xxl-job 原理:
quarts的缺点:
随机负载(for update );不能分片
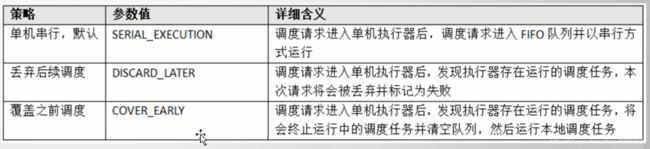
阻塞处理策略:
分片原理:
for (int i = 0; i < group.getRegistryList().size(); i++) {
// 同时给多个客户端发送命令
processTrigger(group, jobInfo, finalFailRetryCount, triggerType, i, group.getRegistryList().size());
}在代码中可以通过工具类 获得 当前 是第几个分片 n 执行任务:
取数据需要自己从SQL 中处理,保证同一条数据 不会被不同的执行器取到就可以
在 查询数据的时候,将 n 作为 参数
select * from my_job where mod(id,n) = #{n} 作为当前分片要执行的任务
select * from XXL_JOB_QRTZ_TRIGGER_INFO where mod(sha1(id),3) = 1 ;
select * from XXL_JOB_QRTZ_TRIGGER_INFO where mod(id,3) = 1 ;原理:
执行器 怎么 将 线程的运行日志发送给 调度器? 执行器 会将 执行任务日志放到 自己的队列里,有一个线程会消费这个队列,
并通过 http 请求 传给 调度器,调度器去 更新 日志表。1.
调度中心(注册中心): 当一个job 可以执行的时候,调度中心 通过 http 请求 将 任务 传给 某个 worker
注册:
HashMap> appAddressMap = new HashMap>();
key 是 appName ;
value 是: ip 端口 ;
while 循环
------> JobScheduleHelper : select * from xxl_job_lock where lock_name = 'schedule_lock' for update
------> 系统当前时间 大于 jobInfo.getTriggerNextTime()
------> 触发
------> 更新下一次的触发时间
jobInfo.setTriggerLastTime(jobInfo.getTriggerNextTime());
jobInfo.setTriggerNextTime(nextValidTime.getTime());
UPDATE xxl_job_info
SET
trigger_last_time = #{triggerLastTime},
trigger_next_time = #{triggerNextTime},
trigger_status = #{triggerStatus}
WHERE id = #{id}
while 循环 里的伪代码如下:
try {
Connection conn = null;
Boolean connAutoCommit = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
// 注册中心(调度中心) 有多台机器,防止多个机器 同时给 一个 执行器发送 http 请求,此处需要加 悲观锁,
// 同一时刻只能 有 一个 注册中心,给某一个 worker 发送任务
select * from xxl_job_lock where lock_name = 'schedule_lock' for update
// 获取 job 集合
for (XxlJobInfo jobInfo: scheduleList) {
// 触发 ThreadPoolExecutor 线程池 中 去执行任务(向客户端发送请求)------> 分片的话,一个时间 选择一台机器发送请求
// 更新 xxl_job_info 中 ,下一次任务的执行时间(long 类型的)
}
} catch(Exception e){
} finally(){
{
// commit
if (conn != null) {
try {
// 释放锁
conn.commit();
} catch (SQLException e) {
if (!scheduleThreadToStop) {
logger.error(e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
try {
conn.setAutoCommit(connAutoCommit);
} catch (SQLException e) {
if (!scheduleThreadToStop) {
logger.error(e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
if (!scheduleThreadToStop) {
logger.error(e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
}
// close PreparedStatement
if (null != preparedStatement) {
try {
preparedStatement.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
if (!scheduleThreadToStop) {
logger.error(e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
}
}
}
调度中心: 通过 http 向 客户端发送 请求后(URI 为 /run) 客户端接收到请求后:
客户端在收到 服务端的执行任务指令后如何操作的?
① 客户端引入了 xxl-job-core 包,这个包在 spring bean注册完之后,会有一个回调函数,
将 bean 中 含有 @xxlJob 注解 的Component 和 method 方法 组装成一个 MethodJobHandler 对象
同事以 @xxlJob 上的value 为key ,MethodJobHandler 实例 为value 放到一个 ConcurrentHashMap 中
② 服务端的执行任务指令过来,会根据 服务端传来的 xxlJob 注解上的value 从 ConcurrentHashMap 获取对应的 Handler 对象
③ 注册并开启一个工作线程,执行任务,并在 jobHandler 方法里 写入执行结果(不是return success ) ,而是调用官方的方法,通过 InhertableTheadLocal
将执行结果写入到线程私有变量里,并将finally 代码块将执行结果 推到 回调线程里
④ 回调线程 反馈任务运行结果,服务端接受到结果后根据日志id 更新日志 表客户端在服务启动的时候,将被xxlJob 标记的method 和相关Component 组成对象,并保存到map里,供调用(有点类似策略模式)
// 伪代码如下:
xxl job core 项目 在 bean 注册到容器 里后,有一个回调方法(通过实现 SmartInitializingSingleton 接口实现,重写方法)
回调方法的作用:
获取 容器中 的bean ,主要是 方法被 @XxlJob 注解标记的 bean,
// bean spring 中的bean ,executeMethod 被 xxlJob 标注的方法,
registJobHandler(name, new MethodJobHandler(bean, executeMethod, initMethod, destroyMethod));
// name 是 Bean 里 加在方法上的 XxlJob 注解
public static IJobHandler registJobHandler(String name, IJobHandler jobHandler){
logger.info(">>>>>>>>>>> xxl-job register jobhandler success, name:{}, jobHandler:{}", name, jobHandler);
return jobHandlerRepository.put(name, jobHandler);
}
map 结构如下:
private static ConcurrentMap jobHandlerRepository = new ConcurrentHashMap(); 反射调用目标方法:
MethodJobHandler extends IJobHandler 中有如下方法:
@Override
public void execute() throws Exception {
Class[] paramTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
if (paramTypes.length > 0) {
method.invoke(target, new Object[paramTypes.length]); // method-param can not be primitive-types
} else {
// 反射调用 被 xxlJob 标注的目标方法
// method 是目标方法,target 是目标方法所在的bean
method.invoke(target);
}
}③ 注册并开启 工作线程
public static JobThread registJobThread(int jobId, IJobHandler handler, String removeOldReason){
JobThread newJobThread = new JobThread(jobId, handler);
// 开启新线程
newJobThread.start();
logger.info(">>>>>>>>>>> xxl-job regist JobThread success, jobId:{}, handler:{}", new Object[]{jobId, handler});
// 获取上传一次的 旧线程
JobThread oldJobThread = jobThreadRepository.put(jobId, newJobThread); // putIfAbsent | oh my god, map's put method return the old value!!!
if (oldJobThread != null) {
// 通过变量 让线程 终止(线程执行完也算是终止)
oldJobThread.toStop(removeOldReason);
oldJobThread.interrupt();
}
return newJobThread;
}
工作线程:
public class JobThread extends Thread{
private static Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(JobThread.class);
private int jobId;
// 封装了Bean 和目标方法 ,这样反射就可以 调用目标方法
private IJobHandler handler;
private LinkedBlockingQueue triggerQueue;
private Set triggerLogIdSet; // avoid repeat trigger for the same TRIGGER_LOG_ID
// 通过一个变量 让一个线程 结束运行,运行完就算线程销毁了(不会旧线程一直 while 循环)
private volatile boolean toStop = false;
private String stopReason;
private boolean running = false; // if running job
private int idleTimes = 0; // idel times
public JobThread(int jobId, IJobHandler handler) {
this.jobId = jobId;
this.handler = handler;
// 每个线程 都有自己的私有 队列
this.triggerQueue = new LinkedBlockingQueue();
this.triggerLogIdSet = Collections.synchronizedSet(new HashSet());
}
public IJobHandler getHandler() {
return handler;
}
/**
* new trigger to queue
*
* @param triggerParam
* @return
*/
public ReturnT pushTriggerQueue(TriggerParam triggerParam) {
// avoid repeat
if (triggerLogIdSet.contains(triggerParam.getLogId())) {
logger.info(">>>>>>>>>>> repeate trigger job, logId:{}", triggerParam.getLogId());
return new ReturnT(ReturnT.FAIL_CODE, "repeate trigger job, logId:" + triggerParam.getLogId());
}
triggerLogIdSet.add(triggerParam.getLogId());
triggerQueue.add(triggerParam);
return ReturnT.SUCCESS;
}
/**
* kill job thread
*
* @param stopReason
*/
public void toStop(String stopReason) {
/**
* Thread.interrupt只支持终止线程的阻塞状态(wait、join、sleep),
* 在阻塞出抛出InterruptedException异常,但是并不会终止运行的线程本身;
* 所以需要注意,此处彻底销毁本线程,需要通过共享变量方式;
*/
this.toStop = true;
this.stopReason = stopReason;
}
/**
* is running job
* @return
*/
public boolean isRunningOrHasQueue() {
return running || triggerQueue.size()>0;
} 重点看下执行任务的 run 方法:
// 没有终止就一直运行
while(!toStop){
try{
// log filename, like "logPath/yyyy-MM-dd/9999.log"
String logFileName = XxlJobFileAppender.makeLogFileName(new Date(triggerParam.getLogDateTime()), triggerParam.getLogId());
XxlJobContext xxlJobContext = new XxlJobContext(
triggerParam.getJobId(),
triggerParam.getExecutorParams(),
logFileName,
triggerParam.getBroadcastIndex(),
triggerParam.getBroadcastTotal());
// init job context
//底层: InheritableThreadLocal contextHolder = new InheritableThreadLocal()
// 线程私有变量的传递 ; 在自定义的 jobHandler 方法里写的日志 要用官方的日志 组件 ,会将 日志内容写入到日志文件里
// eg:他获取文件名称的方法 String logFileName = xxlJobContext.getJobLogFileName();
XxlJobContext.setXxlJobContext(xxlJobContext);
// execute
XxlJobHelper.log("
----------- xxl-job job execute start -----------
----------- Param:" + xxlJobContext.getJobParam());
// 有过期时间用 FutureTask (这个可以设置超时时间)
if (triggerParam.getExecutorTimeout() > 0) {
// limit timeout
Thread futureThread = null;
try {
FutureTask futureTask = new FutureTask(new Callable() {
@Override
public Boolean call() throws Exception {
// init job context
XxlJobContext.setXxlJobContext(xxlJobContext);
// 反射调用 目标方法
handler.execute();
return true;
}
});
futureThread = new Thread(futureTask);
futureThread.start();
Boolean tempResult = futureTask.get(triggerParam.getExecutorTimeout(), TimeUnit.SECONDS);
} catch (TimeoutException e) {
XxlJobHelper.log("
----------- xxl-job job execute timeout");
XxlJobHelper.log(e);
// handle result
XxlJobHelper.handleTimeout("job execute timeout ");
} finally {
futureThread.interrupt();
}
} else {
// 没有过期时间
// just execute
// 反射调用 目标方法
handler.execute();
}
}catch{
}finally{
if(triggerParam != null) {
// callback handler info
if (!toStop) {
// 往回调线程里 push 消息,通知执行完结果
TriggerCallbackThread.pushCallBack(new HandleCallbackParam(
triggerParam.getLogId(),
triggerParam.getLogDateTime(),
// 这个是在哪里设置的值? 在 自己写的任务 xxJobHandler 方法里(底层 调用 InheritableThreadLocal 获取当前线程的私有属性,然后设置成功吗)
// 代码如下:
// if (exitValue == 0) {
// default success
//} else {
// XxlJobHelper.handleFail("command exit value("+exitValue+") is failed");
//}
XxlJobContext.getXxlJobContext().getHandleCode(),
XxlJobContext.getXxlJobContext().getHandleMsg() )
);
} else {
// is killed
TriggerCallbackThread.pushCallBack(new HandleCallbackParam(
triggerParam.getLogId(),
triggerParam.getLogDateTime(),
XxlJobContext.HANDLE_COCE_FAIL,
stopReason + " [job running, killed]" )
);
}
}
}
} ④ 回调线程 通过http 请求 反馈工作 线程 执行结果
说明:没有执行完任务后直接回调,而是 放到一个队列里,批量 反馈,减少了网络开销
主要属性和方法:
LinkedBlockingQueue callBackQueue = new LinkedBlockingQueue()
// 添加执行结果
public static void pushCallBack(HandleCallbackParam callback){
getInstance().callBackQueue.add(callback);
logger.debug(">>>>>>>>>>> xxl-job, push callback request, logId:{}", callback.getLogId());
} @Override
public void run() {
// normal callback
while(!toStop){
try {
HandleCallbackParam callback = getInstance().callBackQueue.take();
if (callback != null) {
// callback list param
List callbackParamList = new ArrayList();
int drainToNum = getInstance().callBackQueue.drainTo(callbackParamList);
callbackParamList.add(callback);
// callback, will retry if error
if (callbackParamList!=null && callbackParamList.size()>0) {
// 通过 http 进行回调
doCallback(callbackParamList);
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!toStop) {
logger.error(e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
}
// last callback
try {
List callbackParamList = new ArrayList();
int drainToNum = getInstance().callBackQueue.drainTo(callbackParamList);
if (callbackParamList!=null && callbackParamList.size()>0) {
doCallback(callbackParamList);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!toStop) {
logger.error(e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
logger.info(">>>>>>>>>>> xxl-job, executor callback thread destory.");
}
});
继续进入:
@Override
public ReturnT callback(List callbackParamList) {
return XxlJobRemotingUtil.postBody(addressUrl+"api/callback", accessToken, timeout, callbackParamList, String.class);
} 1. 注册中心收到 请求后的操作:
api/callback
public ReturnT callback(List callbackParamList) {
// 线程池
callbackThreadPool.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
for (HandleCallbackParam handleCallbackParam: callbackParamList) {
ReturnT callbackResult = callback(handleCallbackParam);
logger.debug(">>>>>>>>> JobApiController.callback {}, handleCallbackParam={}, callbackResult={}",
(callbackResult.getCode()== ReturnT.SUCCESS_CODE?"success":"fail"), handleCallbackParam, callbackResult);
}
}
});
return ReturnT.SUCCESS;
} callBack 方法如下:
private ReturnT callback(HandleCallbackParam handleCallbackParam) {
// valid log item
XxlJobLog log = XxlJobAdminConfig.getAdminConfig().getXxlJobLogDao().load(handleCallbackParam.getLogId());
if (log == null) {
return new ReturnT(ReturnT.FAIL_CODE, "log item not found.");
}
if (log.getHandleCode() > 0) {
return new ReturnT(ReturnT.FAIL_CODE, "log repeate callback."); // avoid repeat callback, trigger child job etc
}
// handle msg
StringBuffer handleMsg = new StringBuffer();
if (log.getHandleMsg()!=null) {
handleMsg.append(log.getHandleMsg()).append("
");
}
if (handleCallbackParam.getHandleMsg() != null) {
handleMsg.append(handleCallbackParam.getHandleMsg());
}
// success, update log ;(说明:insert log 是 在服务端向客户端发送请求的时候插入的)
log.setHandleTime(new Date());
log.setHandleCode(handleCallbackParam.getHandleCode());
log.setHandleMsg(handleMsg.toString());
XxlJobCompleter.updateHandleInfoAndFinish(log);
return ReturnT.SUCCESS;
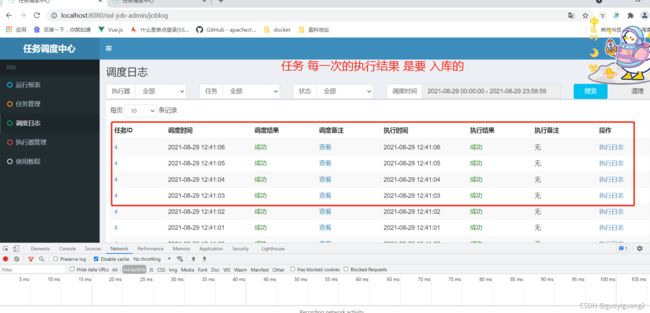
} 调度日志的显示:
点击 页面 执行日志,执行了两部操作:
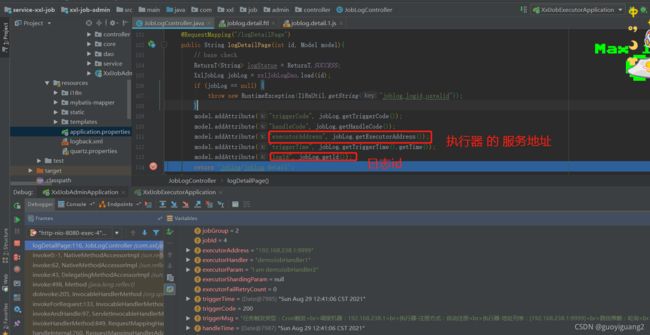
首先从 调度器获取 日志id(日志文件的文件名 日志id.log ),日志所在执行器服务器信息 ② 通过页面 ajax 请求 访问执行器 日志文件(配置文件里配置的路径)
代码如下:
① 页面 获取日志id,执行器服务器信息 如下:
说明:
文件名称 和 日志id 有关:(每次执行完一个任务,就生成一个文件,而不是 所有日志文件堆积在一起 )
log filename: logPath/yyyy-MM-dd/9999.log
② 读取日志文件(说明:如果 调度中心和 执行器不在一台服务器上,得修改源码,将本地读取日志文件改为 远程读取日志文件)
@RequestMapping("/logDetailCat")
@ResponseBody
public ReturnT logDetailCat(String executorAddress, long triggerTime, int logId, int fromLineNum){
try {
ExecutorBiz executorBiz = XxlJobDynamicScheduler.getExecutorBiz(executorAddress);
// 读取日志文件的内容
ReturnT logResult = executorBiz.log(triggerTime, logId, fromLineNum);
// is end
if (logResult.getContent()!=null && logResult.getContent().getFromLineNum() > logResult.getContent().getToLineNum()) {
XxlJobLog jobLog = xxlJobLogDao.load(logId);
if (jobLog.getHandleCode() > 0) {
logResult.getContent().setEnd(true);
}
}
return logResult;
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error(e.getMessage(), e);
return new ReturnT(ReturnT.FAIL_CODE, e.getMessage());
}
} 读取方法:
@Override
public ReturnT log(long logDateTim, int logId, int fromLineNum) {
//获取日志名称,说明 9999 是 日志id
// log filename: logPath/yy yy-MM-dd/9999.log
String logFileName = XxlJobFileAppender.makeLogFileName(new Date(logDateTim), logId);
// 读取日志
LogResult logResult = XxlJobFileAppender.readLog(logFileName, fromLineNum);
return new ReturnT(logResult);
} 如何获取日志文件名称?
public static String makeLogFileName(Date triggerDate, int logId) {
// filePath/yyyy-MM-dd
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd"); // avoid concurrent problem, can not be static
File logFilePath = new File(getLogPath(), sdf.format(triggerDate));
if (!logFilePath.exists()) {
logFilePath.mkdir();
}
// filePath/yyyy-MM-dd/9999.log
String logFileName = logFilePath.getPath()
.concat(File.separator)
// 拼接 logId 为日志名称
.concat(String.valueOf(logId))
// 日志后缀
.concat(".log");
return logFileName;
}读取日志的方法:
public static LogResult readLog(String logFileName, int fromLineNum){
// valid log file
if (logFileName==null || logFileName.trim().length()==0) {
return new LogResult(fromLineNum, 0, "readLog fail, logFile not found", true);
}
// 创建文件对象
File logFile = new File(logFileName);
if (!logFile.exists()) {
return new LogResult(fromLineNum, 0, "readLog fail, logFile not exists", true);
}
// read file
StringBuffer logContentBuffer = new StringBuffer();
int toLineNum = 0;
LineNumberReader reader = null;
try {
//reader = new LineNumberReader(new FileReader(logFile));
reader = new LineNumberReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(logFile), "utf-8"));
String line = null;
while ((line = reader.readLine())!=null) {
toLineNum = reader.getLineNumber(); // [from, to], start as 1
if (toLineNum >= fromLineNum) {
// 读完一行就换行
logContentBuffer.append(line).append("\n");
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
logger.error(e.getMessage(), e);
} finally {
if (reader != null) {
try {
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
logger.error(e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
}
// 返回结果集
LogResult logResult = new LogResult(fromLineNum, toLineNum, logContentBuffer.toString(), false);
return logResult;
}