vec_len (plugin_path); i++)
{
dp = opendir ((char *) plugin_path[i]);
if (dp == 0)
continue;
//遍历插件路径数组,打开每个路径对应的目录,并遍历目录中的每个文件项
while ((entry = readdir (dp)))
{
u8 *plugin_name;
u8 *filename;
//如果设置了插件名过滤,将会检查文件名是否满足过滤条件。如果不满足,则跳过当前文件项
if (pm->plugin_name_filter)
{
int j;
for (j = 0; j < vec_len (pm->plugin_name_filter); j++)
if (entry->d_name[j] != pm->plugin_name_filter[j])
goto next;
}
//检查文件的扩展名是否是 .so,并且通过 stat 函数检查文件是否可读
filename = format (0, "%s/%s%c", plugin_path[i], entry->d_name, 0);
char *ext = strrchr ((const char *) filename, '.');
/* unreadable */
if (!ext || (strcmp (ext, ".so") != 0) ||
stat ((char *) filename, &statb) < 0)
{
ignore:
vec_free (filename);
continue;
}
/* 检查文件是否是一个常规文件,即普通文件,而不是目录或其他类型的文件 */
if (!S_ISREG (statb.st_mode))
goto ignore;
//如果文件是有效的插件文件,将其信息添加到插件信息数组中,并在哈希表中建立插件名称到插件信息的映射
plugin_name = format (0, "%s%c", entry->d_name, 0);
p = hash_get_mem (pm->plugin_by_name_hash, plugin_name);
if (p == 0)
{
/* No, add it to the plugin vector */
vec_add2 (pm->plugin_info, pi, 1);
pi->name = plugin_name;
pi->filename = filename;
pi->file_info = statb;
pi->handle = 0;
hash_set_mem (pm->plugin_by_name_hash, plugin_name,
pi - pm->plugin_info);
}
next:
;
}
closedir (dp);
vec_free (plugin_path[i]);
}
vec_free (plugin_path);
/*
根据插件名称对插件信息数组进行排序,确保插件按照名称的字典顺序排列
*/
vec_sort_with_function (pm->plugin_info, plugin_name_sort_cmp);
/*
遍历插件信息数组,并尝试加载每个插件,如果加载失败,则记录下来
*/
for (i = 0; i < vec_len (pm->plugin_info); i++)
{
pi = vec_elt_at_index (pm->plugin_info, i);
if (load_one_plugin (pm, pi, from_early_init))
{
/* Make a note of any which fail to load */
vec_add1 (not_loaded_indices, i);
}
}
/*
处理未能成功加载的插件,以及通过覆盖列表进行覆盖的插件
*/
for (i = 0; i < vec_len (pm->plugin_info); i++)
{
uword *p;
pi = vec_elt_at_index (pm->plugin_info, i);
p = hash_get_mem (pm->plugin_overrides_by_name_hash, pi->name);
/* Plugin overridden? */
if (p)
{
PLUGIN_LOG_NOTICE ("Plugin '%s' overridden by '%s'", pi->name,
p[0]);
vec_add1 (not_loaded_indices, i);
}
}
/*
删除未加载的插件信息,并对插件信息数组进行调整
*/
vec_sort_with_function (not_loaded_indices, index_cmp);
for (i = 0; i < vec_len (not_loaded_indices); i++)
{
if (i < vec_len (not_loaded_indices) - 1)
{
if (not_loaded_indices[i + 1] == not_loaded_indices[i])
{
vec_delete (not_loaded_indices, 1, i);
i--;
}
}
}
/* Remove plugin info vector elements corresponding to load failures */
if (vec_len (not_loaded_indices) > 0)
{
for (i = vec_len (not_loaded_indices) - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
pi = vec_elt_at_index (pm->plugin_info, not_loaded_indices[i]);
hash_unset_mem (pm->plugin_by_name_hash, pi->name);
if (pi->handle)
{
dlclose (pi->handle);
PLUGIN_LOG_NOTICE ("Unloaded plugin: %s", pi->name);
}
vec_free (pi->name);
vec_free (pi->filename);
vec_delete (pm->plugin_info, 1, not_loaded_indices[i]);
}
vec_free (not_loaded_indices);
}
/* Recreate the plugin name hash */
hash_free (pm->plugin_by_name_hash);
pm->plugin_by_name_hash = hash_create_string (0, sizeof (uword));
重新创建插件名称哈希表,以反映加载成功的插件信息
for (i = 0; i < vec_len (pm->plugin_info); i++)
{
pi = vec_elt_at_index (pm->plugin_info, i);
hash_set_mem (pm->plugin_by_name_hash, pi->name, pi - pm->plugin_info);
}
return 0;
}
接下来看是怎么加载一个插件的load_one_plugin
static int
load_one_plugin (plugin_main_t * pm, plugin_info_t * pi, int from_early_init)
{
void *handle;
int reread_reg = 1;
clib_error_t *error;
elf_main_t em = { 0 };
elf_section_t *section;
u8 *data;
char *version_required;
vlib_plugin_registration_t *reg;
vlib_plugin_r2_t *r2;
plugin_config_t *pc = 0;
uword *p;
//使用 ELF 解析库读取插件文件,将文件内容解析为 ELF 结构
if (elf_read_file (&em, (char *) pi->filename))
return -1;
检查是否存在新的插件注册结构,如果存在,将解析该结构并进行处理
error = elf_get_section_by_name (&em, ".vlib_plugin_r2", §ion);
if (error == 0)
{
data = elf_get_section_contents (&em, section->index, 1);
r2 = (vlib_plugin_r2_t *) data;
reg = clib_mem_alloc (sizeof (*reg));
memset (reg, 0, sizeof (*reg));
reg->default_disabled = r2->default_disabled != 0;
error = r2_to_reg (&em, r2, reg);
if (error)
{
PLUGIN_LOG_ERR ("Bad r2 registration: %s\n", (char *) pi->name);
return -1;
}
if (pm->plugins_default_disable)
reg->default_disabled = 1;
reread_reg = 0;
goto process_reg;
}
else
clib_error_free (error);
//检查是否存在老版本的插件注册结构,如果不存在,则表示不是一个有效的插件
error = elf_get_section_by_name (&em, ".vlib_plugin_registration",
§ion);
if (error)
{
PLUGIN_LOG_ERR ("Not a plugin: %s\n", (char *) pi->name);
return -1;
}
//处理插件注册结构,检查大小是否匹配,并根据需要进行默认禁用
data = elf_get_section_contents (&em, section->index, 1);
reg = (vlib_plugin_registration_t *) data;
if (vec_len (data) != sizeof (*reg))
{
PLUGIN_LOG_ERR ("vlib_plugin_registration size mismatch in plugin %s\n",
(char *) pi->name);
goto error;
}
if (pm->plugins_default_disable)
reg->default_disabled = 1;
process_reg:
//根据插件名称在配置信息中查找是否需要禁用插
p = hash_get_mem (pm->config_index_by_name, pi->name);
if (p)
{
pc = vec_elt_at_index (pm->configs, p[0]);
if (pc->is_disabled)
{
PLUGIN_LOG_NOTICE ("Plugin disabled: %s", pi->name);
goto error;
}
if (reg->default_disabled && pc->is_enabled == 0)
{
PLUGIN_LOG_NOTICE ("Plugin disabled (default): %s", pi->name);
goto error;
}
}
else if (reg->default_disabled)
{
PLUGIN_LOG_NOTICE ("Plugin disabled (default): %s", pi->name);
goto error;
}
//检查插件所需的版本是否与应用版本匹配
version_required = str_array_to_vec ((char *) ®->version_required,
sizeof (reg->version_required));
if ((strlen (version_required) > 0) &&
(strncmp (vlib_plugin_app_version, version_required,
strlen (version_required))))
{
PLUGIN_LOG_ERR ("Plugin %s version mismatch: %s != %s",
pi->name, vlib_plugin_app_version,
reg->version_required);
if (!(pc && pc->skip_version_check == 1))
{
vec_free (version_required);
goto error;
}
}
处理当前插件覆盖的其他插件,记录覆盖关系
if (reg->overrides[0])
{
const char *overrides = reg->overrides;
u8 *override_name_copy, *overridden_by_name_copy;
u8 *sp, *ep;
uword *p;
sp = ep = (u8 *) overrides;
while (1)
{
if (*sp == 0
|| (sp >= (u8 *) overrides + ARRAY_LEN (reg->overrides)))
break;
if (*sp == ' ' || *sp == ',')
{
sp++;
continue;
}
ep = sp;
while (*ep && *ep != ' ' && *ep != ',' &&
ep < (u8 *) overrides + ARRAY_LEN (reg->overrides))
ep++;
if (*ep == ' ' || *ep == ',')
ep--;
override_name_copy = extract (sp, ep);
p = hash_get_mem (pm->plugin_overrides_by_name_hash,
override_name_copy);
/* Already overridden... */
if (p)
vec_free (override_name_copy);
else
{
overridden_by_name_copy = format (0, "%s%c", pi->name, 0);
hash_set_mem (pm->plugin_overrides_by_name_hash,
override_name_copy, overridden_by_name_copy);
}
sp = *ep ? ep + 1 : ep;
}
}
vec_free (version_required);
//使用 dlopen 函数加载插件的动态库,返回句柄
handle = dlopen ((char *) pi->filename,
RTLD_LAZY | (reg->deep_bind ? RTLD_DEEPBIND : 0));
if (handle == 0)
{
PLUGIN_LOG_ERR ("%s", dlerror ());
PLUGIN_LOG_ERR ("Failed to load plugin '%s'", pi->name);
goto error;
}
pi->handle = handle;
/*dlsym 函数用于从已加载的共享库中获取一个符号的地址,该符号代表了一个结构体,
其中包含了插件的注册信息。插件在加载时,通常会在共享库中定义一个名为
"vlib_plugin_registration" 的全局变量,该变量包含了插件的配置和信息*/
if (reread_reg)
reg = dlsym (pi->handle, "vlib_plugin_registration");
pi->reg = reg;
pi->version = str_array_to_vec ((char *) ®->version,
sizeof (reg->version));
//如果插件指定了早期初始化函数,调用该函数进行初始化
if (reg->early_init)
{
clib_error_t *(*ei) (vlib_main_t *);
void *h;
h = dlsym (pi->handle, reg->early_init);
if (h)
{
ei = h;
error = (*ei) (pm->vlib_main);
if (error)
{
u8 *err = format (0, "%s: %U%c", pi->name,
format_clib_error, error, 0);
PLUGIN_LOG_ERR ((char *) err);
clib_error_free (error);
dlclose (pi->handle);
pi->handle = 0;
goto error;
}
}
else
PLUGIN_LOG_ERR ("Plugin %s: early init function %s set but not found",
(char *) pi->name, reg->early_init);
}
//记录插件加载成功的信息
if (reg->description)
PLUGIN_LOG_NOTICE ("Loaded plugin: %s (%s)", pi->name, reg->description);
else
PLUGIN_LOG_NOTICE ("Loaded plugin: %s", pi->name);
//释放临时分配的内存,并返回成功加载的状态
vec_free (data);
elf_main_free (&em);
return 0;
//在加载失败的情况下,释放资源并返回失败的状态
error:
vec_free (data);
elf_main_free (&em);
return -1;
}
线程函数,作为独立线程的入口点 thread0
/**
* 线程函数,作为独立线程的入口点。
*
* @param arg 传递给线程函数的参数。在这个上下文中,应该是一个指向 vlib_main_t 结构的指针。
* @return vlib_main 函数的返回值。
*/
static uword thread0(uword arg) {
// 将参数转换为 vlib_main_t 指针
vlib_main_t *vm = (vlib_main_t *)arg;
// 获取全局 VLIB 主结构
vlib_global_main_t *vgm = vlib_get_global_main();
// 初始化一个用于命令行解析的输入结构
unformat_input_t input;
// 用于存储 vlib_main 函数的返回值
int i;
// 通知 VLIB 线程已完成切换到其堆栈
vlib_process_finish_switch_stack(vm);
// 使用全局 argv 初始化命令行输入
unformat_init_command_line(&input, (char **)vgm->argv);
// 调用 VLIB 主循环函数并存储其返回值
i = vlib_main(vm, &input);
// 释放命令行输入结构使用的资源
unformat_free(&input);
// 返回 vlib_main 函数的返回值
return i;
}
各种初始化操作,调用初始化函数、配置函数、主循环函数、以及一系列的清理操作vlib_main
/* 主函数 */
int vlib_main(vlib_main_t *volatile vm, unformat_input_t *input) {
vlib_global_main_t *vgm = vlib_get_global_main();
clib_error_t *volatile error;
vlib_node_main_t *nm = &vm->node_main;
// 设置队列信号回调为占位符函数
vm->queue_signal_callback = placeholder_queue_signal_callback;
/* 重新配置事件日志,这个日志在非常早期就被启用 */
if (vgm->configured_elog_ring_size &&
vgm->configured_elog_ring_size != vgm->elog_main.event_ring_size)
elog_resize(&vgm->elog_main, vgm->configured_elog_ring_size);
vl_api_set_elog_main(vlib_get_elog_main());
(void)vl_api_set_elog_trace_api_messages(1);
/* 默认名称 */
if (!vgm->name)
vgm->name = "VLIB";
if ((error = vlib_physmem_init(vm))) {
clib_error_report(error);
goto done;
}
if ((error = vlib_log_init(vm))) {
clib_error_report(error);
goto done;
}
if ((error = vlib_stats_init(vm))) {
clib_error_report(error);
goto done;
}
if ((error = vlib_buffer_main_init(vm))) {
clib_error_report(error);
goto done;
}
if ((error = vlib_thread_init(vm))) {
clib_error_report(error);
goto done;
}
// 注册节点 ifunction 变体
vlib_register_all_node_march_variants(vm);
// 注册静态节点以便初始化函数可以使用它们
vlib_register_all_static_nodes(vm);
// 设置随机数生成器的种子
if (!unformat(input, "seed %wd", &vm->random_seed))
vm->random_seed = clib_cpu_time_now();
clib_random_buffer_init(&vm->random_buffer, vm->random_seed);
// 初始化节点图
if ((error = vlib_node_main_init(vm))) {
// 在调试模式下,将图连接错误设置为非致命错误
if (CLIB_DEBUG > 0)
clib_error_report(error);
else
goto done;
}
// 初始化 vpe_api
if ((error = vpe_api_init(vm))) {
clib_error_report(error);
goto done;
}
if ((error = vlibmemory_init(vm))) {
clib_error_report(error);
goto done;
}
if ((error = map_api_segment_init(vm))) {
clib_error_report(error);
goto done;
}
// 检查 init_functions_called 是否为 0,如果是则创建哈希表
if (vgm->init_functions_called == 0)
vgm->init_functions_called = hash_create(0, /* value bytes */ 0);
// 调用所有的 init 函数
if ((error = vlib_call_all_init_functions(vm)))
goto done;
// 分配节点主循环的定时轮数据结构
nm->timing_wheel = clib_mem_alloc_aligned(sizeof(TWT(tw_timer_wheel)),
CLIB_CACHE_LINE_BYTES);
vec_validate(nm->data_from_advancing_timing_wheel, 10);
vec_set_len(nm->data_from_advancing_timing_wheel, 0);
// 创建进程定时轮
TW(tw_timer_wheel_init)((TWT(tw_timer_wheel) *)nm->timing_wheel,
0 /* no callback */,
10e-6 /* timer period 10us */,
~0 /* max expirations per call */);
vec_validate(vm->pending_rpc_requests, 0);
vec_set_len(vm->pending_rpc_requests, 0);
vec_validate(vm->processing_rpc_requests, 0);
vec_set_len(vm->processing_rpc_requests, 0);
// 如果配置了缓冲区分配错误注入,则设置默认参数
if (VLIB_BUFFER_ALLOC_FAULT_INJECTOR > 0) {
vm->buffer_alloc_success_seed = 0xdeaddabe;
vm->buffer_alloc_success_rate = 0.80;
}
// 调用所有的配置函数
if ((error = vlib_call_all_config_functions(vm, input, 0 /* is_early */)))
goto done;
/*
* 使用指数平滑法,半衰期为 1 秒
* reported_rate(t) = reported_rate(t-1) * K + rate(t)*(1-K)
*
* 每 20ms 进行一次采样,即每秒 50 个样本
* K = exp (-1.0/20.0);
* K = 0.95
*/
vm->damping_constant = exp(-1.0 / 20.0);
// 对 per-thread init 函数进行排序,然后启动线程
vlib_sort_init_exit_functions(&vgm->worker_init_function_registrations);
// 调用所有的 main loop enter 函数
{
clib_error_t *sub_error;
sub_error = vlib_call_all_main_loop_enter_functions(vm);
if (sub_error)
clib_error_report(sub_error);
}
switch (clib_setjmp(&vm->main_loop_exit, VLIB_MAIN_LOOP_EXIT_NONE)) {
case VLIB_MAIN_LOOP_EXIT_NONE:
vm->main_loop_exit_set = 1;
break;
case VLIB_MAIN_LOOP_EXIT_CLI:
goto done;
default:
error = vm->main_loop_error;
goto done;
}
// 开始主循环
vlib_main_loop(vm);
done:
vlib_worker_thread_barrier_sync(vm);
/* 调用所有的 exit 函数 */
{
clib_error_t *sub_error;
sub_error = vlib_call_all_main_loop_exit_functions(vm);
if (sub_error)
clib_error_report(sub_error);
}
vlib_worker_thread_barrier_release(vm);
// 如果有错误,报告错误
if (error)
clib_error_report(error);
return vm->main_loop_exit_status;
}
调用所有初始化函数vlib_call_all_init_functions
/**
* 调用所有初始化函数
*
* @param vm VLIB 主数据结构的指针
* @return clib_error_t 指向错误对象的指针,如果没有错误则为 NULL
*/
clib_error_t *
vlib_call_all_init_functions(vlib_main_t *vm) {
vlib_global_main_t *vgm = vlib_get_global_main();
// 调用占位符函数,确保纯静态模块被连接
// 这里使用 foreach_vlib_module_reference 宏来展开对各个模块的引用
#define _(f) vlib_##f##_reference();
foreach_vlib_module_reference;
#undef _
// 调用初始化/退出函数
return vlib_call_init_exit_functions(vm, &vgm->init_function_registrations,
1 /* call_once */, 1 /* is_global */);
}
初始化/退出/主循环进入函数的内部实现:实现了一个通用的函数调用机制,用于调用一组初始化、退出或者主循环进入函数。这个机制可以根据需要对函数链表进行排序,并且支持设置仅调用一次的标志。在遍历函数链表时,会检查是否已经调用过函数,如果设置为仅调用一次,并且函数未被调用过,则调用该函数。这样的机制可以方便地调用一组函数来完成初始化、退出或者进入主循环等操作。call_init_exit_functions_internal
/**
* @brief 调用一组初始化/退出/主循环进入函数
*
* @param vm vlib_main_t 结构体的指针
* @param headp 指向函数链表头指针的指针
* @param call_once 标志,指示是否仅调用一次
* @param do_sort 标志,指示是否对函数链表进行排序
* @param is_global 标志,指示是否为全局函数
* @return clib_error_t 指向错误对象的指针,如果没有错误则为 NULL
*/
static inline clib_error_t *
call_init_exit_functions_internal(vlib_main_t *vm,
_vlib_init_function_list_elt_t **headp,
int call_once, int do_sort, int is_global) {
vlib_global_main_t *vgm = vlib_get_global_main();
clib_error_t *error = 0;
_vlib_init_function_list_elt_t *i;
// 如果需要排序,进行排序操作
if (do_sort && (error = vlib_sort_init_exit_functions(headp)))
return (error);
i = *headp;
while (i) {
uword *h;
// 检查是否已经调用过这个函数
if (is_global)
h = hash_get(vgm->init_functions_called, i->f);
else
h = hash_get(vm->worker_init_functions_called, i->f);
// 如果设置为仅调用一次,并且函数未被调用过,则调用函数
if (call_once && !h) {
if (call_once) {
if (is_global)
hash_set1(vgm->init_functions_called, i->f);
else
hash_set1(vm->worker_init_functions_called, i->f);
}
error = i->f(vm);
if (error)
return error;
}
i = i->next_init_function;
}
return error;
}
注册所有静态节点(static nodes)的函数。静态节点是预定义的节点,其功能在整个系统的生命周期中保持不变vlib_register_all_static_nodes
void vlib_register_all_static_nodes(vlib_main_t *vm) {
vlib_global_main_t *vgm = vlib_get_global_main();
vlib_node_registration_t *r;
static char *null_node_error_strings[] = {
"blackholed packets",
};
static vlib_node_registration_t null_node_reg = {
.function = null_node_fn, // 空节点的处理函数
.vector_size = sizeof(u32),
.n_errors = 1,
.error_strings = null_node_error_strings,
};
// 注册一个名为 "null-node" 的节点
// 这是一个特殊的节点,用于处理被黑洞的数据包
vlib_register_node(vm, &null_node_reg, "null-node");
// 遍历所有节点注册
r = vgm->node_registrations;
while (r) {
// 注册每个节点
vlib_register_node(vm, r, "%s", r->name);
r = r->next_registration;
}
}
VLIB 主循环或工作线程循环的核心部分。它处理节点的调度和执行,以及一些循环计数和时间间隔的计算vlib_main_or_worker_loop:
static_always_inline void vlib_main_or_worker_loop(vlib_main_t * vm, int is_main) {
// 获取主循环的相关数据结构
vlib_node_main_t *nm = &vm->node_main;
vlib_thread_main_t *tm = vlib_get_thread_main();
uword i;
u64 cpu_time_now;
f64 now;
vlib_frame_queue_main_t *fqm;
u32 frame_queue_check_counter = 0;
// 初始化 pending_frames 数组,用于存储待处理的帧
if (is_main) {
vec_resize(nm->pending_frames, 32);
vec_set_len(nm->pending_frames, 0);
}
// 标记主循环开始的时间
if (is_main) {
cpu_time_now = vm->clib_time.last_cpu_time;
vm->cpu_time_main_loop_start = cpu_time_now;
} else
cpu_time_now = clib_cpu_time_now();
// 预分配中断运行时索引和锁
vec_alloc_aligned(nm->pending_interrupts, 1, CLIB_CACHE_LINE_BYTES);
// 预分配过期节点
if (!nm->polling_threshold_vector_length)
nm->polling_threshold_vector_length = 10;
if (!nm->interrupt_threshold_vector_length)
nm->interrupt_threshold_vector_length = 5;
// 获取当前 CPU ID 和 NUMA 节点信息
vm->cpu_id = clib_get_current_cpu_id();
vm->numa_node = clib_get_current_numa_node();
os_set_numa_index(vm->numa_node);
// 启动所有进程
if (is_main) {
uword i;
// 执行初始的屏障同步
vlib_worker_thread_initial_barrier_sync_and_release(vm);
nm->current_process_index = ~0;
for (i = 0; i < vec_len(nm->processes); i++)
cpu_time_now = dispatch_process(vm, nm->processes[i], /* frame */ 0, cpu_time_now);
}
while (1) {
vlib_node_runtime_t *n;
// 处理 RPC 请求
if (PREDICT_FALSE(_vec_len(vm->pending_rpc_requests) > 0)) {
if (!is_main)
vl_api_send_pending_rpc_requests(vm);
}
// 检查 worker 线程屏障
if (!is_main)
vlib_worker_thread_barrier_check();
// 检查帧队列是否有工作
if (PREDICT_FALSE(vm->check_frame_queues + frame_queue_check_counter)) {
u32 processed = 0;
vlib_frame_queue_dequeue_fn_t *fn;
if (vm->check_frame_queues) {
frame_queue_check_counter = 100;
vm->check_frame_queues = 0;
}
vec_foreach(fqm, tm->frame_queue_mains) {
fn = fqm->frame_queue_dequeue_fn;
processed += (fn)(vm, fqm);
}
// 没有找到帧队列的工作?
if (processed)
frame_queue_check_counter = 100;
else
frame_queue_check_counter--;
}
// 执行 worker 线程主循环回调函数
if (PREDICT_FALSE(vec_len(vm->worker_thread_main_loop_callbacks)))
clib_call_callbacks(vm->worker_thread_main_loop_callbacks, vm, cpu_time_now);
// 处理 pre-input 节点
cpu_time_now = clib_cpu_time_now();
vec_foreach(n, nm->nodes_by_type[VLIB_NODE_TYPE_PRE_INPUT])
cpu_time_now = dispatch_node(vm, n, VLIB_NODE_TYPE_PRE_INPUT, VLIB_NODE_STATE_POLLING, /* frame */ 0, cpu_time_now);
// 处理 input 节点
vec_foreach(n, nm->nodes_by_type[VLIB_NODE_TYPE_INPUT])
cpu_time_now = dispatch_node(vm, n, VLIB_NODE_TYPE_INPUT, VLIB_NODE_STATE_POLLING, /* frame */ 0, cpu_time_now);
// 如果是主循环且队列信号挂起,触发队列信号回调
if (PREDICT_TRUE(is_main && vm->queue_signal_pending == 0))
vm->queue_signal_callback(vm);
// 处理挂起的中断事件
if (__atomic_load_n(nm->pending_interrupts, __ATOMIC_ACQUIRE)) {
int int_num = -1;
*nm->pending_interrupts = 0;
while ((int_num = clib_interrupt_get_next(nm->interrupts, int_num)) != -1) {
vlib_node_runtime_t *n;
clib_interrupt_clear(nm->interrupts, int_num);
n = vec_elt_at_index(nm->nodes_by_type[VLIB_NODE_TYPE_INPUT], int_num);
cpu_time_now = dispatch_node(vm, n, VLIB_NODE_TYPE_INPUT, VLIB_NODE_STATE_INTERRUPT, /* frame */ 0, cpu_time_now);
}
}
// 处理 input 节点可能已经添加到 pending_frames 数组中的工作
for (i = 0; i < _vec_len(nm->pending_frames); i++)
cpu_time_now = dispatch_pending_node(vm, i, cpu_time_now);
// 重置 pending_frames 数组,准备下一轮迭代
vec_set_len(nm->pending_frames, 0);
if (is_main) {
// ELOG_TYPE_DECLARE 定义用于事件日志记录
ELOG_TYPE_DECLARE(es) = {
.format = "process tw start",
.format_args = "",
};
ELOG_TYPE_DECLARE(ee) = {
.format = "process tw end: %d",
.format_args = "i4",
};
struct {
int nready_procs;
} *ed;
// 检查是否有节点从定时轮中过期
ASSERT(nm->data_from_advancing_timing_wheel != 0);
if (PREDICT_FALSE(vm->elog_trace_graph_dispatch))
ed = ELOG_DATA(&vlib_global_main.elog_main, es);
nm->data_from_advancing_timing_wheel =
TW(tw_timer_expire_timers_vec)
((TWT(tw_timer_wheel) *)nm->timing_wheel, vlib_time_now(vm),
nm->data_from_advancing_timing_wheel);
ASSERT(nm->data_from_advancing_timing_wheel != 0);
if (PREDICT_FALSE(vm->elog_trace_graph_dispatch)) {
ed = ELOG_DATA(&vlib_global_main.elog_main, ee);
ed->nready_procs = _vec_len(nm->data_from_advancing_timing_wheel);
}
if (PREDICT_FALSE(_vec_len(nm->data_from_advancing_timing_wheel) > 0)) {
uword i;
for (i = 0; i < _vec_len(nm->data_from_advancing_timing_wheel); i++) {
u32 d = nm->data_from_advancing_timing_wheel[i];
u32 di = vlib_timing_wheel_data_get_index(d);
if (vlib_timing_wheel_data_is_timed_event(d)) {
vlib_signal_timed_event_data_t *te =
pool_elt_at_index(nm->signal_timed_event_data_pool, di);
vlib_node_t *n = vlib_get_node(vm, te->process_node_index);
vlib_process_t *p = vec_elt(nm->processes, n->runtime_index);
void *data;
data = vlib_process_signal_event_helper(nm, n, p,
te->event_type_index,
te->n_data_elts,
te->n_data_elt_bytes);
if (te->n_data_bytes < sizeof(te->inline_event_data))
clib_memcpy_fast(data, te->inline_event_data,
te->n_data_bytes);
else {
clib_memcpy_fast(data, te->event_data_as_vector,
te->n_data_bytes);
vec_free(te->event_data_as_vector);
}
pool_put(nm->signal_timed_event_data_pool, te);
} else {
cpu_time_now = clib_cpu_time_now();
cpu_time_now = dispatch_suspended_process(vm, di, cpu_time_now);
}
}
vec_set_len(nm->data_from_advancing_timing_wheel, 0);
}
}
// 增加主循环计数
vlib_increment_main_loop_counter(vm);
// 记录时间戳,以防没有启用的节点和上述调用未更新时间戳
cpu_time_now = clib_cpu_time_now();
vm->loops_this_reporting_interval++;
now = clib_time_now_internal(&vm->clib_time, cpu_time_now);
// 是否需要更新 loops_per_second?
if (PREDICT_FALSE(now >= vm->loop_interval_end)) {
// 下一次采样在 20 毫秒后结束
if (vm->loop_interval_start) {
f64 this_loops_per_second;
this_loops_per_second =
((f64)vm->loops_this_reporting_interval) / (now - vm->loop_interval_start);
vm->loops_per_second =
vm->loops_per_second * vm->damping_constant +
(1.0 - vm->damping_constant) * this_loops_per_second;
if (vm->loops_per_second != 0.0)
vm->seconds_per_loop = 1.0 / vm->loops_per_second;
else
vm->seconds_per_loop = 0.0;
}
// 新的间隔从现在开始,20 毫秒后结束
vm->loop_interval_start = now;
vm->loop_interval_end = now + 2e-4;
vm->loops_this_reporting_interval = 0;
}
}
}
负责管理进程的调度、执行和暂停等。根据进程的状态和标志,它会判断是否继续执行进程,启动定时器等。执行完毕后,会更新性能计数器、事件日志以及进程的统计信息 dispatch_process:
static u64
dispatch_process(vlib_main_t *vm,
vlib_process_t *p, vlib_frame_t *f, u64 last_time_stamp)
{
vlib_node_main_t *nm = &vm->node_main;
vlib_node_runtime_t *node_runtime = &p->node_runtime;
vlib_node_t *node = vlib_get_node(vm, node_runtime->node_index);
u32 old_process_index;
u64 t;
uword n_vectors, is_suspend;
// 检查节点状态和进程标志,判断是否可以继续执行
if (node->state != VLIB_NODE_STATE_POLLING ||
(p->flags & (VLIB_PROCESS_IS_SUSPENDED_WAITING_FOR_CLOCK |
VLIB_PROCESS_IS_SUSPENDED_WAITING_FOR_EVENT)))
return last_time_stamp;
// 设置进程标志,表示进程正在运行
p->flags |= VLIB_PROCESS_IS_RUNNING;
t = last_time_stamp;
// 记录事件日志,表示节点即将执行
vlib_elog_main_loop_event(vm, node_runtime->node_index, t,
f ? f->n_vectors : 0, /* is_after */ 0);
// 保存当前进程索引,以便在之后恢复
old_process_index = nm->current_process_index;
nm->current_process_index = node->runtime_index;
// 在进程启动之前更新性能计数器
vlib_node_runtime_perf_counter(vm, node_runtime, f, 0, last_time_stamp,
VLIB_NODE_RUNTIME_PERF_BEFORE);
// 调用进程的启动函数,获取处理的向量数目
n_vectors = vlib_process_startup(vm, p, f);
// 恢复之前的进程索引
nm->current_process_index = old_process_index;
// 判断进程的处理结果,可能是继续运行、暂停等
ASSERT(n_vectors != VLIB_PROCESS_RETURN_LONGJMP_RETURN);
is_suspend = n_vectors == VLIB_PROCESS_RETURN_LONGJMP_SUSPEND;
if (is_suspend) {
// 进程被暂停,处理暂停逻辑
vlib_pending_frame_t *pf;
n_vectors = 0;
// 从进程的暂停帧池中获取帧
pool_get(nm->suspended_process_frames, pf);
pf->node_runtime_index = node->runtime_index;
pf->frame = f;
pf->next_frame_index = ~0;
p->n_suspends += 1;
p->suspended_process_frame_index = pf - nm->suspended_process_frames;
if (p->flags & VLIB_PROCESS_IS_SUSPENDED_WAITING_FOR_CLOCK) {
// 如果进程等待时钟,则启动定时器
TWT(tw_timer_wheel) *tw = (TWT(tw_timer_wheel) *)nm->timing_wheel;
p->stop_timer_handle =
TW(tw_timer_start)(tw,
vlib_timing_wheel_data_set_suspended_process
(node->runtime_index) /* [sic] pool idex */,
0 /* timer_id */, p->resume_clock_interval);
}
} else {
// 进程未被暂停,清除运行标志
p->flags &= ~VLIB_PROCESS_IS_RUNNING;
}
t = clib_cpu_time_now();
// 记录事件日志,表示节点执行结束
vlib_elog_main_loop_event(vm, node_runtime->node_index, t, is_suspend,
/* is_after */ 1);
// 更新节点运行时的性能计数器
vlib_node_runtime_perf_counter(vm, node_runtime, f, n_vectors, t,
VLIB_NODE_RUNTIME_PERF_AFTER);
// 更新进程的统计信息
vlib_process_update_stats(vm, p,
/* n_calls */ !is_suspend,
/* n_vectors */ n_vectors,
/* n_clocks */ t - last_time_stamp);
return t;
}
通过调用 clib_setjmp 设置了一个返回点,然后通过条件判断选择不同的执行路径。如果返回值 r 是 VLIB_PROCESS_RETURN_LONGJMP_RETURN,说明进程还没有启动,那么会通过 vlib_process_start_switch_stack 切换到进程的新堆栈,然后调用 vlib_process_bootstrap 函数来执行进程的启动逻辑。如果 r 不是 VLIB_PROCESS_RETURN_LONGJMP_RETURN,说明进程已经启动过,此时会调用 vlib_process_finish_switch_stack 完成堆栈切换,然后返回 r。这样,通过 setjmp 和长跳转,进程可以在不同的堆栈上运行,实现了进程的启动与切换 vlib_process_startup:
/* 在主堆栈中调用。 */
static_always_inline uword
vlib_process_startup(vlib_main_t *vm, vlib_process_t *p, vlib_frame_t *f)
{
vlib_process_bootstrap_args_t a;
uword r;
// 设置参数
a.vm = vm;
a.process = p;
a.frame = f;
// 使用 setjmp 保存上下文,以便进行长跳转
r = clib_setjmp(&p->return_longjmp, VLIB_PROCESS_RETURN_LONGJMP_RETURN);
if (r == VLIB_PROCESS_RETURN_LONGJMP_RETURN) {
// 切换到进程的新堆栈,然后调用 vlib_process_bootstrap 函数
vlib_process_start_switch_stack(vm, p);
r = clib_calljmp(vlib_process_bootstrap, pointer_to_uword(&a),
(void *)p->stack + (1 << p->log2_n_stack_bytes));
} else {
// 完成堆栈切换
vlib_process_finish_switch_stack(vm);
}
return r;
}
从参数 _a 中还原了一个结构体 vlib_process_bootstrap_args_t,其中包含了所需的参数。然后,获取了进程的主要信息,如 vm、p(进程对象)、f(帧对象)、node(进程节点运行时对象)。接着,通过调用 node->function 来执行进程的主要逻辑,返回值 n 将用于表示进程的执行结果。
在进程函数执行完成后,代码通过 vlib_process_stack_is_valid 确保进程的堆栈仍然是有效的。然后,通过调用 vlib_process_start_switch_stack 切换回主堆栈,并使用 clib_longjmp 进行长跳转,将执行结果 n 返回给调用者,也就是 vlib_process_startup 函数。
总之,这段代码负责在进程的堆栈上执行进程函数,然后将执行结果返回给调用者。这种跳转和切换堆栈的方式使得进程能够在独立的堆栈上运行,实现了并发执行 vlib_process_bootstrap:
/* 在进程堆栈中调用。 */
static uword
vlib_process_bootstrap(uword _a)
{
vlib_process_bootstrap_args_t *a;
vlib_main_t *vm;
vlib_node_runtime_t *node;
vlib_frame_t *f;
vlib_process_t *p;
uword n;
// 从参数 _a 中还原参数结构体
a = uword_to_pointer(_a, vlib_process_bootstrap_args_t *);
// 获取参数
vm = a->vm;
p = a->process;
// 完成堆栈切换
vlib_process_finish_switch_stack(vm);
f = a->frame;
node = &p->node_runtime;
// 调用进程函数并获取返回值
n = node->function(vm, node, f);
// 确保进程堆栈是有效的
ASSERT(vlib_process_stack_is_valid(p));
// 切换回主堆栈,使用 clib_longjmp 返回结果
vlib_process_start_switch_stack(vm, 0);
clib_longjmp(&p->return_longjmp, n);
return n;
}
可以看到,这里就调用到了我们注册一个node之后,真正的处理函数,也就是我们新加node生效的地方。