Octave Conv 全面解析(原理解析+代码解析)
Octave Conv
Octave Convolution 代码详解_octconv代码_zghydx1924的博客-CSDN博客
1 简单介绍
2 结构图
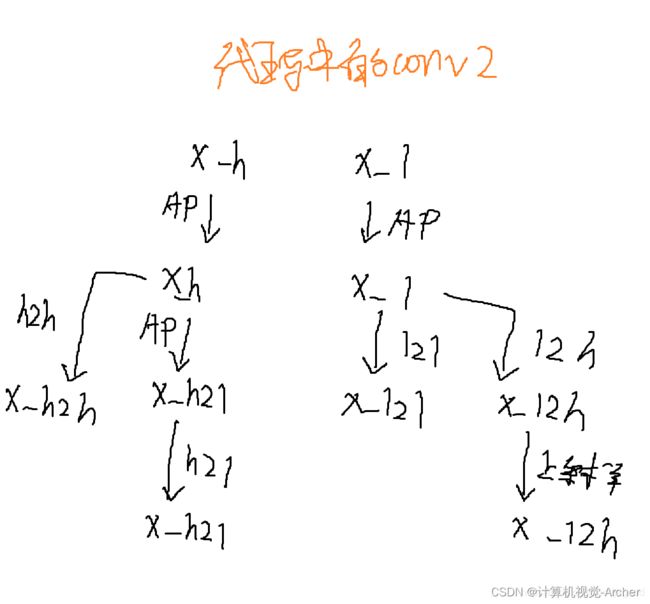
我的理解
输入:XH、XL是两个feature
pool(XH, 2)下采样操作:是stride=2,kernal=2的average pooling
l2l, h2h ,l2h , h2h 四个conv:的默认stride都是1,kernal size作为参数输入,高低维互相转换是由f(X,W)操作完成的,在代码中f体现为普通的卷积;
alpha:默认为0.75,alpha是低频率L的feature所占(高+低通道数)比例;
四个conv的输入通道数:
high对应(1-a)*Cin
low对应a*Cin
四个conv的输出通道数:
high对应(1-a)*Cout
low对应a*Cout
这里的Cin和Cout是根据具体情况设置,另外输入和输出位置会特殊,这里暂不讨论
高纬度间转换:
l2h:经过conv后upsample
h2l:经过average pooling后conv
技术细节: 用AP的原因
高低维度的feature间转换的时候,因为高维的w,h是低维两倍,卷积会导致以上问题(卷积前后的特征图不能整数对其),所以高低维转换时候会有upsample和average_pooling的操作
3 代码逻辑 (参考下述博客)
OctaveConv解读_ptgood的博客-CSDN博客
代码实现:https://github.com/lxtGH/OctaveConv_pytorch/tree/master/libs/nn
4 核心代码参数
h2h: 128x64x(k*k) 128是h的(1-a)*Cout 64是h的(1-a)*Cin
h2l: 384x64x(k*k)
l2h: 128x192x(k*k)
l2l: 384x192x(k*k) 384是l的a*Cout 192是l的a*Cin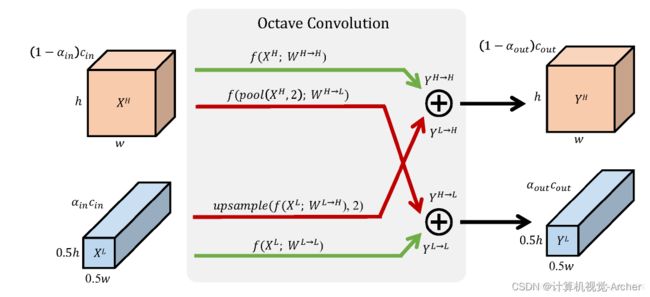
5 具体代码实现
def forward(self, x):
X_h, X_l = x
if self.stride ==2:
X_h, X_l = self.h2g_pool(X_h), self.h2g_pool(X_l)
X_h2l = self.h2g_pool(X_h)
# X_h2l指的是对输入进行下采样,下采样的方法时卷积核大小2×2,步长为2的平均池化。
end_h_x = int(self.in_channels*(1- self.alpha_in))
end_h_y = int(self.out_channels*(1- self.alpha_out))
# 假设输入的通道数为256,输出的通道数为512,alpha_in=alpha_out=0.75。那么end_h_x=64,end_h_y=128。
X_h2h = F.conv2d(X_h, self.weights[0:end_h_y, 0:end_h_x, :,:], self.bias[0:end_h_y], 1,
self.padding, self.dilation, self.groups)
X_l2l = F.conv2d(X_l, self.weights[end_h_y:, end_h_x:, :,:], self.bias[end_h_y:], 1,
self.padding, self.dilation, self.groups)
X_h2l = F.conv2d(X_h2l, self.weights[end_h_y:, 0: end_h_x, :,:], self.bias[end_h_y:], 1,
self.padding, self.dilation, self.groups)
X_l2h = F.conv2d(X_l, self.weights[0:end_h_y, end_h_x:, :,:], self.bias[0:end_h_y], 1,
self.padding, self.dilation, self.groups)
X_l2h = F.upsample(X_l2h, scale_factor=2, **self.up_kwargs)
#低频分量的分辨率为高频分量的一般,因此需要上采样后进行计算
X_h = X_h2h + X_l2h
X_l = X_l2l + X_h2l
return X_h, X_l