圆的反演 hdu 6158
欢迎关注更多精彩
关注我,学习常用算法与数据结构,一题多解,降维打击。
题目大意
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=6158
给定2个相内切的圆,往两圆之间空隙处加入圆,依次加入,每次加入的圆尽可能大,求加入圆的总面积。
基本思路
圆的反演有如下性质:
- 圆C的圆心为O,则如果有一个圆过点O,则该圆对C的反演是一条直线。反之直线可以反演成圆。
- 如果两个圆相切,则反演后的几何形状还是相切。
根据题目的要求,每次加入的圆肯定与初始给定圆相切,也与之前加入过的最近的圆相切。
对这些圆进行反演后可以得到如下图形。
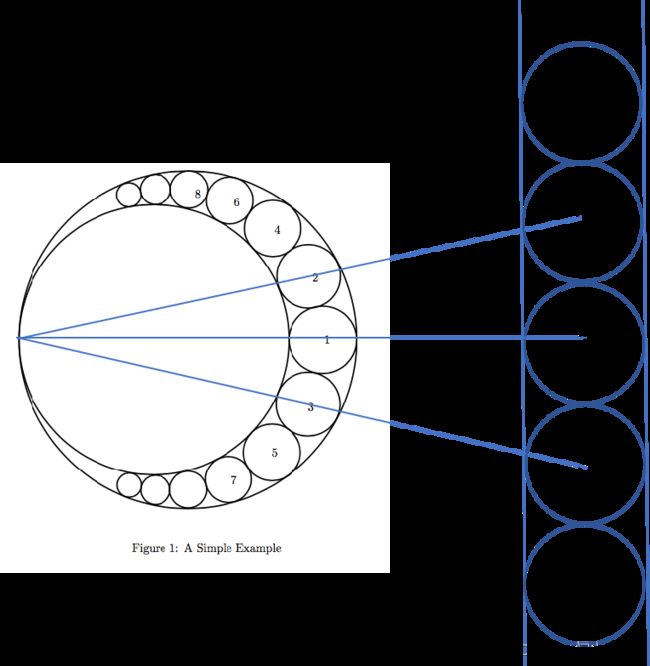
反演后的小圆是比较容易求得的。
错解
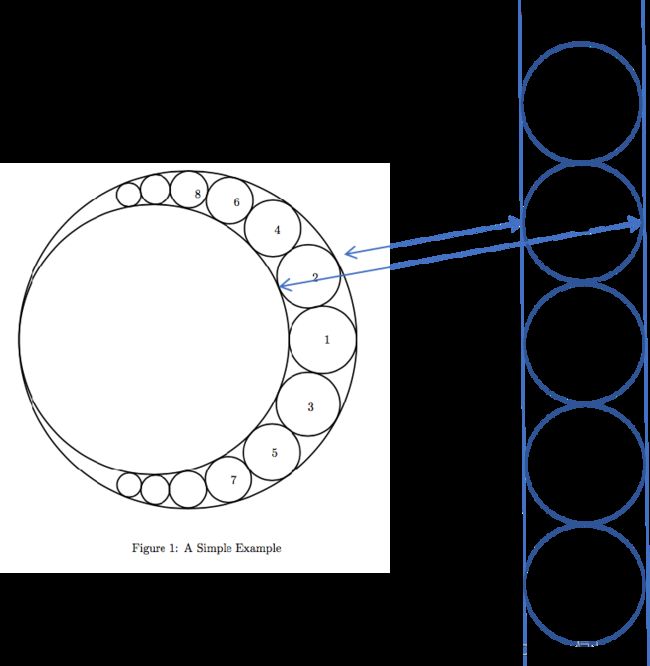
错解:对圆与直线切点进行反演作为直径的两点。
以圆2为例,对圆与直线两点进行反演得到的两点不能组成圆的直径。
证明如下:
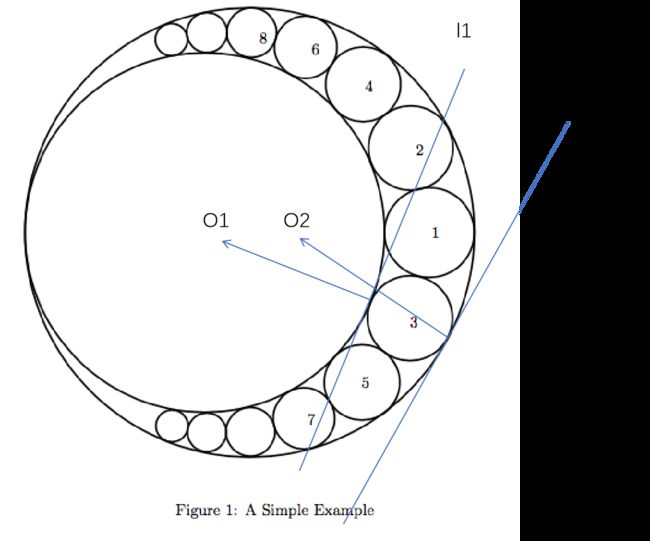
如果反演后的点可以构成直径,那么直径所在直线必然要经过相切圆的圆心,且与公切线垂直。
对圆与内圆和外圆的切点作公切线,公切线的法线肯定要过圆心。
两个公切线的法线分别经过O1和O2, O1和O2显然不是一个点。
也就是说反演后的点连线不能经过相切圆的圆心。
代码实现
#include本人码农,希望通过自己的分享,让大家更容易学懂计算机知识。
![]()