PCL中GreedyProjection三角化算法简介与示例
文章目录
- 前言
- 一、PCL点云三角化
-
- 1.1 Delaunay三角剖分
- 1.2 贪婪三角化
- 二、程序示例
- 总结
前言
Delaunay三角剖分最初应用于2维领域,而与Greedy三角化算法的结合,使之成为目前在三维重建领域最为基础的算法原理之一,很多学者针对其原理进行改进用以三维点云模型的构建。
一、PCL点云三角化
1.1 Delaunay三角剖分
定义:假设点集中的一条边e(两个端点为a,b),e若满足下列条件,则称之为Delaunay边:存在一个圆经过a,b两点,圆内(圆上最多三点共圆)不含点集中任何其他的点。而Delaunay三角化就是指三角网格均是由Delaunay边组成,并满足最小角最大原则(在点集可能形成的三角剖分中,Delaunay三角剖分所形成的三角形的最小角最大)。
针对以上定义,目前已提出了很多经典的剖分算法,如Lawson算法、Bowyer-Watson算法。以上算法都很有意思,通过点插法实现,具体原理可以查看以下链接。
技术分享:Delaunay三角剖分算法介绍
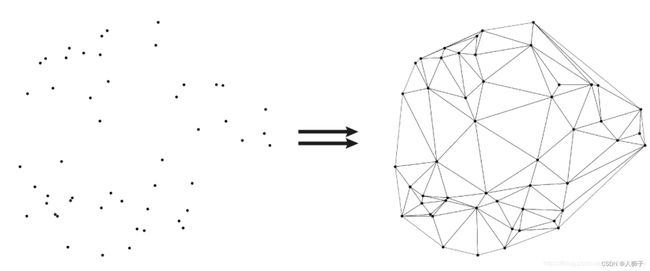
1.2 贪婪三角化
PCL中采用将三维点云投影到二维平面的方法来实现三角剖分, 具体采用贪婪三角化算法。
其过程为:
1:计算点云中点的法线,再将点云通过法线投影到二维坐标平面。
2:使用基于Delaunay三角剖分的空间区域增长算法完成平面点集的三角化。
3:根据投影点云的连接关系确定原始三维点云间的拓扑关系,最终得到曲面模型。
PCL中的NormalEstimation和GreedyProjectionTriangulation类实现该计算过程。
源代码:
FFN和SFN是指两个不同方向的边缘邻域集,在connectPoint方法里完成计算。
/** \brief Index of the current query point **/
int R_;
std::vector ffn_;
std::vector sfn_;
// Locating FFN and SFN to adapt distance threshold
double sqr_source_dist = (coords_[R_] - coords_[source_[R_]]).squaredNorm ();
double sqr_ffn_dist = (coords_[R_] - coords_[ffn_[R_]]).squaredNorm ();
double sqr_sfn_dist = (coords_[R_] - coords_[sfn_[R_]]).squaredNorm ();
double max_sqr_fn_dist = (std::max)(sqr_ffn_dist, sqr_sfn_dist);
double sqr_dist_threshold = (std::min)(sqr_max_edge, sqr_mu * sqrDists[1]); //sqr_mu * sqr_avg_conn_dist);
if (max_sqr_fn_dist > sqrDists[nnn_-1])
{
if (0 == increase_nnn4fn)
PCL_WARN("Not enough neighbors are considered: ffn or sfn out of range! Consider increasing nnn_... Setting R=%d to be BOUNDARY!\n", R_);
increase_nnn4fn++;
state_[R_] = BOUNDARY;
continue;
}
double max_sqr_fns_dist = (std::max)(sqr_source_dist, max_sqr_fn_dist);
if (max_sqr_fns_dist > sqrDists[nnn_-1])
{
if (0 == increase_nnn4s)
PCL_WARN("Not enough neighbors are considered: source of R=%d is out of range! Consider increasing nnn_...\n", R_);
increase_nnn4s++;
}
计算法线:
// Get the normal estimate at the current point
const Eigen::Vector3f nc = (*input_)[(*indices_)[R_]].getNormalVector3fMap ();
三角化:
// Triangulating
if (angles_[2].visible == false)
{
if ( !( (angles_[0].index == ffn_[R_] && angles_[1].index == sfn_[R_]) || (angles_[0].index == sfn_[R_] && angles_[1].index == ffn_[R_]) ) )
{
state_[R_] = BOUNDARY;
}
else
{
if ((source_[R_] == angles_[0].index) || (source_[R_] == angles_[1].index))
state_[R_] = BOUNDARY;
else
{
if (sqr_max_edge < (coords_[ffn_[R_]] - coords_[sfn_[R_]]).squaredNorm ())
{
state_[R_] = BOUNDARY;
}
else
{
tmp_ = coords_[source_[R_]] - proj_qp_;
uvn_s[0] = tmp_.dot(u_);
uvn_s[1] = tmp_.dot(v_);
double angleS = std::atan2(uvn_s[1], uvn_s[0]);
double dif = angles_[1].angle - angles_[0].angle;
if ((angles_[0].angle < angleS) && (angleS < angles_[1].angle))
{
if (dif < 2*M_PI - maximum_angle_)
state_[R_] = BOUNDARY;
else
closeTriangle (polygons);
}
else
{
if (dif >= maximum_angle_)
state_[R_] = BOUNDARY;
else
closeTriangle (polygons);
}
}
}
}
continue;
}
源码中大量代码关注于三角形的连接问题。
最后调用MeshConstruction类的reconstruct方法进行表面重建。
template <typename PointInT> void
MeshConstruction<PointInT>::reconstruct (std::vector<pcl::Vertices> &polygons)
{
if (!initCompute ())
{
polygons.clear ();
return;
}
// Check if a space search locator was given
if (check_tree_)
{
if (!tree_)
{
if (input_->isOrganized ())
tree_.reset (new pcl::search::OrganizedNeighbor<PointInT> ());
else
tree_.reset (new pcl::search::KdTree<PointInT> (false));
}
// Send the surface dataset to the spatial locator
tree_->setInputCloud (input_, indices_);
}
// Set up the output dataset
//polygons.clear ();
//polygons.reserve (2 * indices_->size ()); /// NOTE: usually the number of triangles is around twice the number of vertices
// Perform the actual surface reconstruction
performReconstruction (polygons);
deinitCompute ();
}
二、程序示例
//----------------------------------法线计算-----------------------------------
pcl::NormalEstimation<pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::Normal> n;
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>::Ptr normals(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>);
pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr tree1(new pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>);
tree->setInputCloud(cloud);
n.setInputCloud(cloud);
n.setSearchMethod(tree1);
n.setKSearch(20);
n.compute(*normals);
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointNormal>::Ptr cloud_with_normals(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointNormal>);
pcl::concatenateFields(*cloud, *normals, *cloud_with_normals);//连接点云和法线
pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointNormal>::Ptr tree2(new pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointNormal>);
tree2->setInputCloud(cloud_with_normals);
pcl::GreedyProjectionTriangulation<pcl::PointNormal> gp;
pcl::PolygonMesh triangles;
gp.setSearchRadius(0.025);//设置搜索半径,即连接点的最大距离
gp.setMu(2.5); //加权因子,对于每个样本点,其映射所选球的半径由mu与离样本点最近点的距离乘积决定,用以解决点云密度不均匀的问题,mu一般取值2.5-3
gp.setMaximumNearestNeighbors(600); //最大领域点个数
gp.setMaximumSurfaceAngle(M_PI / 4);//临近点的法线和样本点法线的最大偏离角度
gp.setMinimumAngle(M_PI / 18); //三角形最小角
gp.setMaximumAngle(2 * M_PI / 3);//三角形最大角
gp.setNormalConsistency(false); //保证法线朝向一致
gp.setInputCloud(cloud_with_normals);
gp.setSearchMethod(tree2);
gp.reconstruct(triangles);
总结
彻底理解三角化的源代码比较困难,缺少相关学习资料,欢迎共同研究,提出意见。
